Abstract
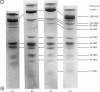
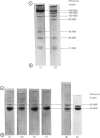
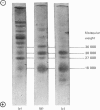
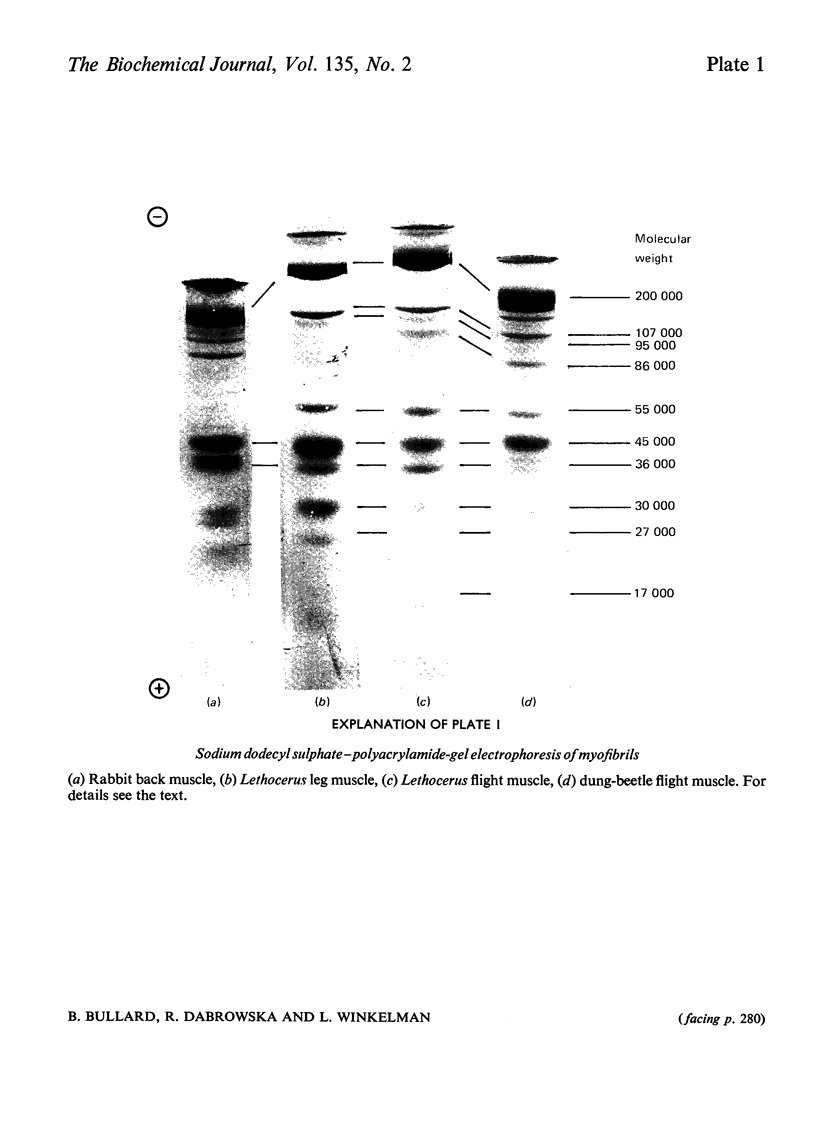
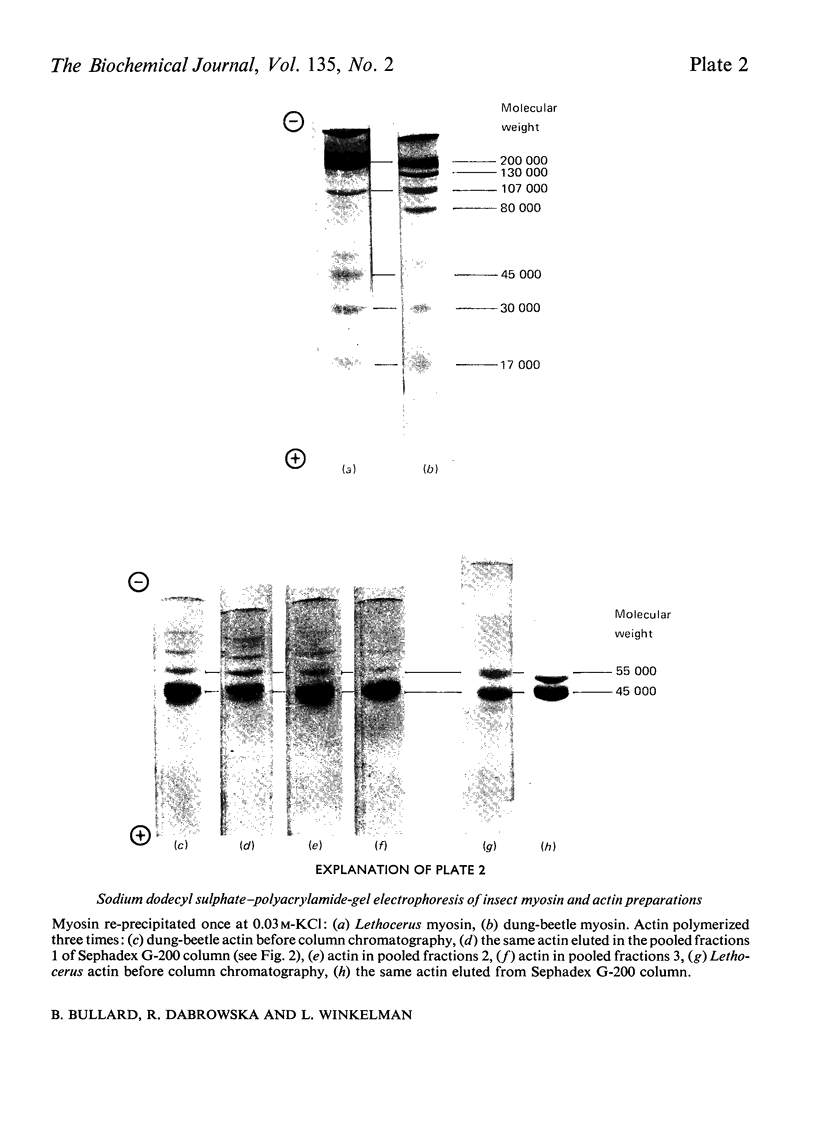
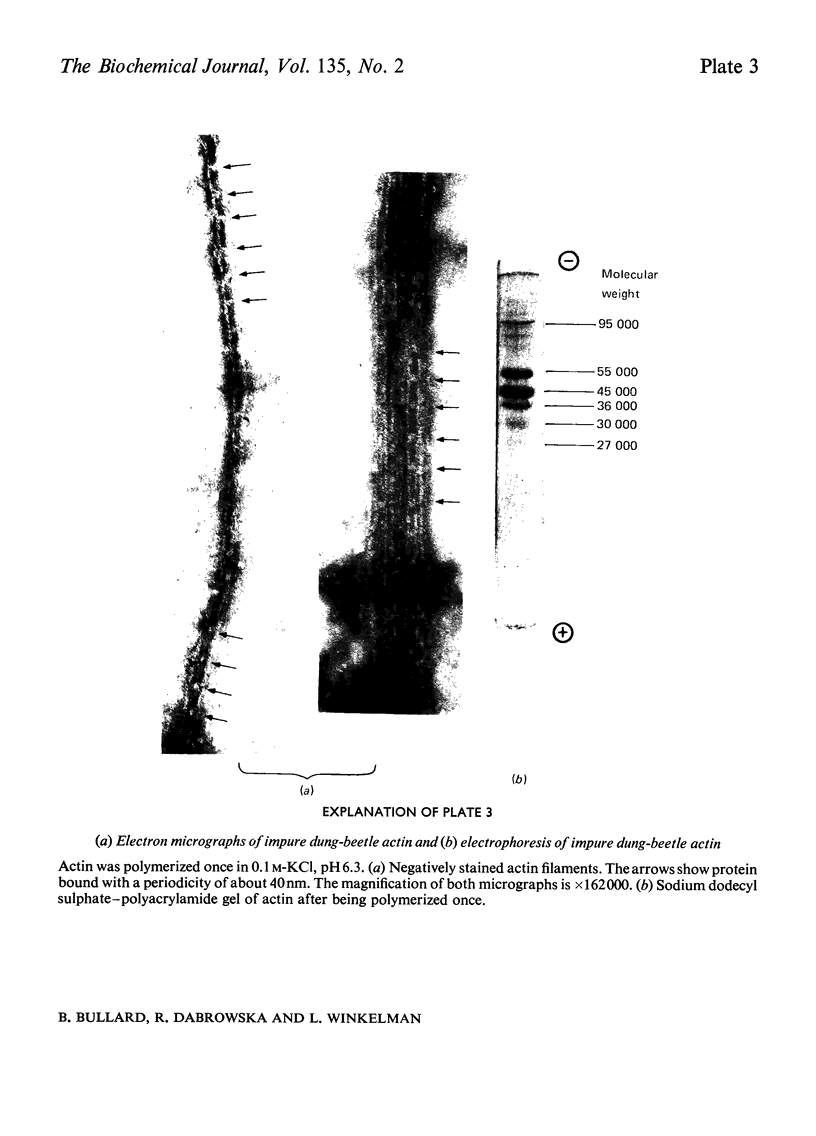
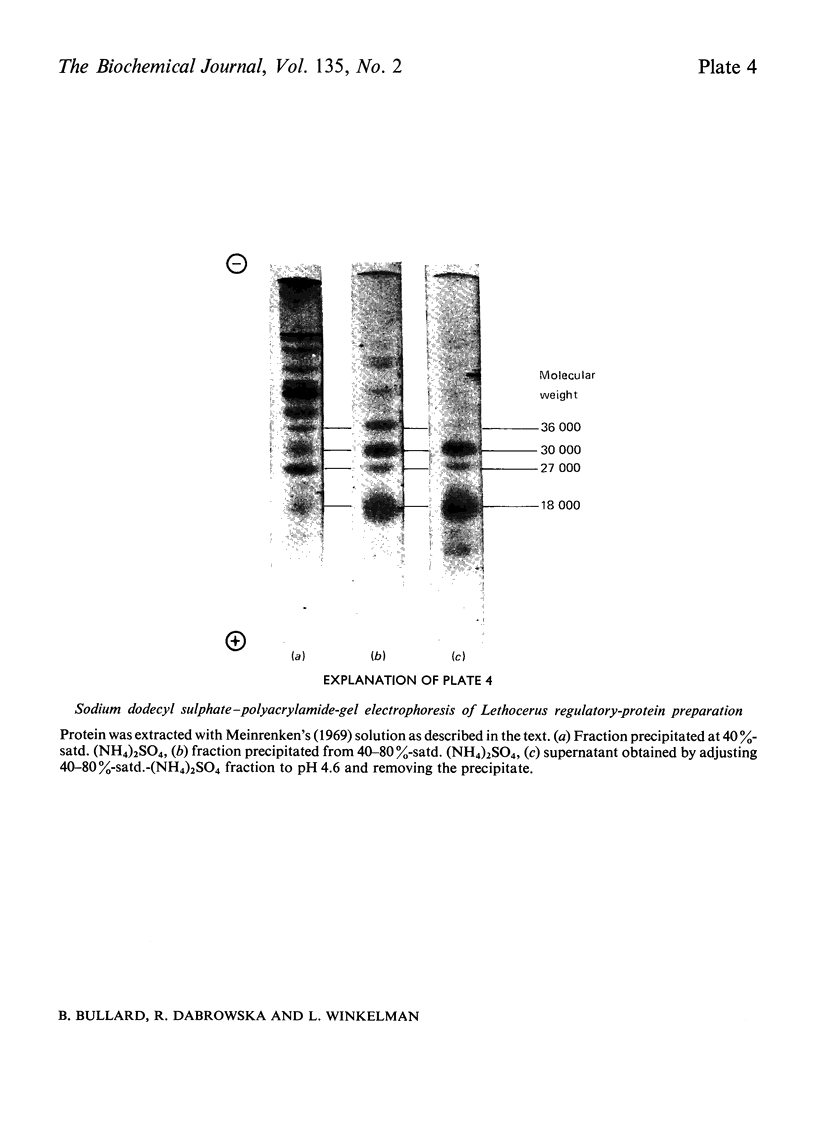
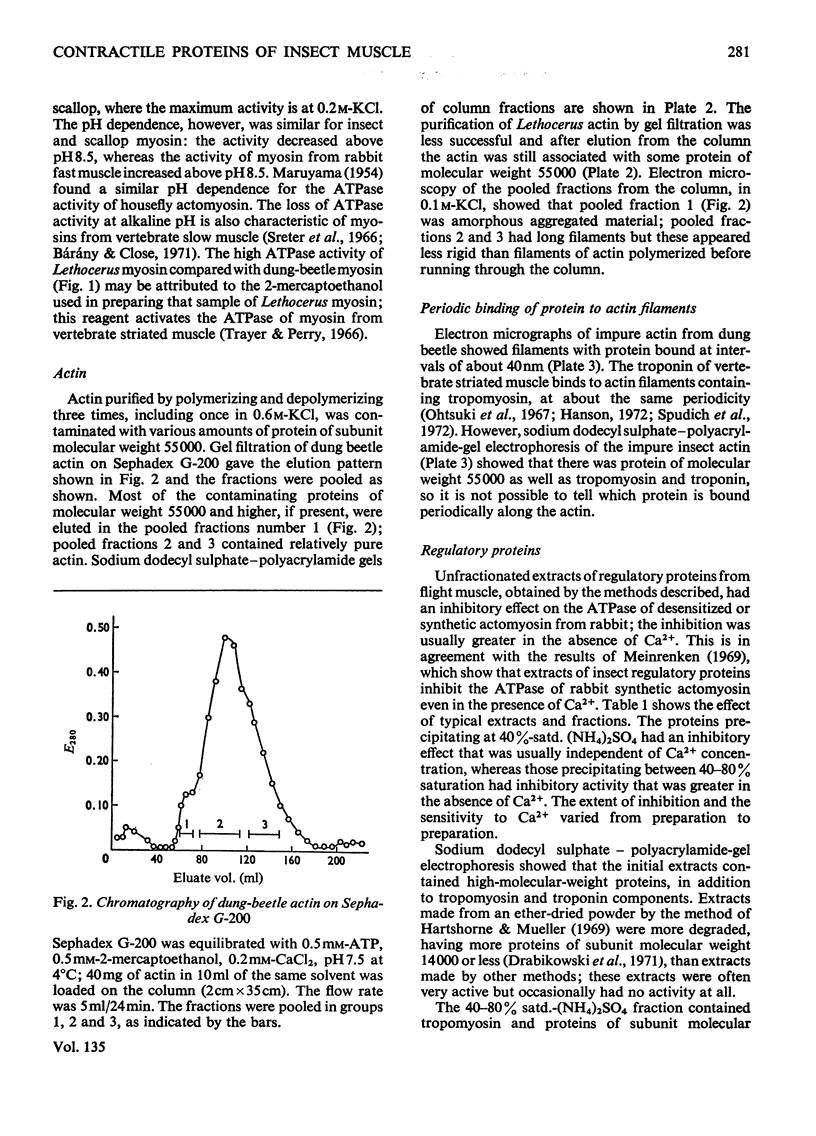
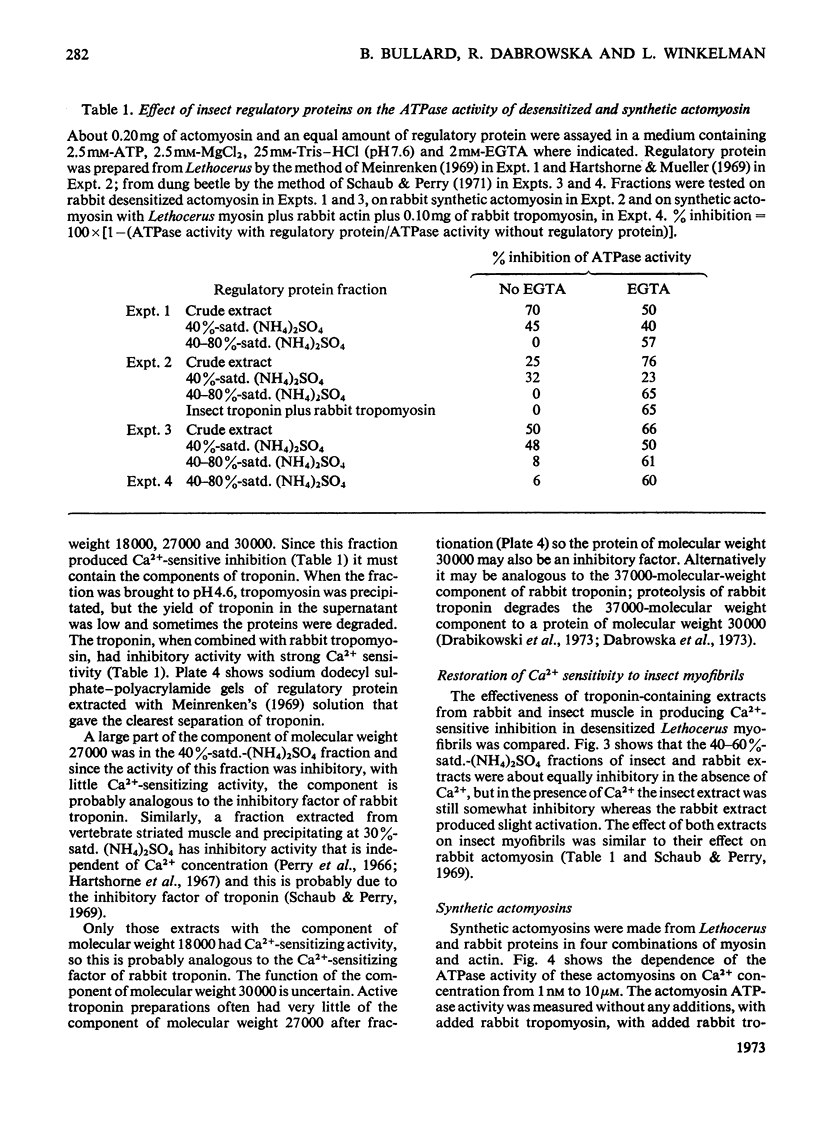
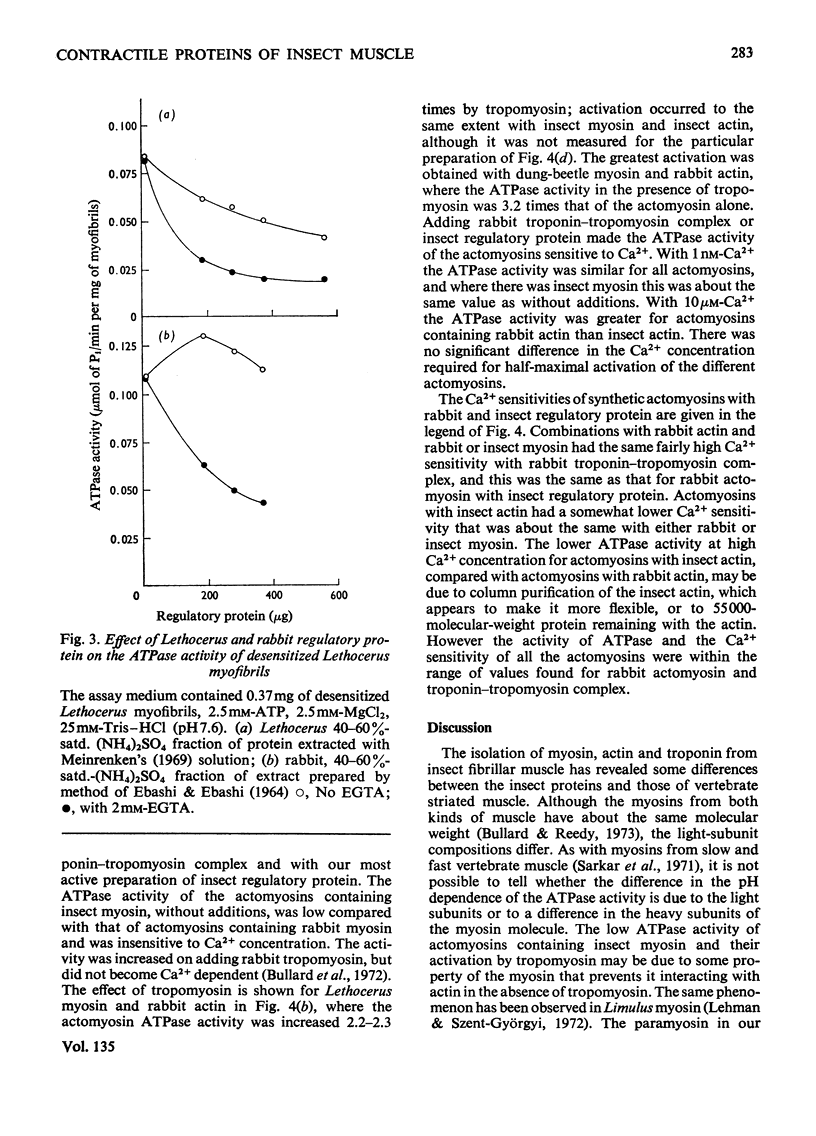
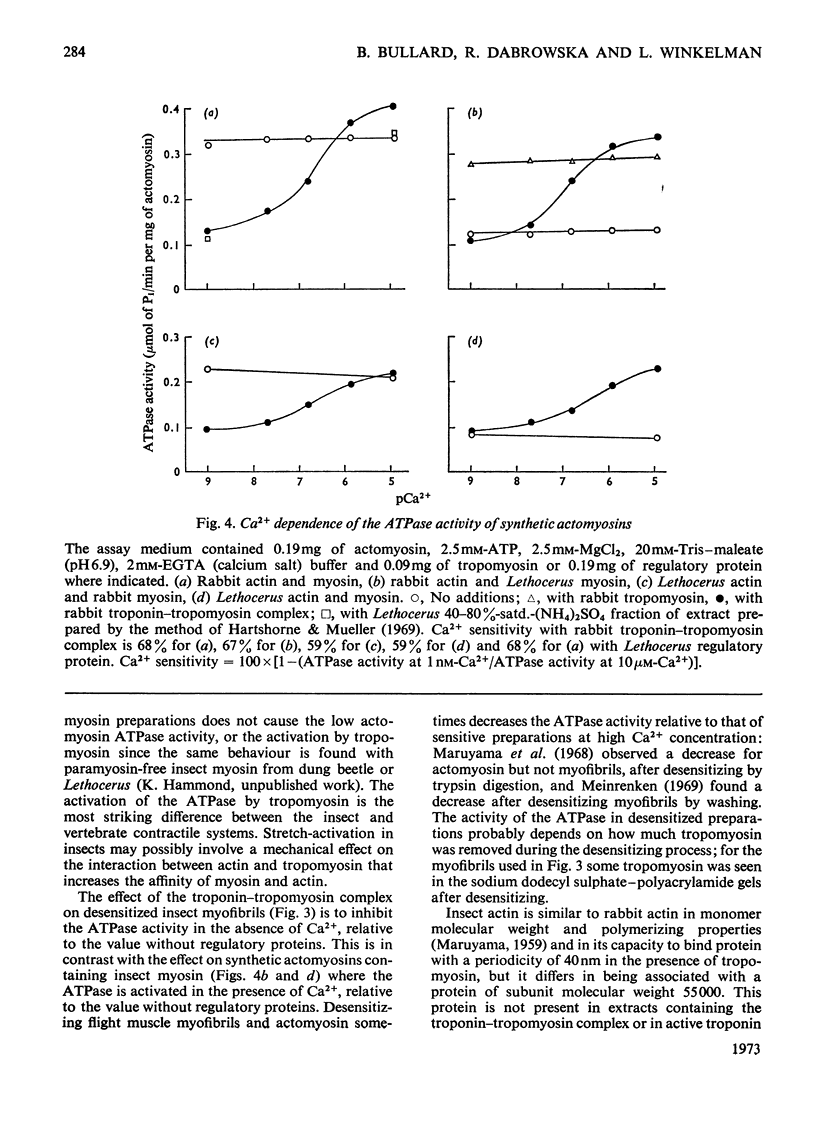
1. Myosin, actin and the regulatory proteins were prepared from insect flight muscle. 2. The light subunit composition of the myosin differed from that of vertebrate muscle myosin. The ionic strength and pH dependence of the myosin adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) were measured. 3. Actin was associated with a protein of subunit molecular weight 55000 and was purified by gel filtration. Impure actin had protein bound at a periodicity of about 40nm. 4. Regulatory protein extracts had tropomyosin and troponin components of subunit molecular weight 18000, 27000 and 30000. Crude extracts of regulatory proteins inhibited the ATPase activity of desensitized or synthetic actomyosin; this inhibition was relatively insensitive to high Ca2+ concentrations. Purified insect regulatory protein produced as much sensitivity to Ca2+ as did the rabbit troponin–tropomyosin complex. 5. Synthetic actomyosins were made from rabbit and insect proteins. Actomyosins containing insect myosin had a low ATPase activity that was activated by tropomyosin. The Ca2+ sensitivity of actomyosins containing insect myosin or actin, with added troponin–tropomyosin complex from rabbit, was comparable with that of rabbit actomyosin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott R. H., Chaplain R. A. Preparation and properties of the contractile element of insect fibrillar muscle. J Cell Sci. 1966 Sep;1(3):311–330. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey K. Tropomyosin: a new asymmetric protein component of the muscle fibril. Biochem J. 1948;43(2):271–279. doi: 10.1042/bj0430271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocke HH vom The activating effects of calcium ions on the contractile systems of insect fibrillar flight muscle. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;290(1):70–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00362620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Luke B., Winkelman L. The paramyosin of insect flight muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M., Close R. I. The transformation of myosin in cross-innervated rat muscles. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(2):455–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplain R. A. The effect of Ca2+ and fibre elongation on the activation of the contractile mechanism of insect fibrillar flight muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 8;131(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(67)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska R., Barylko B., Nowak E., Drabikowski W. The origin of 30,000 dalton protein in troponin preparations. FEBS Lett. 1973 Feb 1;29(3):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabikowski W., Rafalowska U., Dabrowska R., Szpacenko A., Barylko B. The effect of proteolytic enzymes on the troponin complex. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 15;19(3):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBASHI S., EBASHI F. A NEW PROTEIN COMPONENT PARTICIPATING IN THE SUPERPRECIPITATION OF MYOSIN B. J Biochem. 1964 Jun;55:604–613. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Wakabayashi T., Ebashi F. Troponin and its components. J Biochem. 1971 Feb;69(2):441–445. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson J. Evidence from electron microscope studies on actin paracrystals concerning the origin of the cross-striation in the thin filaments of vertebrate skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Feb 27;183(1070):39–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H. The preparation of tropomyosin and troponin from natural actomyosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar;175(2):301–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Perry S. V., Schaub M. C. A protein factor inhibiting the magnesium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of desensitized actomyosin. Biochem J. 1967 Sep;104(3):907–913. doi: 10.1042/bj1040907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOMINZ D. R., MARUYAMA K., LEVENBOOK L., LEWIS M. Tropomyosin, myosin and actin from the blowfly, Phormia regina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Sep 10;63:106–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi G. Activation of the adenosine triphosphatase of Limulus polyphemus actomyosin by tropomyosin. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Apr;59(4):375–387. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOMMAERTS W. F. Chemical investigation of muscular tissues. Methods Med Res. 1958;7:1–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Pringle J. W., Tregear R. T. The calcium sensitivity of ATPase activity of myofibrils and actomyosins from insect flight and leg muscles. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Feb 27;169(1016):229–240. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinrenken W. Calciumionen-unabhängige Kontraktion und ATPase bei glycerinierten Muskelfasern nach alkalischer Extraktion von Troponin. Pflugers Arch. 1969;311(3):243–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00590528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki I., Masaki T., Nonomura Y., Ebashi S. Periodic distribution of troponin along the thin filament. J Biochem. 1967 Jun;61(6):817–819. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Davies V., Hayter D. Natural tropomyosin and the factor sensitizing actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase to ethylenedioxybis(ethyleneamino)tetra-acetic acid. Biochem J. 1966 Apr;99(1):1C–2C. doi: 10.1042/bj0990001c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees M. K., Young M. Studies on the isolation and molecular properties of homogeneous globular actin. Evidence for a single polypeptide chain structure. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4449–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg J. C., Tregear R. T. Mechanical factors affecting the ATPase activity of glycerol-extracted insect fibrillar flight muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Oct 11;165(1001):497–512. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIDEL J. C., GERGELY J. STUDIES ON MYOFIBRILLAR ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE WITH CALCIUM-FREE ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE. I. THE EFFECT OF ETHYLENEDIAMINETETRAACETATE, CALCIUM, MAGNESIUM, AND ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3648–3653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Light chains of myosins from white, red, and cardiac muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):946–950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Perry S. V. The regulatory proteins of the myofibril. Characterization and properties of the inhibitory factor (troponin B). Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(3):367–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1230367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub M. C., Perry S. V. The relaxing protein system of striated muscle. Resolution of the troponin complex into inhibitory and calcium ion-sensitizing factors and their relationship to tropomyosin. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):993–1004. doi: 10.1042/bj1150993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seraydarian K., Briskey E. J., Mommaerts W. F. The modification of actomyosin by alpha- actinin. I. A survey of experimental conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 11;133(3):399–411. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90544-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Taylor E. W. Properties of the protein subunit of central-pair and outer-doublet microtubules of sea urchin flagella. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):304–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Huxley H. E., Finch J. T. Regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. II. Structural studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):619–632. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreter F. A., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. Studies on myosin from red and white skeletal muscles of the rabbit. I. Adenosine triphosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5772–5776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. On the structural protein of flagellar outer fibers. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Lowey S. Substructure of the myosin molecule. II. The light chains of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):701–725. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C., Borisy G. G., Taylor E. W. The colchicine-binding protein of mammalian brain and its relation to microtubules. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4466–4479. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]