Abstract
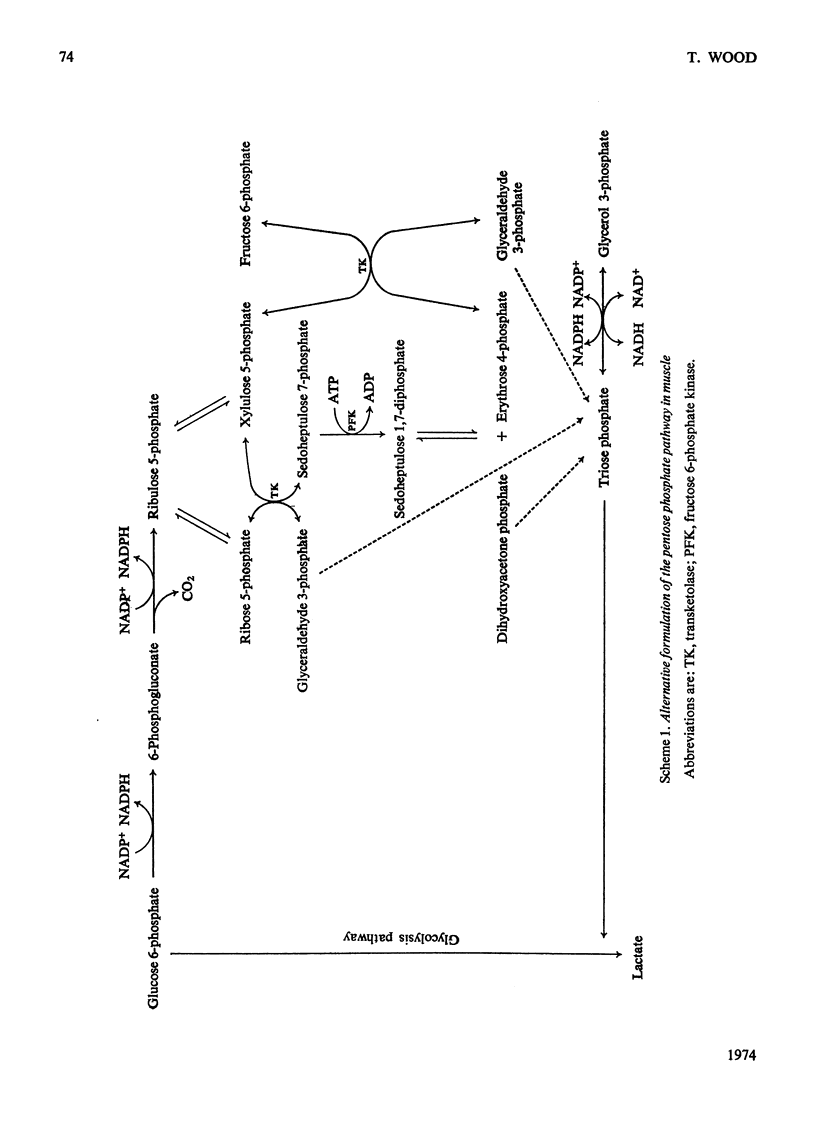
1. The enzymes of the pentose phosphate pathway were assayed in supernatant fractions from rat muscle, liver and uterus. 2. On incubation of ribose 5-phosphate with uterus and liver supernatants, triose phosphate, sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and hexose monophosphate accumulated. 3. When a muscle supernatant was used, glycerol 3-phosphate instead of triose phosphate appeared and there was a negligible accumulation of hexose monophosphate. 4. Hexose monophosphate production from ribose 5-phosphate was also followed by measuring NADP+ reduction in the presence of an excess of phosphoglucose isomerase, glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. 5. With a muscle supernatant, NADPH was reoxidized as rapidly as it was formed owing to the presence of a NADPH–triose phosphate oxidoreductase. 6. A modification of the pentose phosphate pathway in skeletal muscle incorporating this enzyme is proposed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORREBAEK B., ABRAHAM S., CHAIKOFF I. L. OXIDATION OF REDUCED NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE BY SOLUBLE RAT MUSCLE ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. A COMPARISON WITH PURIFIED LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE AND MALATE DEHYDROGENASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 22;96:237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baquer N. Z., McLean P. Evidence for the existence and functional activity of the pentose phosphate pathway in the large particle fraction isolated from rat tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90646-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., McLEAN P. Further studies on the properties and assay of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase of rat liver. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):400–408. doi: 10.1042/bj0550400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiely M. E., Stuart A. L., Wood T. Partial purification and kinetic properties of ribose-5-phosphate ketol-isomerase and ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase from various sources. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 15;293(2):534–541. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90360-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novello F., McLean P. The pentose phosphate pathway of glucose metabolism. Measurement of the non-oxidative reactions of the cycle. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(6):775–791. doi: 10.1042/bj1070775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHONK C. E., BOXER G. E. ENZYME PATTERNS IN HUMAN TISSUES. I. METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF GLYCOLYTIC ENZYMES. Cancer Res. 1964 May;24:709–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieben A. S., Perlin A. S., Simpson F. J. An improved preparative method for D-erythrose 4-phosphate. Can J Biochem. 1966 Jun;44(6):663–669. doi: 10.1139/o66-083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. L., Wood T. Enzymes of the pentose phosphate cycle in muscles of rat, ox, frog, lobster, chicken, northern pike and carp, and Ehrlich ascites cells. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Nov 15;31(4):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T., Poon W. M. The preparation and assay of sedoheptulose-7-phosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Dec;141(2):440–446. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. Spectrophotometric ass for D-ribose-5-phosphateketol-isomerase and for D-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. The detection and identification of intermediates of the pentose phosphate cycle and related compounds. J Chromatogr. 1968 Jun 18;35(3):352–361. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82396-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. The forward and reverse reactions of transaldolase. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 1;25(1):153–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80474-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von FELLENBERG, EPPENBERGER H., RICHTERICH R., AEBI H. [The glycolytic erzyme pattern in the liver, kidney, skeletal muscle, heart muscle and brain of rats and mice]. Biochem Z. 1962;336:334–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


