Abstract
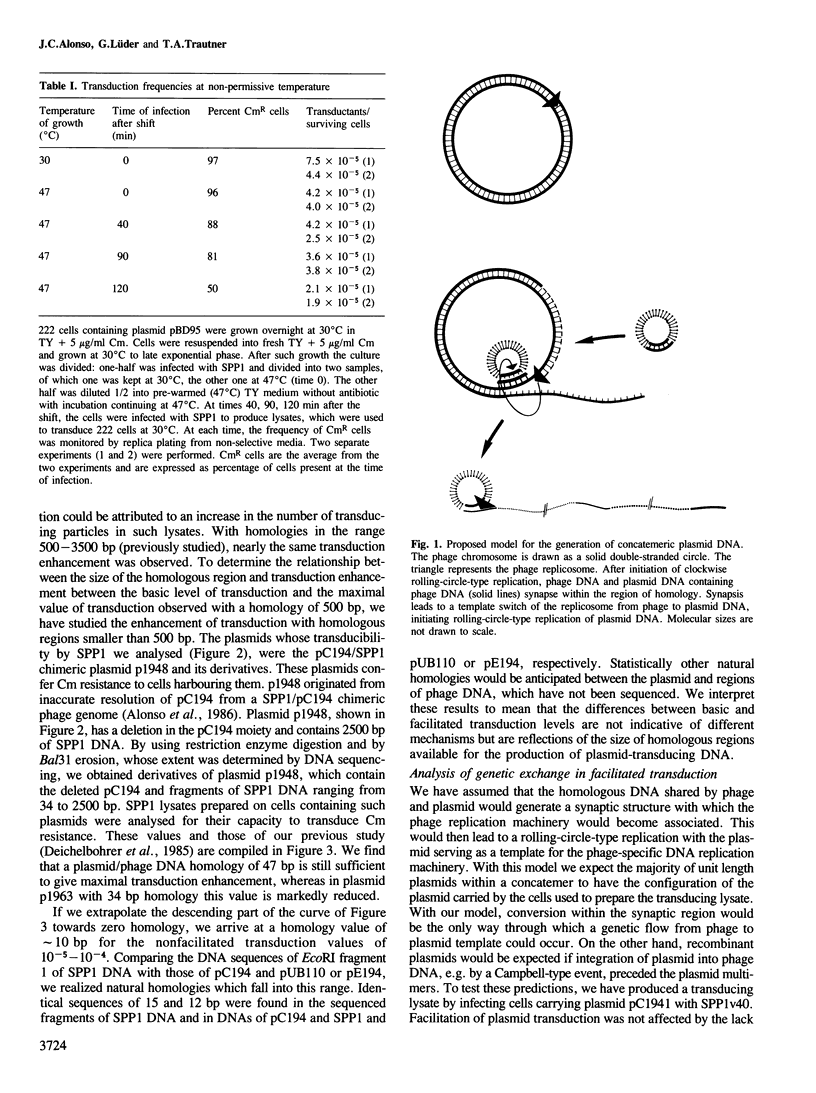
We had previously proposed that the production of concatemeric plasmid DNA in plasmid-transducing SPP1 particles is a consequence of phage-directed rolling-circle-type replication of plasmid DNA. The production of such DNA was greatly enhanced when DNA/DNA homology was provided between phage and plasmid DNAs (facilitation of transduction). Here we present evidence that synthesis of concatemeric plasmid DNA can proceed after phage infection under conditions non-permissive for plasmid replication. We also propose that the naturally occurring homology between plasmid and phage is sufficient to account for the frequency of transduction observed in the absence of facilitating homology. Homology of greater than 47 bp gives the maximal facilitation of plasmid transduction. Recombination is not an essential part in the synthesis of concatemeric plasmid DNA.
Full text
PDF



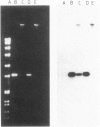
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canosi U., Lüder G., Trautner T. A. SPP1-mediated plasmid transduction. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):431–436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.431-436.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canosi U., Morelli G., Trautner T. A. The relationship between molecular structure and transformation efficiency of some S. aureus plasmids isolated from B. subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 9;166(3):259–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00267617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Jones I., Goze A., Romac S., Niaudet B., Ehrlich S. D. Replication functions of pC194 are necessary for efficient plasmid transduction by M13 phage. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01764.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
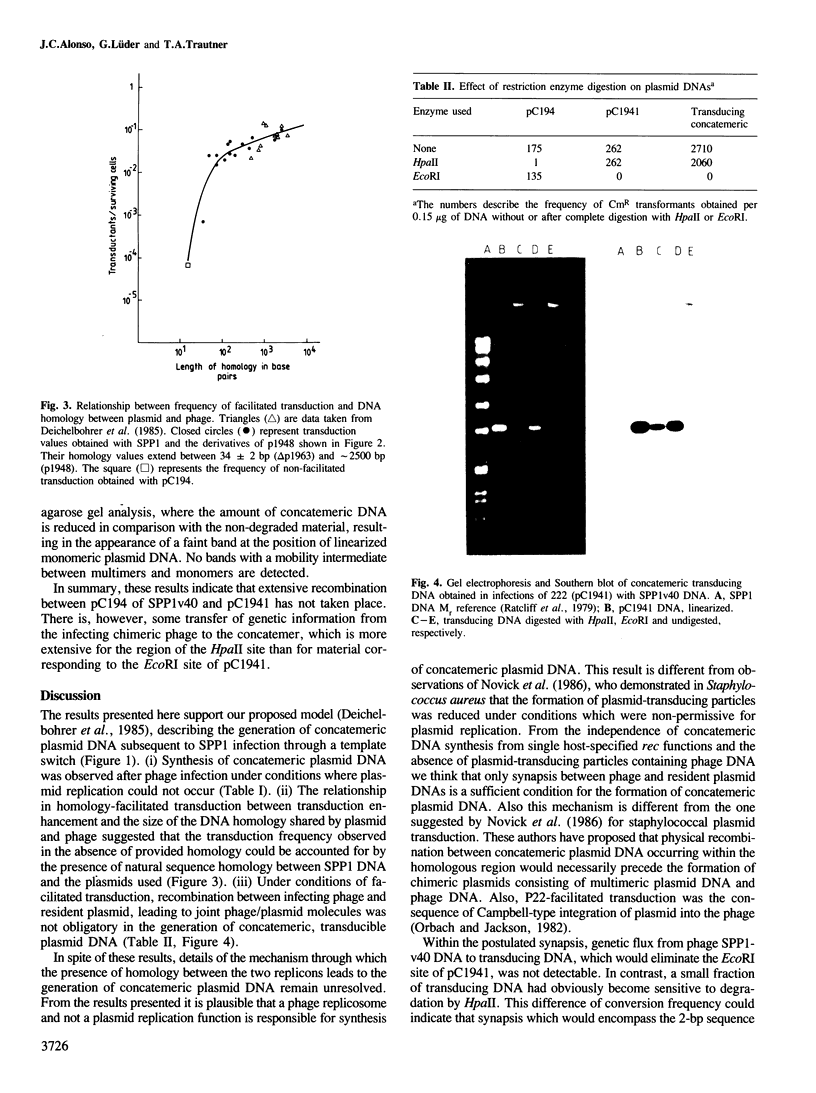
- Deichelbohrer I., Alonso J. C., Lüder G., Trautner T. A. Plasmid transduction by Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPP1: effects of DNA homology between plasmid and bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1238–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1238-1243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. M., Cross T. A., DiVerdi J. A., Opella S. J. Protein dynamics by solid-state NMR: aromatic rings of the coat protein in fd bacteriophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):101–105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Hahn J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Replication and incompatibility properties of plasmid pE194 in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):722–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.722-735.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilmann H., Reeve J. N. Construction and use of SPP1v, a viral cloning vector for Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Weisblum B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):815–825. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.815-825.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordănescu S. Recombinant plasmid obtained from two different, compatible staphylococcal plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):597–601. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.597-601.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. R., Richardson J. P. Role of homology and pathway specificity for recombination between plasmids and bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00330201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfdahl S., Sjöström J. E., Philipson L. Cloning of restriction fragments of DNA from staphylococcal bacteriophage phi 11. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):795–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.795-801.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Jackson E. N. Transfer of chimeric plasmids among Salmonella typhimurium strains by P22 transduction. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):985–994. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.985-994.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliff S. W., Luh J., Ganesan A. T., Behrens B., Thompson R., Montenegro M. A., Morelli G., Trautner T. A. The genome of Bacillus subtilis phage SPP1: the arrangement of restriction endonuclease generated fragments. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 10;168(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00431442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Polsinelli M., Falaschi A. A new phage of Bacillus subtilis with infectious DNA having separable strands. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 28;35(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottländer E., Trautner T. A. Genetic and transfection studies with B, subtilis phage SP 50. I. Phage mutants with restricted growth on B. subtilis strain 168. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(1):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00343184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer-Abramowitz J., Gryczan T. J., Dubnau D. Origin and mode of replication of plasmids pE194 and pUB110. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P., Huang H. V. Homologous recombination in Escherichia coli: dependence on substrate length and homology. Genetics. 1986 Mar;112(3):441–457. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. S., Gold L., Gauss P., Doherty D. H. Determination of the amount of homology required for recombination in bacteriophage T4. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautner T. A., Pawlek B., Bron S., Anagnostopoulos C. Restriction and modification in B. subtilis. Biological aspects. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(3):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00267958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt V. M., Ingles C. J., Urdea M. S., Rutter W. J. Homology requirements for recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4768–4772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Riele H., Michel B., Ehrlich S. D. Single-stranded plasmid DNA in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2541–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]