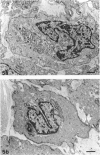
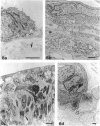
Abstract
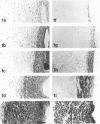
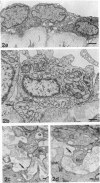
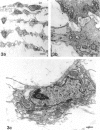
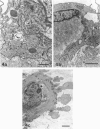
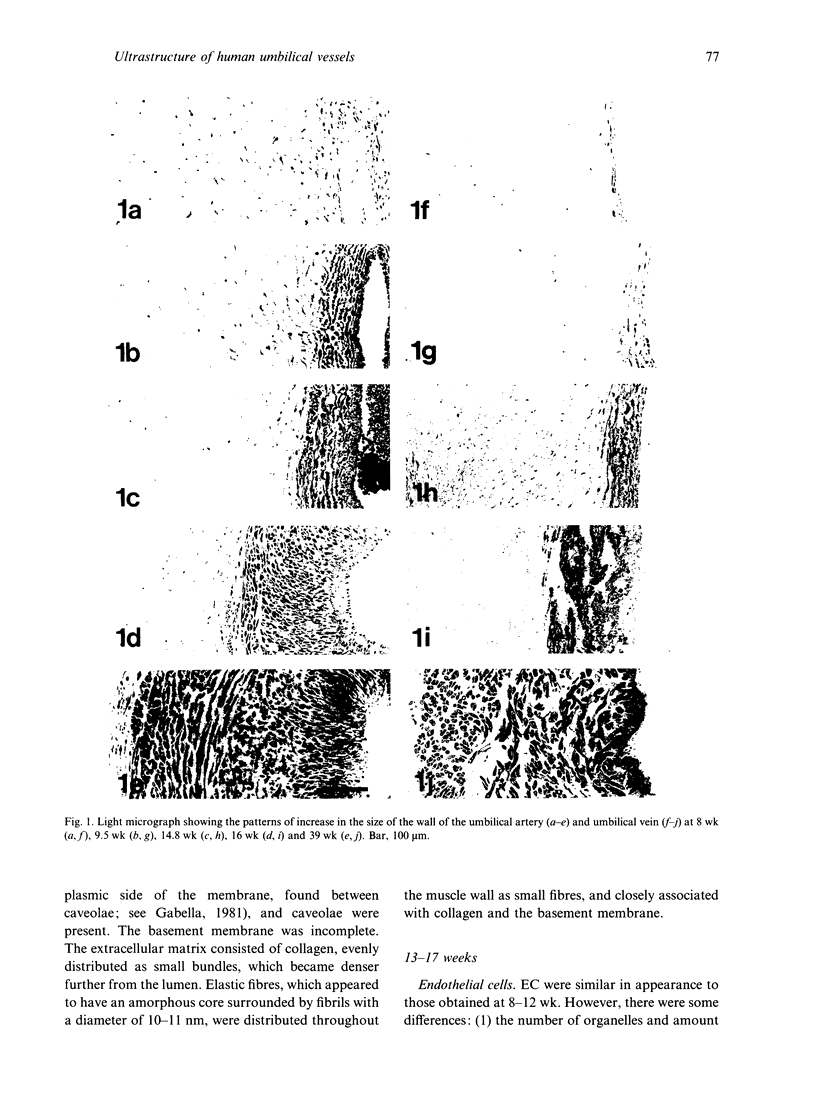
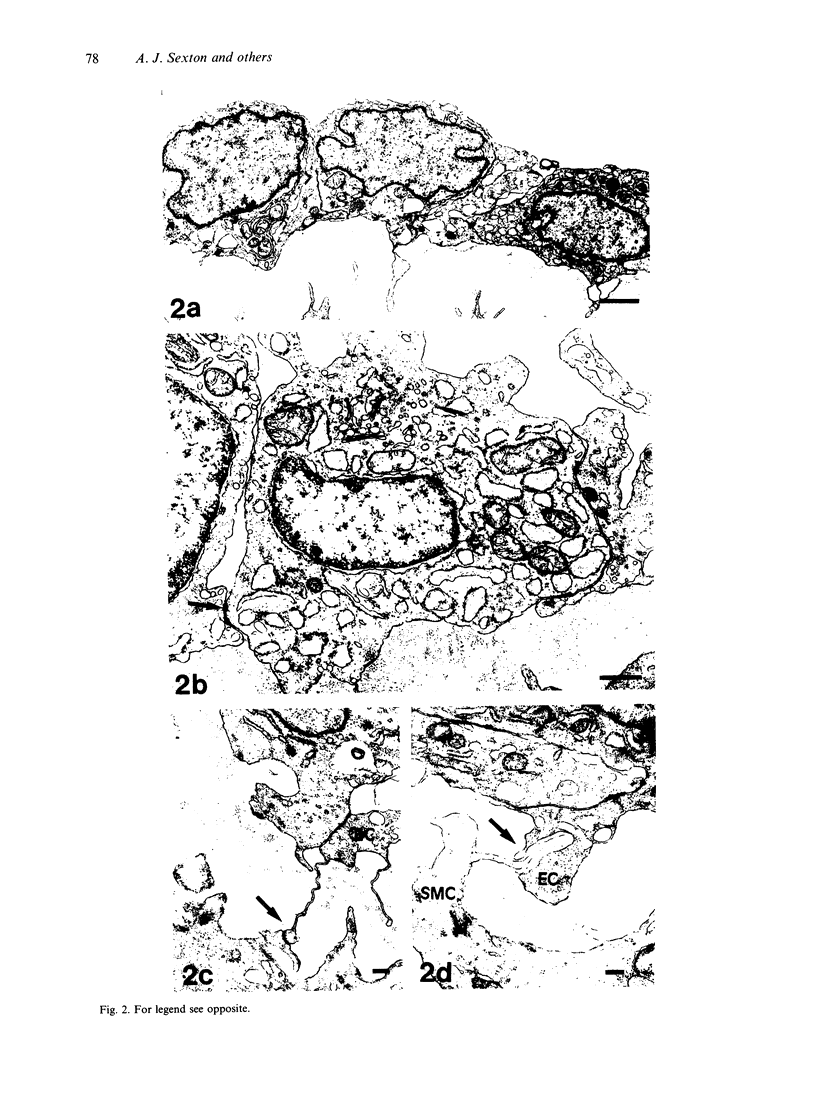
Electron microscopic techniques were used to examine the ultrastructure of developing human umbilical arteries and vein (8-12, 13-17 and 37-40 wk gestational age). These showed that with increasing age there is (1) an increase in the size of the lumen and the thickness of the media; (2) an increase in the ratio of contractile smooth muscle phenotypic cells; (3) an increase in the myofilament content of the smooth muscle cells and the number of Weibel-Palade bodies; (4) a decrease in the glycogen content; (5) an appearance of microvilli on the luminal surface of the endothelium. Lipid vesicles, nerves and vasa vasorum were not observed in any region of the umbilical vein or arteries.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus J. A., Cocks T. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(1-2):303–352. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asmussen I., Kjeldsen K. Intimal ultrastructure of human umbilical arteries. Observations on arteries from newborn children of smoking and nonsmoking mothers. Circ Res. 1975 May;36(5):579–589. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beham A., Denk H., Desoye G. The distribution of intermediate filament proteins, actin and desmoplakins in human placental tissue as revealed by polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. Placenta. 1988 Sep-Oct;9(5):479–492. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(88)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury F. M., Ockleford C. D. A confocal and conventional epifluorescence microscope study of the intermediate filaments in chorionic villi. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:173–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Q., Bodin P., Loesch A., Sexton A., Burnstock G. Endothelium of human umbilical blood vessels: ultrastructural immunolocalization of neuropeptides. J Vasc Res. 1993 Nov-Dec;30(6):348–355. doi: 10.1159/000159017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Q., Bodin P., Sexton A., Loesch A., Burnstock G. Localization of neuropeptide Y and atrial natriuretic peptide in the endothelial cells of human umbilical blood vessels. Cell Tissue Res. 1993 Apr;272(1):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00323584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadak C., Ulrich W., Sinzinger H. Morphological changes in the umbilical arteries of babies born to pre-eclamptic mothers: an ultrastructural study. Placenta. 1984 Sep-Oct;5(5):419–426. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(84)80022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. B., Khong T. Y. Lack of innervation of human umbilical cord. An immunohistological and histochemical study. Placenta. 1990 Jan-Feb;11(1):59–62. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80443-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebrane-Younes J., Hoang N. M., Orcel L. Ultrastructure of human umbilical vessels: a possible role in amniotic fluid formation? Placenta. 1986 Mar-Apr;7(2):173–185. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(86)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hustin J., Schaaps J. P. Echographic [corrected] and anatomic studies of the maternotrophoblastic border during the first trimester of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Jul;157(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauniaux E., Jurkovic D., Campbell S., Hustin J. Doppler ultrasonographic features of the developing placental circulation: Correlation with anatomic findings. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Feb;166(2):585–587. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(92)91678-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khong T. Y., Lane E. B., Robertson W. B. An immunocytochemical study of fetal cells at the maternal-placental interface using monoclonal antibodies to keratins, vimentin and desmin. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;246(1):189–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00219017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner P., Kirkpatrick K. A., Ralevic V., Toothill V., Pearson J., Burnstock G. Endothelial cells cultured from human umbilical vein release ATP, substance P and acetylcholine in response to increased flow. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Sep 22;241(1302):245–248. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockleford C., Malak T., Hubbard A., Bracken K., Burton S. A., Bright N., Blakey G., Goodliffe J., Garrod D., d'Lacey C. Confocal and conventional immunofluorescence and ultrastructural localisation of intracellular strength-giving components of human amniochorion. J Anat. 1993 Dec;183(Pt 3):483–505. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry E. W., Abramovich D. R. The ultrastructure of human umbilical vessel endothelium from early pregnancy to full term. J Anat. 1972 Jan;111(Pt 1):29–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly F. D., Russell P. T. Neurohistochemical evidence supporting an absence of adrenergic and cholinergic innervation in the human placenta and umbilical cord. Anat Rec. 1977 Jul;188(3):277–286. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091880302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodesch F., Simon P., Donner C., Jauniaux E. Oxygen measurements in endometrial and trophoblastic tissues during early pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Aug;80(2):283–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Leszczynski D., Toda T., Kummerow F., Nishimori I. Ultrastructure of human umbilical artery and vein. Characterization and quantification of lipid laden cells. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1985 Sep;35(5):1047–1055. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1985.tb00997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takechi K., Kuwabara Y., Mizuno M. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies of Wharton's jelly umbilical cord cells. Placenta. 1993 Mar-Apr;14(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(05)80264-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., PALADE G. E. NEW CYTOPLASMIC COMPONENTS IN ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIA. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:101–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. S., Komuro T. Interstitial cells associated with the deep muscular plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine, with special reference to the interstitial cells of Cajal. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 May;268(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00318788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]