Abstract
1. A convenient spectrophotometric assay for the determination of l-ergothioneine in solution including deproteinized blood haemolysate was developed. 2. The method consists of deproteinization by heat precipitation and Cu2+-catalysed oxidation of thiols such as glutathione and of l-ascorbic acid, both in alkaline media, and titration of l-ergothioneine (which is not oxidized under these conditions) by its virtually instantaneous reaction with 2,2′-dipyridyl disulphide at pH1. 3. This method and the results obtained with it for the analysis of human, horse, sheep and pig blood are compared with existing methods of l-ergothioneine analysis and the results obtained thereby.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ACKERMANN D., LIST P. H., MENSSEN H. G. Uber das Vorkommen von Herzynin neben Ergothionein in der Samenflussigkeit des Ebers sowie in Rinder-Erythrocyten und die biologische Beziehung. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1959;314(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avanzino G. L., Bradley P. B., Comis S. D., Wolstencroft J. H. A comparison of the actions of ergothioneine and chlorpromazine applied to single neurones by two different methods. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1966 Jul;5(4):331–333. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(66)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALDRIDGE R. C., LEWIS H. B. Diet and the ergothioneine content of blood. J Biol Chem. 1953 May;202(1):169–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs I. Ergothioneine in the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1972 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K., Little G. Reactions of papain and of low-molecular-weight thiols with some aromatic disulphides. 2,2'-Dipyridyl disulphide as a convenient active-site titrant for papain even in the presence of other thiols. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):67–80. doi: 10.1042/bj1330067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K., Little G. Reactivities of the various protonic states in the reactions of papain and of L-cysteine with 2,2'- and with 4,4'- dipyridyl disulphide: evidence for nucleophilic reactivity in the un-ionized thiol group of the cysteine-25 residue of papain occasioned by its interaction with the histidine-159-asparagine-175 hydrogen-bonded system. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(2):471–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1280471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
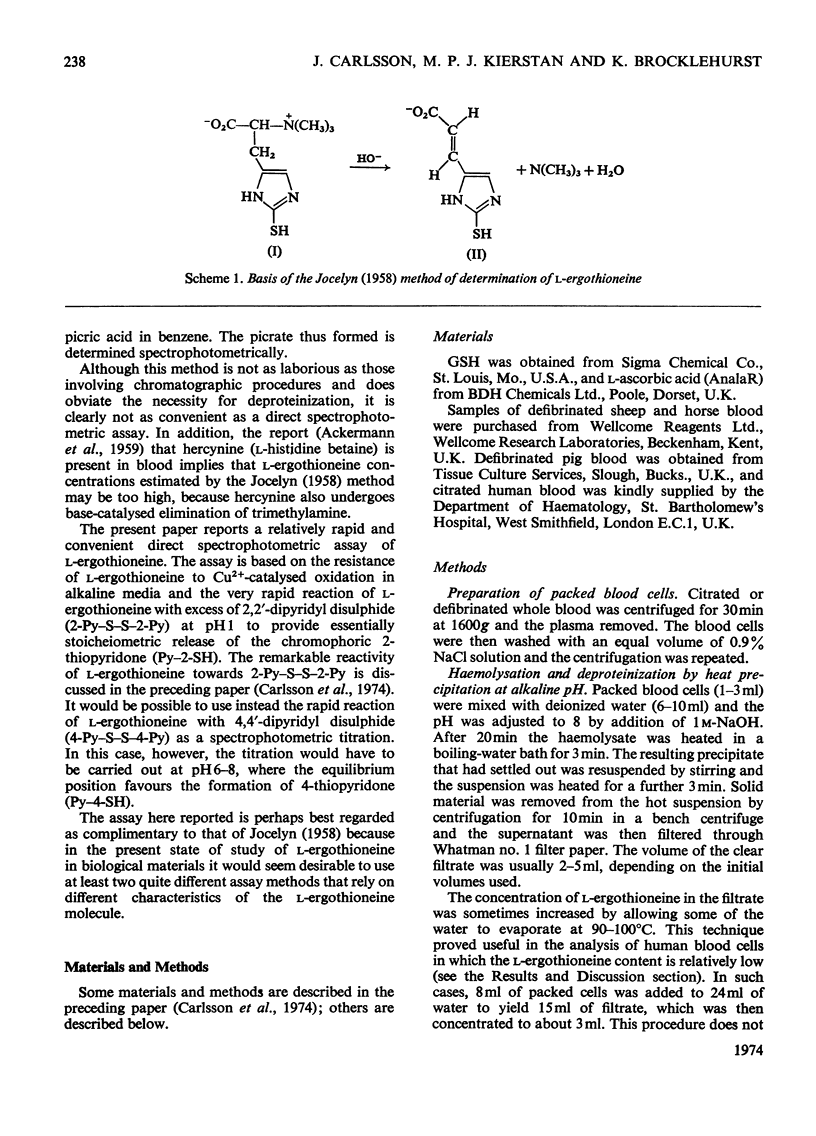
- Carlsson J., Kierstan M. P., Brocklehurst K. Reactions of L-ergothioneine and some other aminothiones with2,2'-and 4,4'-dipyridyl disulphides and of L-ergothioneine with iodoacetamide. 2-Mercaptoimidazoles, 2- and 4-thiopyridones, thiourea and thioacetamide as highly reactive neutral sulphur nucleophils. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;139(1):221–235. doi: 10.1042/bj1390221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland J., Mitchell J., Woodruff G. N. The presence of ergothioneine in the central nervous system and its probable identity with the cerebellar factor. J Physiol. 1966 Jan;182(2):427–438. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassetti D. R., Murray J. F., Jr Determination of sulfhydryl groups with 2,2'- or 4,4'-dithiodipyridine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Mar;119(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH H., TOENNIES G. The preparation and properties of ergothioneine disulphide. Biochem J. 1958 Feb;68(2):204–210. doi: 10.1042/bj0680204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEATH H., WILDY J. The biosynthesis of ergothioneine and histidine by Claviceps purpurea. I. The incorporation of [2-14C]acetate. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):612–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0640612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. A new test for ergothioneine upon which is based a method for its estimation in simple solution and in blood-filtrates. Biochem J. 1928;22(1):4–10. doi: 10.1042/bj0220004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOCELYN P. C. The distribution of ergothioneine in blood as determined by a new method of estimation. Biochem J. 1958 Dec;70(4):656–660. doi: 10.1042/bj0700656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWSON A., MORLEY H. V., WOOLF L. I. Specificity and mechanism of the Hunter reaction for ergothioneine. Nature. 1951 Jan 13;167(4237):82–83. doi: 10.1038/167082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWSON A., MORLEY H. V., WOOLF L. I. The determination of ergothioneine; the non-occurrence of ergothioneine in urine. Biochem J. 1950 Nov-Dec;47(5):513–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0470513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsett M. N., Doctor B. P. Studies on tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid, a sulfur-rich species from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4072–4077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELVILLE D. B., HORNER W. H., LUBSCHEZ R. Tissue ergothioneine. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jan;206(1):221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELVILLE D. B., LUBSCHEZ R. A method for the determination of ergothioneine in blood. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):275–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheit K. H., Faerber P. The interactions of 2-thiopyrimidine bases with hydroxymercurybenzene sulfonate. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 15;33(3):545–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


