Abstract
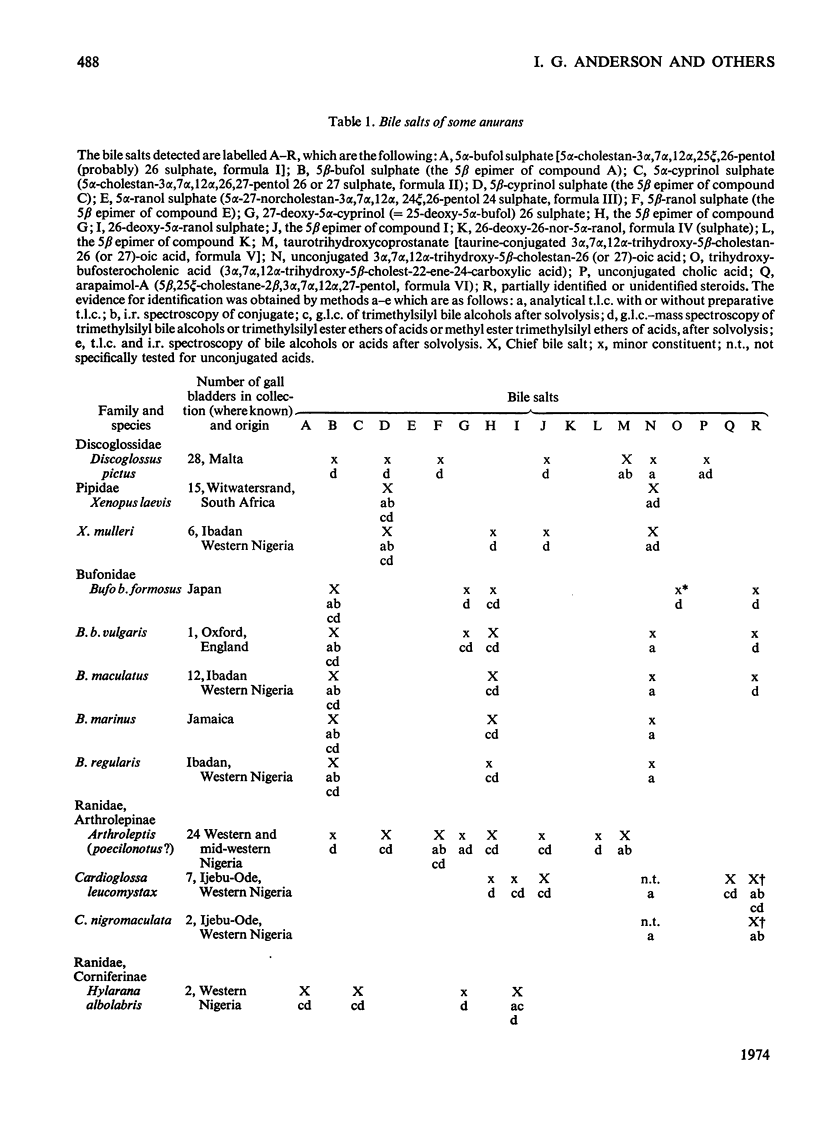
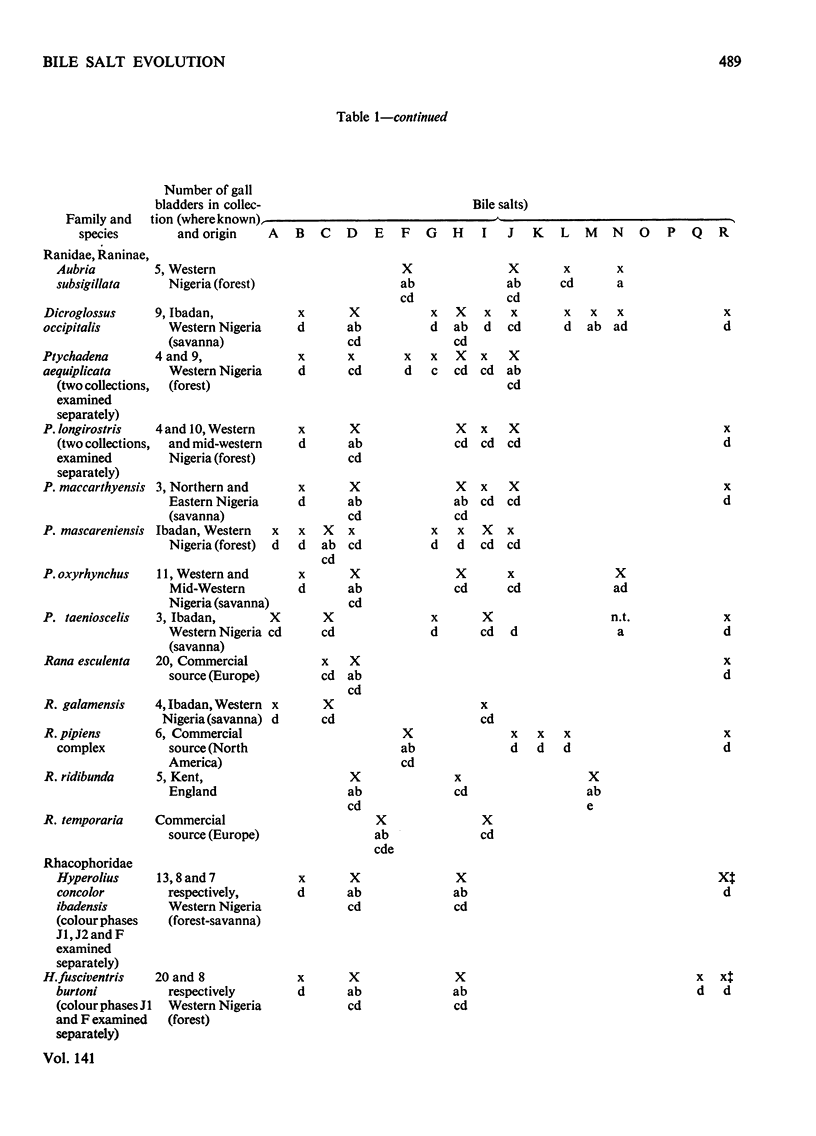
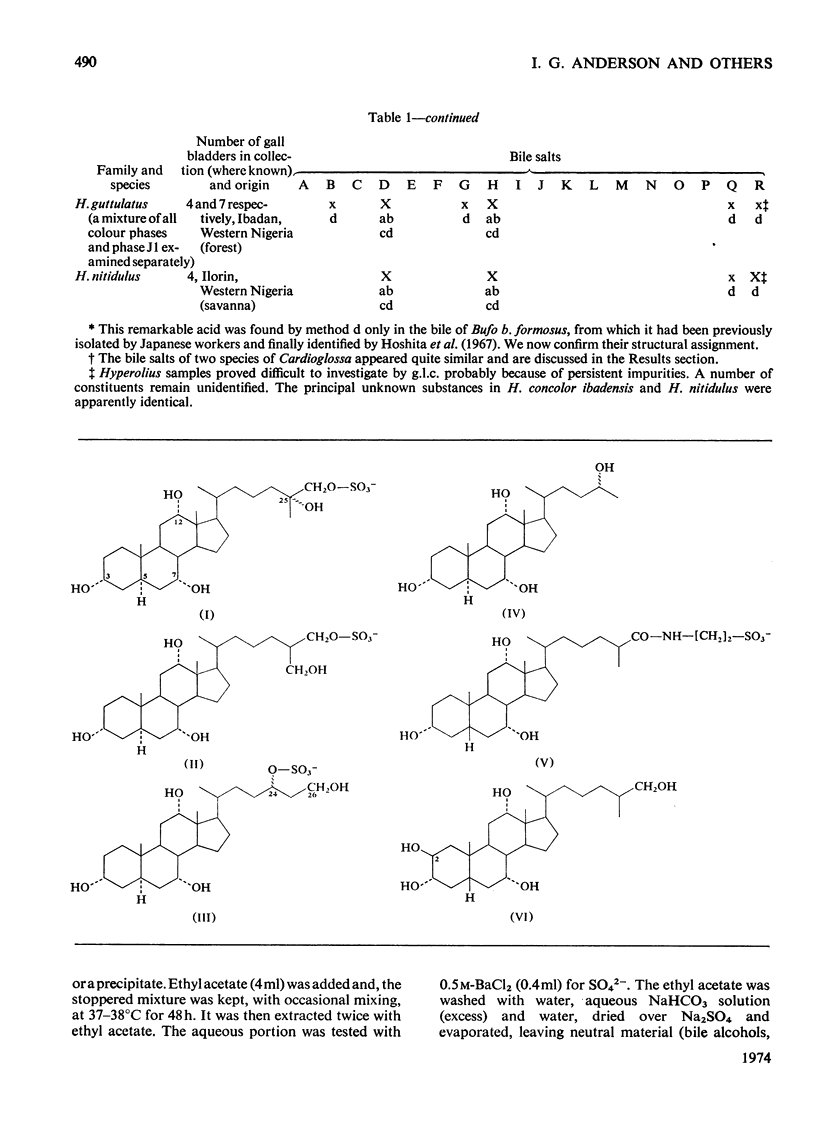
1. Methods have been developed for the isolation and identification of small amounts of bile salts and of bile acids and alcohols obtained by solvolysis. These methods involve preparative and analytical t.l.c., purification on columns of protonated Al2O3 and Sephadex LH-20 and also g.l.c.–mass spectroscopy of solvolysis products. 2. Application to 29 species of frogs and toads has confirmed the constancy of bile salt patterns in a single species, including colour phases in two instances, and has revealed great variations between different species in some genera (e.g. Rana, Ptychadena) and little difference between widely distributed species in others (e.g. Bufo). 3. Taxonomic deductions should be made with caution and with regard to the physiological significance of the biochemical character considered. The molecular differences found might be interpreted as indicating variations in the rate of evolution.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson I. G., Haslewood G. A. Comparative studies of bile salts. 5 alpha-Chimaerol, a new bile alcohol from the white sucker Catostomus commersoni Lacépède. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(4):581–585. doi: 10.1042/bj1160581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURSTEIN S., LIEBERMAN S. Hydrolysis of ketosteroid hydrogen sulfates by solvolysis procedures. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):331–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslewood G. A. Bile salts of germ-free domestic fowl and pigs. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):15–18. doi: 10.1042/bj1230015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslewood G. A., Tökés L. Comparative studies of bile salts. A new type of bile salt from Arapaima gigas (Cuvier) (family Osteoglossidae). Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1161–1170. doi: 10.1042/bj1261161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslewood G. A., Tökés L. Comparative studies of bile salts. Bile salts of the lamprey Petromyzon marinus L. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):179–184. doi: 10.1042/bj1140179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshita T., Okuda K., Kazuno T. Stero-bile acids and bile alcohols. XCV. Synthesis of 3-alpha, 7-alpha, 12-alpha-trihydroxy-5-beta-cholestane-24-carboxylic acid and the chemical structure of trihydroxybufosterocholenic acid isolated from toad bile. J Biochem. 1967 Jun;61(6):756–759. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramoto T., Kikuchi H., Sanemori H., Hoshita T. Bile salts of anura. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1973 May;21(5):952–959. doi: 10.1248/cpb.21.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlejohn M. J., Oldham R. S. Rana pipiens complex: mating call structure and taxonomy. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1003–1005. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. G., Maxson L. R., Wilson A. C. Albumin evolution in frogs: a test of the evolutionary clock hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3127–3129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


