Abstract
We have cloned and sequenced a single copy gene encoding a ribosomal protein from the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila. The gene product was identified as ribosomal protein S25 by comparison of the migration in two-dimensional polyacrylamide gels of the protein synthesized by translation in vitro of hybrid-selected mRNA and authentic ribosomal proteins. The proteins show strong homology to ribosomal protein S12 from Escherichia coli. The coding region of the gene is interrupted by a 979-bp intron 68 bp downstream of the translation start. This is the first intron in a protein encoding gene of a ciliate to be described at the nucleotide sequence level. The intron obeys the GT/AG rule for splice junctions of nuclear mRNA introns from higher eukaryotes but lacks the pyrimidine stretch usually found in the immediate vicinity of the 3' splice junction. The structure of the intron and the fact that it is found together with the well described self-splicing rRNA intron is discussed in relation to the evolution of RNA splicing.
Keywords: intron, ribosomal protein, Tetrahymena
Full text
PDF


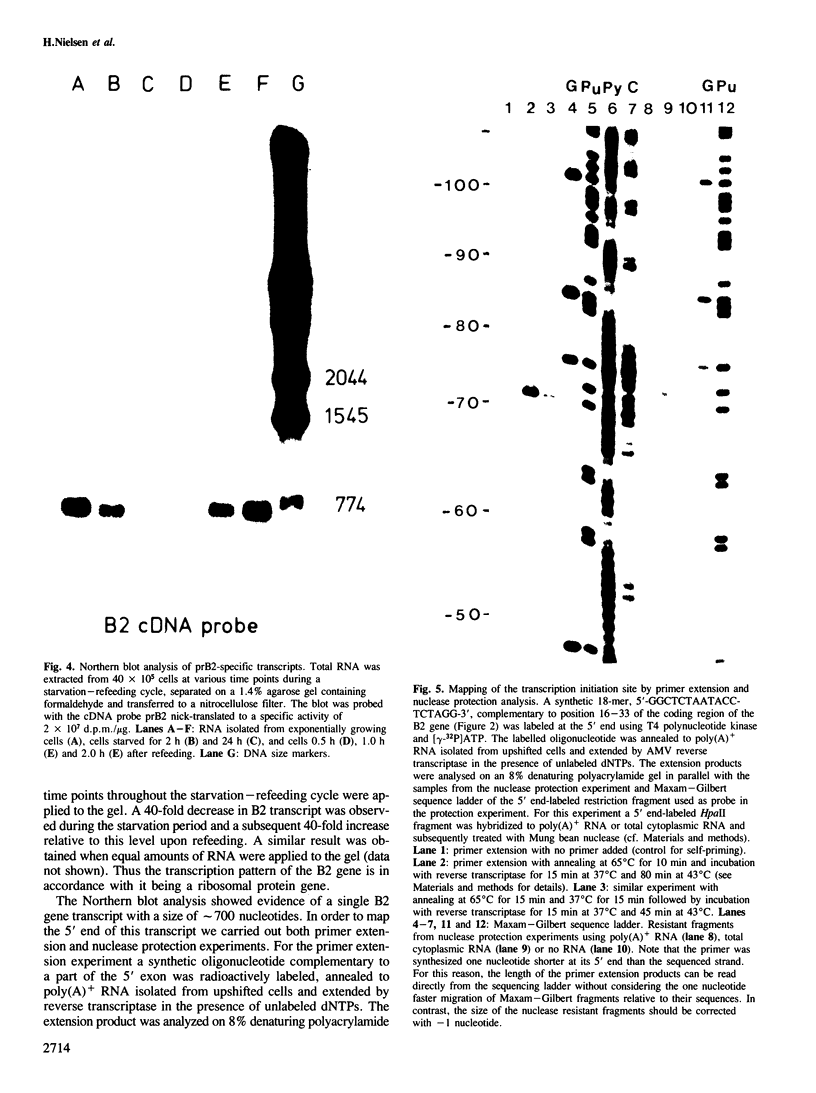
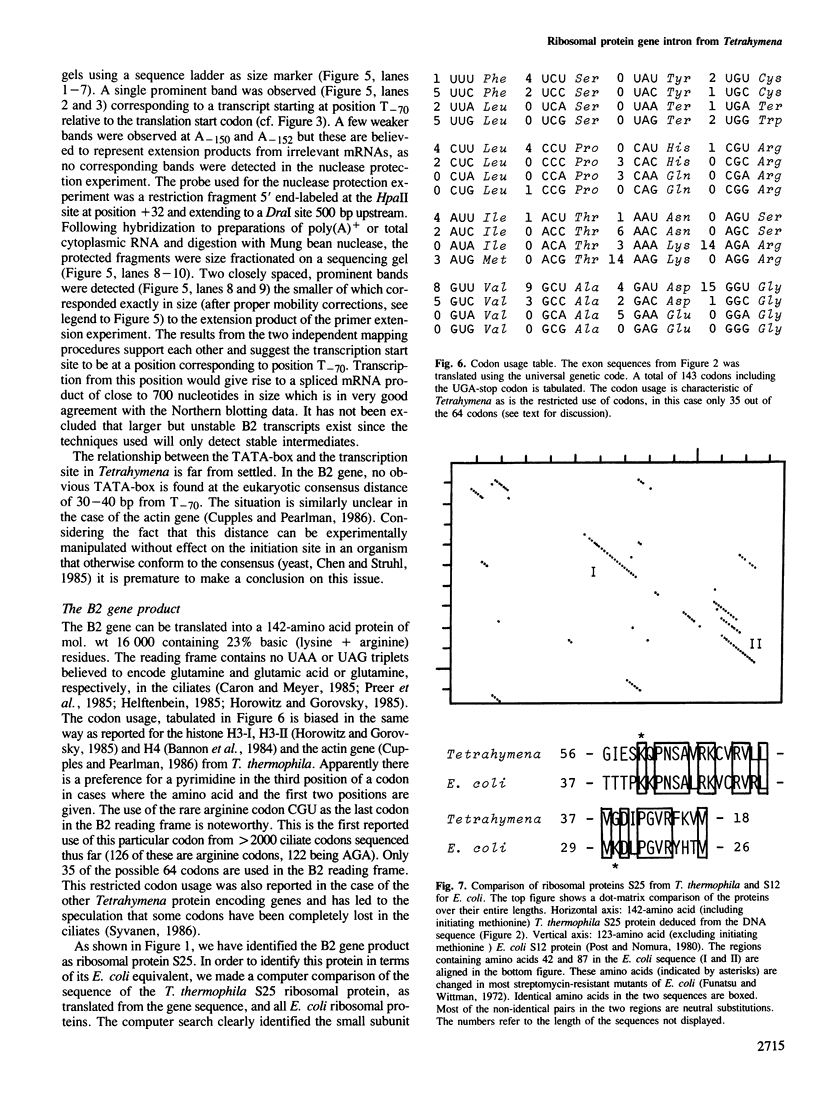


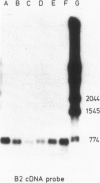
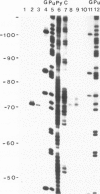
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. H., Dreisig H., Kristiansen K. Regulation of ribosome synthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. 3. Analysis by translation in vitro of RNA isolated during nutritional shift-down and nutritional shift-up. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):485–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon G. A., Bowen J. K., Yao M. C., Gorovsky M. A. Tetrahymena H4 genes: structure, evolution and organization in macro- and micronuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):1961–1975. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm S. L., Cech T. R. Fate of an intervening sequence ribonucleic acid: excision and cyclization of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid intervening sequence in vivo. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2390–2397. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron F., Meyer E. Does Paramecium primaurelia use a different genetic code in its macronucleus? Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):185–188. doi: 10.1038/314185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: implications for evolution. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:3–22. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Yeast mRNA initiation sites are determined primarily by specific sequences, not by the distance from the TATA element. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3273–3280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreisig H., Andreasen P. H., Kristiansen K. Regulation of ribosome synthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. 1. Coordination of synthesis of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA during nutritional shift-down. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreisig H., Andreasen P. H., Kristiansen K. Regulation of ribosome synthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. 2. Coordination of synthesis of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA during nutritional shift-up. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. 33. Location of amino-acid replacements in protein S12 isolated from Escherichia coli mutants resistant to streptomycin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helftenbein E. Nucleotide sequence of a macronuclear DNA molecule coding for alpha-tubulin from the ciliate Stylonychia lemnae. Special codon usage: TAA is not a translation termination codon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):415–433. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Murray K. Packaging recombinant DNA molecules into bacteriophage particles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Gorovsky M. A. An unusual genetic code in nuclear genes of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2452–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. The RNA lariat: a new ring to the splicing of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):423–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90449-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobutcher L. A., Jahn C. L., Prescott D. M. Internal sequences are eliminated from genes during macronuclear development in the ciliated protozoan Oxytricha nova. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1045–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen K., Krüger A. Ribosomal proteins in growing and starved Tetrahymena pyriformis. Starvation-induced phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 21;521(2):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., Van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Conserved sequences upstream of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Curr Genet. 1985;9(4):273–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00419955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martindale D. W., Martindale H. M., Bruns P. J. Tetrahymena conjugation-induced genes: structure and organization in macro- and micronuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1341–1354. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E., Caron F., Guiard B. Blocking of in vitro translation of Paramecium messenger RNAs is due to messenger RNA primary structure. Biochimie. 1984 May;66(5):403–412. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(84)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen H., Simon E. M., Engberg J. Updating rDNA restriction enzyme maps of Tetrahymena reveals four new intron-containing species. J Protozool. 1985 Aug;32(3):480–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb04046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N., Hellung-Larsen P., Engberg J. Small nuclear RNAs in the ciliate Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4203–4224. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Nomura M. DNA sequences from the str operon of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4660–4666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B., Rudman B. M., Barnett A. J. Deviation from the universal code shown by the gene for surface protein 51A in Paramecium. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):188–190. doi: 10.1038/314188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Cech T. R. The intervening sequence RNA of Tetrahymena is an enzyme. Science. 1986 Jan 31;231(4737):470–475. doi: 10.1126/science.3941911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]