Abstract
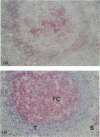
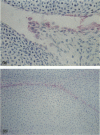
Murine monoclonal antibody Mab 67 was originally shown on histochemical screening to bind to synovial intimal fibroblasts (SIF), cells in lymphoid follicles and elastic fibres. As part of a programme to isolate the antigen recognised by Mab 67 and determine its function, a wider histochemical study was performed. Cryostat sections were prepared from normal human adult synovium, skin, placenta, amnion, kidney, tonsil, breast, thyroid, colon and pericardium, fetal limb tissues and rheumatoid arthritic synovium. Sections were stained with Mab 67, anti-CD3, as isotype matched control, and anti-VCAM-1 using alkaline phosphatase -anti-alkaline phosphatase. Selected sections were double labelled for nonspecific esterase activity. Staining by Mab 67 of SIF, identified as NSE-negative intimal cells, and follicle centre cells was confirmed. Staining with Mab 67 was also seen on Bowman's capsule and juxtaglomerular apparatus, stratum granulosum of skin, pulmonary alveolar cells, amniotic epithelium, chorionic villi, fetal synovium, bone marrow stromal cells and epidermis, and interstitial elastic fibres in most tissues, but not at other sites in these tissues or in pericardium, muscle, colon, breast, thyroid, salivary gland or vein. The staining pattern with Mab 67 suggests that the antigen is pericellular. Its distribution does not match any molecule known to us but overlaps at several sites with VCAM-1 (SIF, follicle centres, Bowman's capsule and bone marrow stroma). We suggest that the antigen involved may possible by similarly involved in cell-matrix interaction.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashhurst D. E., Bland Y. S., Levick J. R. An immunohistochemical study of the collagens of rabbit synovial interstitium. J Rheumatol. 1991 Nov;18(11):1669–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bröker B. M., Edwards J. C., Fanger M. W., Lydyard P. M. The prevalence and distribution of macrophages bearing Fc gamma R I, Fc gamma R II, and Fc gamma R III in synovium. Scand J Rheumatol. 1990;19(2):123–135. doi: 10.3109/03009749009102116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. C. The nature and origins of synovium: experimental approaches to the study of synoviocyte differentiation. J Anat. 1994 Jun;184(Pt 3):493–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. C., Wilkinson L. S., Jones H. M., Soothill P., Henderson K. J., Worrall J. G., Pitsillides A. A. The formation of human synovial joint cavities: a possible role for hyaluronan and CD44 in altered interzone cohesion. J Anat. 1994 Oct;185(Pt 2):355–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. C., Wilkinson L. S., Speight P., Isenberg D. A. Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 and alpha 4 and beta 1 integrins in lymphocyte aggregates in Sjögren's syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Nov;52(11):806–811. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.11.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Palmer D. G., Revell P. A. Mononuclear phagocytes of normal and rheumatoid synovial membrane identified by monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1985 Dec;56(4):673–681. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Burrows J. C., Haines G. K., Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M., Leibovich S. J. Immunolocalization of endothelial and leukocyte adhesion molecules in human rheumatoid and osteoarthritic synovial tissues. Lab Invest. 1991 Mar;64(3):313–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCachren S. S., Lightner V. A. Expression of human tenascin in synovitis and its regulation by interleukin-1. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Oct;35(10):1185–1196. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Ducret J., Wayner E., Elices M. J., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Zvaifler N. J., Firestein G. S. Alpha 4/beta 1 integrin (VLA-4) ligands in arthritis. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in synovium and on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1424–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. G., Selvendran Y., Allen C., Revell P. A., Hogg N. Features of synovial membrane identified with monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Mar;59(3):529–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock L. E., Lalor P., Revell P. A. Type IV collagen and laminin in the synovial intimal layer: an immunohistochemical study. Rheumatol Int. 1990;9(6):277–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00541324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. E., Munro J. M., Corless C., Bevilacqua M. P. Vascular and nonvascular expression of INCAM-110. A target for mononuclear leukocyte adhesion in normal and inflamed human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):385–393. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. R., Mapp P. I., Revell P. A. A monoclonal antibody (Mab 67) marks type B synoviocytes. Rheumatol Int. 1990;10(3):103–106. doi: 10.1007/BF02274823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. S., Edwards J. C., Poston R. N., Haskard D. O. Expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in normal and inflamed synovium. Lab Invest. 1993 Jan;68(1):82–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. S., Pitsillides A. A., Worrall J. G., Edwards J. C. Light microscopic characterization of the fibroblast-like synovial intimal cell (synoviocyte). Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Oct;35(10):1179–1184. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J., Carsons S. E. Distribution of type VI collagen expression in synovial tissue and cultured synoviocytes: relation to fibronectin expression. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Jul;50(7):493–496. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.7.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrall J. G., Wilkinson L. S., Bayliss M. T., Edwards J. C. Zonal distribution of chondroitin-4-sulphate/dermatan sulphate and chondroitin-6-sulphate in normal and diseased human synovium. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Jan;53(1):35–38. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]