Abstract
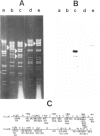
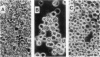
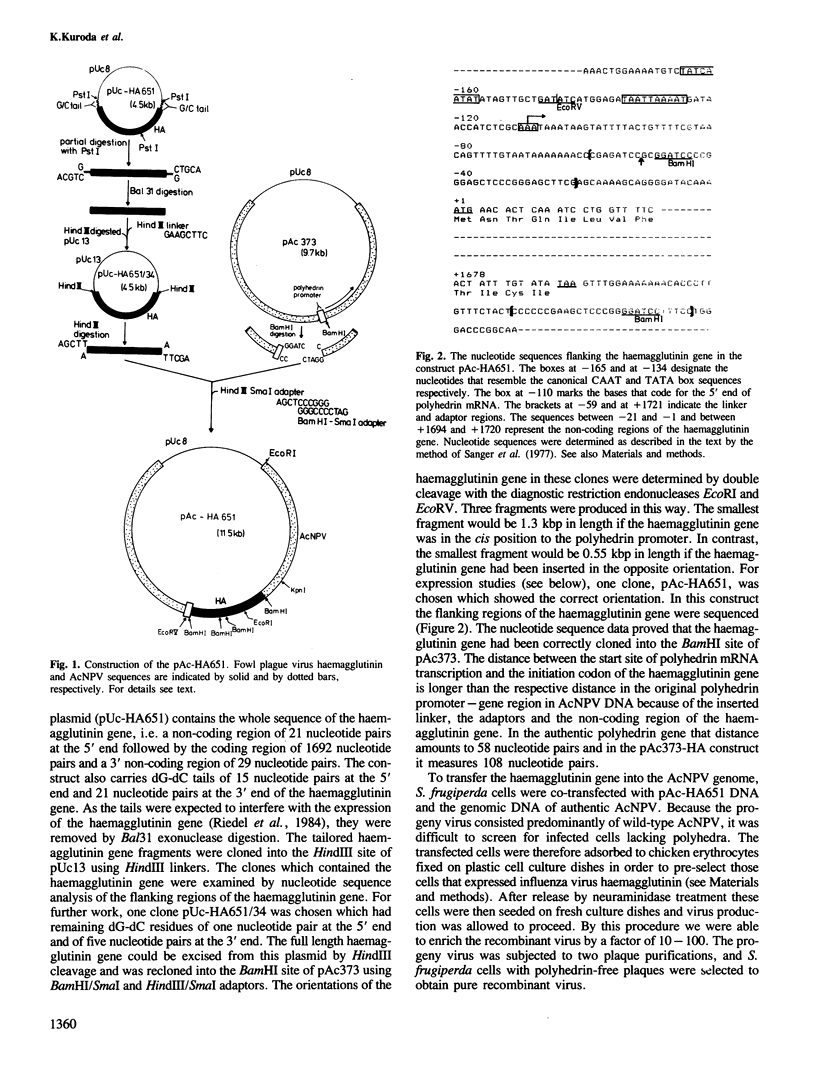
The insect baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcNPV) has played a major role in studies on the molecular biology of insect DNA viruses. Recently, this system has been effectively adapted as a highly efficient vector in insect cells for the expression of several mammalian genes. A cDNA sequence of the influenza (fowl plague) virus haemagglutinin gene has been inserted into the BamHI site of the pAc373 polyhedrin vector. Spodoptera frugiperda cells were co-transfected with this construct, pAc-HA651, and authentic AcNPV DNA. Recombinant virus was selected by adsorption of transfected cells to erythrocytes followed by serial plaque passages on S. frugiperda cells. We have determined the site of insertion of the haemagglutinin gene into the AcNPV genome by restriction enzyme cleavage and Southern blot hybridization analyses using haemagglutinin cDNA as a probe. The influenza haemagglutinin gene is located in the polyhedrin gene of AcNPV DNA. Immunofluorescent labelling, immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analyses with specific antisera revealed that S. frugiperda cells produce immune reactive haemagglutinin after infection with the recombinant virus. The haemagglutinin is expressed at the cell surface and has haemolytic capacity that has been activated by post-translational proteolytic cleavage. When chickens were immunized with S. frugiperda cells expressing haemagglutinin, they developed haemagglutinin-inhibiting and neutralizing antibodies and were protected from infection with fowl plague virus. These observations demonstrate that the haemagglutinin is processed in insect cells in a similar fashion as in fowl plaque virus-infected vertebrate cells and that it has full biological activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carstens E. B., Tjia S. T., Doerfler W. Infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus I. Synthesis of intracellular proteins after virus infection. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W., Stabel S., Ibelgaufts H., Sutter D., Neumann R., Groneberg J., Scheidtmann K. H., Deuring R., Winterhoff U. Selectivity in integration sites of adenoviral DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):551–564. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Bosch F. X., Linder D., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Proteolytic activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin: The structure of the cleavage site and the enzymes involved in cleavage. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Klenk H. D. Characterization of the carboxypeptidase involved in the proteolytic cleavage of the influenza haemagglutinin. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2127–2137. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Linder D., Rott R., Klenk H. D. The cleavage site of the hemagglutinin of fowl plague virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90387-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Influenza viruses cause hemolysis and fusion of cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil W., Geyer R., Dabrowski J., Dabrowski U., Niemann H., Stirm S., Klenk H. D. Carbohydrates of influenza virus. Structural elucidation of the individual glycans of the FPV hemagglutinin by two-dimensional 1H n.m.r. and methylation analysis. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2711–2720. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Becht H. On the structure of the influenza virus envelope. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R. Cotranslational and posttranslational processing of viral glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1980;90:19–48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67717-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Wöllert W., Rott R., Scholtissek C. Association of influenza virus proteins with cytoplasmic fractions. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert H., Doerfler W. Mapping of Early and Late Transcripts Encoded by the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Is Viral RNA Spliced? J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.497-506.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert H., Doerfler W. Transcription of overlapping sets of RNAs from the genome of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: a novel method for mapping RNAs. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):255–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.255-265.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda S., Kawai T., Obinata M., Fujiwara H., Horiuchi T., Saeki Y., Sato Y., Furusawa M. Production of human alpha-interferon in silkworm using a baculovirus vector. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):592–594. doi: 10.1038/315592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Ohnishi S. Activation of influenza virus by acidic media causes hemolysis and fusion of erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C., Smith G. E., Farrell-Towt J., Chizzonite R., Summers M. D., Ju G. Production of human c-myc protein in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2860–2865. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K. Simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens using the peroxidase-labeled antibody method: a study on pituitary glands of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Sep;16(9):557–560. doi: 10.1177/16.9.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennock G. D., Shoemaker C., Miller L. K. Strong and regulated expression of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in insect cells with a baculovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):399–406. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Kondor-Koch C., Garoff H. Cell surface expression of fusogenic vesicular stomatitis virus G protein from cloned cDNA. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1477–1483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01999.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. A., Datema R., Schwarz R. T. N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, a novel inhibitor of glycoprotein processing, and its effect on fowl plague virus maturation. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Orlich M., Klenk H. D., Wang M. L., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Studies on the adaptation of influenza viruses to MDCK cells. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3329–3332. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S. B., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S. Hemolytic activity of influenza virus hemagglutinin glycoproteins activated in mildly acidic environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3153–3157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Fraser M. J., Summers M. D. Molecular Engineering of the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Deletion Mutations Within the Polyhedrin Gene. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):584–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.584-593.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Ju G., Ericson B. L., Moschera J., Lahm H. W., Chizzonite R., Summers M. D. Modification and secretion of human interleukin 2 produced in insect cells by a baculovirus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8404–8408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D., Fraser M. J. Production of human beta interferon in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2156–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Quinn P. S., Chan S. J., Marsh J., Tager H. S. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjia S. T., Carstens E. B., Doerfler W. Infection of Spodoptera frugiperda cells with Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus II. The viral DNA and the kinetics of its replication. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):399–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. W. Structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;94-95:1–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68120-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]