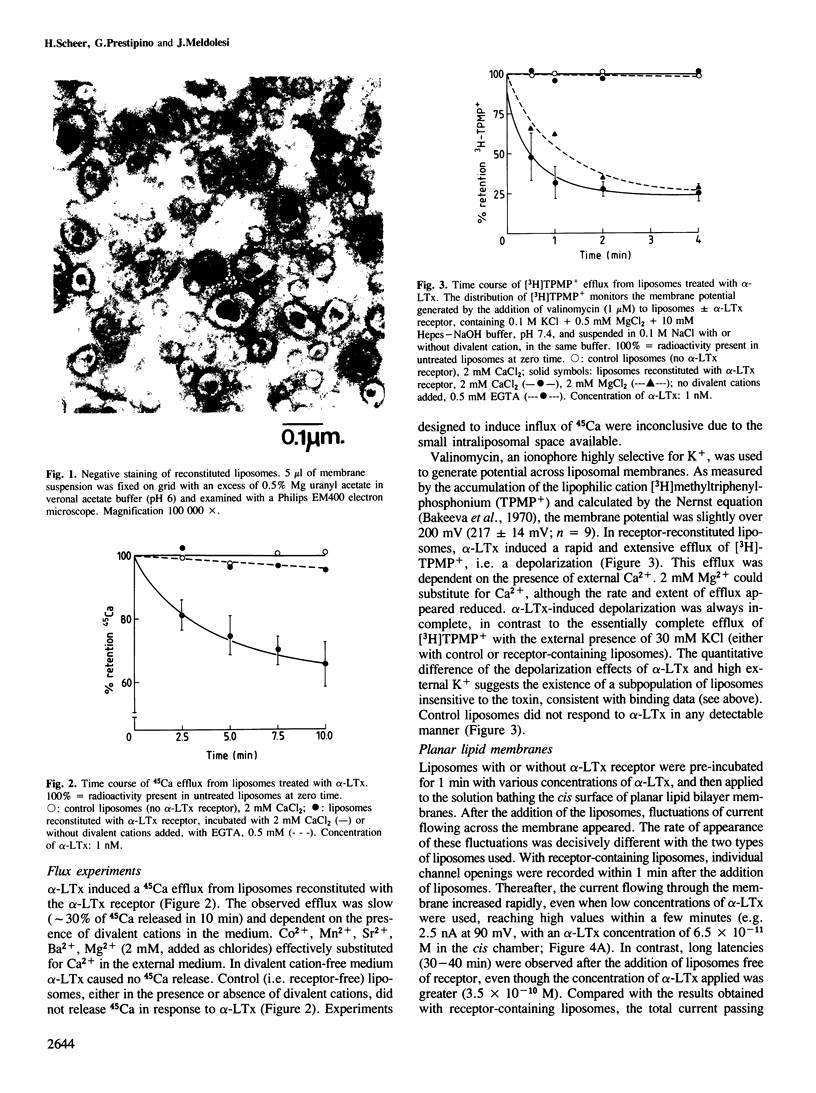
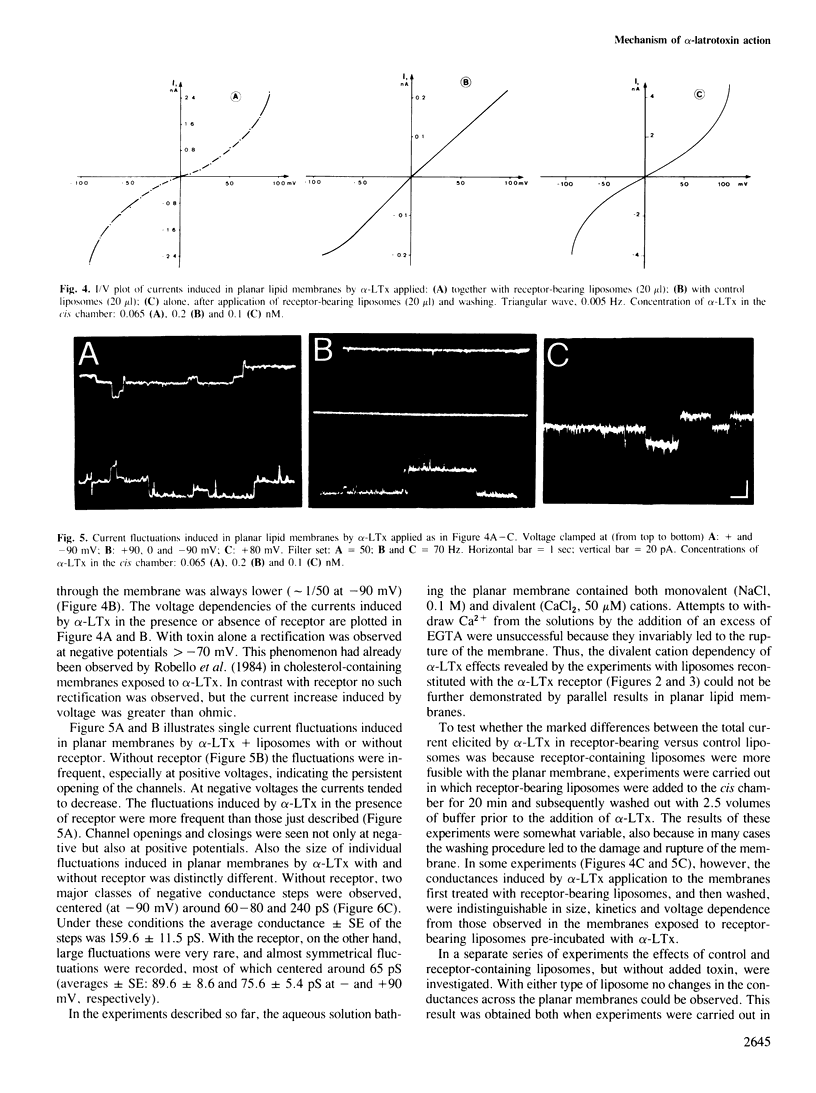
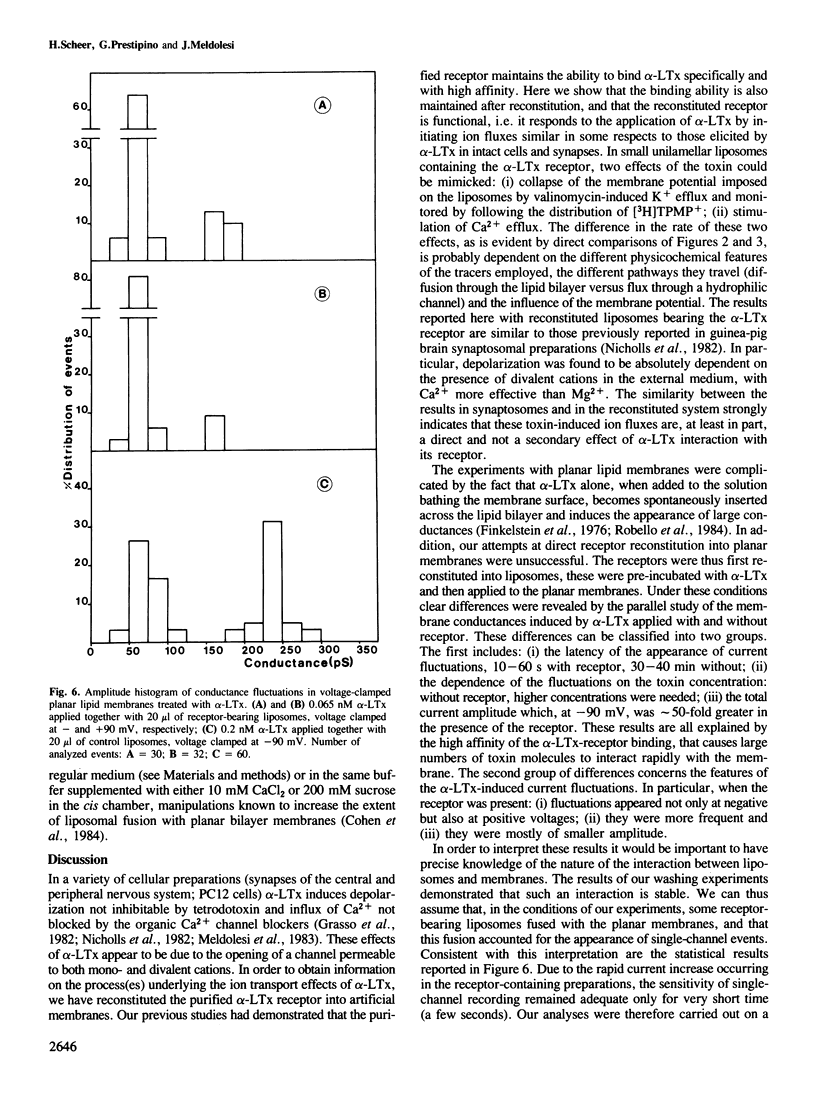
Abstract
The receptor of alpha-latrotoxin (the major toxin of the black widow spider venom), purified from bovine synaptosomal membranes, was reconstituted into small unilamellar liposomes. These (but not control) liposomes exhibited high-affinity, specific binding of [125I]alpha-latrotoxin. In the receptor-bearing liposomes alpha-latrotoxin induced depolarization and stimulated 45Ca efflux. These responses to alpha-latrotoxin, that were observed only in the presence of external divalent cations, resembled those previously demonstrated in mammalian brain synaptosomes. The alpha-latrotoxin-activated ion fluxes are therefore, at least in part, the result of the direct interaction of the toxin with its receptor. When control and receptor-bearing liposomes were pre-incubated with alpha-latrotoxin and then added to a solution bathing a planar lipid bilayer membrane, single channel cationic conductances were observed. In the presence of the receptor, the conductances induced by alpha-latrotoxin were markedly different from those observed without the receptor, but not identical to those observed without the receptor, but not identical to those recently characterized by patch clamping in the cells of a line (PC12) sensitive to alpha-latrotoxin. These results demonstrate that the reconstituted receptor is functional, and suggest that the cationic channel activated by the toxin-receptor interaction is modulated by additional component(s) in the membrane of synapses and cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakeeva L. E., Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A., Kuliene V. V., Levitsky D. O., Liberman E. A., Severina I. I., Skulachev V. P. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. II. Intact mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. S., Akabas M. H., Zimmerberg J., Finkelstein A. Parameters affecting the fusion of unilamellar phospholipid vesicles with planar bilayer membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN A., Rubin L. L., Tzeng M. C. Black widow spider venom: effect of purified toxin on lipid bilayer membranes. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1009–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.948756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frontali N., Ceccarelli B., Gorio A., Mauro A., Siekevitz P., Tzeng M. C., Hurlbut W. P. Purification from black widow spider venom of a protein factor causing the depletion of synaptic vesicles at neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):462–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasso A., Pelliccia M., Alemà S. Characterization of alpha-latrotoxin interaction with rat brain synaptosomes and PC12 cells. Toxicon. 1982;20(1):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(82)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbut W. P., Ceccarelli B. Use of black widow spider venom to study the release of neurotransmitters. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1979;3:87–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Madeddu L., Torda M., Gatti G., Niutta E. The effect of alpha-latrotoxin on the neurosecretory PC12 cell line: studies on toxin binding and stimulation of transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):997–1009. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J. Studies on alpha-latrotoxin receptors in rat brain synaptosomes: correlation between toxin binding and stimulation of transmitter release. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1559–1569. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Hurlbut W. P. Action of black widow spider venom on quantized release of acetylcholine at the frog neuromuscular junction: dependence upon external Mg2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):991–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer H., Meldolesi J. Purification of the putative alpha-latrotoxin receptor from bovine synaptosomal membranes in an active binding form. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):323–327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03632.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng M. C., Cohen R. S., Siekevitz P. Release of neurotransmitters and depletion of synaptic vesicles in cerebral cortex slices by alpha-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng M. C., Siekevitz P. The binding interaction between alpha-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom and a dog cerebral cortex synaptosomal membrane preparation. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtorta F., Madeddu L., Meldolesi J., Ceccarelli B. Specific localization of the alpha-latrotoxin receptor in the nerve terminal plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):124–132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke E., Ferroni A., Gattanini P., Meldolesi J. alpha Latrotoxin of the black widow spider venom opens a small, non-closing cation channel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):320–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90565-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]