Abstract
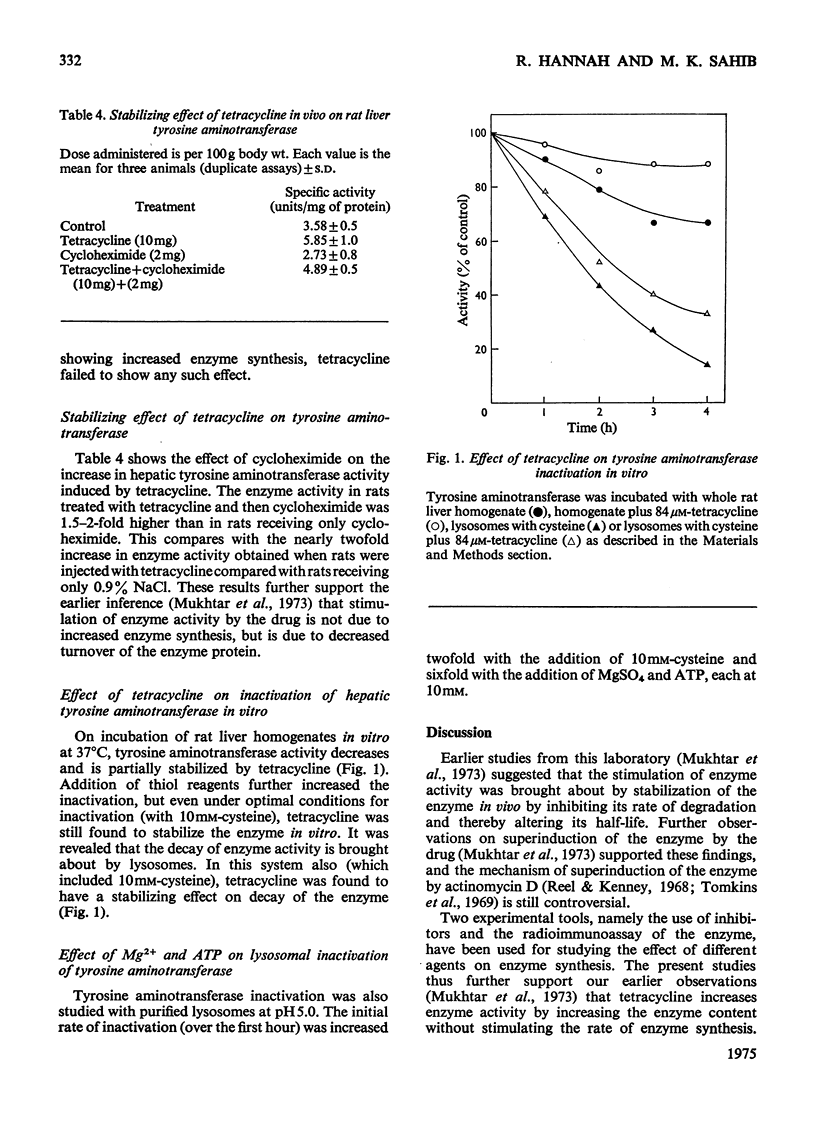
Rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase was purified 200-fold and an antiserum raised against it in rabbits. 2. Hepatic tyrosine aminotransferase activity was increased fourfold by tyrosine, twofold by tetracycline, 2.5-fold by cortisone 21-acetate and ninefold by a combination of tyrosine and cortisol administered intraperitoneally to rats. 3. Radioimmunoassay with 14C-labelled tyrosine aminotransferase, in conjunction with rabbit antiserum against the enzyme, revealed that cortisol stimulates the synthesis of the enzyme de novo, but that tetracycline has no such effect. 4. Incubation of rat liver homogenates with purified tyrosine aminotransferase in vitro leads to a rapid inactivation of the enzyme, which tetracycline partially inhibits. 5. The inactivation is brought about by intact lysosomes, and the addition of 10mM-cysteine increases the rate of enzyme inactivation, which is further markedly increased by 10mM-Mg2+ and 10mM-ATP. Here again tetracycline partially inhibits the decay rate, leading to the inference that the increase of tyrosine aminotransferase activity in vivo by tetracycline is brought about by the latter inhibiting the lysosomal catheptic action.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auricchio F., Mollica L., Liguori A. Inactivation of tyrosine aminotransferase in neutral homogenates and rat liver slices. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1131–1138. doi: 10.1042/bj1291131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cihak A., Lamar C., Jr, Pitot H. C. Studies on the mechanism of the stimulation of tyrosine aminotransferase activity in vivo by pyrimidine analogs: the role of enzyme synthesis and degradation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 May;156(1):176–187. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civen M., Trimmer B. M., Brown C. B. The induction of hepatic tyrosine alpha-ketoglutarate and phenylalanine pyruvate transaminases by glucagon. Life Sci. 1967 Jun 15;6(12):1331–1338. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D. K., Hayashi S., Thompson E. B., Tomkins G. M. Stimulation of tyrosine aminotransferase synthesis by dexamethasone phosphate in cell culture. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard O., Baker G. T. Glucagon, starvation, and the induction of liver enzymes by hydrocortisone. Science. 1966 Dec 16;154(3755):1461–1462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager C. B., Kenney F. T. Regulation of tyrosine-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase in rat liver. VII. Hormonal effects of synthesis in the isolated, perfused liver. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3296–3300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Hiroi Y., Natori Y. Effect of ATP on protein degradation in rat liver lysosomes. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):163–166. doi: 10.1038/newbio242163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S. I., Granner D. K., Tomkins G. M. Tyrosine aminotransferase. Purificaton and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):3998–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holten D., Kenney F. T. Regulation of tyrosine alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase in rat liver. VI. Induction by pancreatic hormones. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4372–4377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., KNOX W. E. Adaptation of the rat liver tyrosine-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtar H., Murti C. R. Induction of rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase by pharmacologically unrelated drugs. Indian J Biochem. 1971 Jun;8(2):116–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtar H., Sahib M. K., Murti C. R. Stabilization of rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase by drugs. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;10(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B. D. Hepatic lysosome and serum enzyme alterations in rats exposed to high altitude. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):651–655. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal B., Ray T. K., Ghosh J. J. Effect of tranquillizer drugs on liver tyrosine-alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Aug;18(8):2047–2049. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reel J. R., Kenney F. T. "Superinduction" of tyrosine transaminase in hepatoma cell cultures: differential inhibition of synthesis and turnover by actionomycin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):200–206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., SWEENEY E. W., BERLIN C. M. THE ROLES OF SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF RAT LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:322–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULL K. H., ASHMORE J., MAYER J. Hexokinase, glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphorylase levels in hereditarily obese-hyperglycemic mice. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 May;62(1):210–216. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Maruyama M. Immunological study of carbon tetrachloride-mediated induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M., Gelehrter T. D., Granner D., Martin D., Jr, Samuels H. H., Thompson E. B. Control of specific gene expression in higher organisms. Expression of mammalian genes may be controlled by repressors acting on the translation of messenger RNA. Science. 1969 Dec 19;166(3912):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3912.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeriote F. A., Auricchio F., Tomkins G. M., Riley D. Purification and properties of rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3618–3624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


