Abstract
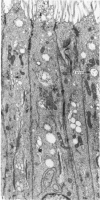
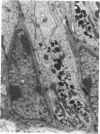
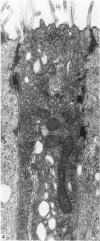
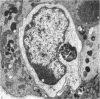
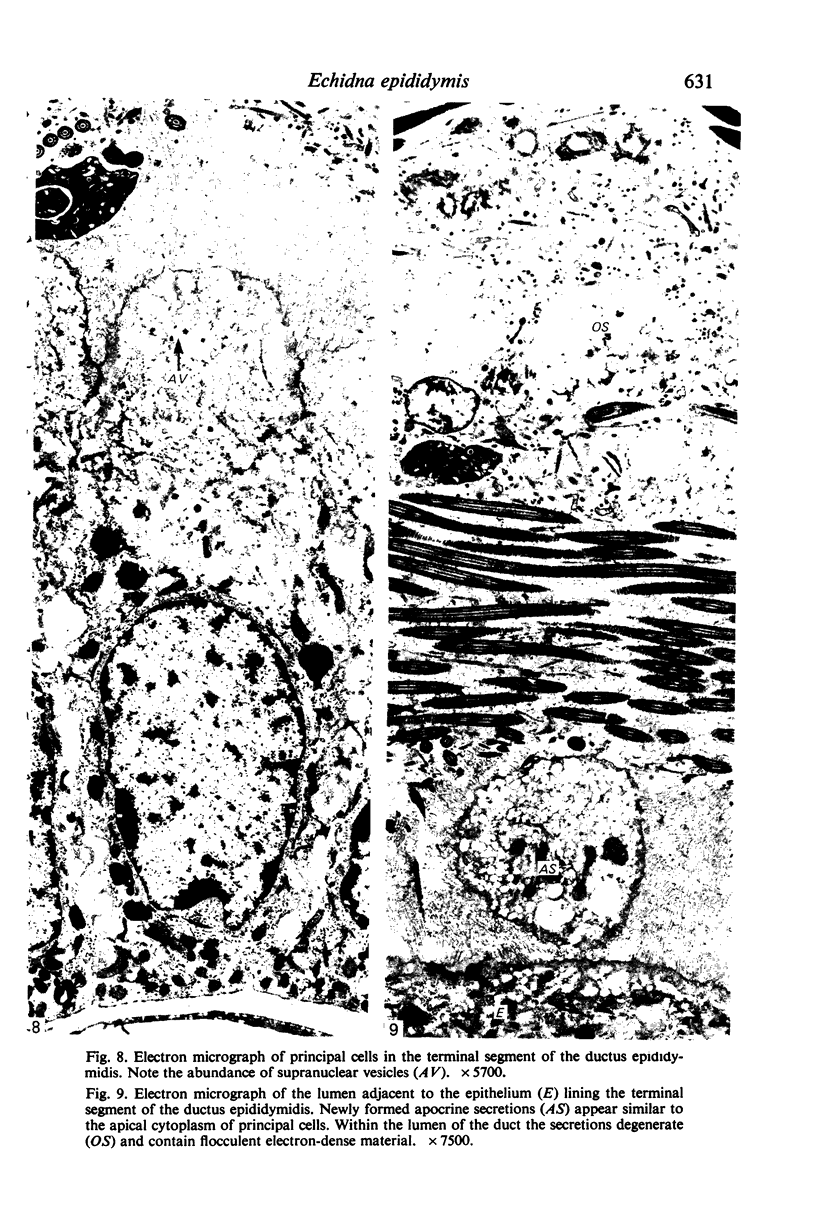
It is concluded that the ductus epididymidis of the echidna is divided into only two structurally distinct segments which are each homogeneous along their length. The initial segment in the echidna is structurally very similar to the initial segment proper in the epididymis of all other mammals which have been studied, whereas the terminal segment is structurally quite different from the terminal segment in other mammals. The terminal segment in the echidna is involved in considerable apocrine secretion of highly membranous material. The secretions gradually degenerate and occupy a large proportion of the lumen of the duct.
Full text
PDF
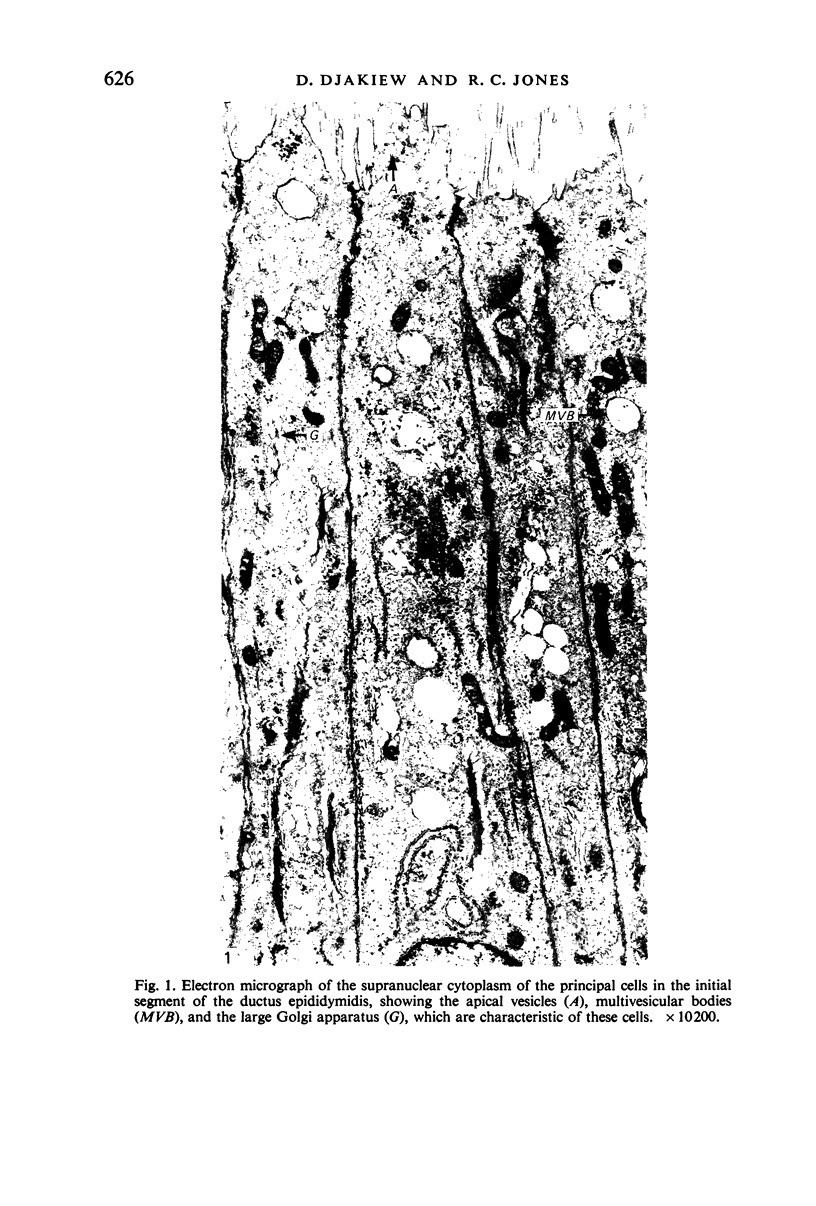




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedford J. M., Rifkin J. M. An evolutionary view of the male reproductive tract and sperm maturation in a monotreme mammal--the echidna, Tachyglossus aculeatus. Am J Anat. 1979 Oct;156(2):207–230. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001560204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djakiew D., Jones R. C. Structural differentiation of the male genital ducts of the echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus). J Anat. 1981 Mar;132(Pt 2):187–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Hoffer A. P. Failure of exogenous androgen to prevent regression of the initial segments of the rat epididymis after efferent duct ligation or orchidectomy. Biol Reprod. 1979 Mar;20(2):162–181. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod20.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flickinger C. J., Howards S. S., English H. F. Ultrastructural differences in efferent ducts and several regions of the epididymis of the hamster. Am J Anat. 1978 Aug;152(4):557–585. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001520409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forssmann W. G., Ito S., Weihe E., Aoki A., Dym M., Fawcett D. W. An improved perfusion fixation method for the testis. Anat Rec. 1977 Jul;188(3):307–314. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091880304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover T. D., Nicander L. Some aspects of structure and function in the mammalian epididymis. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1971 May;13(Suppl):39–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton B. T., White R. W., Setchell B. P. Concentrations of myo-inositol in the luminal fluid of the mammalian testis and epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1980 Mar;58(2):395–399. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0580395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer A. P., Hamilton D. W., Fawcett D. W. The ultrastructure of the principal cells and intraepithelial leucocytes in the initial segment of the rat epididymis. Anat Rec. 1973 Feb;175(2):169–201. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091750205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt W. V., Jones R. C., Skinner J. D. Studies of the deferent ducts from the testis of the African elephant, Loxodonta africana. II. Histochemistry of the epididymis. J Anat. 1980 Mar;130(Pt 2):367–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. C., Brosnan M. F. Studies of the deferent ducts from the testis of the African elephant, Loxodonta africana. I. Structural differentiation. J Anat. 1981 May;132(Pt 3):371–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. C. Luminal composition and maturation of spermatozoa in the genital ducts of the African elephant (Loxodonta africana). J Reprod Fertil. 1980 Sep;60(1):87–93. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0600087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. C. Preparation of spermatozoa for electron and light microscopy. J Reprod Fertil. 1973 Apr;33(1):145–149. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0330145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. D., Bedford J. M. The differential absorptive activity of epithelial cells of the rat epididymus before and after castration. Anat Rec. 1979 Feb;193(2):313–327. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091930210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicander L., Glover T. D. Regional histology and fine structue of the epididymal duct in the golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). J Anat. 1973 Apr;114(Pt 3):347–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun E. L., Flickinger C. J. Morphological characteristics of cells with apical nuclei in the initial segment of the adult rat epididymis. Anat Rec. 1980 Mar;196(3):285–293. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091960304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki F., Racey P. A. Fine structural changes in the epididymal epithelium of moles (Talpa europaea) throughout the year. J Reprod Fertil. 1976 May;47(1):47–54. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0470047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Kistler G. S., Scherle W. F. Practical stereological methods for morphometric cytology. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):23–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]