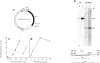Abstract
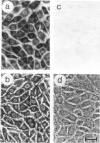
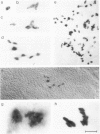
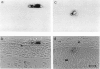
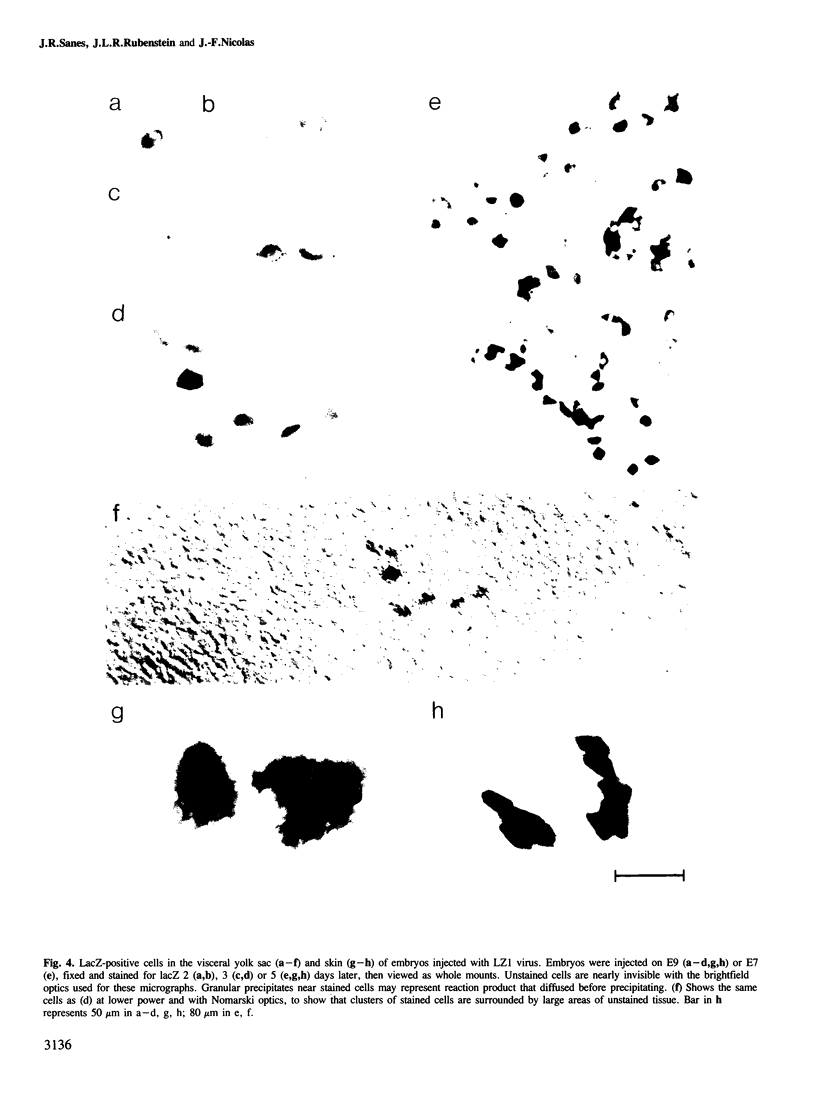
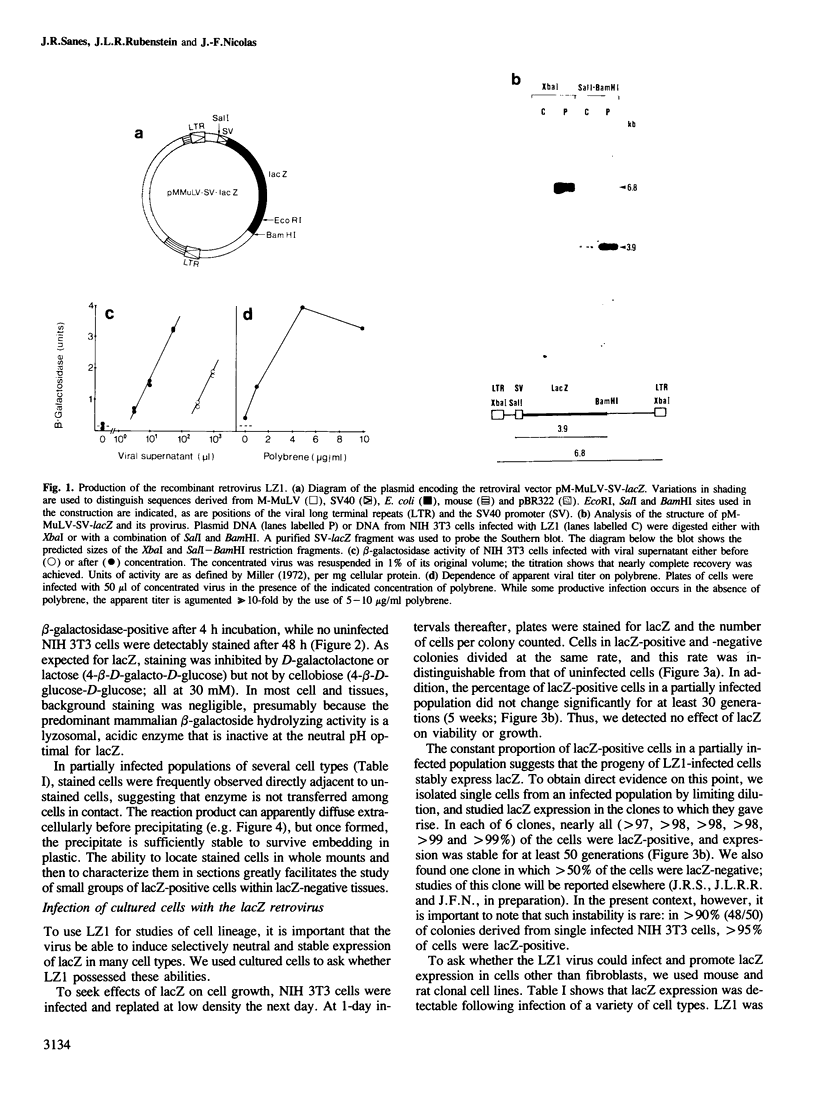
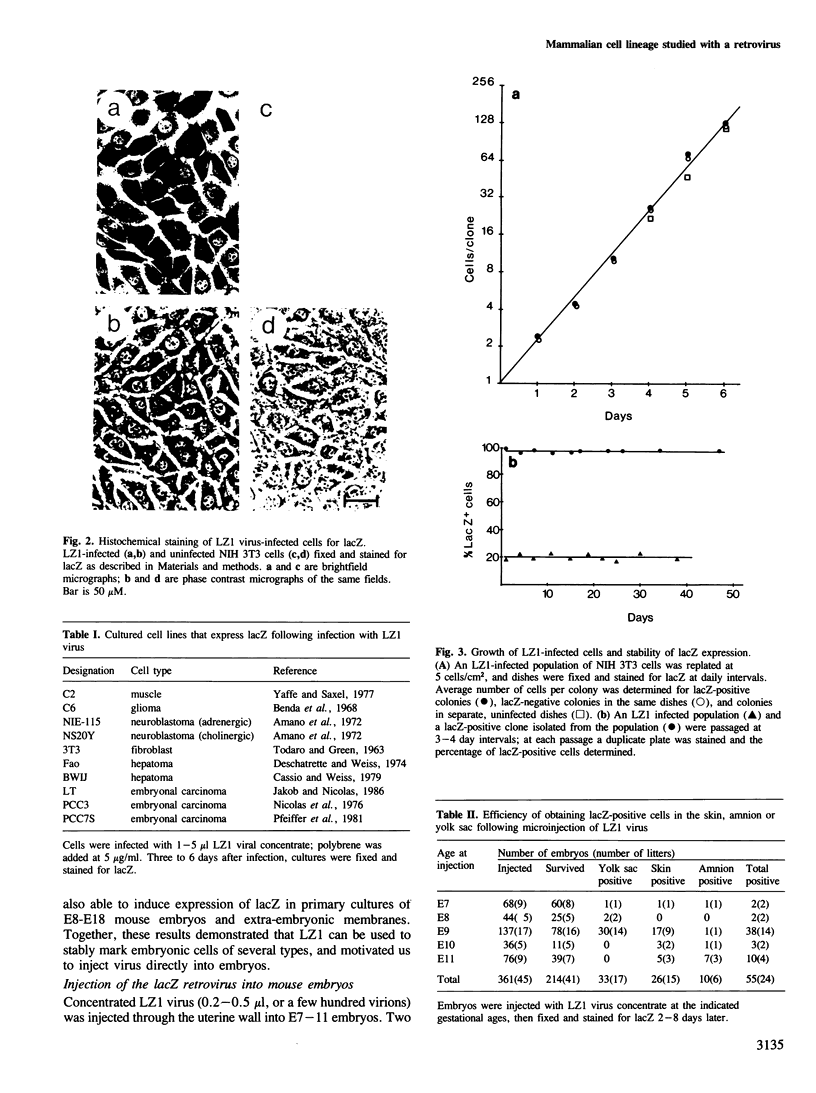
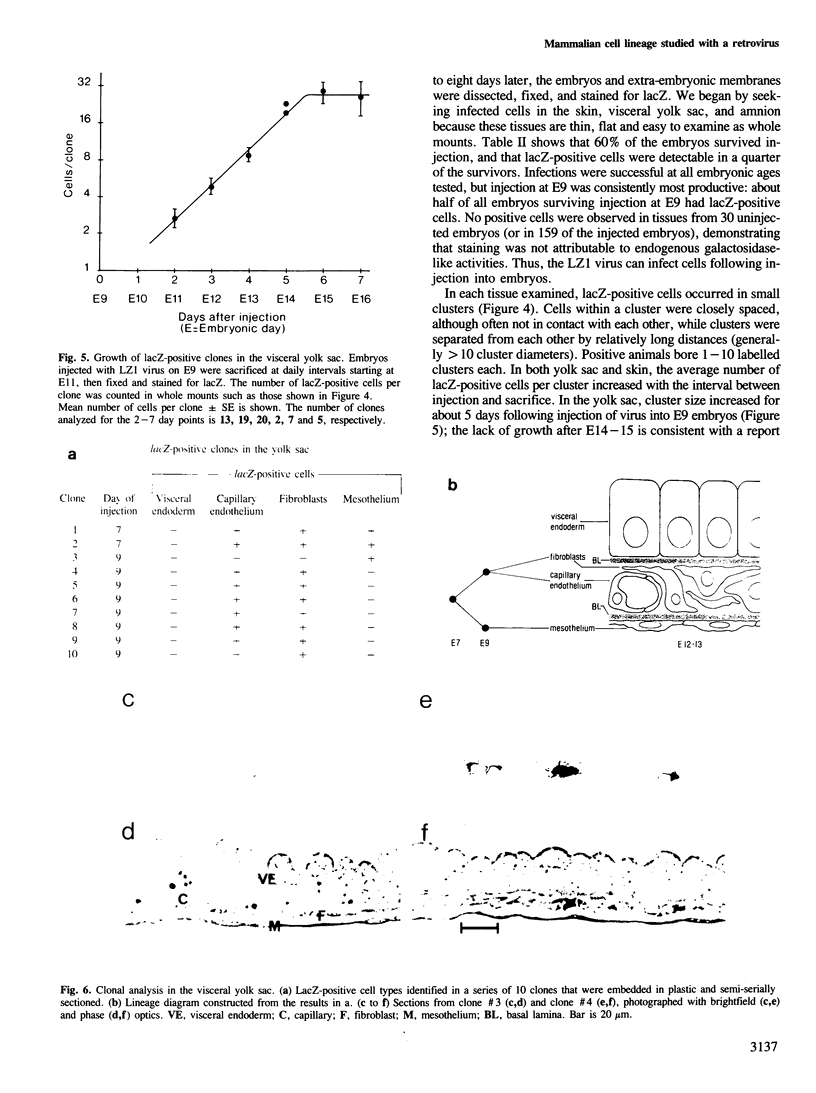
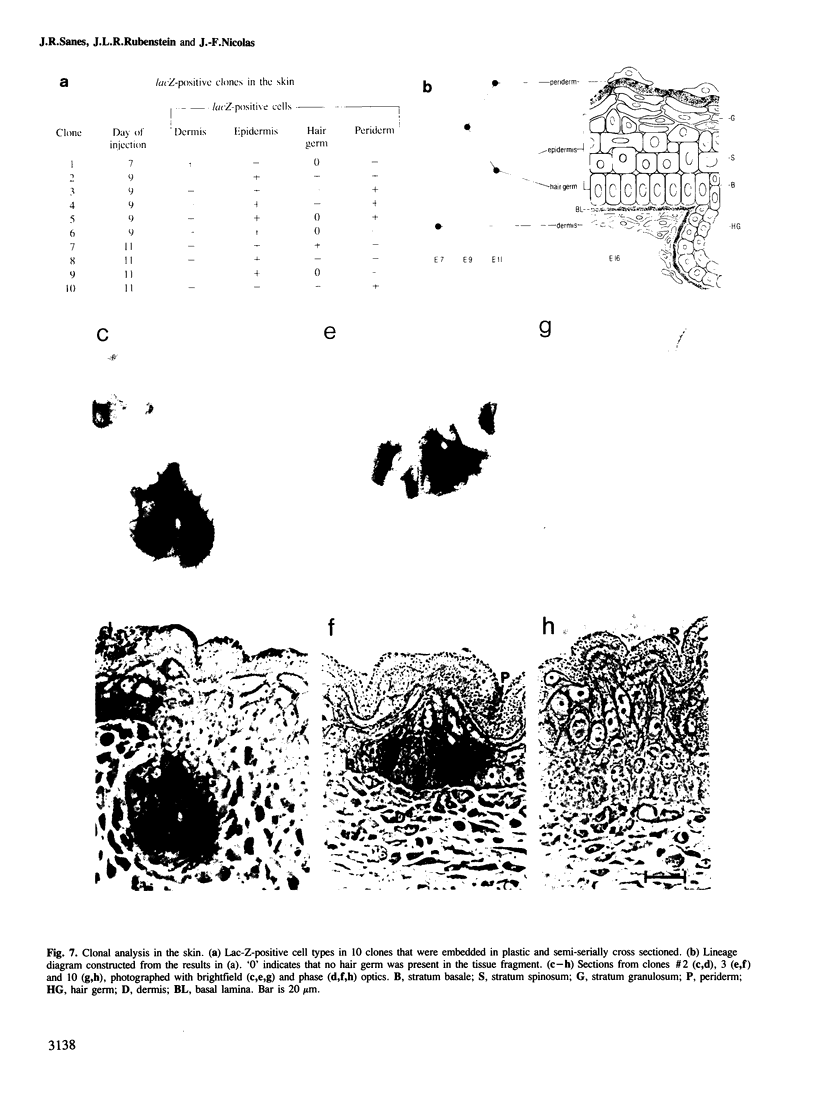
We show that a gene introduced into cells of mouse embryos by a retrovirus can serve as a heritable marker for the study of cell lineage in vivo. We constructed a defective recombinant retrovirus in which the Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase (lacZ) gene is inserted in the genome of a Muloney murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV). Expression of lacZ was detected with a histochemical stain that can be applied to cultured cells and embryonic tissue. Infection of cultured cells showed that lacZ has no detectable deleterious effects on cell viability or growth, that the enzyme is stably expressed in the progeny of infected cells for many generations in the absence of selective pressure, and that the virus can induce lacZ in a variety of cell types. Following injection of the virus into mid-gestation mouse embryos, clones of lacZ-positive cells were detected in skin, skull, meninges, brain, visceral yolk sac, and amnion. We identified the cell types comprising a series of lacZ-positive clones in the visceral yolk sac and skin to learn the lineage relationships of the labelled cells. In each tissue, we obtained evidence that several cell types have a pluripotential ancestor and that cell fate is progressively restricted as development proceeds.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano T., Richelson E., Nirenberg M. Neurotransmitter synthesis by neuroblastoma clones (neuroblast differentiation-cell culture-choline acetyltransferase-acetylcholinesterase-tyrosine hydroxylase-axons-dendrites). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):258–263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bałakier H., Pedersen R. A. Allocation of cells to inner cell mass and trophectoderm lineages in preimplantation mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Apr;90(2):352–362. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benda P., Lightbody J., Sato G., Levine L., Sweet W. Differentiated rat glial cell strain in tissue culture. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):370–371. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneville M. A. Observations on epidermal differentiation in the fetal rat. Am J Anat. 1968 Jul;123(1):147–164. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001230107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassio D., Weiss M. C. Expression of fetal and neonatal hepatic functions by mouse hepatoma-rat hepatoma hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):719–738. doi: 10.1007/BF01542637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Weiss M. C. Characterization of differentiated and dedifferentiated clones from a rat hepatoma. Biochimie. 1974;56(11-12):1603–1611. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Patterson P. H., Landis S. C. Small intensely fluorescent cells in culture: role of glucocorticoids and growth factors in their development and interconversions with other neural crest derivatives. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2143–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc-Nguyen H. Enhancing effect of diethylaminoethyl-dextran on the focus-forming titer of a murine sarcoma virus (Harvey strain). J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):643–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.643-644.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haar J. L., Ackerman G. A. A phase and electron microscopic study of vasculogenesis and erythropoiesis in the yolk sac of the mouse. Anat Rec. 1971 Jun;170(2):199–223. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091700206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson J. The histogenesis of the epidermis in the rat and mouse. J Anat. 1947 Apr;81(Pt 2):174–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. DNA methylation and gene expression: endogenous retroviral genome becomes infectious after molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. F., Kent A. P. The sequence of events in the differentiation of the epidermis in fetal rats with particular reference to membrane-coating granules. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;227(3):619–631. doi: 10.1007/BF00204792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. Clonal analysis and cell lineages of the vertebrate central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:71–102. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Jähner D., Nobis P., Simon I., Löhler J., Harbers K., Grotkopp D. Chromosomal position and activation of retroviral genomes inserted into the germ line of mice. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G., Paige C., Gilboa E., Wagner E. F. Expression of a foreign gene in myeloid and lymphoid cells derived from multipotent haematopoietic precursors. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):149–154. doi: 10.1038/318149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel C. B., Warga R. M. Tissue-specific cell lineages originate in the gastrula of the zebrafish. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):365–368. doi: 10.1126/science.231.4736.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lojda Z. Indigogenic methods for glycosidases. II. An improved method for beta-D-galactosidase and its application to localization studies of the enzymes in the intestine and in other tissues. Histochemie. 1970;23(3):266–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00306428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Sieburg C. E., Whitlock C. A., Weissman I. L. Isolation of two early B lymphocyte progenitors from mouse marrow: a committed pre-pre-B cell and a clonogenic Thy-1-lo hematopoietic stem cell. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Avner P., Gaillard J., Guenet J. L., Jakob H., Jacob F. Cell lines derived from teratocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4224–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsot C., Saint-Girons I., Cossart P. DNA sequence change of a deletion mutation abolishing attenuation control of the threonine operon of E. coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):455–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00330048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer S. E., Jakob H., Mikoshiba K., Dubois P., Guenet J. L., Nicolas J. F., Gaillard J., Chevance G., Jacob F. Differentiation of a teratocarcinoma line: preferential development of cholinergic neurons. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):57–66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Abney E. R., Miller R. H. Two glial cell lineages diverge prenatally in rat optic nerve. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F., Jacob F. Construction of a retrovirus capable of transducing and expressing genes in multipotential embryonic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7137–7140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccoman F. M., Morgan C. F., Wells L. J. Radioautographic studies of DNA synthesis in the developing extraembryonic membranes of the mouse. Anat Rec. 1967 Jun;158(2):197–205. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091580209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Jaenisch R. Retroviruses as probes for mammalian development: allocation of cells to the somatic and germ cell lineages. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90856-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern I. B., Dayton L., Duecy J. The uptake of tritiated thymidine by the dorsal epidermis of the fetal and newborn rat. Anat Rec. 1971 Jun;170(2):225–234. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091700207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Cone R., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Introduction of a selectable gene into different animal tissue by a retrovirus recombinant vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7151–7155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISLOCKI G. B., PADYKULA H. A. Reichert's membrane and the yolk sac of the rat investigated by histochemical means. Am J Anat. 1953 Jan;92(1):117–150. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000920104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Vanek M., Vennström B. Transfer of genes into embryonal carcinoma cells by retrovirus infection: efficient expression from an internal promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):663–666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]