Abstract
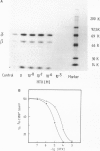
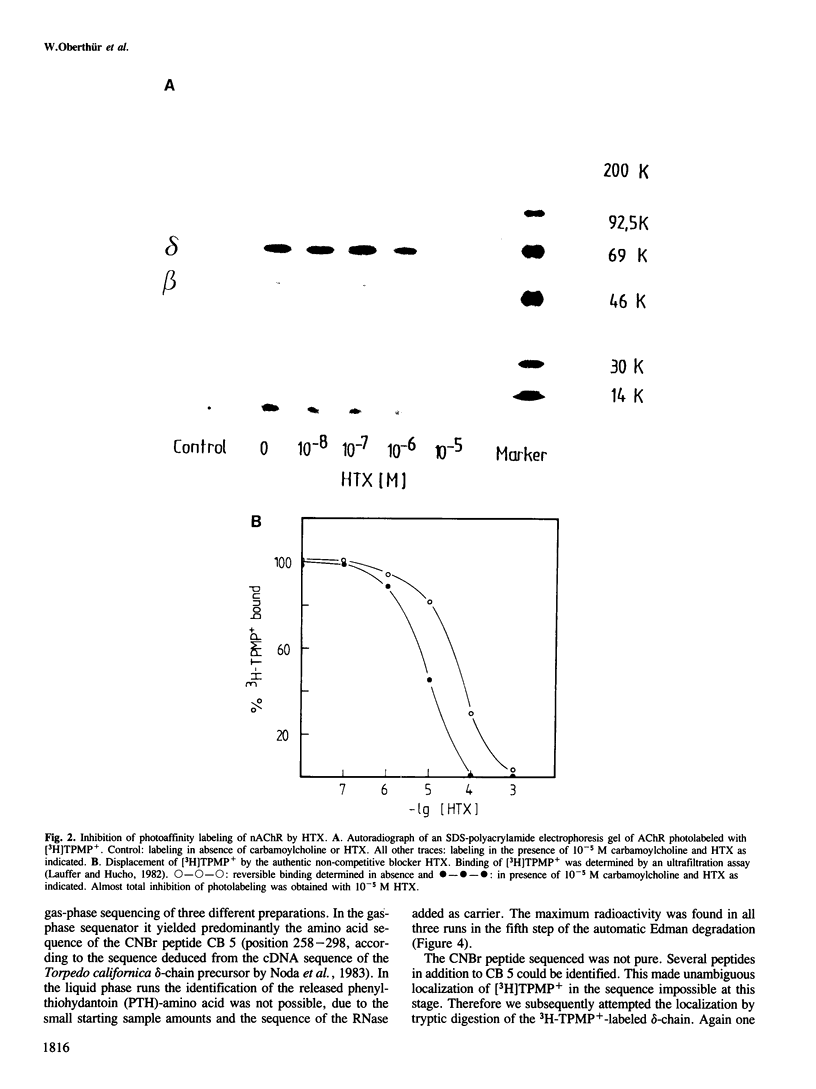
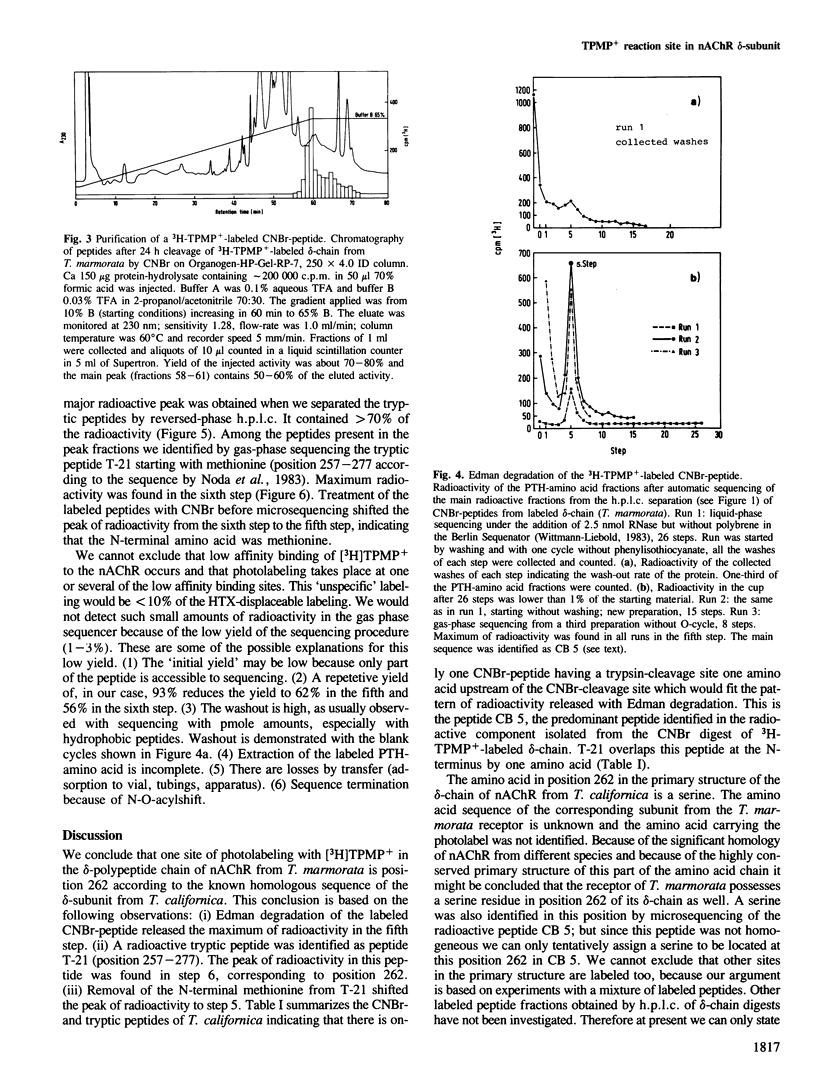
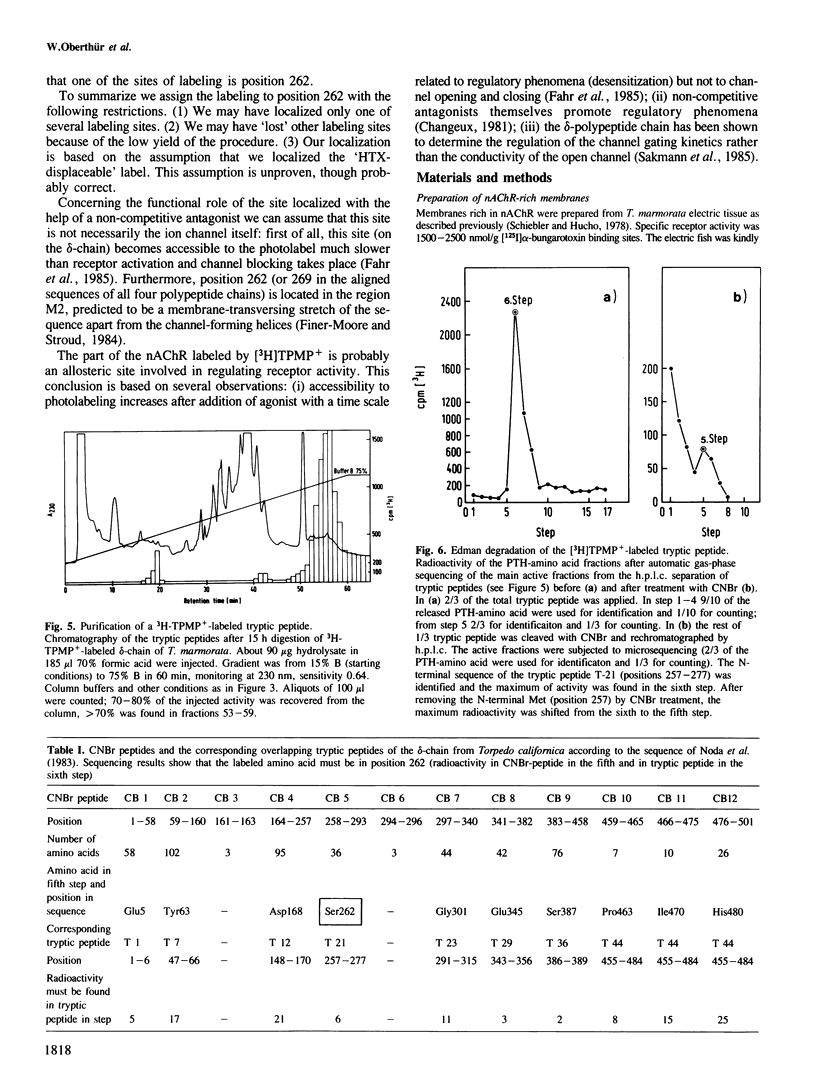
A site in the primary structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo marmorata covalently labeled with the non-competitive antagonist [3H]triphenylmethylphosphonium (TPMP+) was localized. The label was found in position 262 of the delta-polypeptide chain. This site is specifically labeled in the presence of the agonist carbamoylcholine. Labeling is prevented by the non-competitive antagonist histrionicotoxin. Position 262, probably a serine, is located in the highly conserved membrane-spanning helix M2 (according to the predicted folding scheme of Finer-Moore and Stroud (1984). The relationship of this site to the receptor's ion channel and its regulation is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Barnard E. A., Chiu T. H., Lapa A. J., Dolly J. O., Jansson S. E., Daly J., Witkop B. Acetylcholine receptor and ion conductance modulator sites at the murine neuromuscular junction: evidence from specific toxin reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):949–953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P. The acetylcholine receptor: an "allosteric" membrane protein. Harvey Lect. 1979 1980;75:85–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahr A., Lauffer L., Schmidt D., Heyn M. P., Hucho F. Covalent labeling of functional states of the acetylcholine receptor. Effects of antagonists on the receptor conformation. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 15;147(3):483–487. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-2956.1985.00483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G., Changeux J. P. Studies on the effect of histrionicotoxin on the monocellular electroplax from Electrophorus electricus and on the binding of (3H)acetylcholine to membrane fragments from Torpedo marmorata. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;12(1):92–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffer L., Hucho F. Triphenylmethylphosphonium is an ion channel ligand of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2406–2409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhn P., Hucho F. Covalent labeling of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electric tissue with the channel blocker [3H]triphenylmethylphosphonium by ultraviolet irradiation. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 18;22(2):421–425. doi: 10.1021/bi00271a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Methfessel C., Mishina M., Takahashi T., Takai T., Kurasaki M., Fukuda K., Numa S. Role of acetylcholine receptor subunits in gating of the channel. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):538–543. doi: 10.1038/318538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiebler W., Hucho F. Membranes rich in acetylcholine receptor: characterization and reconstitution to excitable membranes from exogenous lipids. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):55–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]