Abstract
A method is described for preparing insect myosin, tropomyosin and alpha-actinin. The amino acid compositions of the myosin and alpha-actinin are given, and some of the properties of the purified proteins are discussed.
Full text
PDF

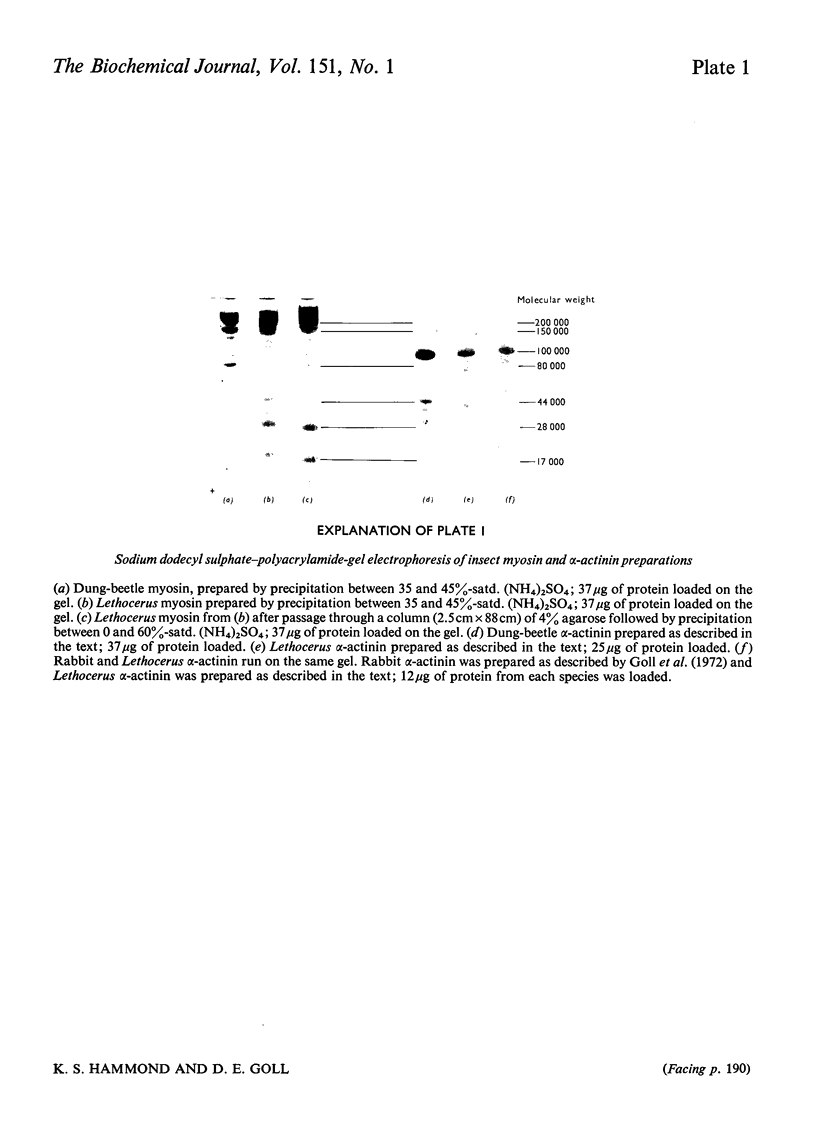
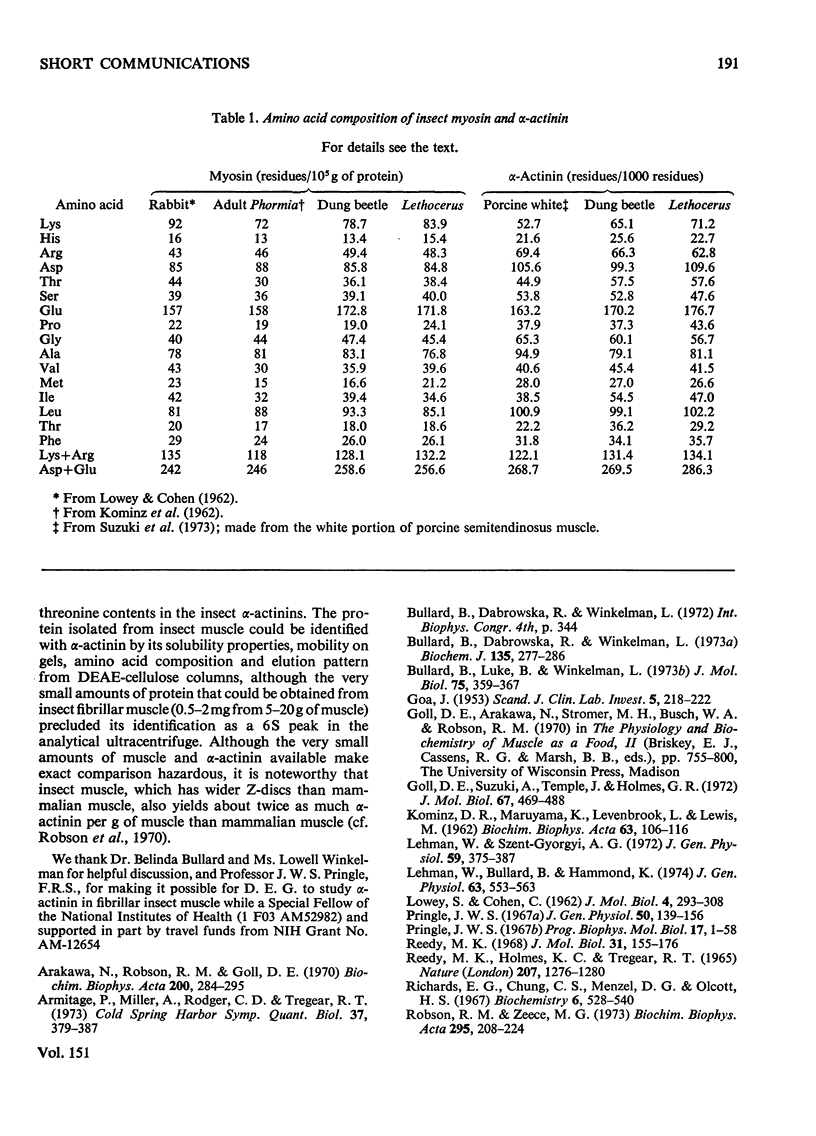

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa N., Robson R. M., Goll D. E. An improved method for the preparation of alpha-actinin from rabbit striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):284–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Dabrowska R., Winkelman L. The contractile and regulatory proteins of insect flight muscle. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):277–286. doi: 10.1042/bj1350277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Luke B., Winkelman L. The paramyosin of insect flight muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goli D. E., Suzuki A., Temple J., Holmes G. R. Studies on purified -actinin. I. Effect of temperature and tropomyosin on the -actinin-F-actin interaction. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):469–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOMINZ D. R., MARUYAMA K., LEVENBOOK L., LEWIS M. Tropomyosin, myosin and actin from the blowfly, Phormia regina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Sep 10;63:106–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWEY S., COHEN C. Studies on the structure of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1962 Apr;4:293–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Bullard B., Hammond K. Calcium-dependent myosin from insect flight muscles. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):553–563. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman W., Szent-Györgyi G. Activation of the adenosine triphosphatase of Limulus polyphemus actomyosin by tropomyosin. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Apr;59(4):375–387. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. W. Evidence from insect fibrillar muscle about the elementary contractile process. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):139–156. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. W. The contractile mechanism of insect fibrillar muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1967;17:1–60. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(67)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. K., Holmes K. C., Tregear R. T. Induced changes in orientation of the cross-bridges of glycerinated insect flight muscle. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1276–1280. doi: 10.1038/2071276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedy M. K. Ultrastructure of insect flight muscle. I. Screw sense and structural grouping in the rigor cross-bridge lattice. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):155–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards E. G., Chung C. S., Menzel D. B., Olcott H. S. Chromatography of myosin on diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex A-50. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):528–540. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. M., Goll D. E., Arakawa N., Stromer M. H. Purification and properties of alpha-actinin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):296–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R. M., Zeece M. G. Comparative studies of -actinin from porcine cardiac and skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 25;295(1):208–224. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. Polypeptide chains of intermediate molecular weight in myosin preparations. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 2;15(1):40–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Goll D. E., Stromer M. H., Temple J. -actinin from red and white porcine muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 25;295(1):188–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C., Kendrick-Jones J. Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan "catch" muscles. II. Native filaments: isolation and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):239–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Rigor contraction and the effect of various phosphate compounds on glycerinated insect flight and vertebrate muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):583–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Thorson J. Phosphate starvation and the nonlinear dynamics of insect fibrillar flight muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Sep;60(3):307–336. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



