Abstract
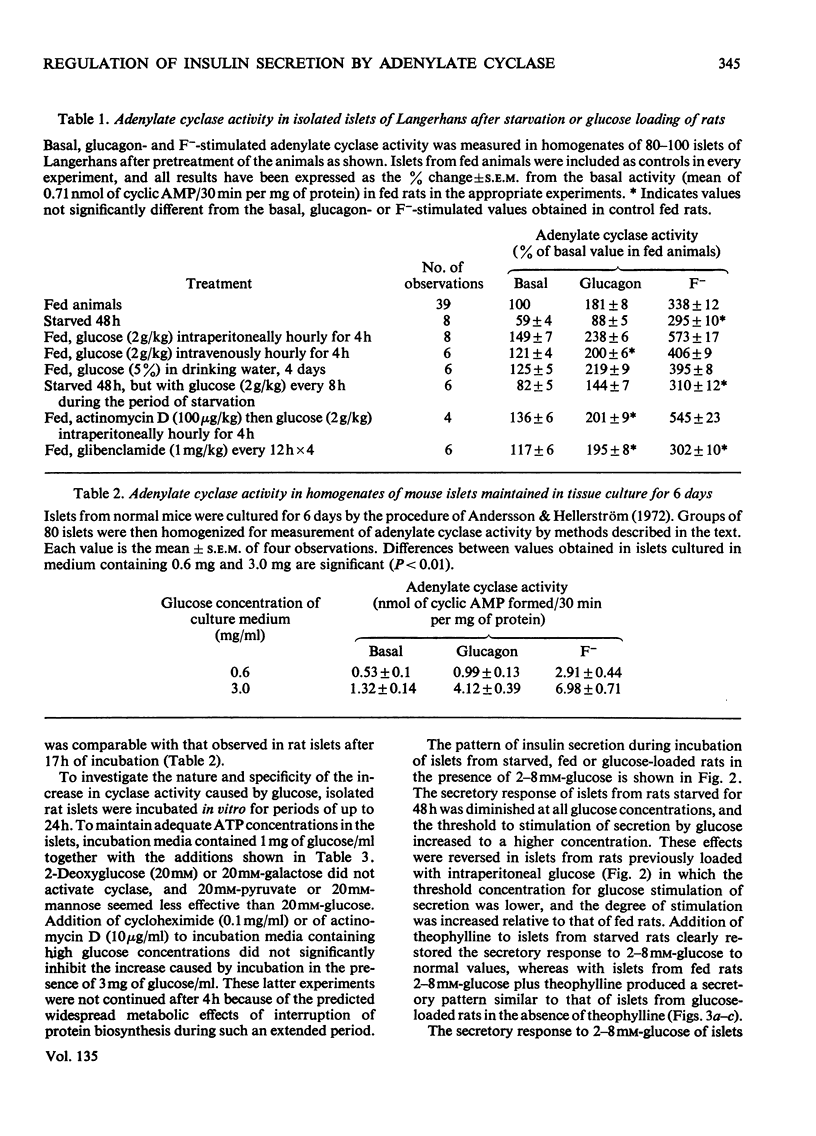
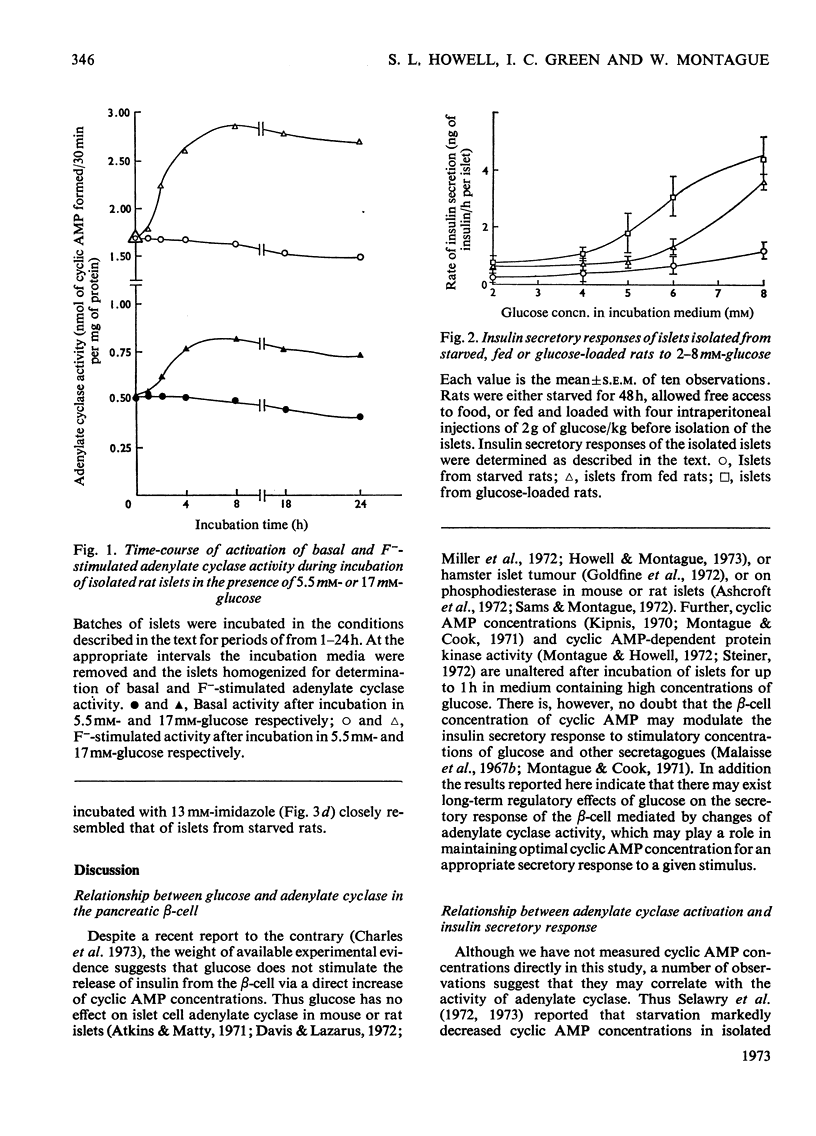
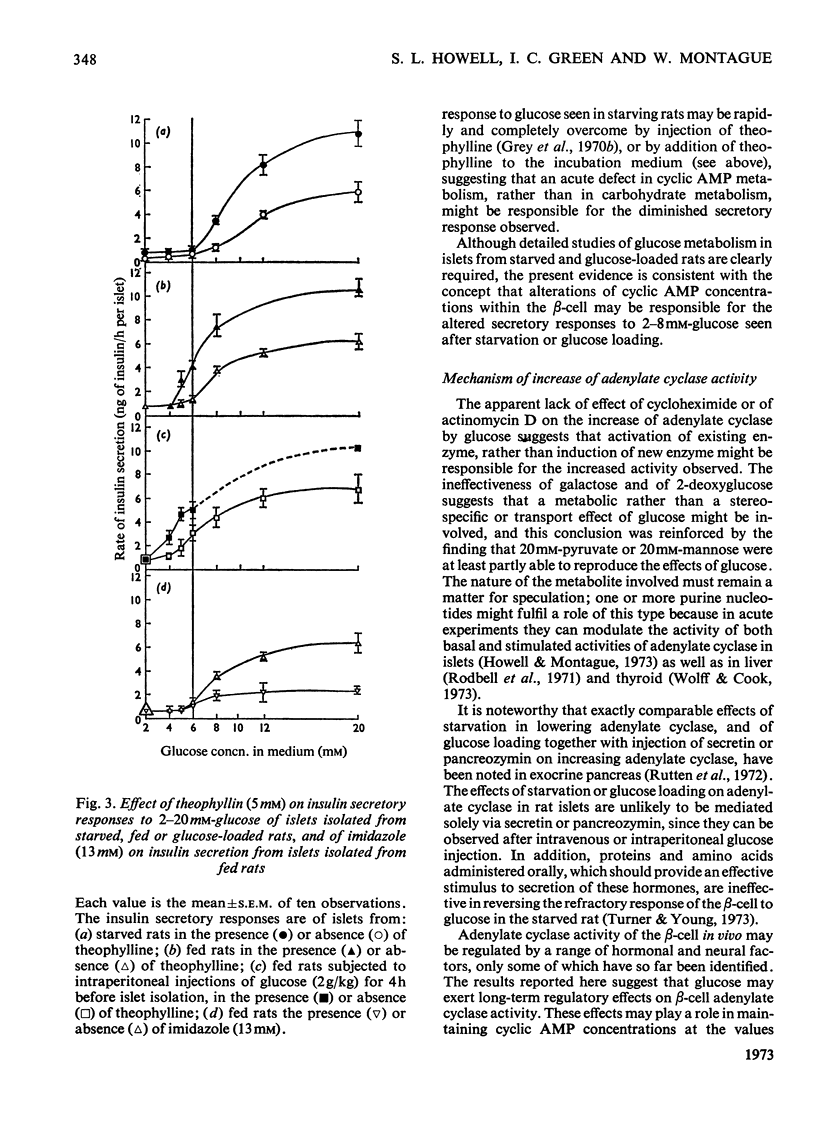
1. Adenylate cyclase activity and patterns of insulin release in response to various concentrations of glucose were determined in islets of Langerhans isolated from starving, fed, or glucose-loaded rats. 2. Basal and glucagon-stimulated activities of adenylate cyclase were lower in islets from starved than from fed rats. The minimum glucose concentration required for stimulation of insulin secretion was higher, whereas the maximum secretory response to glucose was lower, in islets from starved than from fed rats. 3. Adenylate cyclase activity in islets of Langerhans obtained from fed rats loaded with glucose by intermittent intravenous or intraperitoneal injections over 5h was significantly higher than that seen in islets from normal fed rats. Islets obtained from glucose-loaded rats required a lower glucose concentration for stimulation of insulin secretion and attained a higher maximal response to glucose stimulation than those derived from fed rats. 4. Incubation in vitro of islets isolated from normal fed rats, for periods of 1 to 24h in the presence of high concentrations of glucose resulted in an activation of adenylate cyclase that occurred progressively from 2 to 7h and which was maintained during 24h of incubation. The increase of adenylate cyclase activity in isolated islets incubated for 4h in the presence of glucose was not prevented by addition of cycloheximide or actinomycin D. Galactose or 2-deoxyglucose was ineffective in increasing adenylate cyclase activity, and pyruvate (20mm) was less effective than glucose. 5. It is suggested that glucose or a glucose metabolite may exert long-term effects on islet cell adenylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson A., Hellerström C. Metabolic characteristics of isolated pancreatic islets in tissue culture. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):546–554. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J.H., Randle P. J., Täljedal I. -B. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity in normal mouse pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 15;20(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins T., Matty A. J. [Six years' experience with a musculoplastic technic]. J Endocrinol. 1971 Sep;51(1):67–78. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUNSBERG H., GUYVER A. AUTOMATIC LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF HIGH-ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN TISSUE SLICES AND AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS IN THE ABSENCE OF ORGANIC SCINTILLATOR. Anal Biochem. 1965 Jan;10:86–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. The effect of an adenosine--3'5'--monophosphate diesterase inhibitor (aminophylline) on the insulin response to glucose infusion in prediabetic and diabetic subjects. Horm Metab Res. 1969 Jul;1(4):162–168. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. The prediabetic state, its nature and consequences--a look toward the future. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):685–694. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles M. A., Fanska R., Schmid F. G., Forsham P. H., Grodsky G. M. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in pancreatic islets: glucose-induced insulin release. Science. 1973 Feb 9;179(4073):569–571. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4073.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Lazarus N. R. Insulin release from mouse islets. Effect of glucose and hormones on adenylate cyclase. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1290373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Wells L. J., Lazarow A. Organ culture of pancreases of fetuses from normal and diabetic rats: effect of glucose on the insulin content of the media. Metabolism. 1968 Jul;17(7):638–643. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Birnbaumer L. Glucagon receptors in -cells. Binding of 125 I-glucagon and activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1211–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I. C., Taylor K. W. Effects of pregnancy in the rat on the size and insulin secretory response of the islets of Langerhans. J Endocrinol. 1972 Aug;54(2):317–325. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0540317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey N. J., Goldring S., Kipnis D. M. The effect of fasting, diet, and actinomycin D on insulin secretion in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):881–889. doi: 10.1172/JCI106307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerstrom C., Howell S. L., Edwards J. C., Andersson A. An investigation of glucagon biosynthesis in isolated pancreatic islets of guinea pigs. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80418-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Montague W. Adenylate cyclase activity in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Effects of agents which alter rates of insulin secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Effects of glucose concentration on incorporation of [3H]leucine into insulin using isolated mammalian islets of Langerhans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert A. E., Junod A., Stauffahcer W., Jeanrenaud B., Renold A. E. Organ culture of fetal rat pancreas. I. Insulin release induced by caffeine and by sugars and some derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 2;184(3):529–539. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Mayhew D. A possible role for the adenylcyclase system in insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1724–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI105663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Wright P. H. Effect of fasting upon insulin secretion in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1967 Oct;213(4):843–848. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.4.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. A., Wright P. H., Allen D. O. Effect of hormones on accumulation of cyclic AMP-14C in isolated pancreatic islets of rats. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):1117–1119. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Cook J. R. The role of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in the regulation of insulin release by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):115–120. doi: 10.1042/bj1220115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Howell S. L. The mode of action of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in mammalian islets of Langerhans. Preparation and properties of islet-cell protein phosphokinase. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(3):551–560. doi: 10.1042/bj1290551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran J. A new simple method for separation of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate from other nucleotides and its use in the assay of adenyl cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Sep;43(1):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Krans H. M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. V. An obligatory role of guanylnucleotides in glucagon action. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1877–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutten W. J., de Pont J. J., Bonting S. L. Adenylate cyclase in the rat pancreas properties and stimulation by hormones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sams D. J., Montague W. The role of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in the regulation of insulin release. Properties of islet-cell adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate phosphodiesterase. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(4):945–952. doi: 10.1042/bj1290945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selawry H., Gutman R., Fink G., Recant L. The effect of starvation on tissue adenosine 3'-5' monophosphate levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90528-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. S., Young D. A. The effect of fasting and selective re-feeding on insulin release in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1973 Jan;72(1):46–53. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0720046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turtle J. R., Kipnis D. M. An adrenergic receptor mechanism for the control of cyclic 3'5' adenosine monophosphate synthesis in tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):797–802. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. E., Buchanan K. D., Williams R. H. Effect of starvation and refeeding on serum immunoreactive glucagon and insulin levels. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Aug;72(2):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H. Activation of thyroid membrane adenylate cyclase by purine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


