Abstract
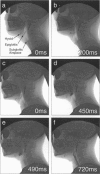
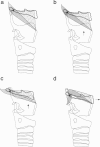
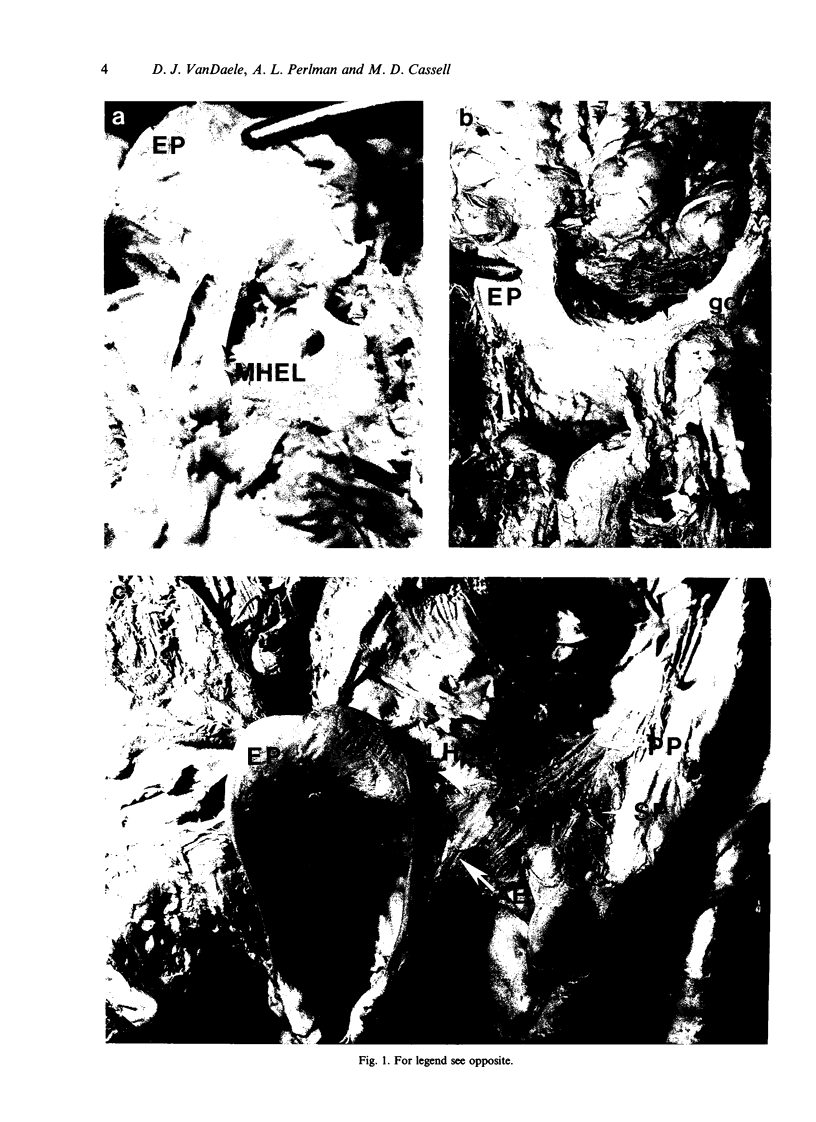
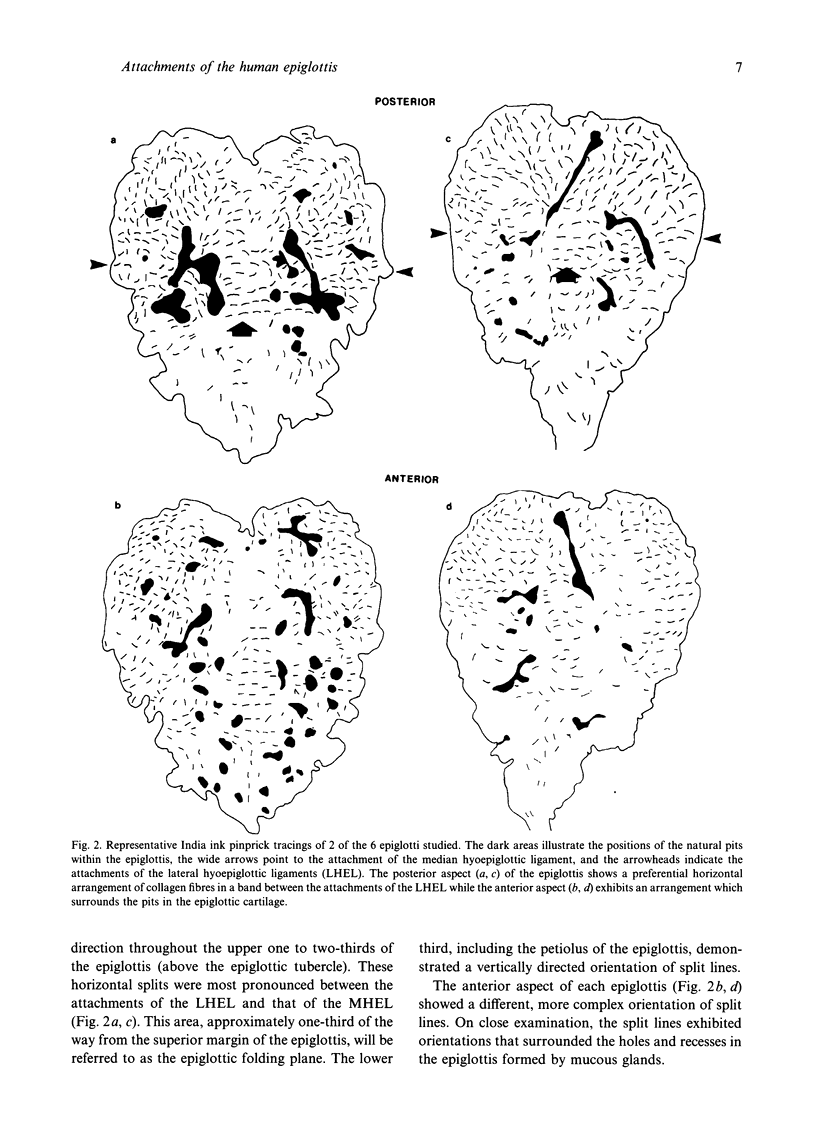
Two mechanisms have been proposed which address the downfolding of the epiglottis during swallowing. The passive mechanism (Fink et al. 1979) focuses on passive mechanical forces transmitted through the median hyoepiglottic ligament and pre-epiglottic adipose tissue to the epiglottis. The active mechanism (Ekberg & Sigurjonsson, 1982) expands the passive mechanism to include active contributions from the aryepiglotticus and thyroepiglotticus muscles. By means of laryngeal microdissection and whole mount orcein staining, distinct bands of fascial condensations were identified running from the lateral edge of the epiglottis just superior to the attachment of the median hyoepiglottic ligament to the hyoid bone near the ends of the greater horns. Neither the proposed active nor the passive mechanisms address the possible contribution of these paired lateral hyoepiglottic ligaments to epiglottic downfolding. Computer image analysis of videofluoroscopic examinations of swallowing was then used to assess the dynamic movements of the larynx during swallowing. It was observed that the downfolding of the epiglottis occurred in the same video frame as initiation of anterior displacement of the hyoid bone and thyrohyoid approximation. Based on the anatomical and dynamic relationship of the epiglottis to other laryngeal structures, we propose that as the larynx elevates and the hyoid bone moves anteriorly, these lateral ligaments exert traction preferentially on the upper third of the epiglottis to bring it to a position below the horizontal.
Full text
PDF





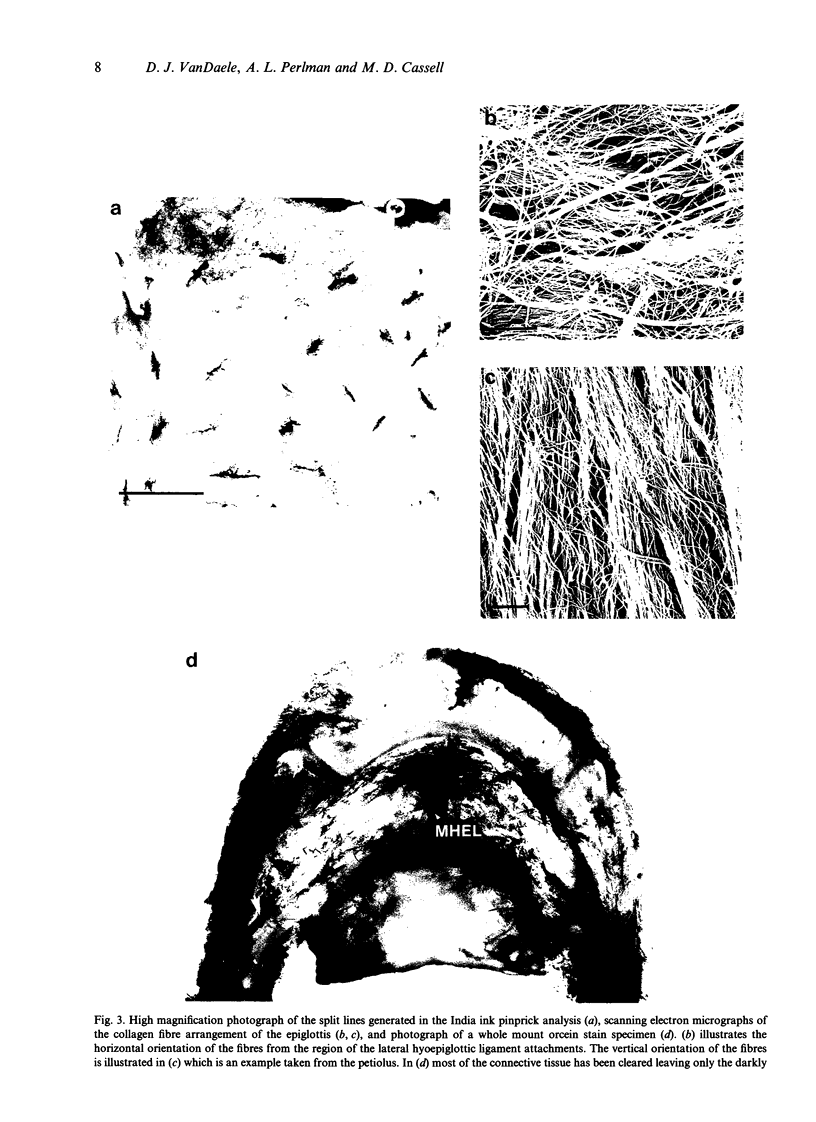

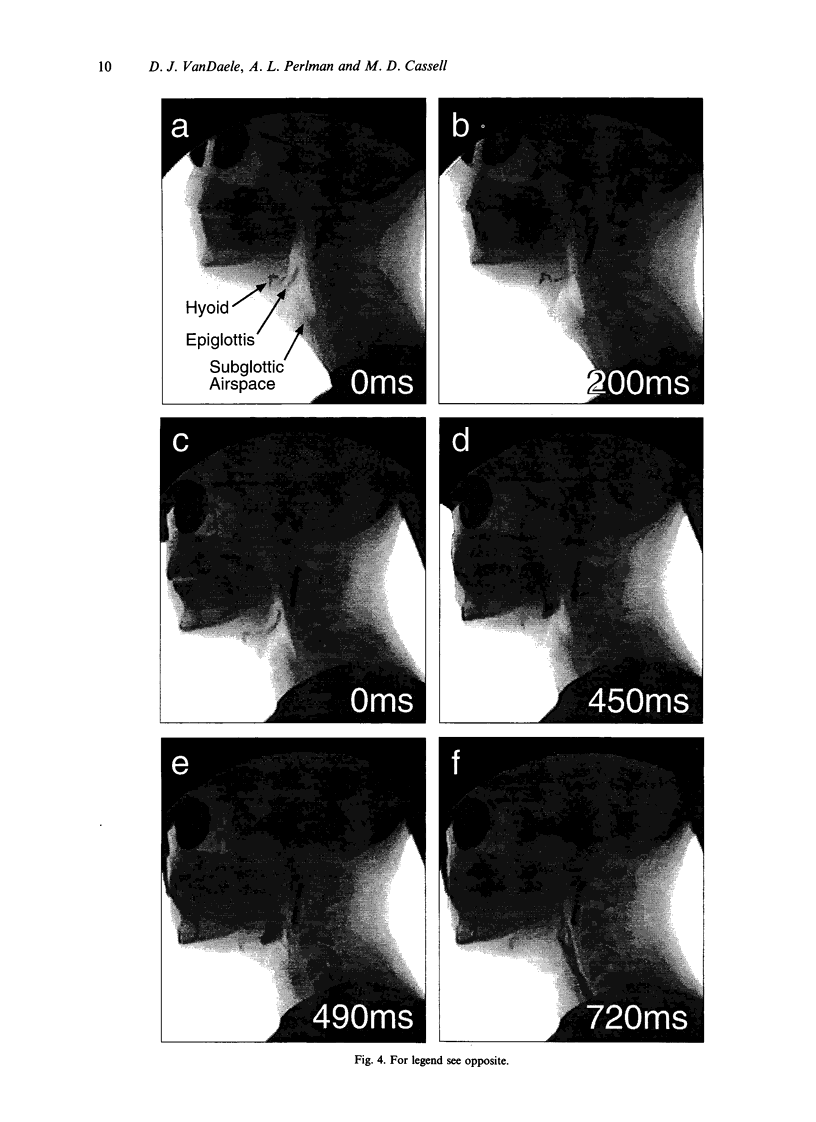
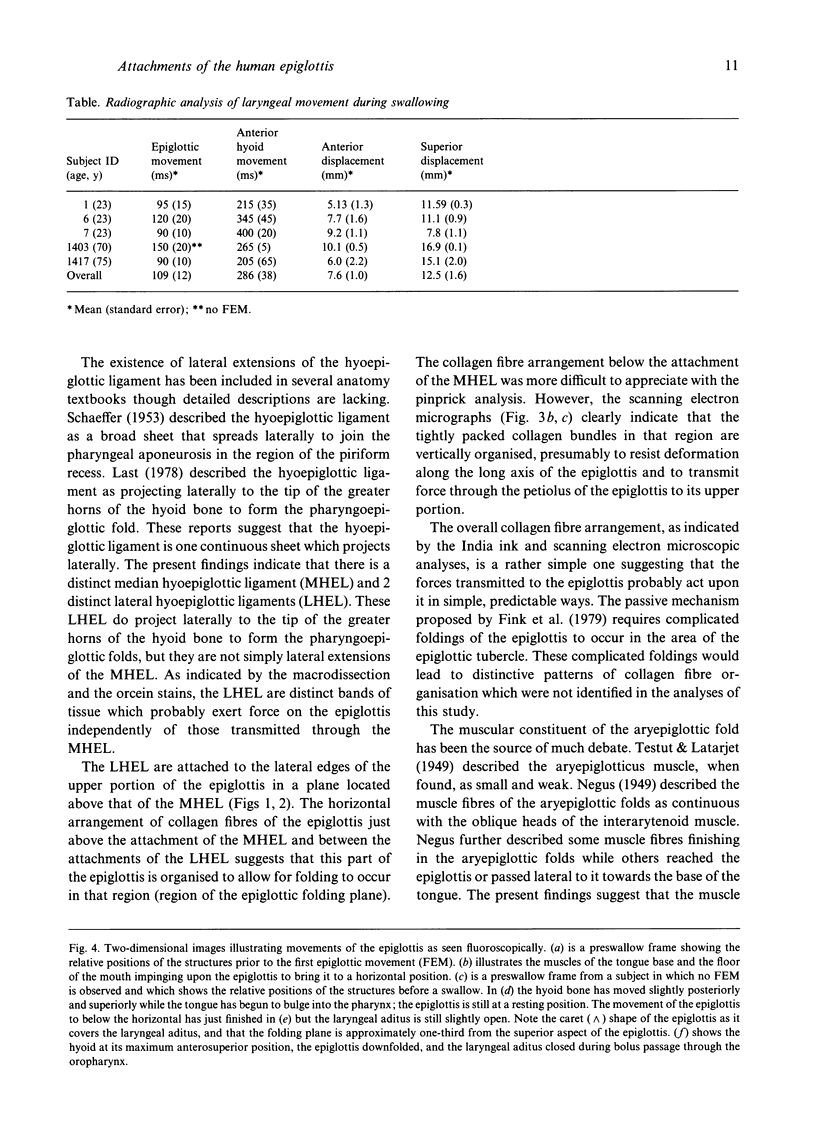


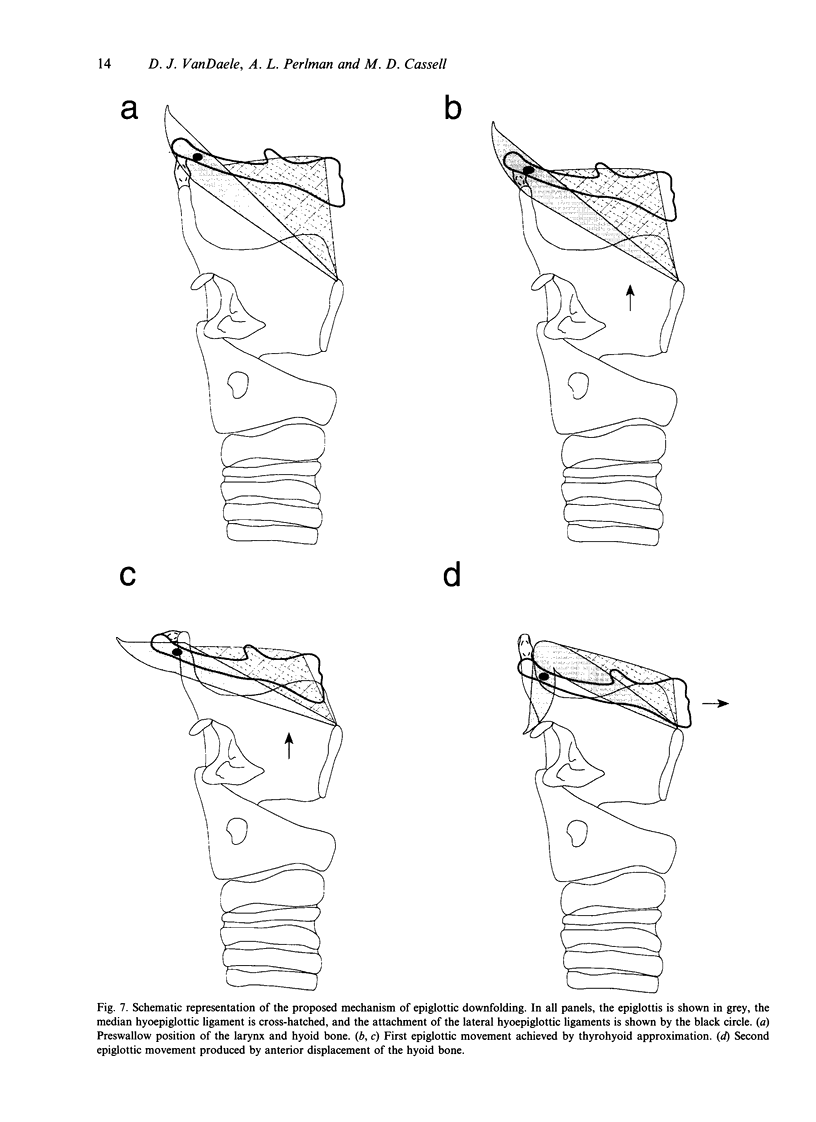

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARDRAN G. M., KEMP F. H. The mechanism of swallowing. Proc R Soc Med. 1951 Dec;44(12):1038–1040. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARDRAN G. M., KEMP F. H. The protection of the laryngeal airway during swallowing. Br J Radiol. 1952 Aug;25(296):406–416. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-25-296-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardran G. M., Kemp F. H. The mechanism of the larynx. II. The epiglottis and closure of the larynx. Br J Radiol. 1967 May;40(473):372–389. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-40-473-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. J., Cruess D. F., Dachman A. H., Maso E. Timing in the normal pharyngeal swallow. Prospective selection and evaluation of 16 normal asymptomatic patients. Invest Radiol. 1984 Nov-Dec;19(6):523–529. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198411000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekberg O., Sigurjónsson S. V. Movement of the epiglottis during deglutition. A cineradiographic study. Gastrointest Radiol. 1982;7(2):101–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01887619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink B. R., Martin R. W., Rohrmann C. A. Biomechanics of the human epiglottis. Acta Otolaryngol. 1979 May-Jun;87(5-6):554–559. doi: 10.3109/00016487909126464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrycyshyn A. W., Basmajian J. V. Electromyography of the oral stage of swallowing in man. Am J Anat. 1972 Mar;133(3):333–340. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001330307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob P., Kahrilas P. J., Logemann J. A., Shah V., Ha T. Upper esophageal sphincter opening and modulation during swallowing. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1469–1478. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90391-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane J. C., Kahn A. R. India ink pinprick experiments on surface organization of cricoarytenoid joints. J Speech Hear Res. 1986 Dec;29(4):544–548. doi: 10.1044/jshr.2904.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. R., Kahane J. C. India ink pinprick assessment of age-related changes in the cricoarytenoid joint (CAJ) articular surfaces. J Speech Hear Res. 1986 Dec;29(4):536–543. doi: 10.1044/jshr.2904.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutz W. Histologische Untersuchungen zur Vaskularisation des Epiglottisknorpels. Anat Anz. 1980;148(5):428–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J. A., Kahrilas P. J., Begelman J., Dodds W. J., Pauloski B. R. Interactive computer program for biomechanical analysis of videoradiographic studies of swallowing. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989 Aug;153(2):277–280. doi: 10.2214/ajr.153.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meachim G., Denham D., Emery I. H., Wilkinson P. H. Collagen alignments and artificial splits at the surface of human articular cartilage. J Anat. 1974 Sep;118(Pt 1):101–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minns R. J., Steven F. S. The collagen fibril organization in human articular cartilage. J Anat. 1977 Apr;123(Pt 2):437–457. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negus V. E. The Function of the Epiglottis. J Anat. 1927 Oct;62(Pt 1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negus V. E. The Mechanism of Swallowing: President's Address. Proc R Soc Med. 1942 Dec;36(2):85–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMSEY G. H., WATSON J. S., GRAMIAK R., WEINBERG S. A. Cinefluorographic analysis of the mechanism of swallowing. Radiology. 1955 Apr;64(4):498–518. doi: 10.1148/64.4.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHMER R. F., HENDRON J. A. The act of deglutition; a cinefluorographic study. J Appl Physiol. 1951 Apr;3(10):622–630. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1951.3.10.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAUNDERS J. B. C. M., DAVIS C., MILLER E. R. The mechanism of deglutition (second stage) as revealed by cine-radiography. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1951 Dec;60(4):897–916. doi: 10.1177/000348945106000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven F. S., Thomas H. Preparation of insoluble collagen from human cartilage. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):245–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1350245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilkman E., Karma P. Vertical hyoid bone displacement and fundamental frequency of phonation. Acta Otolaryngol. 1989 Jul-Aug;108(1-2):142–151. doi: 10.3109/00016488909107406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]