Abstract
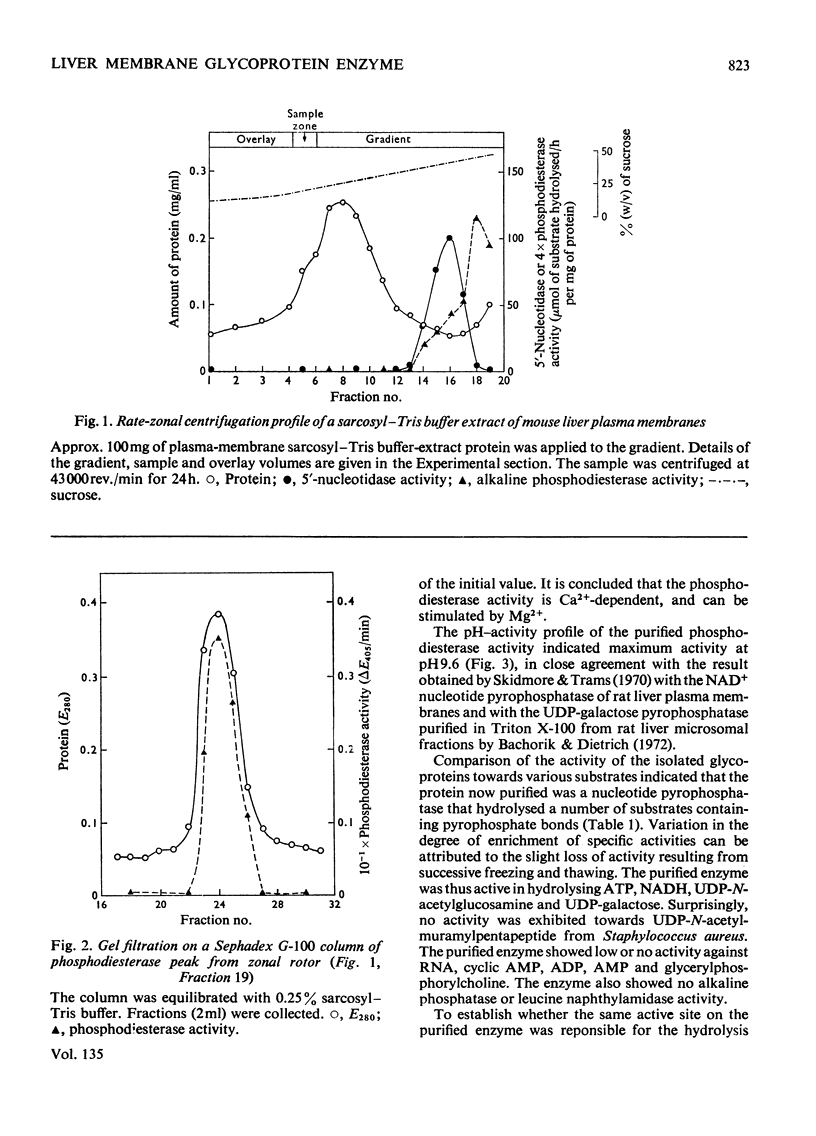
1. A mouse liver plasma-membrane preparation was solubilized in an N-dodecylsarcosinate–Tris buffer, pH7.8, and the proteins and glycoproteins were separated by a rate-zonal centrifugation in sucrose–detergent gradients. 2. A peak of alkaline phosphodiesterase activity which sedimented ahead of the 5′-nucleotidase peak was associated with a major glycoprotein component of the plasma membrane. 3. The phosphodiesterase activity was then purified further by gel filtration and gave a single glycoprotein band after electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels. The apparent molecular weight of the polypeptide at pH7.4 and 8.9 was 128000–130000 and was independent of the polyacrylamide concentration. Electrophoresis in gels containing deoxycholate showed that the protein band was coincident with phosphodiesterase activity. 4. After two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis, with agarose containing rabbit anti-(mouse plasma-membrane) antiserum as second dimension, the enzyme showed one component which was also coincident with the phosphodiesterase activity. 5. An amino acid composition of the glycoprotein is presented. Carbohydrate analysis indicated the presence of glucosamine, neutral sugars and sialic acid. 6. The enzyme was also a nucleotide pyrophosphatase, as shown by a similar enrichment during purification of activity towards ATP, NAD+, UDP-galactose and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine. The phosphodiesterase activity, measured by using dTMP p-nitrophenyl ester as substrate, was competitively inhibited by nucleotide pyrophosphate substrates. The enzyme showed little or no activity towards RNA, cyclic AMP, AMP, ADP and glycerylphosphorylcholine. 7. The significance of this enzyme activity in the plasma membrane is discussed.
Full text
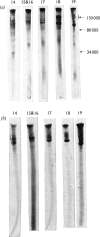
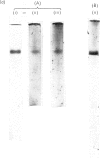
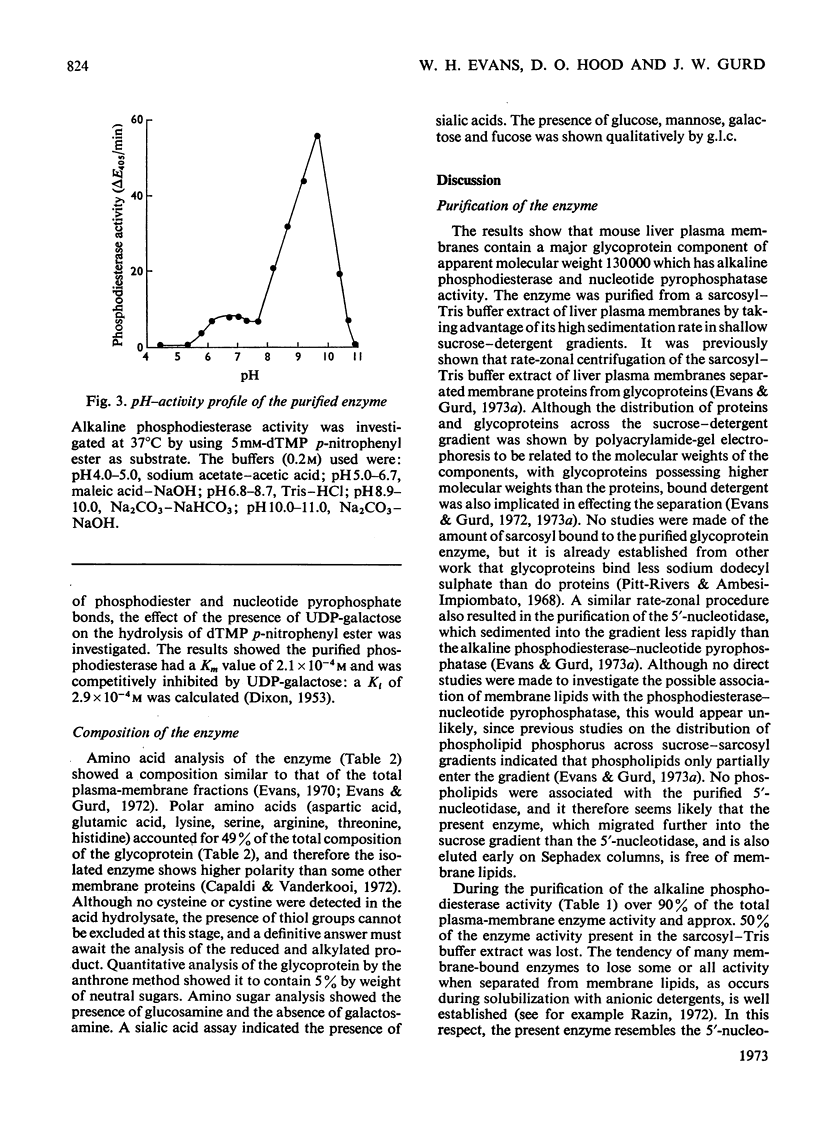
PDF

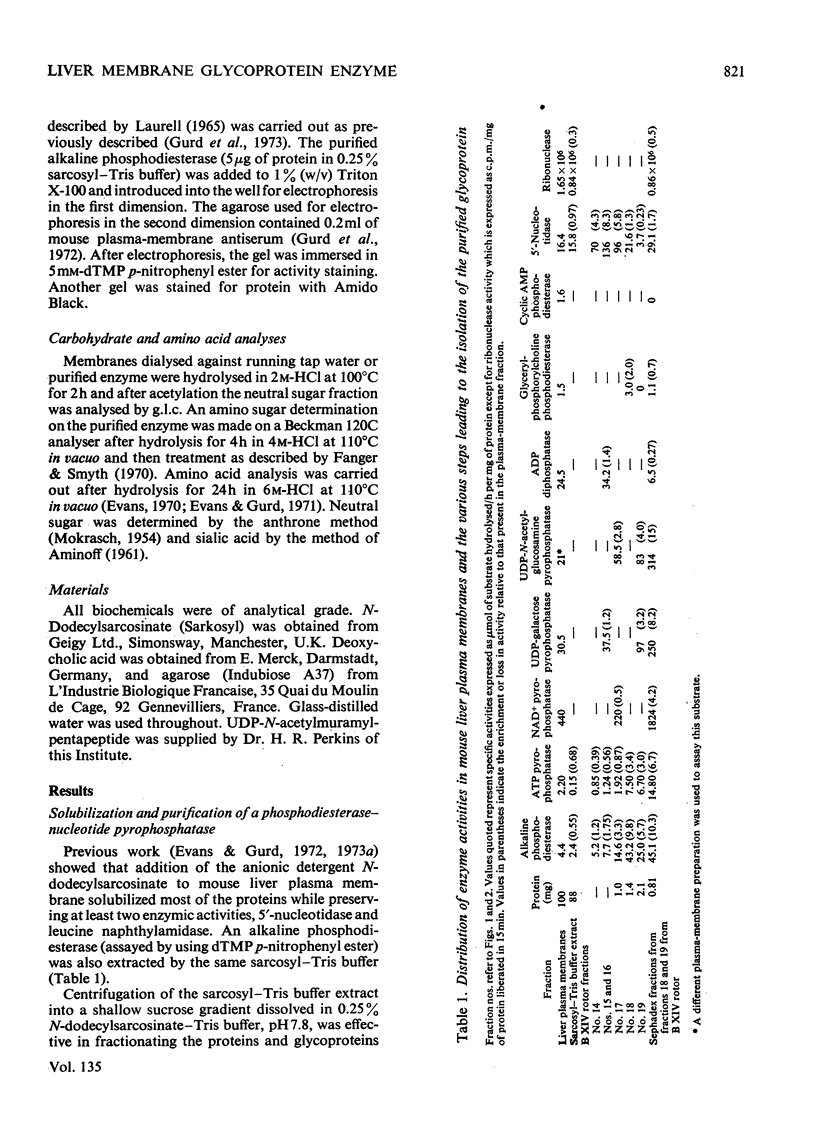

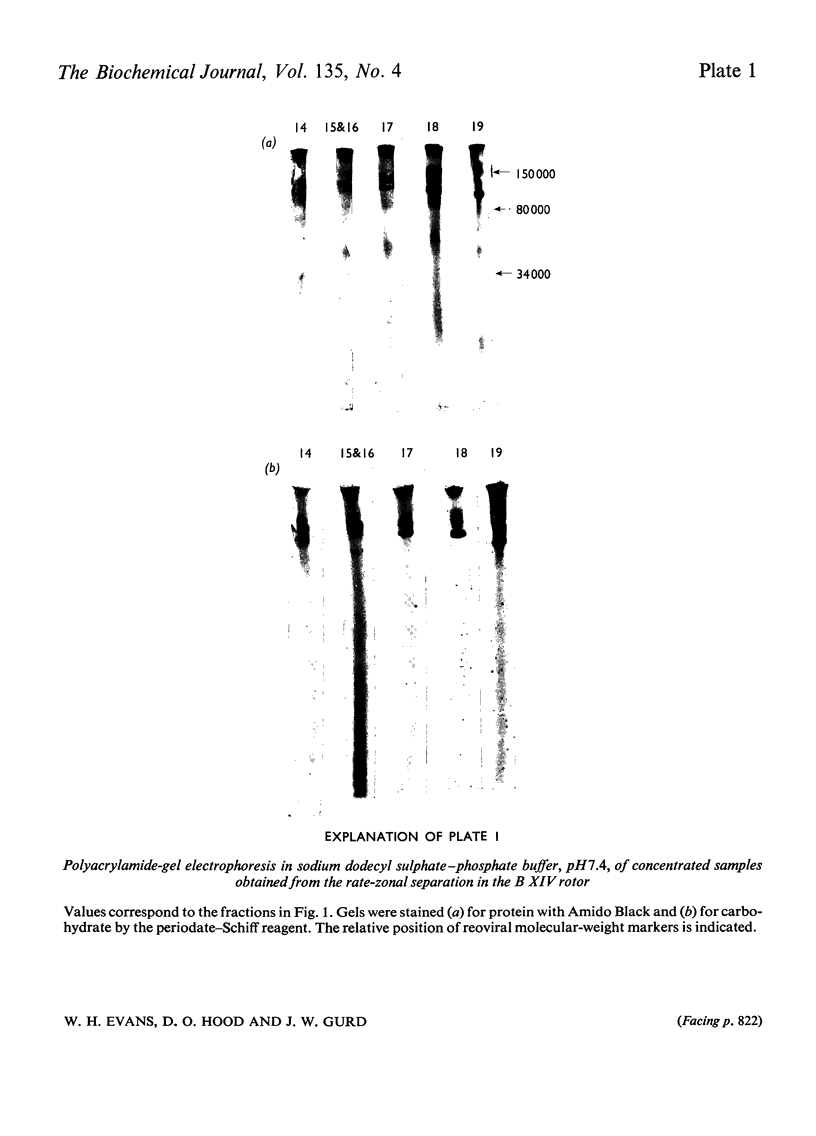



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachorik P. S., Dietrich L. S. The purification and properties of detergent-solubilized rat liver nucleotide pyrophosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5071–5078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastomsky C. H., Zakarija M., McKenzie J. M. Thyroid hydrolysis of cyclic AMP as influenced by thyroid gland activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 23;230(2):286–295. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. The low polarity of many membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker K., Bischoff E. Purification and properties of nucleotide pyrophosphatase from rat liver plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Mar;21(1):95–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Sierakowska H., Shugar D. Intracellular localization of phosphodiesterases I and II in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(3):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H. Fractionation of liver plasma membranes prepared by zonal centrifugation. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):833–842. doi: 10.1042/bj1160833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Gurd J. W. Biosynthesis of liver membranes. Incorporation of ( 3 H)leucine into proteins and of ( 14 C)glucosamine into proteins and lipids of liver microsomal and plasma-membrane fractions. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):615–624. doi: 10.1042/bj1250615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Gurd J. W. Preparation and properties of nexuses and lipid-enriched vesicles from mouse liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):691–700. doi: 10.1042/bj1280691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. H., Gurd J. W. Properties of a 5'-nucleotidase purified from mouse liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):189–199. doi: 10.1042/bj1330189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S., De Duve C. Digestive activity of lysosomes. 3. The digestion of lipids by extracts of rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):471–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Mizuno D. A new phosphodiesterase forming nucleoside 5'-monophosphate from rat liver. Its partial purification and substrate specificity for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and oligonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5301–5307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBARG J. A., RUTENBURG A. M. The colorimetric determination of leucine aminopeptidase in urine and serum of normal subjects and patients with cancer and other diseases. Cancer. 1958 Mar-Apr;11(2):283–291. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195803/04)11:2<283::aid-cncr2820110209>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland R. C., Cori C. F. Separation of phospholipids from glucose-6-phosphatase by gel chromatography. Specificity of phospholipid reactivation. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4712–4718. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Evans W. H., Perkins H. R. Immunochemical characterization of proteins from mouse liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):827–832. doi: 10.1042/bj1350827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurd J. W., Evans W. H., Perkins H. R. The distribution of surface antigens during fractionation of mouse liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):271–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1300271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipata P. L. A coupled optical enzyme assay for 5'-nucleotidase. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman I., Lansing A. I., Lynch W. E. Nucleoside triphosphate pyrophosphohydrolase of the plasma membrane of the liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):736–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Davies K. A., Michell R. H., Coleman R. Glycerylphosphorylcholine phosphodiesterase in rat liver. Subcellular distribution and localization in plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):357–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1270357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOKRASCH L. C. Analysis of hexose phosphates and sugar mixtures with the anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1954 May;208(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Sawada M., Kawada M. Purification and properties of a pyrophosphatase from rat liver microsomes capable of catalyzing the hydrolysis of UDP-glucuronic acid. J Biochem. 1966 Feb;59(2):126–134. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt-Rivers R., Impiombato F. S. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to various proteins. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prospero T. D., Burge M. L., Norris K. A., Hinton R. H., Reid E. Alkaline ribonuclease and phosphodiesterase activity in rat liver plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;132(3):449–458. doi: 10.1042/bj1320449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Reconstruction of biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;265(2):241–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseman S. The synthesis of complex carbohydrates by multiglycosyltransferase systems and their potential function in intercellular adhesion. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Oct;5(1):270–297. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLISELFELD L. H., VANEYS J., TOUSTER O. THE PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF A NUCLEOTIDE PYROPHOSPHATASE OF RAT LIVER NUCLEI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:811–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela B. A., Lis H., Sachs L. Enzymatic hydrolysis of uridine diphosphate-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and uridine diphosphate-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine by normal cells, and blocks in this hydrolysis in transformed cells and their revertants. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7585–7590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore J., Trams E. G. Nucleotide pyrophosphatase activity of rat liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;219(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Appleman M. M. Multiple cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1971 Jan 19;10(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touster O., Aronson N. N., Jr, Dulaney J. T., Hendrickson H. Isolation of rat liver plasma membranes. Use of nucleotide pyrophosphatase and phosphodiesterase I as marker enzymes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):604–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vessey D. A., Zakim D. Regulation of microsomal enzymes by phospholipids. V. Kinetic studies of hepatic uridine diphosphate-glucuronyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3023–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lamirande G., Boileau S., Morais R. Distribution of the nucleases of the microsomal fraction of rat liver between ribosomes and endoplasmic membranes. Can J Biochem. 1966 Feb;44(2):273–279. doi: 10.1139/o66-030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]