Abstract
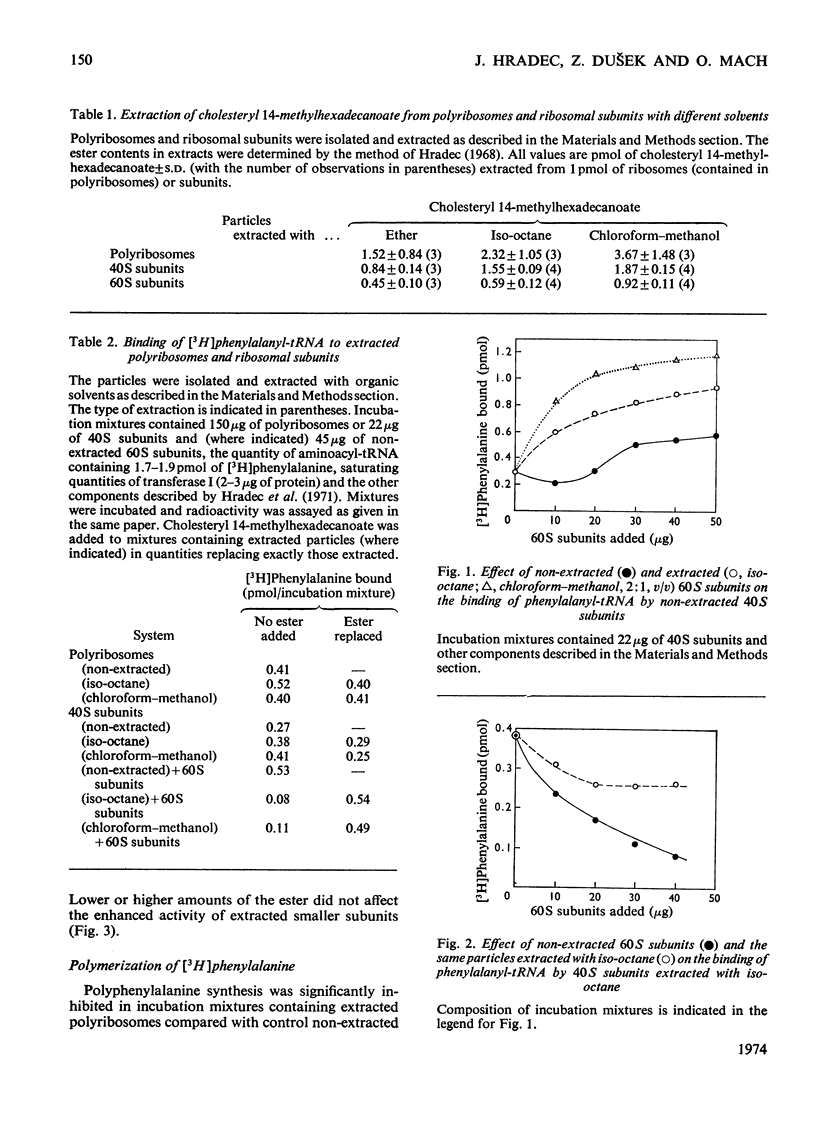
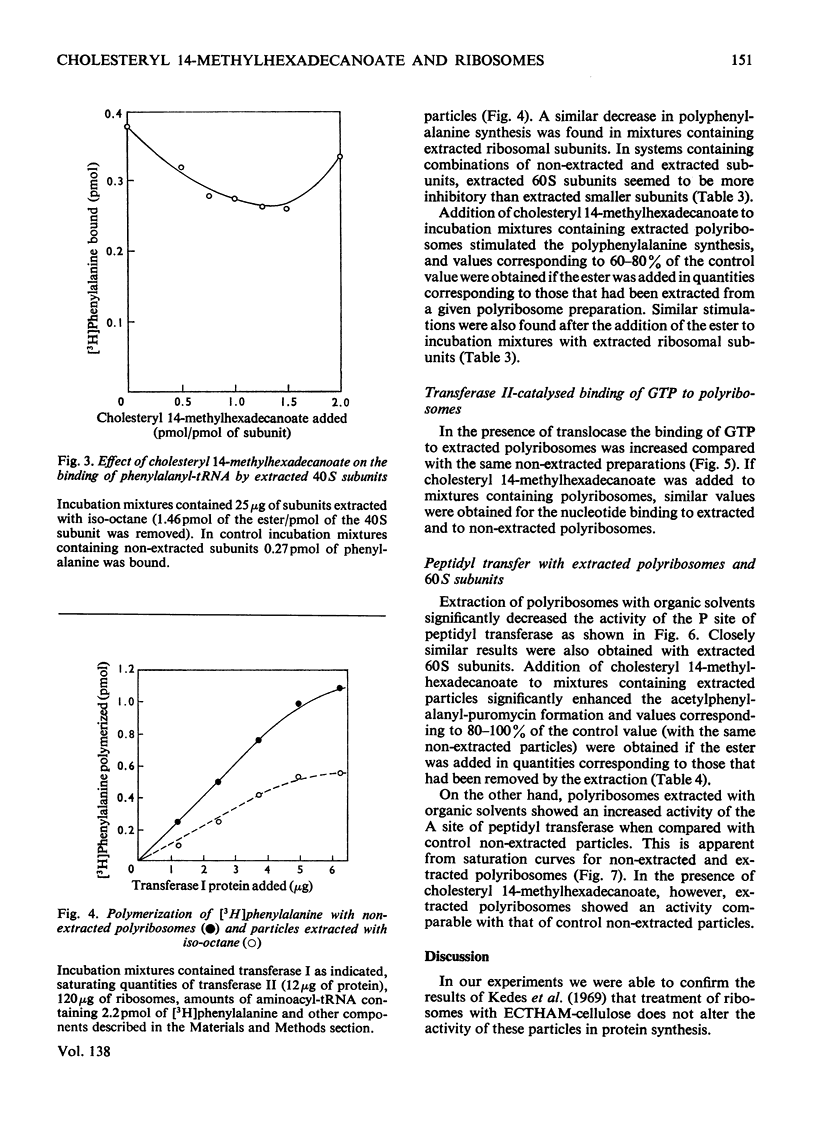
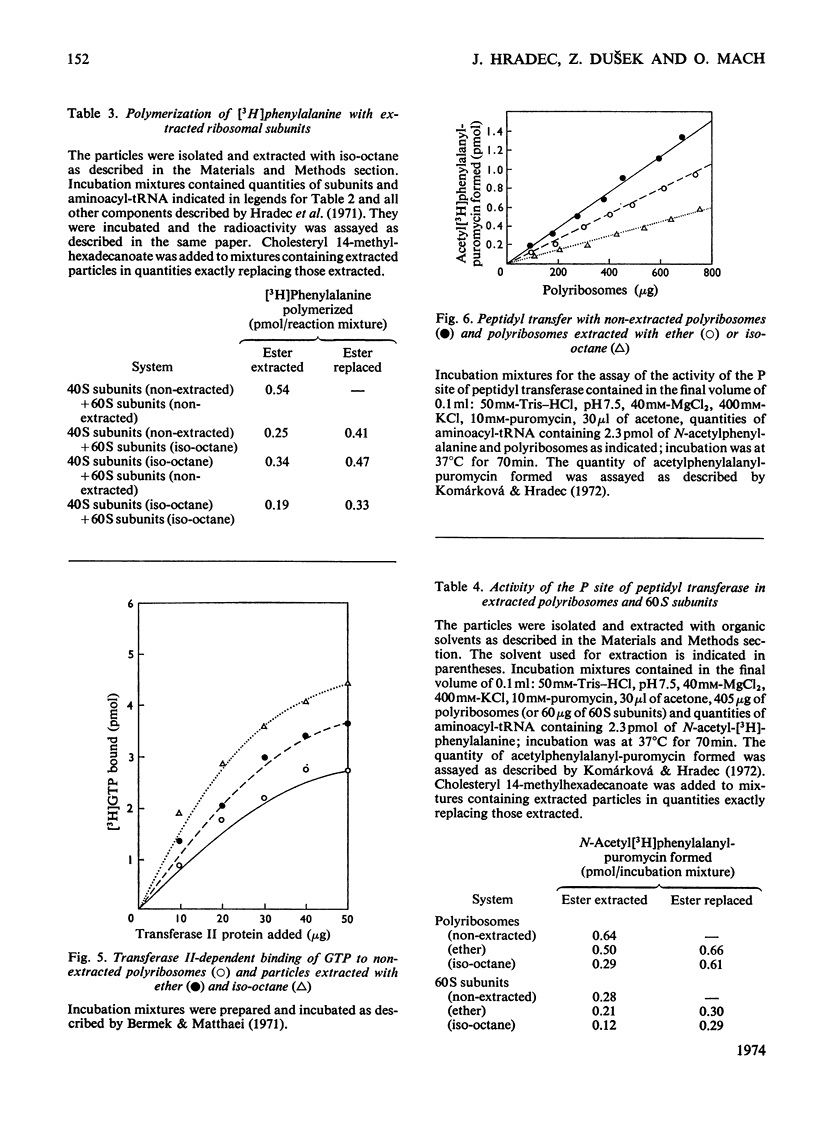
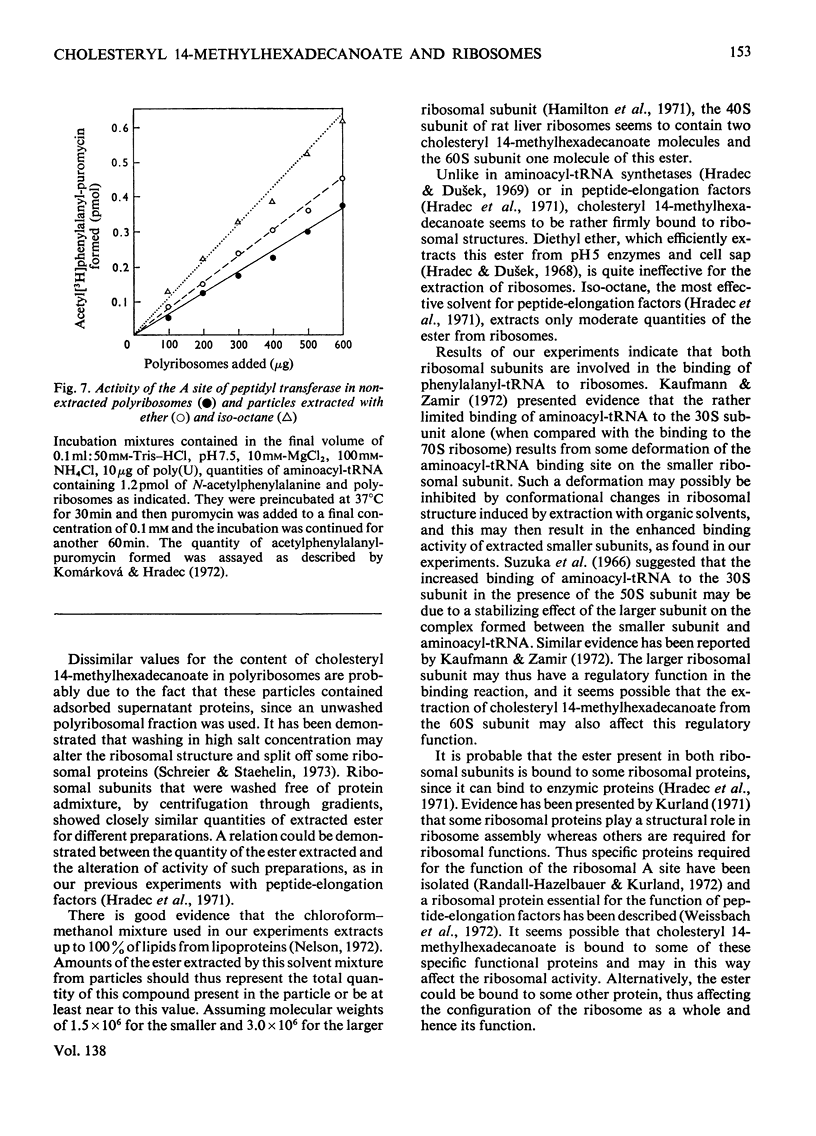
1. Polyribosomes and ribosomal subunits from rat liver were adsorbed on a cellulosic ion-exchange adsorbent, freeze-dried and extracted with organic solvents. The activity of extracted particles in peptide elongation was tested in the presence of purified peptideelongation factors. 2. Chloroform–methanol mixture (2:1, v/v) extracted 1.87±0.15 pmol of cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate/pmol of the smaller ribosomal subunit and 0.92±0.11 pmol/pmol of the larger subunit. 3. In the presence of transferase I, extracted polyribosomes and 40S subunits bound more phenylalanyl-tRNA than did control non-extracted particles. The same binding as in control mixtures was obtained with extracted particles supplemented with cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate in quantities corresponding to those extracted. 4. The polymerization of phenylalanine was greatly decreased with extracted polyribosomes and subunits and addition of the cholesteryl ester could not fully restore the original activity. 5. Extraction significantly decreased the activity of the P site of peptidyl transferase and normal activity was recovered after the addition of the ester. The A site of peptidyl transferase in extracted polyribosomes showed an increased activity when compared with non-extracted polyribosomes. 6. Cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate apparently affects the function of the ribosomal A site and peptidyl transferase site and probably also that of the guanosine triphosphatase site and P site. The presence of different amounts of the ester in polyribosomes may be one of the mechanisms modulating peptide elongation at the ribosomal level.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bermek E., Matthaei H. Interactions between human translocation factor, guanosine triphosphate, and ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4906–4912. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borghetti A. F., Comi P., Franchi R., Gianni A. M., Giglioni B., Ottolenghi S., Guidotti G. G. Ribosomal subunits from rat liver. Isolation and recombination into active ribosomal particles. Ital J Biochem. 1970 Nov-Dec;19(6):397–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey A. K., Staehelin T. Structure and function of mammalian ribosomes. I. Isolation and characterization of active liver ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. G., Pavlovec A., Petermann M. L. Molecular weight, buoyant density, and composition of active subunits of rat liver ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3424–3427. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J. A chromatographic method for the quantitative determination of cholesterol 14-methylhexadecanoate (carcinolipin) in biological materials. J Chromatogr. 1968 Feb 6;32(3):511–518. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dolejs L. The chemical constitution of carcinolipin. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1070129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dusek Z., Bermek E., Matthaei H. The role of cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate in peptide elongation reactions. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):959–966. doi: 10.1042/bj1230959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dusek Z. Effect of cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate on the activity of some amino acid-transfer ribonucleic acid ligases from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):873–880. doi: 10.1042/bj1150873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dusek Z. Effect of lipids, in particular cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate, on the incorporation of labelled amino acids into transfer ribonucleic acid in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bj1100001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J. Intermediate reactions in the binding of aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid to rat liver ribosomes. the interaction of cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1225–1229. doi: 10.1042/bj1261225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann Y., Zamir A. Aminoacyl-transfer RNA binding to active 30 s subunits: effect of 50 s subunits and a new role for elongation factor T. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 28;69(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Kuff E. L., Peterson E. A. Protein synthetic activity of chromatographically isolated mammalian ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2923–2929. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komárková E., Hradec J. Protein synthesis in the liver of rats injected with cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):367–372. doi: 10.1042/bj1290367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Hardesty B. Purification and partial characterization of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding enzyme from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4330–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson E. A., Kuff E. L. Chromatographic isolation of 80S ribosomes from rat liver and mouse plasma cell tumor. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2916–2923. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall-Hazelbauer L. L., Kuland C. G. Identification of three 30S proteins contributing to the ribosomal A site. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(3):234–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00268887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman N., Bodley J. W. Ribosomes cannot interact simultaneously with elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):686–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlík I., Cerná J., Chládek S., Zemlicka J., Haladová Z. Substrate specificity of ribosomal peptidyl transferase: 2'(3')-O-aminoacyl nucleosides as acceptors of the peptide chain on the amino acid site. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Noll H. Conformational changes in ribosomes during protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siler J., Moldave K. Studies on the binding of phenylalanyl transfer RNA to rat-liver ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 19;195(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90608-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogerson L., Moldave K. Characterization of the interaction of aminoacyltransferase II with ribosomes. Binding of transferase II and translocation of peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5354–5360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuka I., Kaji H., Kaji A. Binding of specific sRNA to 30S ribosomal subunits: effect of 50S ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1483–1490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D., Battaner E., Neth R., Heller G., Monro R. E. The function of 80 S ribosomal subunits and effects of some antibiotics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:369–375. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D. THE SYNTHESIS OF PROTEINS UPON RIBOSOMES. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1964;46:1399–1425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Redfield B., Yamasaki E., Davis R. C., Jr, Pestka S., Brot N. Studies on the ribosomal sites involved in factors Tu and G-dependent reactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


