Abstract
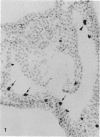
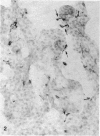
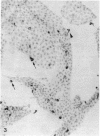
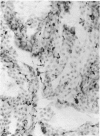
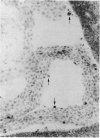
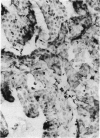
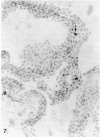
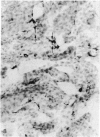
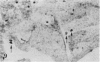
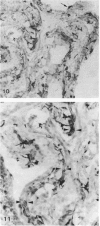
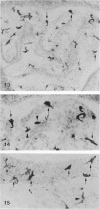
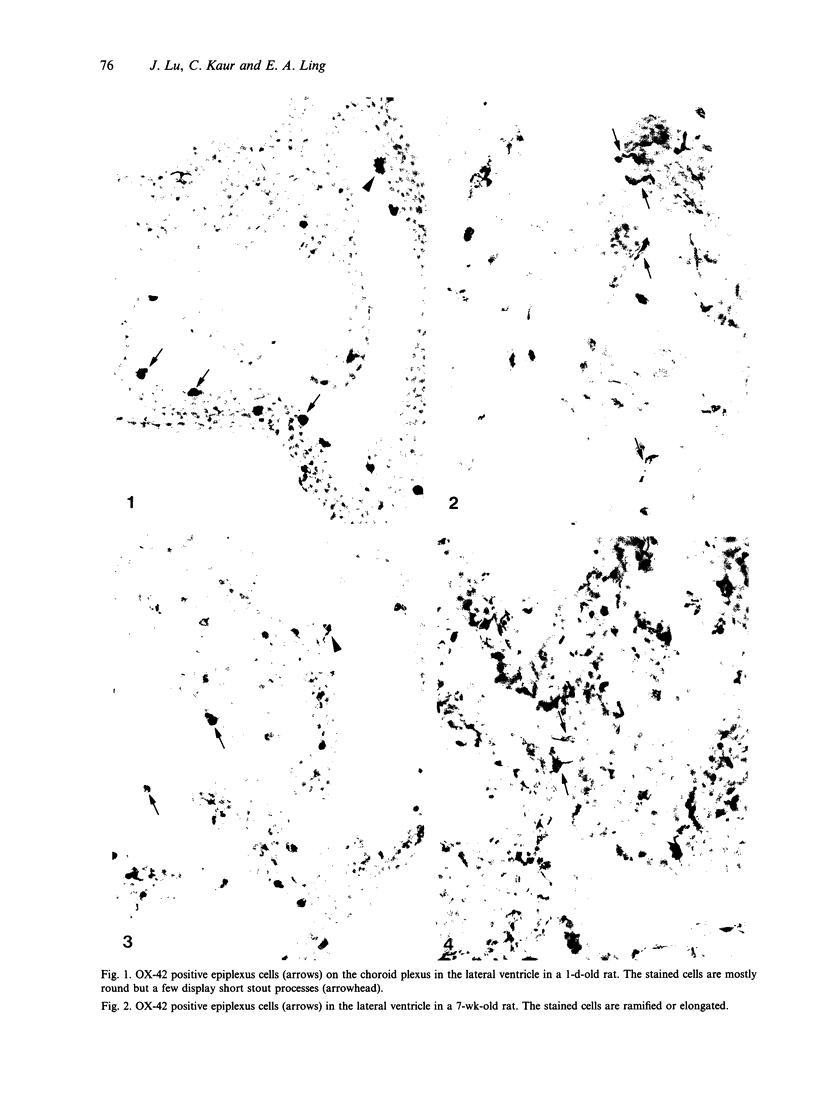
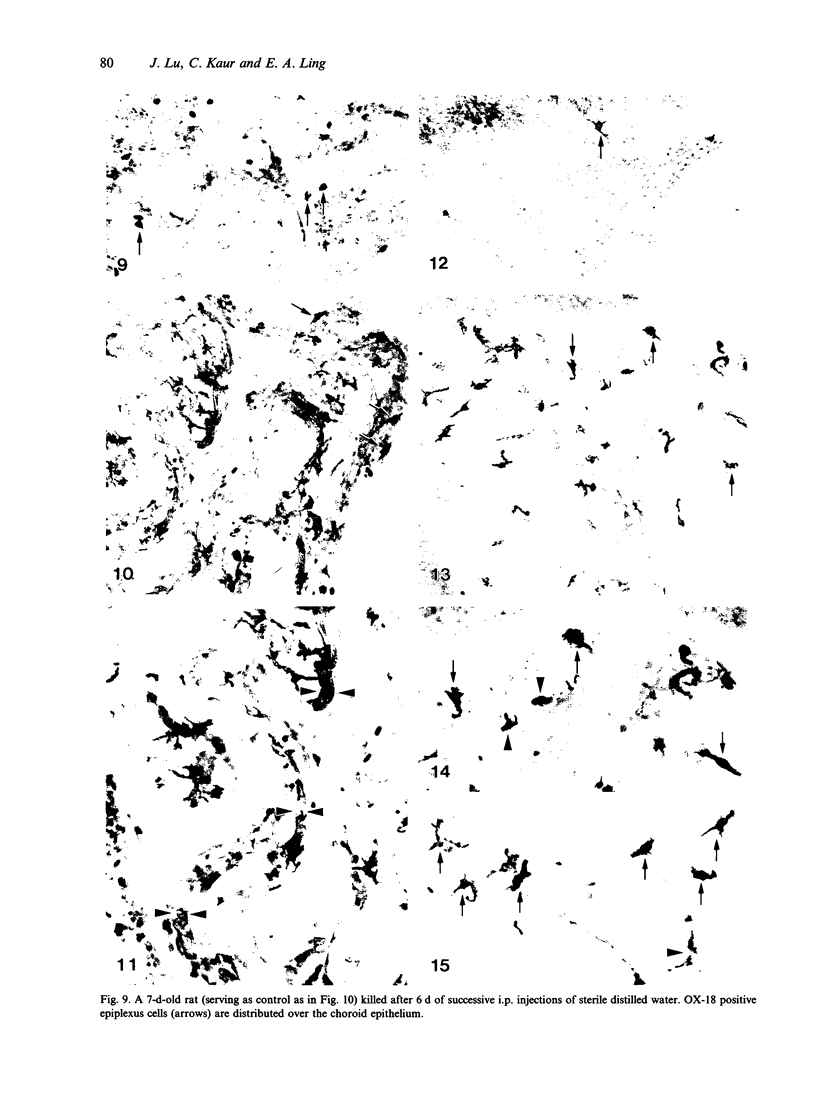
The expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens (class I and II), type 3 complement receptor (CR3) and leucocyte common antigen (LCA) was examined in epiplexus cells in rats of different ages. The cells exhibited intense immunoreactivity with the monoclonal antibody OX-42 which recognizes CR3 receptors. In early postnatal rats (1 d), the immunolabelled cells were mostly round but with increasing age (7 wk), they assumed a ramified or elongated form. The expression of LCA marked by the monoclonal antibody OX-1 followed a similar staining pattern. Class I MHC antigen expression was also demonstrated in some epiplexus cells using the monoclonal antibody OX-18 but they were less numerous than the OX-42 or OX-1 positive cells. Only sporadic OX-6 positive cells were observed in postnatal rats but they showed a marked increase in number in adult rats, suggesting an upregulation of class II MHC antigens with age. The expression of MHC class II antigens was vigorously elevated in postnatal rats receiving 6 successive intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of interferon gamma (IFN-gamma). In these animals, a large number of intensely stained OX-6 positive epiplexus cells were observed. These were mostly elongated or ramified with long processes. The immunostaining of epiplexus cells with OX-18 was also enhanced after IFN-gamma injections but the expression of CR3 and LCA appeared to be unaffected. It is concluded that the expression of MHC class I and II antigens on epiplexus cells is upregulated and induced respectively after successive i.p. injections of IFN-gamma into postnatal rats.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama H., Itagaki S., McGeer P. L. Major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on rat microglia following epidural kainic acid lesions. J Neurosci Res. 1988;20(2):147–157. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490200202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. J. Scanning electron microscopy of epiplexus macrophages (Kolmer cells) in the dog. J Comp Neurol. 1975 May 15;161(2):197–213. doi: 10.1002/cne.901610205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner S. H. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytology: current status and diagnostic applications. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 May;51(3):235–245. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. J., McCarthy L. E., Borison H. L. Electron microscopic study of the epiplexus (Kolmer) cells of the cat choroid plexus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;110(4):471–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00330099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colton C. A., Yao J., Keri J. E., Gilbert D. Regulation of microglial function by interferons. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Sep;40(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groot C. J., Sminia T., Dijkstra C. D., Van der Pal R. H., Lopes-Cardozo M. Interferon-gamma induced IA antigen expression on cultured neuroglial cells and brain macrophages from rat spinal cord and cerebrum. Int J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;59(1-3):53–65. doi: 10.3109/00207459108985449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finsen B. R., Sørensen T., Castellano B., Pedersen E. B., Zimmer J. Leukocyte infiltration and glial reactions in xenografts of mouse brain tissue undergoing rejection in the adult rat brain. A light and electron microscopical immunocytochemical study. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 May;32(2):159–183. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90008-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes G. M., Woodroofe M. N., Cuzner M. L. Microglia are the major cell type expressing MHC class II in human white matter. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;80(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya Y., Fujita T. Scanning electron microscope observation of intraventricular macrophages (Kolmer cells) in the rat brain. Arch Histol Jpn. 1973 Jan;35(2):133–140. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.35.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur C., Ling E. A. Activation and re-expression of surface antigen in microglia following an epidural application of kainic acid in the rat brain. J Anat. 1992 Apr;180(Pt 2):333–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur C., Ling E. A., Gopalakrishnakone P., Wong W. C. Response of intraventricular macrophages to crotoxin-coated microcarrier beads injected into the lateral ventricle of postnatal rats. J Anat. 1990 Feb;168:63–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Gopalakrishnakone P., Tan C. K. Electron-microscopical study of the choroid plexus and epiplexus cells in cats following a cisternal injection of crotoxin complex. Acta Anat (Basel) 1988;131(3):241–248. doi: 10.1159/000146523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Scanning electron microscopic study of epiplexus cells in the lateral ventricles of the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Anat. 1983 Dec;137(Pt 4):645–652. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Tseng C. Y., Wong W. C. An electron microscopical study of epiplexus and supraependymal cells in the prenatal rat brain following a maternal injection of 6-aminonicotinamide. J Anat. 1985 Jan;140(Pt 1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastruct and origin of epiplexus cells in the telencephalic choroid plexus of postnatal rats studied by intravenous injection of carbon particles. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):479–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastructure and mode of formation of epiplexus cells in the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles of the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):555–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Kaur C., Ling E. A. Intraventricular macrophages in the lateral ventricles with special reference to epiplexus cells: a quantitative analysis and their uptake of fluorescent tracer injected intraperitoneally in rats of different ages. J Anat. 1993 Oct;183(Pt 2):405–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Kaur C., Ling E. A. Uptake of tracer by the epiplexus cells via the choroid plexus epithelium following an intravenous or intraperitoneal injection of horseradish peroxidase in rats. J Anat. 1993 Dec;183(Pt 3):609–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Male D., Pryce G. Kinetics of MHC gene expression and mRNA synthesis in brain endothelium. Immunology. 1988 Jan;63(1):37–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matyszak M. K., Lawson L. J., Perry V. H., Gordon S. Stromal macrophages of the choroid plexus situated at an interface between the brain and peripheral immune system constitutively express major histocompatibility class II antigens. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Oct;40(2-3):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell W. L., Hardy I. G., Watt C., McGadey J., Graham D. I., Adams J. H., Gennarelli T. A. Changes in the choroid plexus, responses by intrinsic epiplexus cells and recruitment from monocytes after experimental head acceleration injury in the non-human primate. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;84(1):78–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00427218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell W. L., McGadey J. Response of intraventricular macrophages after a penetrant cerebral lesion. J Anat. 1988 Oct;160:145–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Itagaki S., Tago H., McGeer E. G. Reactive microglia in patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type are positive for the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Aug 18;79(1-2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Kawamata T., Walker D. G., Akiyama H., Tooyama I., McGeer E. G. Microglia in degenerative neurological disease. Glia. 1993 Jan;7(1):84–92. doi: 10.1002/glia.440070114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka T., Streit W. J. Expression of immunomolecules on microglial cells following neonatal sciatic nerve axotomy. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Dec;35(1-3):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mucke L., Oldstone M. B. The expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigens in the brain differs markedly in acute and persistent infections with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV). J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Feb;36(2-3):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90050-U. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Andersson P. B., Gordon S. Macrophages and inflammation in the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Jul;16(7):268–273. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90180-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltorak M., Freed W. J. Immunological reactions induced by intracerebral transplantation: evidence that host microglia but not astroglia are the antigen-presenting cells. Exp Neurol. 1989 Mar;103(3):222–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki A., Levison S. W., Ting J. P. Comparison and quantitation of Ia antigen expression on cultured macroglia and ameboid microglia from Lewis rat cerebral cortex: analyses and implications. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Nov;25(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki A., Nakazato Y. The identity of cells expressing MHC class II antigens in normal and pathological human brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1992 Feb;18(1):13–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1992.tb00761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna M. P., Lampson L. A. Immune modulation within the brain: recruitment of inflammatory cells and increased major histocompatibility antigen expression following intracerebral injection of interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Nov;34(2-3):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90121-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiniger B., van der Meide P. H. Rat ependyma and microglia cells express class II MHC antigens after intravenous infusion of recombinant gamma interferon. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Aug;19(1-2):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streit W. J., Graeber M. B., Kreutzberg G. W. Expression of Ia antigen on perivascular and microglial cells after sublethal and lethal motor neuron injury. Exp Neurol. 1989 Aug;105(2):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90111-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A developmental study of epiplexus cells and supraependymal cells and their possible relationship to microglia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Sep-Oct;4(5):307–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A light microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study of intraventricular macrophages in the brains of aged mice. J Anat. 1983 Jun;136(Pt 4):761–771. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A semithin light microscopic, transmission electron microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study of macrophages in the lateral ventricle of mice from embryonic to adult life. J Anat. 1979 Aug;129(Pt 1):31–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. An ultrastructural study of intraventricular macrophages in the brains of aged mice. Anat Anz. 1988;165(4):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland C. A., McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Purification with monoclonal antibody of a predominant leukocyte-common antigen and glycoprotein from rat thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Feb;9(2):155–159. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vass K., Lassmann H. Intrathecal application of interferon gamma. Progressive appearance of MHC antigens within the rat nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):789–800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vass K., Lassmann H., Wekerle H., Wisniewski H. M. The distribution of Ia antigen in the lesions of rat acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;70(2):149–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00691433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Walker D. G., Akiyama H., McGeer P. L. Herpes simplex virus type I infection of the CNS induces major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on rat microglia. J Neurosci Res. 1990 May;26(1):55–65. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodroofe M. N., Bellamy A. S., Feldmann M., Davison A. N., Cuzner M. L. Immunocytochemical characterisation of the immune reaction in the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. Possible role for microglia in lesion growth. J Neurol Sci. 1986 Jul;74(2-3):135–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]