Abstract
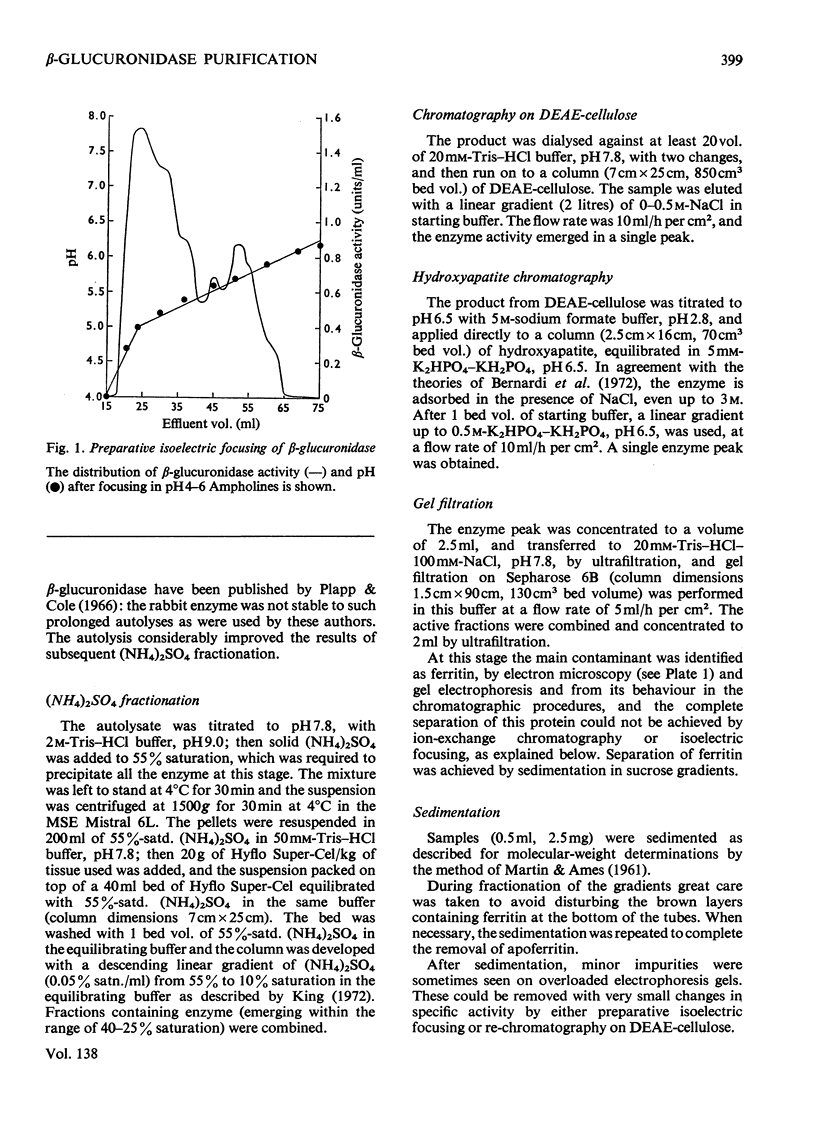
1. β-Glucuronidase (EC 3.2.1.31) was purified from rabbit liver by a procedure involving autolysis, (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, chromatography on DEAE-cellulose and hydroxyapatite, gel filtration, sedimentation in a sucrose gradient, and isoelectric focusing. 2. Electron microscopy revealed ferritin as the major contaminant in later stages of purification and also showed aggregates of enzyme molecules. Particular attention was paid to the removal of ferritin. 3. The purified enzyme was homogeneous in polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis both in non-dissociating conditions and in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate, and in Ouchterlony gel diffusion and immunoelectrophoresis against polyspecific antisera. 4. Sedimentation in sucrose gradients gave a molecular weight of 300000, whereas gel filtration indicated 440000. 5. Subunits of 75000 molecular weight were observed in gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate and in gel filtration in the presence of urea. 6. The Km value for p-nitrophenyl β-d-glucuronide was 0.6mm, and the enzyme was extremely sensitive to lactone inhibitors. It was also inhibited by Hg2+ ions. 7. Multiple forms were observed in the pure enzyme by isoelectric focusing, with pI values of 4.5–5.8. Subunits showed similar heterogeneity. The origin of the multiple forms was investigated in detail, and the possibility of artifact generation largely excluded. Some of the forms of lowest pI disappeared after neuraminidase digestion. The nature of the residual heterogeneity remains to be elucidated.
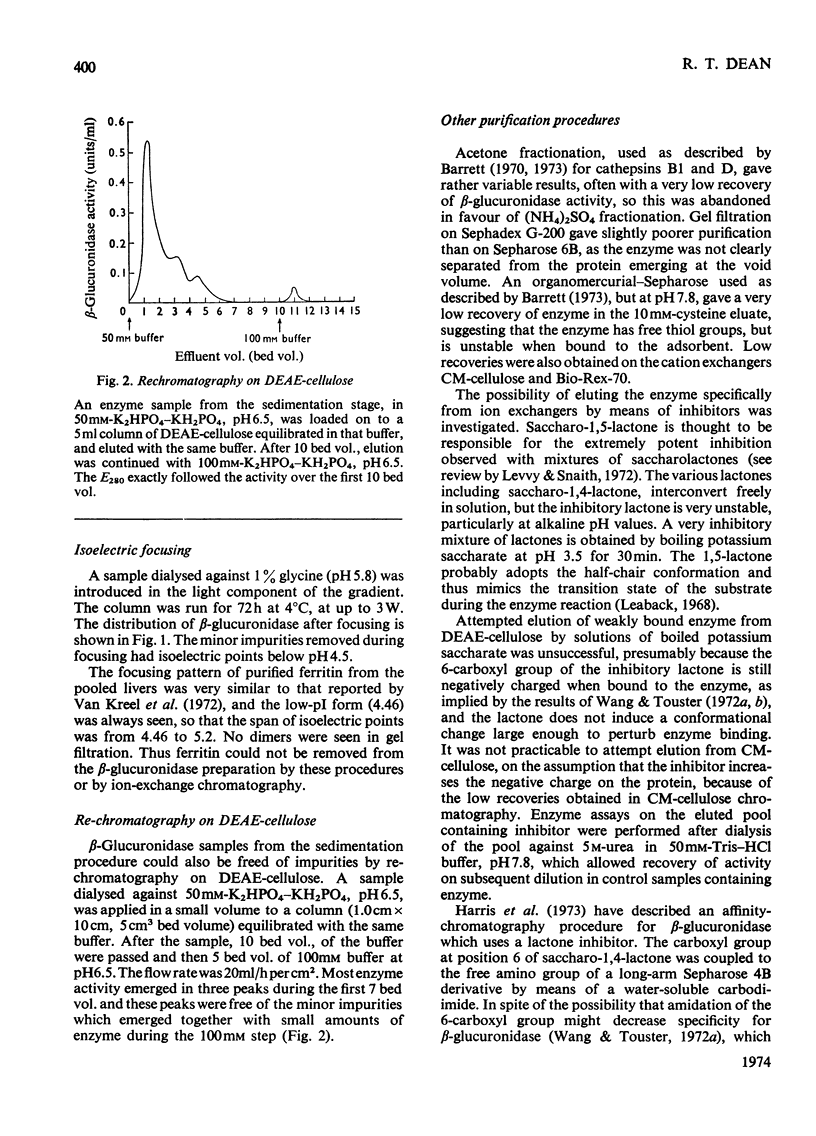
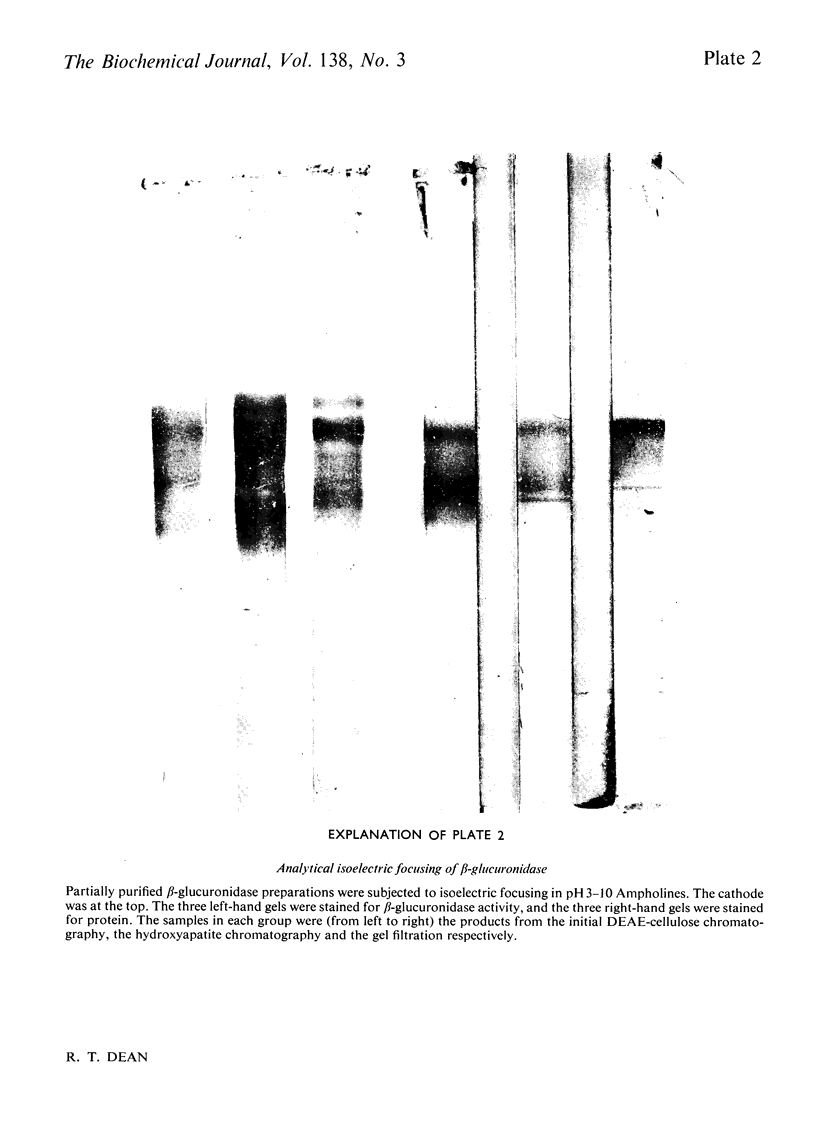
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoshima M., Sakurai Y. Biochemical changes in tumor cells caused by antitumor agent. IV. Influence of antitumor agent on isozyme pattern of beta-glucuronidase. Gan. 1969 Apr;60(2):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNFELD P., JACOBSON S., BERNFELD H. C. Activator-competitive enzyme inhibition; interrelation of dissociation, activation, inhibition and surface inactivation of beta-glucuronidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jul;69:198–209. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Cathepsin D. Purification of isoenzymes from human and chicken liver. Biochem J. 1970 Apr;117(3):601–607. doi: 10.1042/bj1170601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Human cathepsin B1. Purification and some properties of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):809–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1310809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Giro M. G., Gaillard C. Chromatography of polypeptides and proteins on hydroxyapatite columns: some new developments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Oct 31;278(3):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman D. C., Laryea J. U., Weissmann B. The hyaluronidase of rat skin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90554-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutelle R. Auftrennung von -Glukuronidase aus Ehrlich-Aszites-Karzinomzellen und dem Grosshirn der Maus durch Isoelektrofokussierung in Polyakrylamid. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1971;27(4):681–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crichton R. R. The subunit structure of apoferritin and other eicosamers. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):761–764. doi: 10.1042/bj1260761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T. Rabbit beta-glucuronidase. Subcellular distribution and immunochemical properties. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;138(3):407–413. doi: 10.1042/bj1380407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvin E., Gianetto R. The purification of lysosomal rat-liver beta glucuronidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 14;220(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dofuku R., Tettenborn U., Ohno S. Further characterization of Os mutation of mouse beta-glucuronidase locus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 29;234(52):259–261. doi: 10.1038/newbio234259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERNLEY H. N. Effects of some heavy-metal ions on purified mammalian beta-glucuronidase. Biochem J. 1962 Mar;82:500–509. doi: 10.1042/bj0820500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Goldman S. S., DeLellis R. Dual localization of beta-glucuronidase in endoplasmic reticulum and in lysosomes. Nature. 1967 Feb 4;213(5075):457–460. doi: 10.1038/213457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondo E. Y., Jr, Bartalos M. Electrophoretic separation of multiple bands with beta-glucuronidase activity in human sera. Biochem Genet. 1969 Dec;3(6):591–593. doi: 10.1007/BF00485480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funakoshi S., Deutsch H. F. Human carbonic anhydrases. II. Some physicochemical properties of native isozymes and of similar isozymes generated in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3438–3446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganschow R. E., Bunker B. G. Genetic control of glucuronidase in mice. Biochem Genet. 1970 Feb;4(1):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00484025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganschow R., Paigen K. Glucuronidase phenotypes of inbred mouse strains. Genetics. 1968 Jul;59(3):335–349. doi: 10.1093/genetics/59.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganschow R., Paigen K. Separate genes determining the structure and intracellular location of hepatic glucuronidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):938–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstone A., Koenig H., Nayyar R., Hughes C., Lu C. Y. Isolation and characterization of a rough microsomal fraction from rat kidney that is enriched in lysosomal enzymes. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):259–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1320259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstone A., Koenig H. Physicochemical modifications of lysosomal hydrolases during intracellular transport. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):267–282. doi: 10.1042/bj1320267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. G., Rowe J. J., Stewart P. S., Williams D. C. Affinity chromatography of -glucuronidase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultbery B., Ockerman P. A. Artificial substrates in the assay of acid glycosidases. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Jun;39(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffree G. M. Demonstration of beta glucuronidase with naphthol AS-BI-beta-D-glucosiduronic acid by simultaneous coupling. J Microsc. 1969;89(1):55–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1969.tb00649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungalwala F. B., Robins E. Glycosidases in the nervous system. 3. Separation, purification, and substrate specificities of beta-galactosidases and beta-glucuronidase from brain. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4258–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Ide H., Shirahama T., Fishman W. H. Incorporation of [14C] glucosamine and [14C] leucine into mouse kidney beta-glucuronidase induced by gonadotrophin. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;117(1):161–167. doi: 10.1042/bj1170161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P. Separation of proteins by ammonium sulfate gradient solubilization. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 1;11(3):367–371. doi: 10.1021/bi00753a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., McALLAN A., MARSH C. A. Purification of beta-glucuronidase from the preputial gland of the female rat. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):22–27. doi: 10.1042/bj0690022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaback D. H. On the inhibition of beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminidase by 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucono-(1-5)-lactone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Sep 30;32(6):1025–1030. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levvy G. A., Snaith S. M. The inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1972;36:151–181. doi: 10.1002/9780470122815.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin L. G., Allison A. C. Acid phosphatases from different organs and animal forms compared by starch-gel electrophoresis. Acta Chem Scand. 1966;20(9):2579–2592. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.20-2579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE B. W., LEE R. H. Chromatography of rat liver soluble proteins and localization of enzyme activities. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1359–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mameli L., Potier M., Gianetto R. Difference in electrophoretic mobility between the lysosomal and the microsomal -glucuronidase of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):560–563. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi I., Shioya A. Rabbit liver beta-glucuronidase. I. Purification and its properties. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1971 Aug;21(4):541–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi I., Shioya A. Rabbit liver beta-glucuronidase. II. Immunological properties and examination of some species difference. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1971 Aug;21(4):551–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okochi T., Masaki S., Aoki T., Ito F., Yamamura Y. Immunochemical studies on beta-glucuronidase isoenzyme. Med J Osaka Univ. 1968 Dec;19(2):147–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K., Wakabayashi M. Purification and characterization of the preputial gland beta-glucuronidase. Enzymologia. 1970 Aug 31;39(2):109–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAIGEN K. The effect of mutation on the intracellular location of beta-glucuronidase. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Nov;25:286–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90280-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plapp B. V., Cole R. D. Demonstration and partial characterization of multiple forms of bovine liver beta-glucuronidase. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3676–3681. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plapp B. V., Cole R. D. Purification and characterization of bovine liver beta-glucuronidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):193–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Hilz H. Isolation and partial characterization of -glucuronidase from murine mastocytoma cells. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Jul;352(7):947–953. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadahiro R., Takanashi S., Kawada M. Studies on the isozyme of beta-glucuronidase. J Biochem. 1965 Jul;58(1):104–106. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S., Er-El Z. Hydrophobic chromatography: use for purification of glycogen synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):778–781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P. D., Touster O. Beta-glucuronidase of rat liver lysosomes. Purification, properties, subunits. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5398–5406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ui N. Isoelectric points and conformation of proteins. I. Effect of urea on the behavior of some proteins in isoelectric focusing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 23;229(3):567–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kreel B. K., Van Eijk H. G., Leijnse B. The iso-electric fractionation of rabbit ferritin. Acta Haematol. 1972;47(1):59–64. doi: 10.1159/000208496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lancker J. L., Lentz P. L. Study on the site of biosynthesis of beta-glucuronidase and its appearance in lysosome in normal and hypoxic rats. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 Aug;18(8):529–541. doi: 10.1177/18.8.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Touster O. Studies of catalysis by -glucuronidase. Active site. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2644–2649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Touster O. Studies of catalysis by -glucuronidase. The effect of structure on the rate of hydrolysis of substituted phenyl- -d-glucopyranosiduronic acids. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2650–2656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Kuter D. J. Reversible denaturation of enzymes by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4504–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston P. D. A specific antiserum to lysosomal cathepsin D. Immunology. 1969 Sep;17(3):421–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




