Abstract
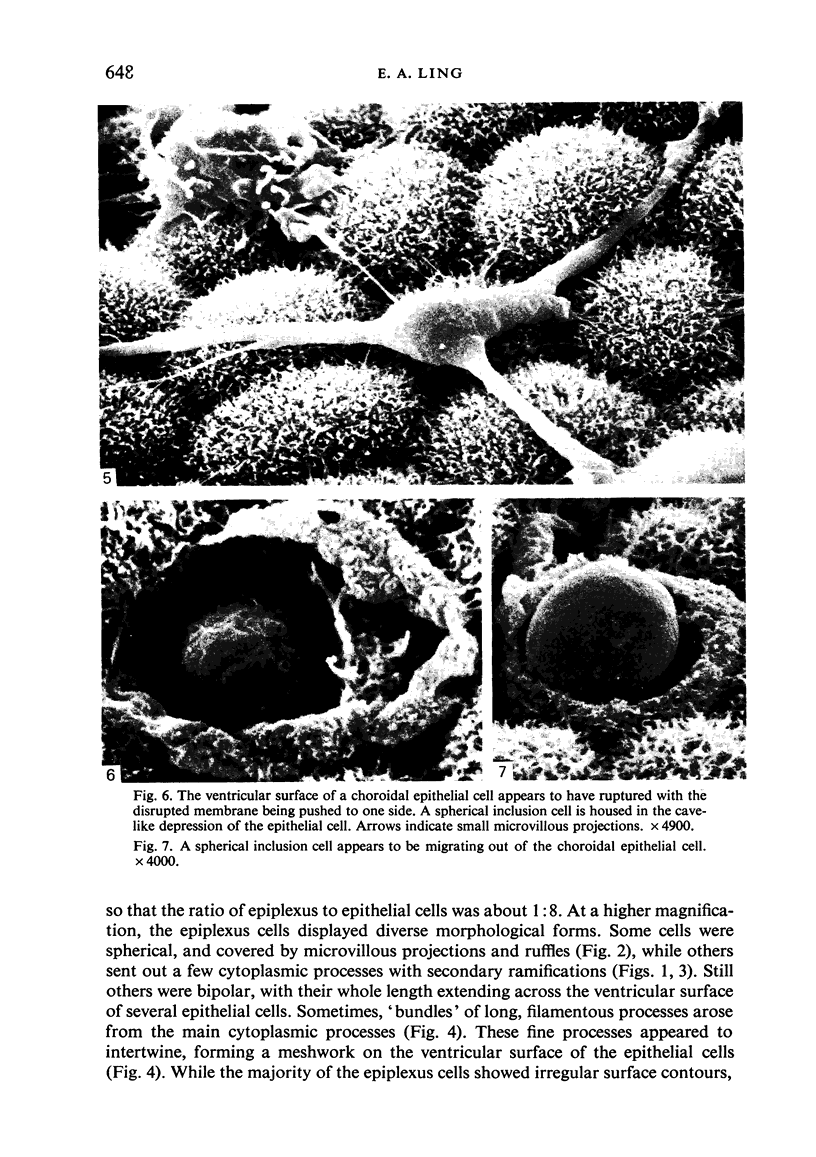
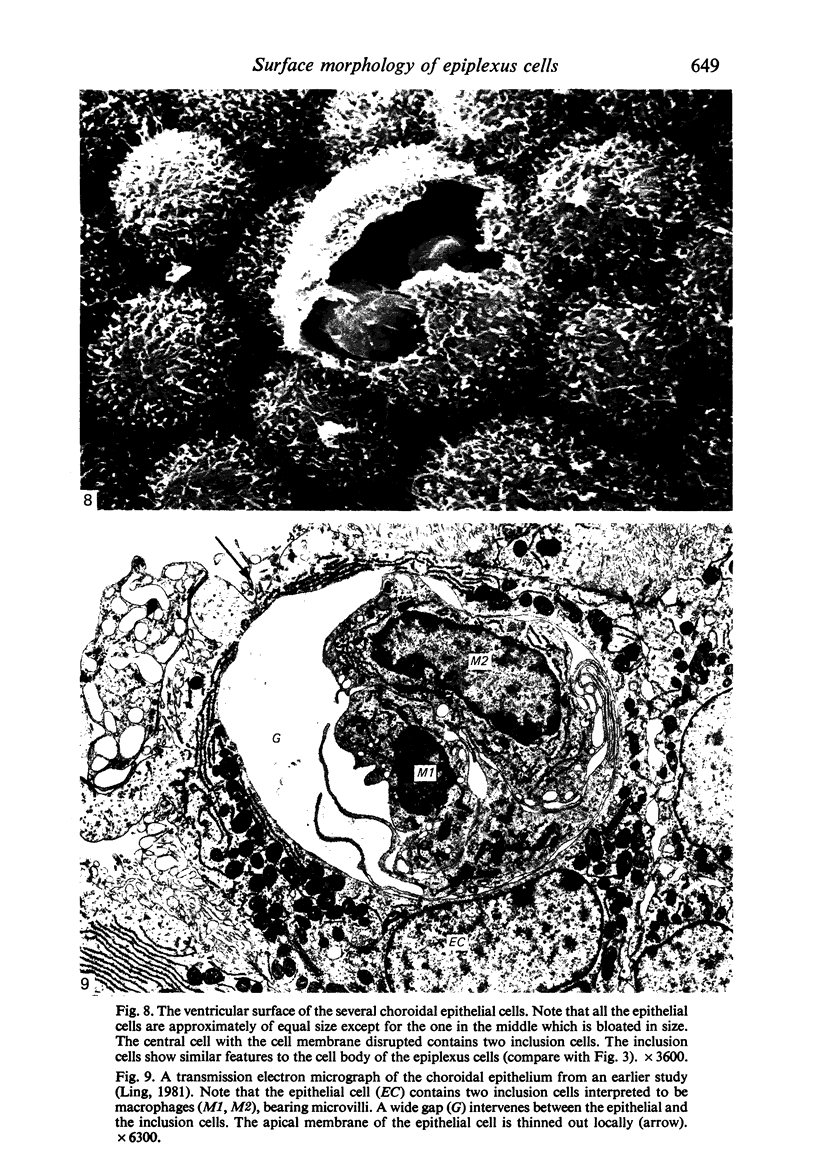
Scanning electron microscopic study of epiplexus cells in the monkey revealed their diverse morphological forms. These pleomorphic cells were round, bipolar or stellate in shape. Their cell body was smooth or displayed various types of microappendages: microvilli, filopodia, pseudopodia and it was sometimes ruffled. Examination of the ventricular surface of the choroidal epithelium showed that the cell membrane of some of the epithelial cells was ruptured. Within these ruptured cells one or two cellular elements could be found which resembled epiplexus cells. The inclusion cell sometimes appeared to be migrating out of the epithelial cell. It is speculated that these cells represent the precursors of epiplexus cells before their release into the ventricle lumen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht R. M., Bleier R. Histochemical, functional, and structural features of isolated adherent supraependymal cells: characterization as resident mononuclear phagocytes. Scan Electron Microsc. 1979;(3):55–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. J., Low F. N. Scanning electron microscopy of the subarachnoid space in the dog. III. Cranial levels. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Jun 15;161(4):515–539. doi: 10.1002/cne.901610404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D. J. Scanning electron microscopy of epiplexus macrophages (Kolmer cells) in the dog. J Comp Neurol. 1975 May 15;161(2):197–213. doi: 10.1002/cne.901610205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. J., McCarthy L. E., Borison H. L. Electron microscopic study of the epiplexus (Kolmer) cells of the cat choroid plexus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;110(4):471–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00330099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Low F. N. Scanning electron microscopy of the subarachnoid space in the dog. I. Spinal cord levels. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Feb 15;153(4):325–368. doi: 10.1002/cne.901530402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deimann W., Fahimi H. D. The appearance of transition forms between monocytes and Kupffer cells in the liver of rats treated with glucan. A cytochemical and ultrastructural study. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):883–897. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson C. A., Trinkaus J. P. Microvilli and blebs as sources of reserve surface membrane during cell spreading. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya Y., Fujita T. Scanning electron microscope observation of intraventricular macrophages (Kolmer cells) in the rat brain. Arch Histol Jpn. 1973 Jan;35(2):133–140. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.35.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastruct and origin of epiplexus cells in the telencephalic choroid plexus of postnatal rats studied by intravenous injection of carbon particles. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):479–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastructure and mode of formation of epiplexus cells in the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles of the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):555–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy J. J., Low F. N. Scanning electron microscopy of the subarachnoid space in the dog. IV. Subarachnoid macrophages. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Jun 1;167(3):257–283. doi: 10.1002/cne.901670302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant R. E., Low F. N. Scanning electron microscopy of the subarachnoid space in the dog. V. Macrophages challenged by bacillus Calmette-Guerin. J Comp Neurol. 1977 Apr 1;172(3):381–407. doi: 10.1002/cne.901720302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parakkal P., Pinto J., Hanifin J. M. Surface morphology of human mononuclear phagocytes during maturation and phagocytosis. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Aug;48(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. The surface fine structure of the choroid plexus and ependymal lining of the rat lateral ventricle. J Neurocytol. 1974 Mar;3(1):99–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01111935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polliack A., Gordon S. Scanning electron microscopy of murine macrophages. Surface characteristics during maturation, activation, and phagocytosis. Lab Invest. 1975 Nov;33(5):469–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polliack A. The contribution of scanning electron microscopy in haematology: its role in defining leucocyte and erythrocyte disorders. J Microsc. 1981 Aug;123(Pt 2):177–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb01293.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A semithin light microscopic, transmission electron microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study of macrophages in the lateral ventricle of mice from embryonic to adult life. J Anat. 1979 Aug;129(Pt 1):31–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng C. Y., Ling E. A., Wong W. C. Scanning electron microscopy of amoeboid microglial cells in the transient cavum septum pellucidum in pre- and postnatal rats. J Anat. 1983 Mar;136(Pt 2):251–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warfel A. H., Elberg S. S. Macrophage membranes viewed through a scanning electron microscope. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):446–447. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]











