Abstract
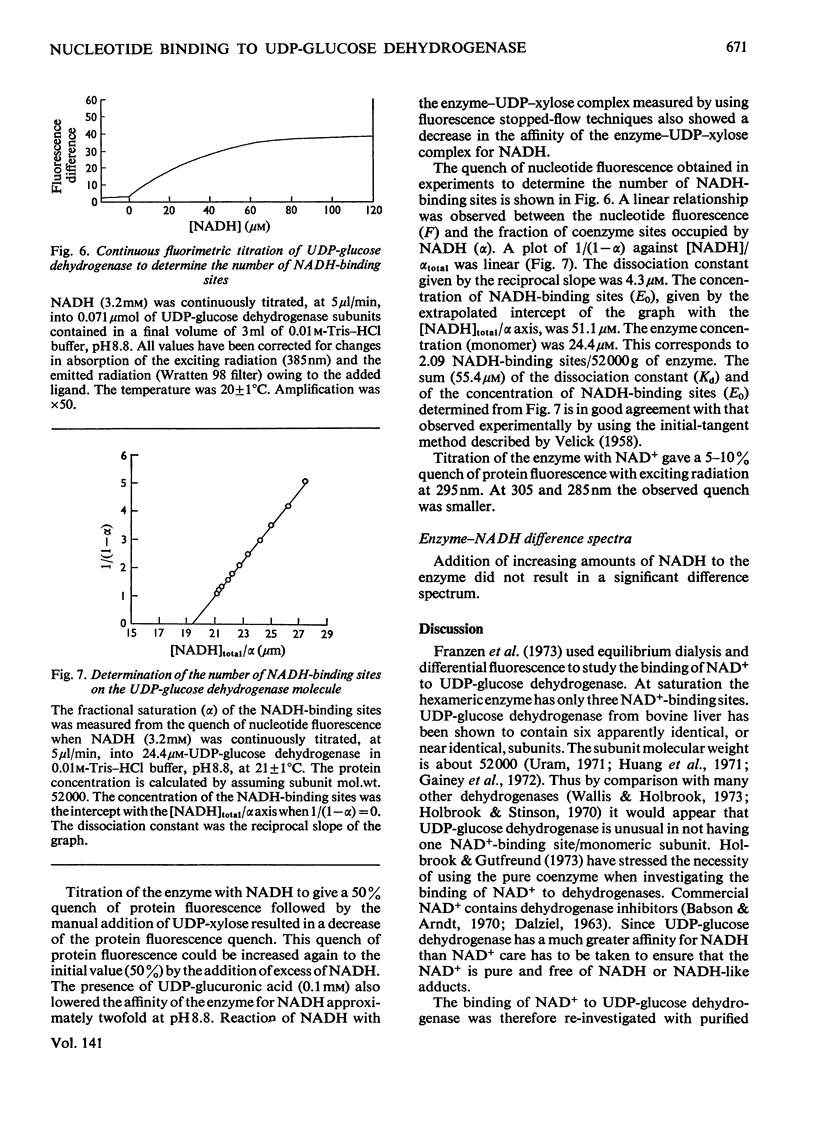
The binding of NAD+ and NADH to bovine liver UDP-glucose dehydrogenase was studied by using gel-filtration and fluorescence-titration methods. The enzyme bound 0.5mol of NAD+ and 2 mol of NADH/mol of subunit at saturating concentrations of both substrate and product. The dissociation constant for NADH was 4.3μm. The binding of NAD+ to the enzyme resulted in a small quench of protein fluorescence whereas the binding of NADH resulted in a much larger (60–70%) quench of protein fluorescence. The binding of NADH to the enzyme was pH-dependent. At pH8.1 a biphasic profile was obtained on titrating the enzyme with NADH, whereas at pH8.8 the titration profile was hyperbolic. UDP-xylose, and to a lesser extent UDP-glucuronic acid, lowered the apparent affinity of the enzyme for NADH.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babson A. L., Arndt E. G. Lactic dehydrogenase inhibitors in NAD. Clin Chem. 1970 Mar;16(3):254–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. The purification of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and kinetic effects of nucleotide impurities. J Biol Chem. 1963 Apr;238:1538–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H. F., Adija D. L., Cross D. G. Dehydrogenae-reduced coenzyme difference spectra, their resolution and relationship to the stereospecificity of hydrogen transfer. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4424–4431. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzen J. S., Kuo I., Eichler A. J., Feingold D. S. UDP-glucose dehydrogenase: substrate binding stoichiometry and affinity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90870-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gainey P. A., Pestell T. C., Phelps C. F. A study of the subunit structure and the thiol reactivity of bovine liver uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(4):821–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1290821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach D., Pfleiderer G., Holbrook J. J. Enzymatische Katalyse der Cyanid-Addition an Nicotinamid-Adenin-Dinucleotid. Biochem Z. 1965 Dec 31;343(4):354–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
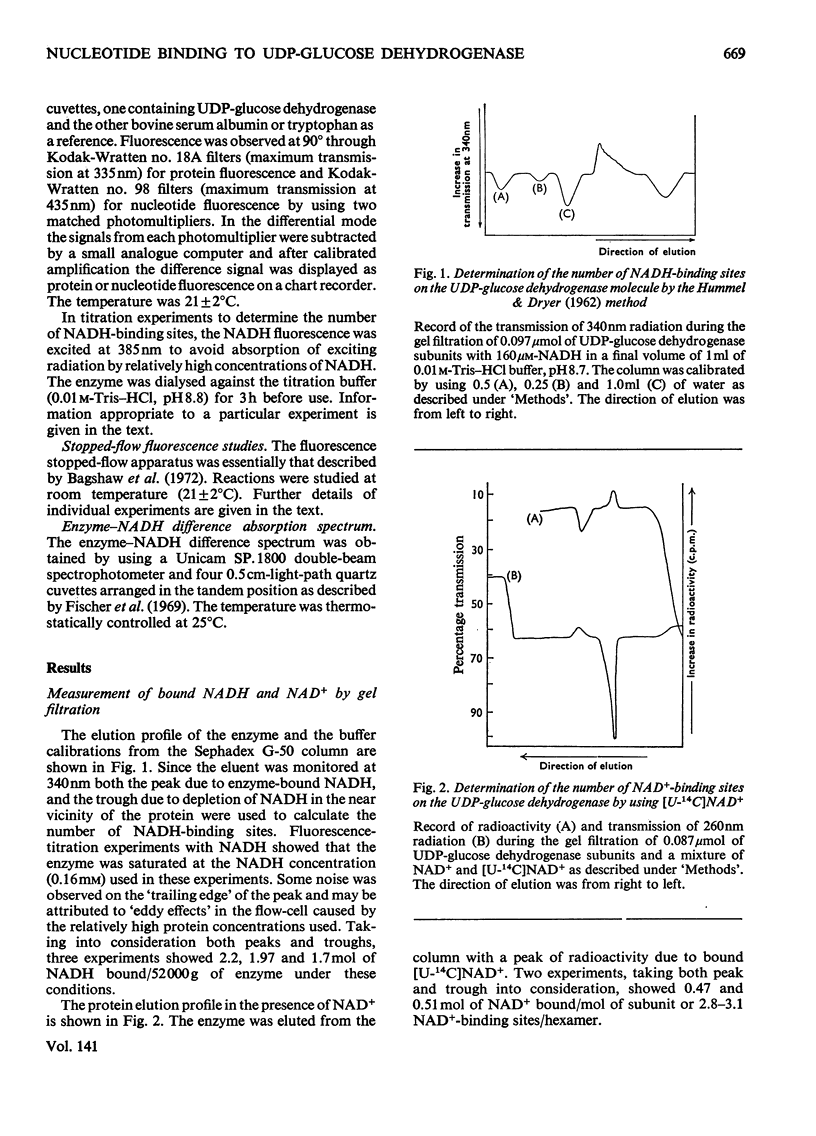
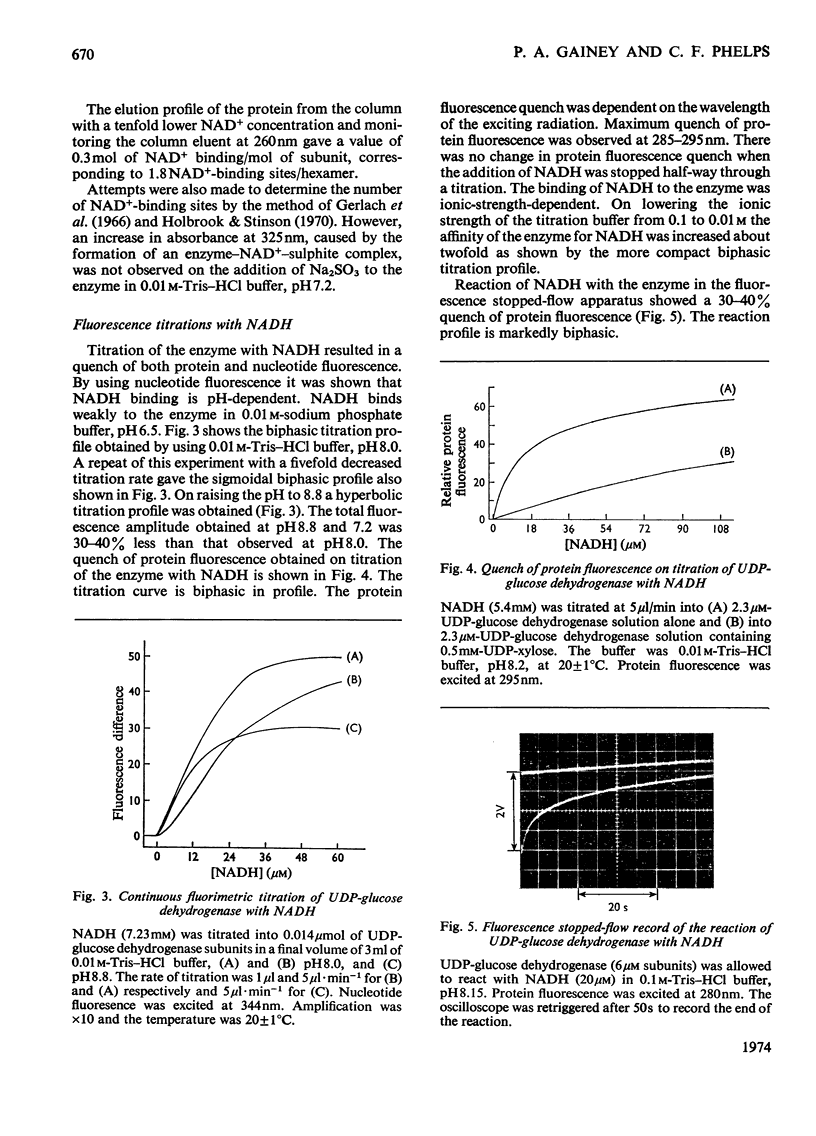
- HUMMEL J. P., DREYER W. J. Measurement of protein-binding phenomena by gel filtration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;63:530–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Gutfreund H. Approaches to the study of enzyme mechanisms lactate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 15;31(2):157–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J. Protein fluorescence of lactate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):921–931. doi: 10.1042/bj1280921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Stinson R. A. Reactivity of the essential thiol group of lactate dehydrogenase and substrate binding. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):289–297. doi: 10.1042/bj1200289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook J. J., Yates D. W., Reynolds S. J., Evans R. W., Greenwood C., Gore M. G. Protein fluorescence of nicotinamide nucleotide-dependent dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):933–940. doi: 10.1042/bj1280933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. H., Roy-Burman P., Visser D. W. Uridine diphosphate glucose dehydrogenase of calf liver. Properties and inhibition characteristics with uridine diphosphate xylose analogues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;20(9):2447–2458. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90245-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jallon J. M., Iwatsubo M. Evidence for two nicotinamide binding sites on L-glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov;45(4):964–971. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90431-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koberstein R., Sund H. Circular dichroism studies on the complex between beef liver glutamate dehydrogenase and NADH. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 1;19(2):149–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80500-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUFELD E. F., HALL C. W. INHIBITION OF UDP-D-GLUCOSE DEHYDROGENASE BY UDP-D-XYLOSE: A POSSIBLE REGULATORY MECHANISM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:456–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Kirkwood S. The mechanism of action of uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase. Uridine diphosphohexodialdoses as intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3824–3834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleiderer G., Auricchio F. The DPNH-binding capacity of various dehydrogenases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 May 22;16(1):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson R. A., Holbrook J. J. Equilibrium binding of nicotinamide nucleotides to lactate dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):719–728. doi: 10.1042/bj1310719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERLICK S. F. Fluorescence spectra and polarization of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and lactic dehydrogenase coenzyme complexes. J Biol Chem. 1958 Dec;233(6):1455–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. B., Holbrook J. J. The effect of modifying lysine-126 on the physical, catalytic and regulatory properties of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1973 May;133(1):173–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1330173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winlund C. C., Chamberlin M. J. Binding of cytidine triphosphate to aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalitis J., Feingold D. S. Purification and properties of UDPG dehydrogenase from beef liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jul;132(2):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]