Abstract
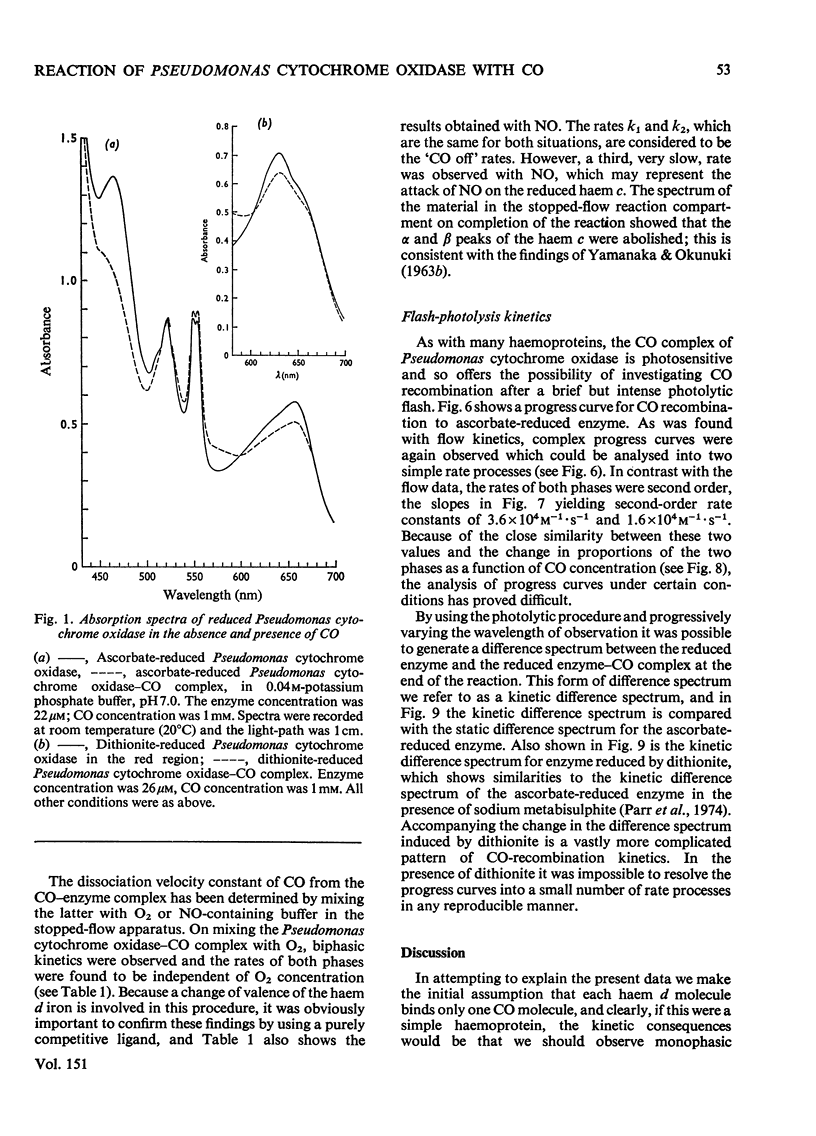
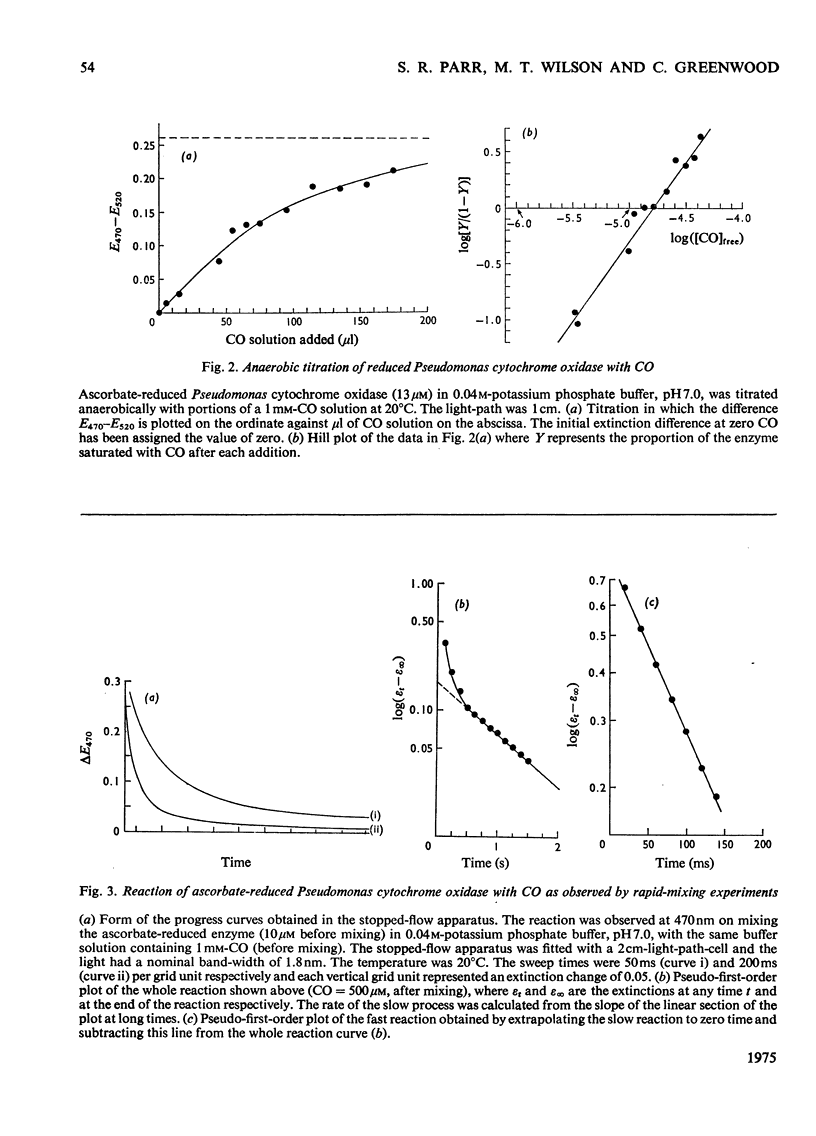
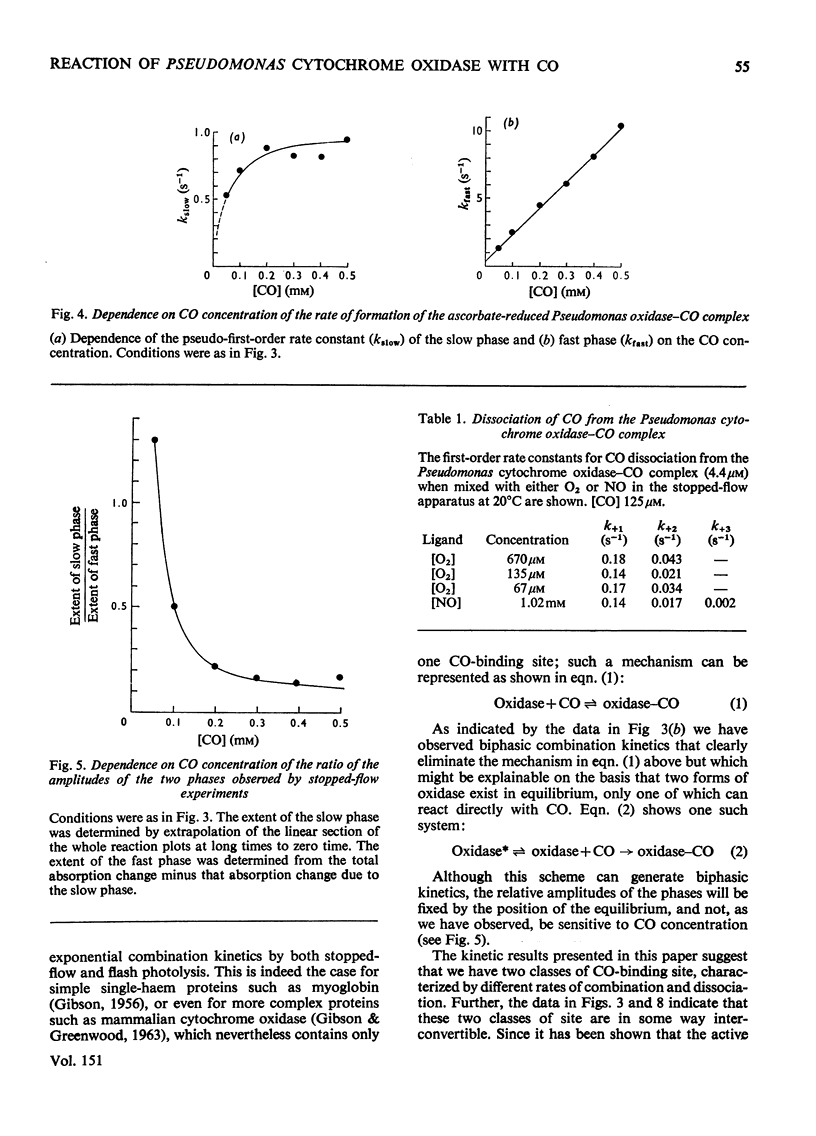
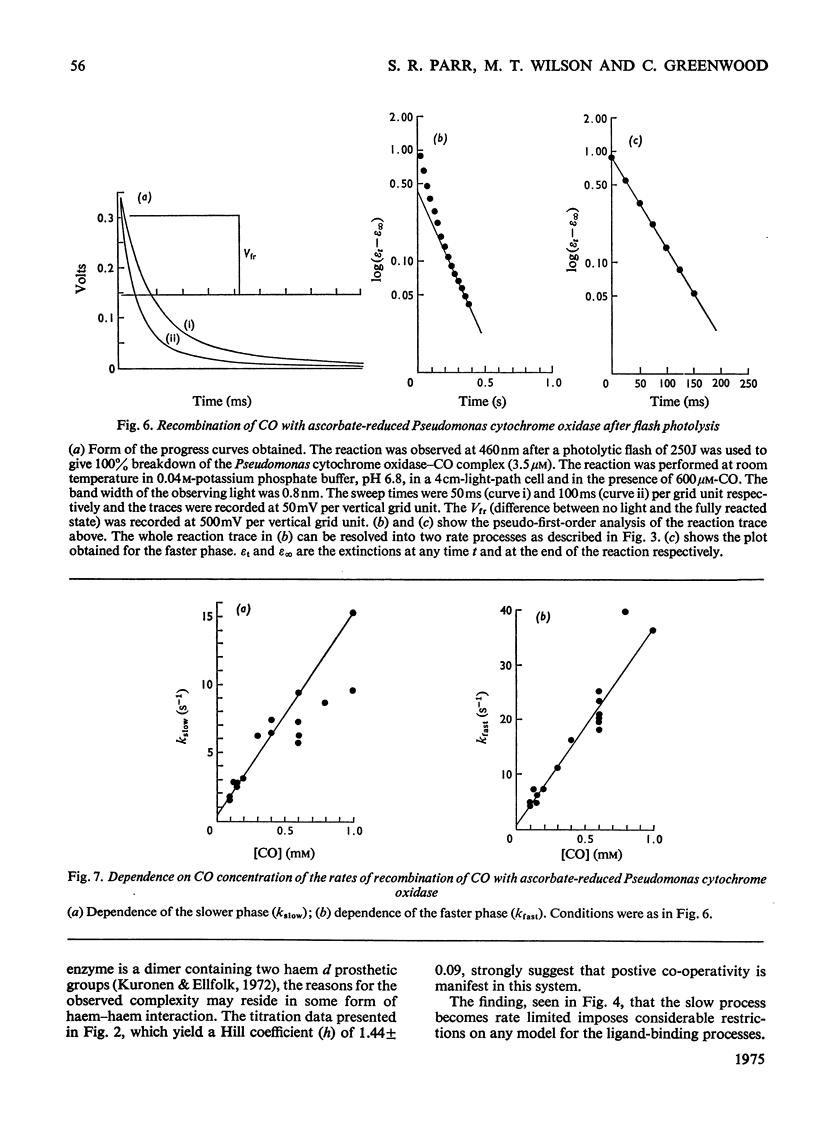
The binding of CO to ascorbate-reduced Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase was investigated by static-titration, stopped-flow and flash-photolytic techniques. Static-titration data indicated that the binding process was non-stoicheiometric, with a Hill number of 1.44. Stopped-flow kinetics obtained on the binding of CO to reduced Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase were biphasic in form; the faster rate exhibited a linear dependence on CO concentration with a second-order rate constant of 2 X 10(4) M-1-s-1, whereas the slower reaction rapidly reached a pseudo-first-order rate limit at approx. 1s-1. The relative proportions of the two phases observed in stopped-flow experiments also showed a dependency on CO concentration, the slower phase increasing as the CO concentration decreased. The kinetics of CO recombination after flash-photolytic dissociation of the reduced Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase-CO complex were also biphasic in character, both phases showing a linear pseudo-first-order rate dependence on CO concentration. The second-order rate constants were determined as 3.6 X 10(4)M-1-s-1 and 1.6 X 10(4)M-1-s-1 respectively. Again the relative proportions of the two phases varied with CO concentration, the slower phase predominating at low CO concentrations. CO dissociation from the enzyme-CO complex measured in the presence of O2 and NO indicated the presence of two rates, of the order of 0.03s-1 and 0.15s-1. When sodium dithionite was used as a reducing agent for the Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase, the CO-combination kinetics observed by both stopped flow and flash photolysis were extremely complex and not able to be simply analysed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GIBSON Q. H., GREENWOOD C. Reactions of cytochrome oxidase with oxygen and carbon monoxide. Biochem J. 1963 Mar;86:541–554. doi: 10.1042/bj0860541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H. The direct determination of the velocity constant of the reaction Hb4 (CO)3 + CO-Hb4(CO)4. J Physiol. 1956 Oct 29;134(1):123–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson Q. H., Milnes L. Apparatus for rapid and sensitive spectrophotometry. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):161–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0910161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Gibson Q. H. The reaction of reduced cytochrome C oxidase with oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1782–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudat J. C., Singh J., Wharton D. C. Cytochrome oxidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Purification and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):376–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORIO T., HIGASHI T., MATSUBARA H., KUSAI K., NAKAI M., OKUNUKI K. High purification and properties of Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Aug;29(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORIO T., HIGASHI T., YAMANAKA T., MATSUBARA H., OKUNUKI K. Purification and properties of cytochrome oxidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem. 1961 Mar;236:944–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuronen T., Ellfolk N. A new purification procedure and molecular properties of Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 20;275(3):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parr S. R., Wilson M. T., Greenwood C. The reaction of Pseudomonas aeurginosa cytochrome c oxidase with sodium metabisulphite. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;139(1):273–276. doi: 10.1042/bj1390273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMANAKA T., KIJIMOTO S., OKUNUKI K. Biological significance of Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biochem. 1963 May;53:416–421. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMANAKA T., KIJIMOTO S., OKUNUKI K., KUSAI K. Preparation of crystalline Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase and some of its properties. Nature. 1962 May 26;194:759–760. doi: 10.1038/194759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMANAKA T., OKUNUKI K. Crystalline Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase. I. Enzymic properties with special reference to the biological specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 12;67:379–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91844-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMANAKA T., OKUNUKI K. Crystalline Pseudomonas cytochrome oxidase. II. Spectral properties of the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 12;67:394–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91845-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMANAKA T., OTA A., OKUNUKI K. A nitrite reducing system reconstructed with purified cytochrome components of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 28;53:294–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90442-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


