Abstract
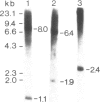
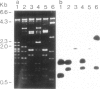
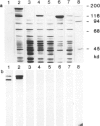
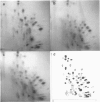
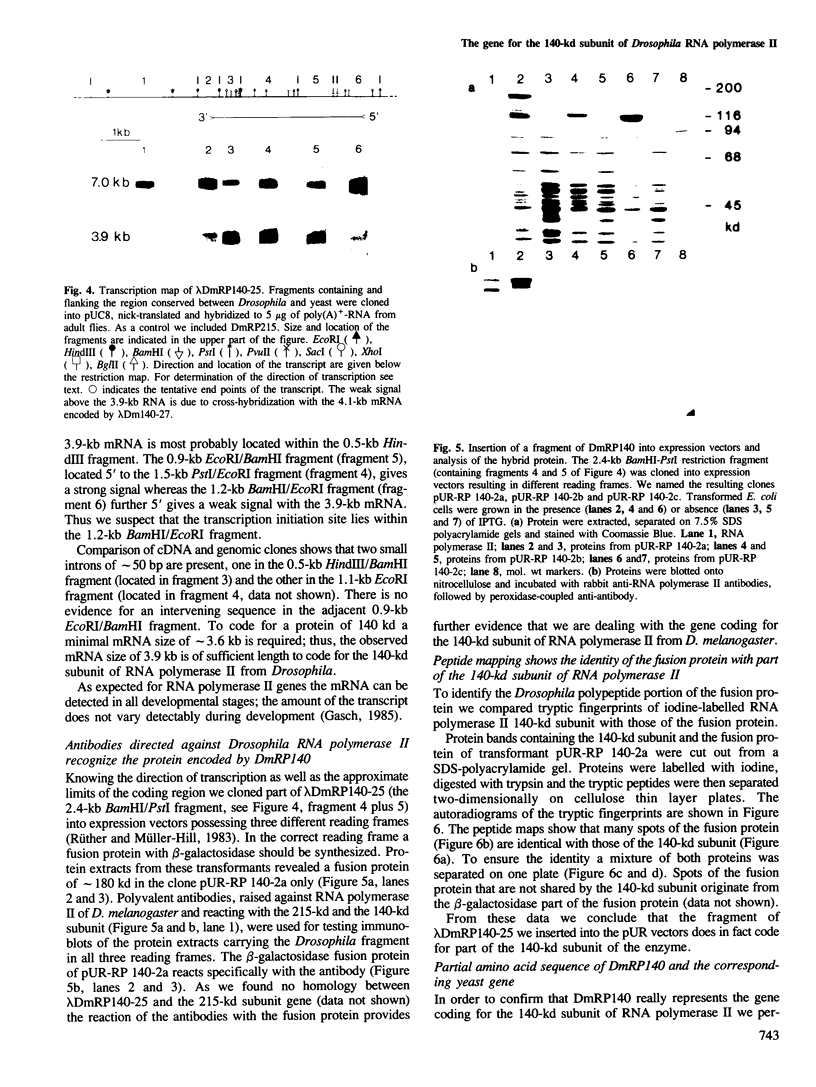
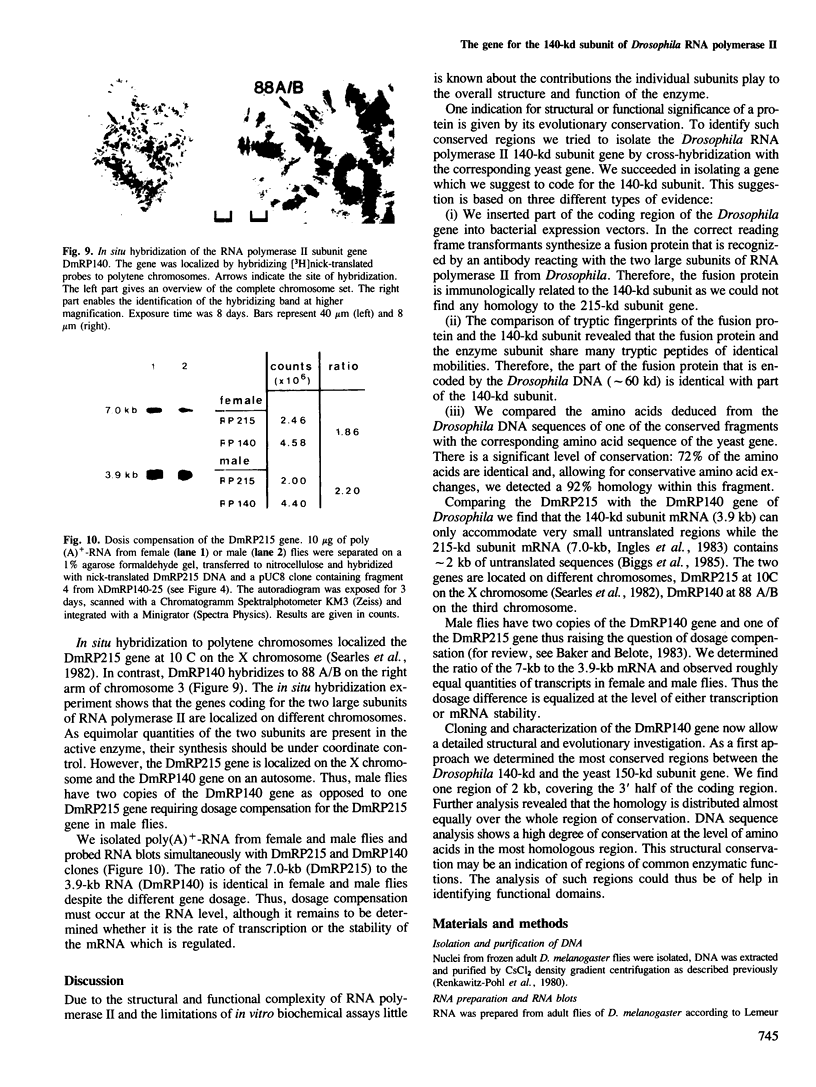
Genomic clones of Drosophila melanogaster were isolated from a λ library by cross-hybridization with the yeast gene coding for the 150-kd subunit of RNA polymerase II. Clones containing a region of ∼2.0 kb with strong homology to the yeast gene were shown to code for a 3.9-kb poly(A)+-RNA. Part of the coding region was cloned into an expression vector. A fusion protein was obtained which reacted with an antibody directed against RNA polymerase II of Drosophila. Peptide mapping of the fusion protein yielded a number of spots identical with spots derived from the 140-kd subunit of Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Sequence comparison of a segment of the Drosophila and the corresponding yeast clone yielded a high degree of homology at the protein level also, suggesting that we had isolated the gene coding for the 140-kd subunit of RNA polymerase II from Drosophila. In situ hybridization localized the DmRP140 gene at 88 A/B on chromosome 3 while the DmRP215 gene has previously been localized at 10 C on the X chromosome. Analysis of the transcripts (7.0 and 3.9 kb) in female and male flies shows dosage compensation for the transcription of the DmRP215 gene.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II genes, Drosophila, peptide mapping, in situ hybridization
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. S., Belote J. M. Sex determination and dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:345–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs J., Searles L. L., Greenleaf A. L. Structure of the eukaryotic transcription apparatus: features of the gene for the largest subunit of Drosophila RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bréant B., Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Analysis of yeast RNA polymerases with subunit-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11968–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhler J. M., Huet J., Davies K. E., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Immunological studies of yeast nuclear RNA polymerases at the subunit level. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9949–9954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Stollar B. D. Conservation of a DNA-binding site in the largest subunit of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 5;170(3):777–790. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L. Amanitin-resistant RNA polymerase II mutations are in the enzyme's largest subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13403–13406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Borsett L. M., Jiamachello P. F., Coulter D. E. Alpha-amanitin-resistant D. melanogaster with an altered RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Spot-immunodetection of conserved determinants in eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Study with antibodies to yeast RNA polymerases subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Biggs J., Wong J. K., Weeks J. R., Greenleaf A. L. Identification of a structural gene for a RNA polymerase II polypeptide in Drosophila melanogaster and mammalian species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J., Himmelfarb H. J., Shales M., Greenleaf A. L., Friesen J. D. Identification, molecular cloning, and mutagenesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Bautz E. K. Immunological relatedness of subunits of RNA polymerase II from insects and mammals. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(3):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMeur M., Glanville N., Mandel J. L., Gerlinger P., Palmiter R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene family: hormonal control of X and Y gene transcription and mRNA accumulation. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):561–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90152-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw R. A., 3rd Dideoxy DNA sequencing with end-labeled oligonucleotide primers. Anal Biochem. 1984 Dec;143(2):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90666-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz-Pohl R., Bialojan S. A DNA sequence of Drosophila melanogaster with a differential telomeric distribution. Chromosoma. 1984;89(3):206–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00295001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz-Pohl R., Glätzer K. H., Kunz W. Characterization of cloned ribosomal DNA from Drosophila hydei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4593–4611. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldt C., Kloetzel P. M. Analysis of cytoplasmic 19 S ring-type particles in Drosophila which contain hsp 23 at normal growth temperature. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searles L. L., Jokerst R. S., Bingham P. M., Voelker R. A., Greenleaf A. L. Molecular cloning of sequences from a Drosophila RNA polymerase II locus by P element transposon tagging. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):585–592. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks J. R., Coulter D. E., Greenleaf A. L. Immunological studies of RNA polymerase II using antibodies to subunits of Drosophila and wheat germ enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5884–5892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]