Abstract
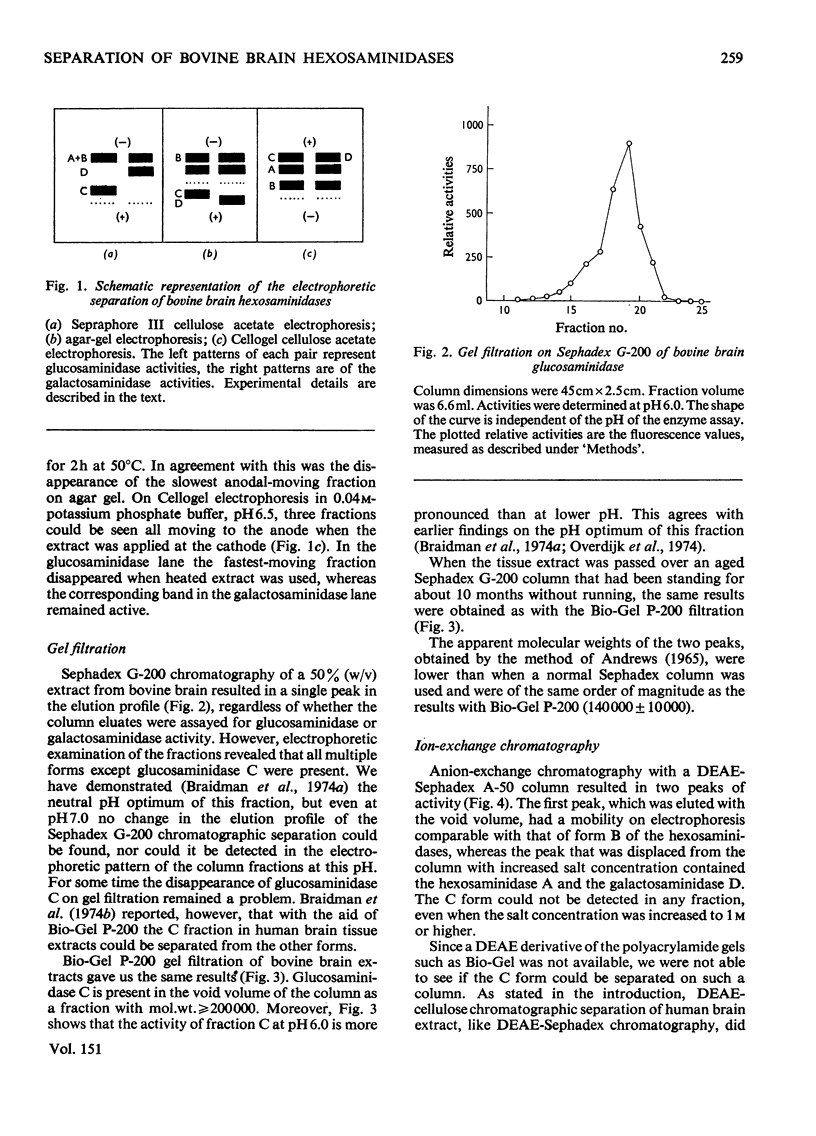
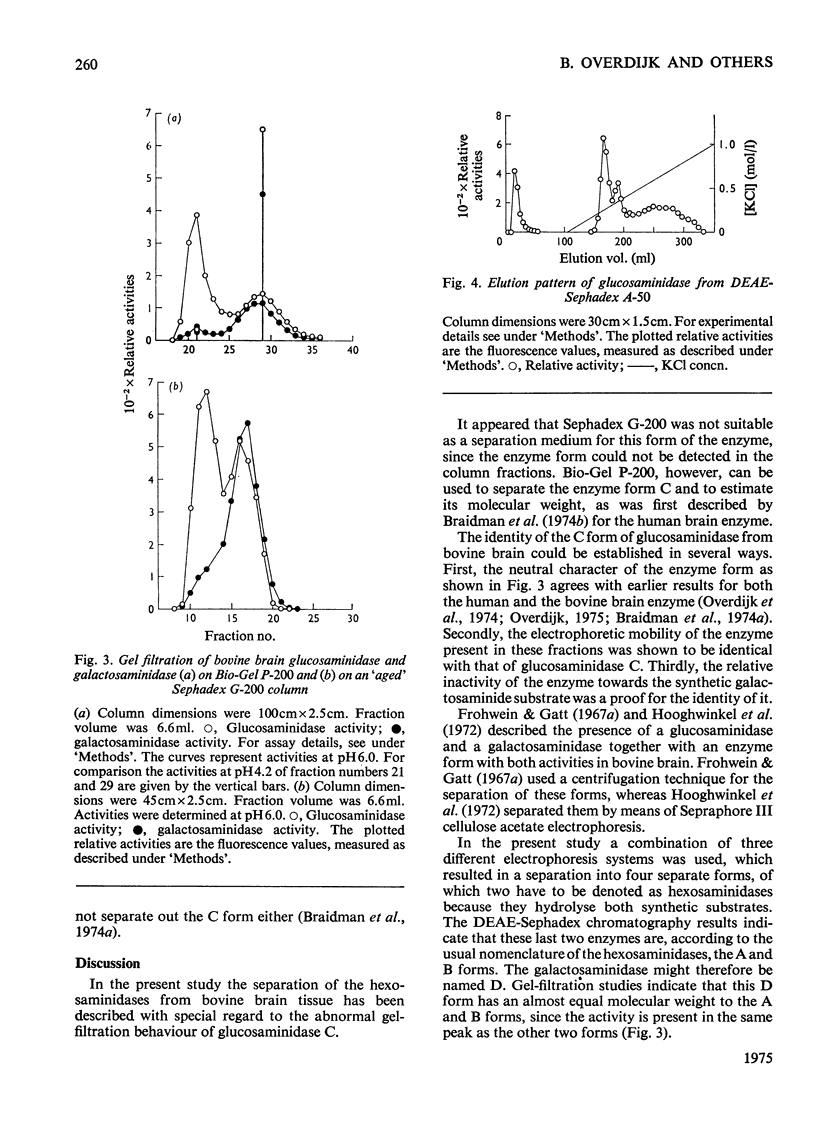
Bovine brain tissue was extracted and the 50 000g supernatant was separated by electrophoresis, DEAE-Sephadex chromatography and gel filtration on Sephadex G-200 and Bio-Gel P-200. The electrophoretic separation showed that the beta-N-acetyl-D-hexosaminidases (hexosaminidases) of bovine brain tissue were composed of four different fractions. Two fractions (A and B) exerted both glucosaminidase and galactosaminidase activity, a third fraction (C) showed only glucosaminidase activity, whereas a fourth form (D) with specificity towards the galactosaminide moiety was found to be present. DEAE-Sephadex chromatography at pH 7.0 showed that the B form was eluted with the void volume, whereas the A and D forms could be eluted in one peak by raising that salt concentration. The C form could not be detected in the eluate. Gel filtration on Sephadex G-200 showed that the B, A and D forms had almost equal molecular weights. In this case also the C form could not be detected in the column eluates. Gel filtration on Bio-Gel P-200 revealed that the C form was eluted with the void volume.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braidman I., Carroll M., Dance N., Robinson D., Poenaru L., Weber A., Dreyfus J. C., Overdijk B., Hooghwinkel G. J. Characterisation of human N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidase C. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braidman I., Carroll M., Dance N., Robinson D. Separation and properties of human brain hexosaminidase C. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):295–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1430295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohwein Y. Z., Gatt S. Enzymatic hydrolysis of sphingolipids. VI. Hydrolysis of ceramide glycosides by calf brain beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2783–2787. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohwein Y. Z., Gatt S. Isolation of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase, beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, and beta-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from calf brain. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2775–2782. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. T., Mazzotta M. Y., Wan C. C., Orth R., Li S. C. Hydrolysis of Tay-Sachs ganglioside by beta-hexosaminidase A of human liver and urine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7512–7515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overdijk B., Veltkamp W. A., Hooghwinkel G. J. Proceedings: Properties of the three multiple forms of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase in human brain tissue. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Oct;355(10):1236–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenaru L., Dreyfus J. C. Electrophoretic study of hexosaminidases. Hexosaminidase C. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Feb 12;43(3):439–442. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90486-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Jordan T. W., Horsburgh T. The N-acetyl- -D-hexosaminidases of calf and human brain. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1975–1985. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Stirling J. L. N-Acetyl-beta-glucosaminidases in human spleen. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):321–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1070321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K. Auftrennung der Säuger-N-Acetyl-beta-D-hexosaminidase in multiple Formen durch Elektrofokusserung. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Sep;349(9):1095–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


