Abstract
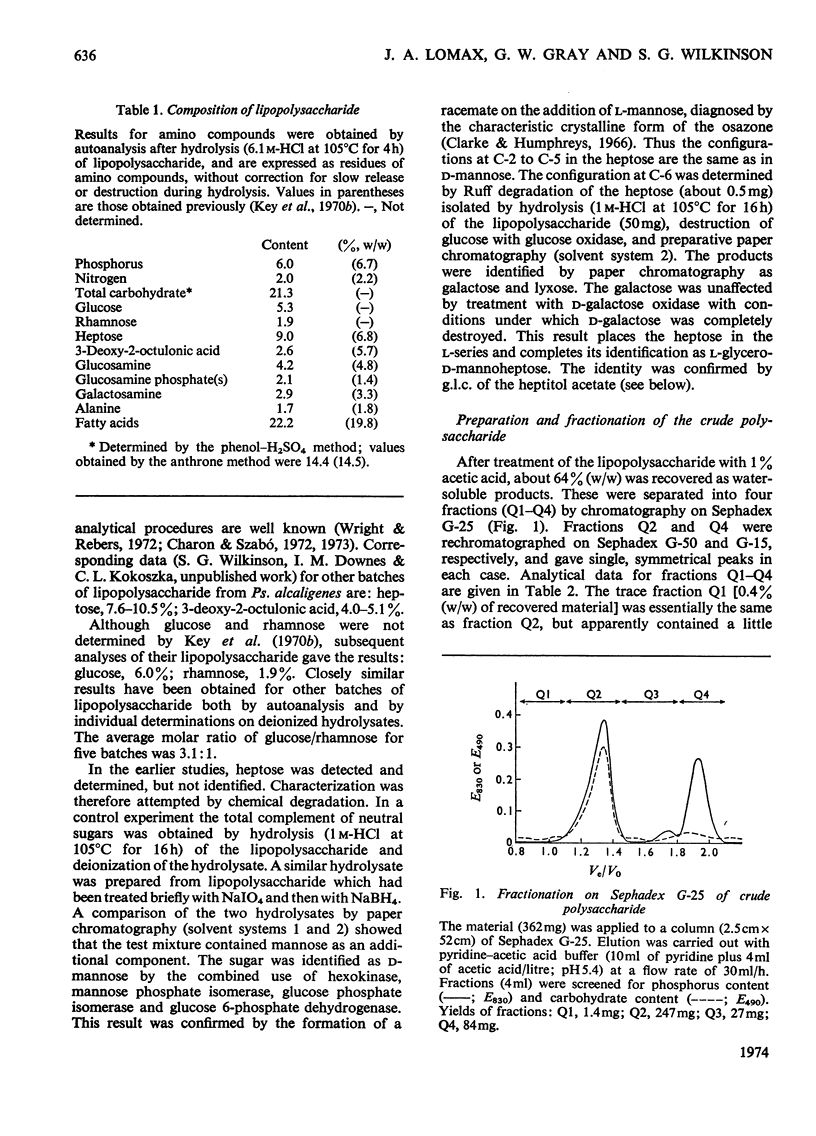
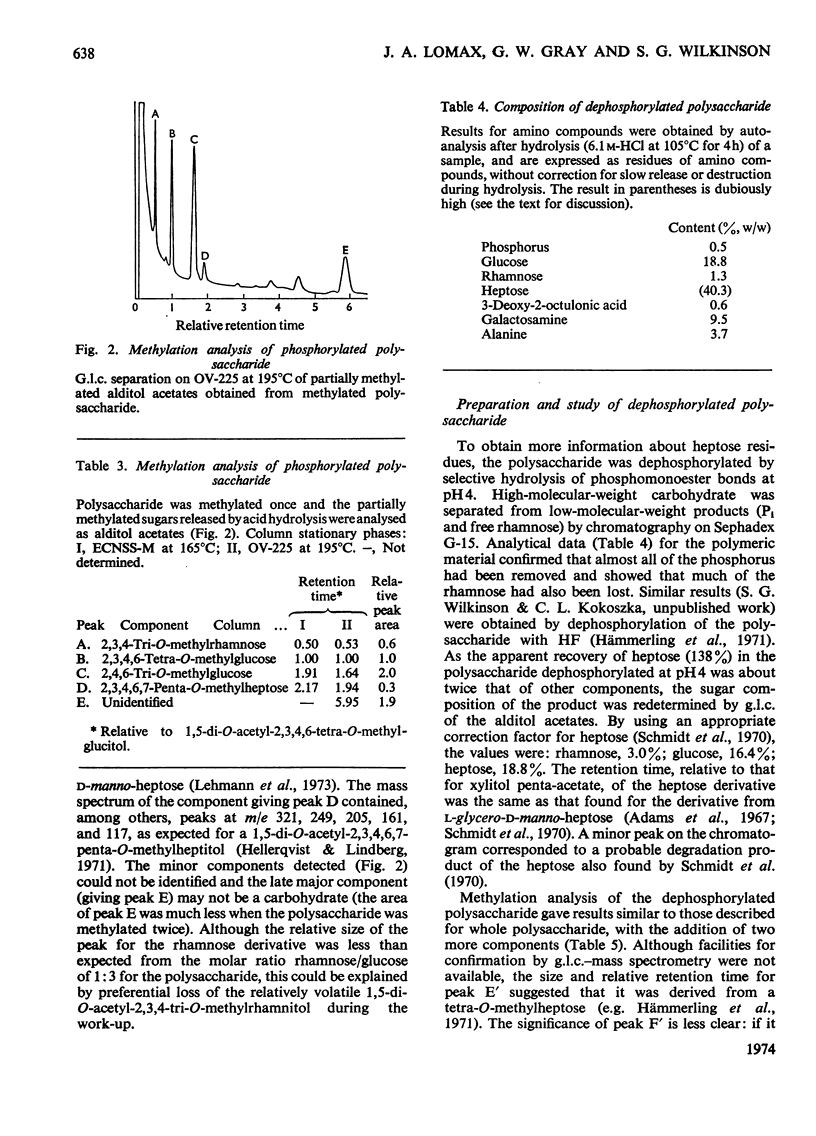
Studies of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas alcaligenes strain BR 1/2 were extended to the polysaccharide moiety. The crude polysaccharide, obtained by mild acid hydrolysis of the lipopolysaccharide, was fractionated by gel filtration. The major fraction was the phosphorylated polysaccharide, for which the approximate proportions of residues were; glucose (2), rhamnose (0.7), heptose (2–3), galactosamine (1), alanine (1), 3-deoxy-2-octulonic acid (1), phosphorus (5–6). The heptose was l-glycero-d-manno-heptose. The minor fractions from gel filtration contained free 3-deoxy-2-octulonic acid, Pi and PPi. The purified polysaccharide was studied by periodate oxidation, methylation analysis, partial hydrolysis, and dephosphorylation. All the rhamnose and part of the glucose and heptose occur as non-reducing terminal residues. Other glucose residues are 3-substituted, and most heptose residues are esterified with condensed phosphate residues, possibly in the C-4 position. Free heptose and a heptosylglucose were isolated from a partial hydrolysate of the polysaccharide. The location of galactosamine in the polysaccharide was not established, but either the C-3 or C-4 position appears to be substituted and a linkage to alanine was indicated. In its composition, the polysaccharide from Ps. alcaligenes resembles core polysaccharides from other pseudomonads: no possible side-chain polysaccharide was detected.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Quadling C., Perry M. B. D-glycero-D-manno-heptose as a component of lipopolysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Dec;13(12):1605–1613. doi: 10.1139/m67-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdian G., Dröge W., Kotelko K., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Vorkommen zweier Heptosen in Lipopolysacchariden enterobakterieller Zellwände: L-Glycero-und D-Glycero-D-mannoheptose. Biochem Z. 1966 Mar 28;344(2):197–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bella A. M., Jr, Kim Y. S. An improved method of separating glucosaminitol from galactosaminitol and their amino sugars on an amino acid analyzer. J Chromatogr. 1970 Sep 16;51(2):314–315. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96872-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon D., Szabó L. Synthesis and acidic degradation of 3-deoxy-ketoaldonic acids. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1973;11:1175–1179. doi: 10.1039/p19730001175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon D., Szabó L. The synthesis of 3-deoxy-5-O-methyloctulosonic acid and its behaviour in the Warren reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 18;29(1):184–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester I. R., Meadow P. M., Pitt T. L. The relationship between the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides and serological specificity in strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different O-serotypes. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Oct;78(2):305–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Low-molecular-weight solutes released during mild acid hydrolysis of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):289–295. doi: 10.1042/bj1300289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Release of ethanolamine pyrophosphate during mild acid hydrolysis of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):400–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewry D. T., Lomax J. A., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. Studies of lipid A fractions from the lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas alcaligenes. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):563–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1330563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Structural investigations on the 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate region of lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1970 May 1;14(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge W., Ruschmann E., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Biochemical studies on lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella R mutants. 4. Phosphate groups linked to heptose units and their absence in some R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Mar;4(1):134–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Gray G. W. The chemical composition of the lipopolyacarideof Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):185–196. doi: 10.1042/bj1140185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fensom A. H., Meadow P. M. Evidence for two regions in the polysaccharide moiety of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8602. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 29;9(2):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A. R. Antigenic variation in a strain of Trypanosoma brucei transmitted by Glossina morsitans and G. palpalis. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Nov;41(2):195–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerqvist C. G., Lindberg B., Samuelsson K., Brubaker R. R. Structural studies on the O-specific side-chains of the cell-wall lipopolysaccharide from Pasteurella pseudo-tuberculosis Group II A. Acta Chem Scand. 1972;26(4):1389–1393. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26-1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerqvist C. G., Lindberg B., Samuelsson K., Brubaker R. R. Structural studies on the O-specific side-chains of the cell-wall lipopolysaccharide from Pasteurella pseudo-tuberculosis Group II B. Acta Chem Scand. 1972;26(4):1394–1398. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26-1394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough L., Jones J. V., Wusteman P. On the automated analysis of neutral monosaccharides in glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res. 1972 Jan;21(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81725-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G., Lehmann V., Lüderitz O. Structural studies on the heptose region of Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 18;38(3):453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Mäkelä P. H. Structural investigations on the core polysaccharide of Escherichia coli 0100. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Oct 14;22(3):331–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. A., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. The effect of ethylenediaminetetra-acetate on Pseudomonas alcaligenes and the composition of the bacterial cell wall. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):721–732. doi: 10.1042/bj1170721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. A., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. The purification and chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas alcaligenes. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):559–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1200559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khym J. X., Uziel M. The use of the cetyltrimethylammonium cation in terminal sequence analyses of ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):422–426. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Hämmerling G., Nurminen M., Minner I., Ruschmann E., Lüderitz O., Kuo T. T., Stocker B. A. A new class of heptose-defective mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 15;32(2):268–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. The linkage of pyrophosphorylethanolamine to heptose in the core of Salmonella minnesota lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Aug 16;21(3):339–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. J., Stewart J. C. Structural studies on the lipopolysaccharide of a rough strain of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 18;29(2):308–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. Biosynthesis of Salmonella lipopolysaccharide. The in vitro transfer of phosphate to the heptose moiety of the core. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Dec;11(2):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J. Structure and biosynthesis of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:501–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G., Fromme I., Mayer H. Immunochemical studies on core lipopolysaccharides of Enterobacteriaceae of different genera. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):357–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G., Jann B., Jann K. Immunochemistry of R lipopolysaccharides of Escherichia coli. Different core regions in the lipopolysaccharides of O group 8. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Oct;10(3):501–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., HARRISON J. S. Studies on yeast metabolism. I. Fractionation and microdetermination of cell carbohydrates. Biochem J. 1952 Jan;50(3):298–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0500298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Cell walls of pseudomonas species sensitive to ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1035–1044. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1035-1044.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G., Galbraith L., Lightfoot G. A. Cell walls, lipids, and lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas species. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):158–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. Studies on the cell walls of pseudomonas species resistant to ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(2):195–213. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. G. The sensitivity of pseudomonads to ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Apr;47(1):67–76. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright B. G., Rebers P. A. Procedure for determining heptose and hexose in lipopolysaccharides. Modification of the cysteine-sulfuric acid method. Anal Biochem. 1972 Oct;49(2):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


