Abstract
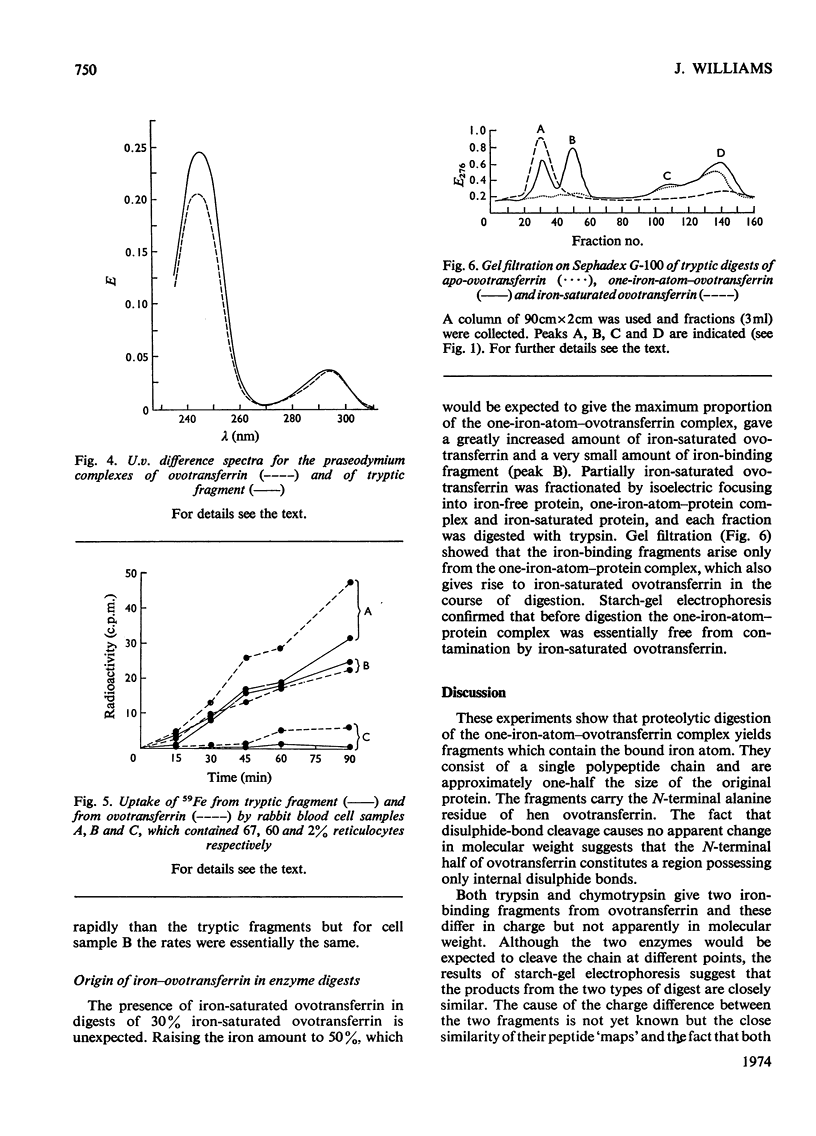
1. Iron was added to hen ovotransferrin to 30% saturation and the protein was digested with trypsin or chymotrypsin. 2. Iron-binding fragments were isolated. They carried one atom of iron/mol (mol.wt. 35000) and consisted of a single polypeptide chain derived from the N-terminal half of the protein. Carbohydrate was not present. 3. The fragments were able to bind a variety of metals and to donate iron to reticulocytes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AASA R., MALMSTROEM B. G., SALTMAN P. THE SPECIFIC BINDING OF IRON(III) AND COPPER(II) TO TRANSFERRIN AND CONALBUMIN. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 24;75:203–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90599-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZARI P. R., FEENEY R. E. Resistance of metal complexes of conalbumin and transferrin to proteolysis and to thermal denaturation. J Biol Chem. 1958 May;232(1):293–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aasa R., Aisen P. An electron paramagnetic resonance study of the iron and copper complexes of transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2399–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisen P. Citrate-mediated exchange of FE3+ among tranferrin molecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 26;32(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisen P., Lang G., Woodworth R. C. Spectroscopic evidence for a difference between the iron-binding sites of conalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):649–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aisen P., Leibman A., Reich H. A. Studies on the binding of iron to transferrin and conalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1666–1671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Hartley B. S. Chemical studies on methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):165–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlwood P. A. Differential sedimentation-velocity and gel-filtration measurements on human apotransferrin and iron-transferrin. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1019–1026. doi: 10.1042/bj1251019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B., SALTMAN P., BENSON S. The stability constants of the iron-transferrin complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 19;8:56–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C., Williams J. The amino acid sequences of cysteic acid-containing peptides from performic acid-oxidized ovotransferrin. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):515–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1160515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H. Comparison of the iron-binding activities of conalbumin and of hydroxylamidoproteins. Arch Biochem. 1950 Oct;28(3):452–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J., Huehns E. R. Function of transferrin. Nature. 1968 Jun 29;218(5148):1211–1214. doi: 10.1038/2181211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene F. C., Feeney R. E. Physical evidence for transferrins as single polypeptide chains. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1366–1371. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEPSON J. B., SMITH I. Multiple dipping procedures in paper chromatography: a specific test for hydroxy-proline. Nature. 1953 Dec 12;172(4389):1100–1101. doi: 10.1038/1721100b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ka Luk C. Study of the nature of the metal-binding sites and estimate of the distance between the metal-binding sites in transferrin using trivalent lanthanide ions as fluorescent probes. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 20;10(15):2838–2843. doi: 10.1021/bi00791a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. The effects of structural modifications on the biologic activity of human transferrin. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):945–954. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Fish W. W., Cox A. C., Tanford C. Single-chain nature of human serum transferrin. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1348–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. Starch gel electrophoresis in a discontinous system of buffers. Nature. 1957 Dec 28;180(4600):1477–1479. doi: 10.1038/1801477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price E. M., Gibson J. F. A re-interpretation of bicarbonate-free ferric transferrin E.P.R. spectra. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):646–651. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONDLE C. J., MORGAN W. T. The determination of glucosamine and galactosamine. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):586–589. doi: 10.1042/bj0610586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratil A. The effect of iron addition to avian egg white on the behaviour of conalbumin fractions in starch gel electrophoresis. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1967 Jul;22(1):227–233. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(67)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan A. T., Woodworth R. C. Ultraviolet difference spectrl studies of conalbumin complexes with transition metal ions. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3711–3716. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengerdy C., Azari P., Tengerdy R. P. Immunochemical reactions of conalbumin and its metal complexes. Nature. 1966 Jul 9;211(5045):203–204. doi: 10.1038/211203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao D., Azari P., Phillips J. L. On the structure of ovotransferrin. I. Isolation and characterization of cyanogen bromide fragments. Reevaluation of the primary structure. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):397–403. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao D., Morris D. H., Azari P., Tengerdy R. P., Phillips J. L. On the structure of ovotransferrin. II. Isolation and characterization of a specific iron-binding fragment after cyanogen bromide cleavage. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):403–407. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER R. C., WEBER I. The preparation of crystalline conalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jul;191(1):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. A comparison of conalbumin and transferrin in the domestic fowl. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:355–364. doi: 10.1042/bj0830355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDLE J. J., WIERSEMA A. K., CLARK J. R., FEENEY R. E. INVESTIGATION OF THE IRON AND COPPER COMPLEXES OF AVIAN CONALBUMINS AND HUMAN TRANSFERRINS BY ELECTRON PARAMAGNETIC RESONANCE. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1341–1345. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINZLER R. J. Determination of serum glycoproteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:279–311. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenn R. V., Williams J. The isoelectric fractionation of hen's-egg ovotransferrin. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):69–74. doi: 10.1042/bj1080069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A comparison of glycopeptides from the ovotransferrin and serum transferrin of the hen. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):57–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1080057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Phelps C. F., Lowe J. M. Ovotransferrin with one iron atom. Nature. 1970 May 30;226(5248):858–859. doi: 10.1038/226858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]