Abstract
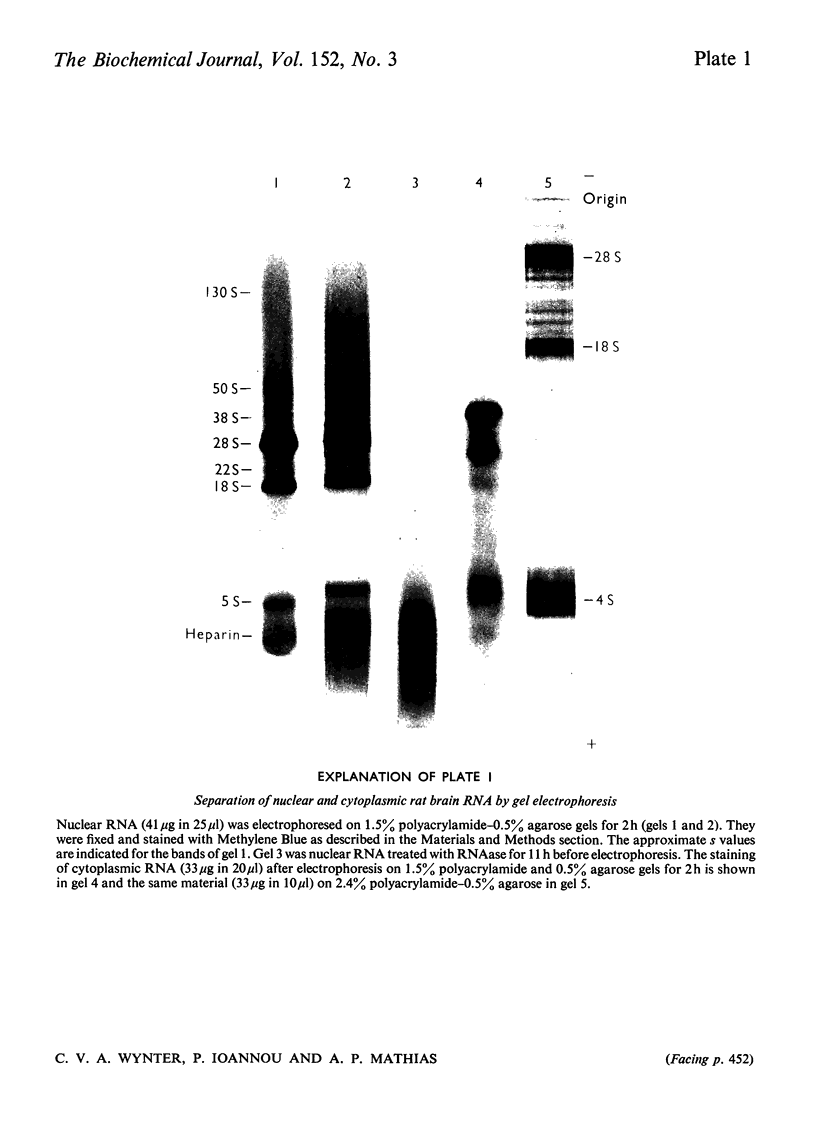
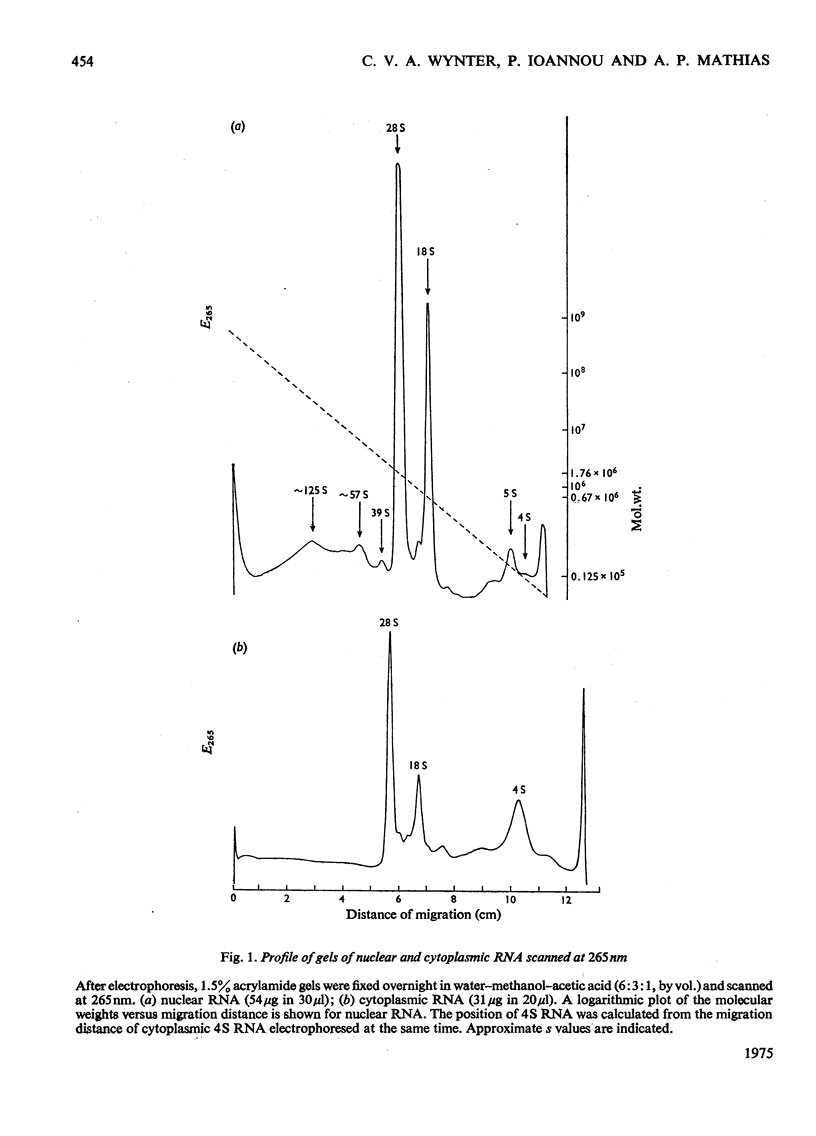
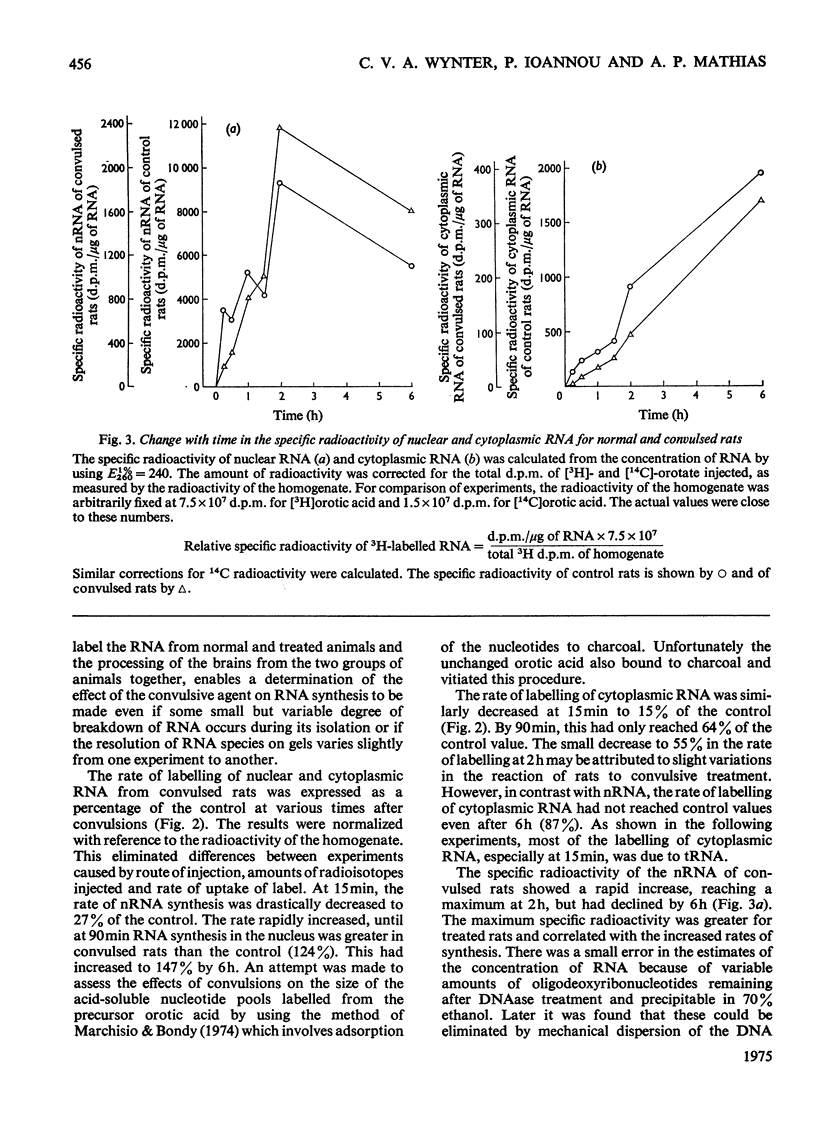
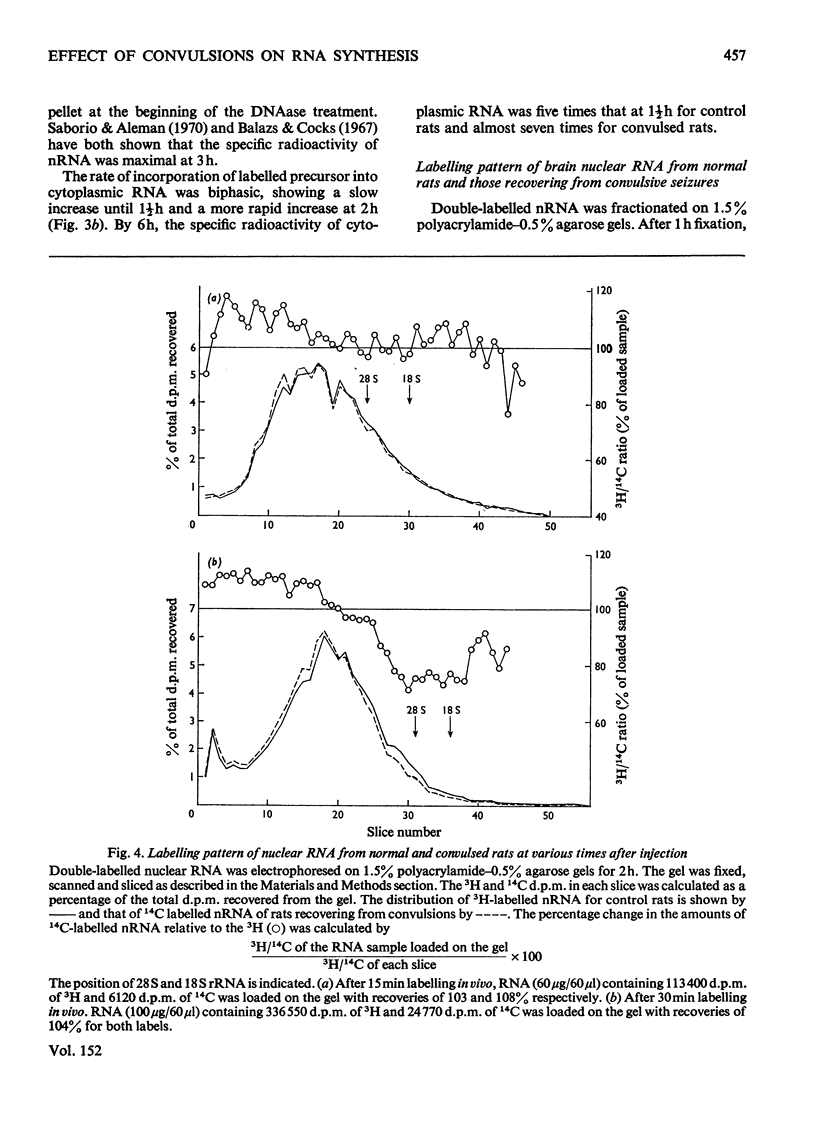
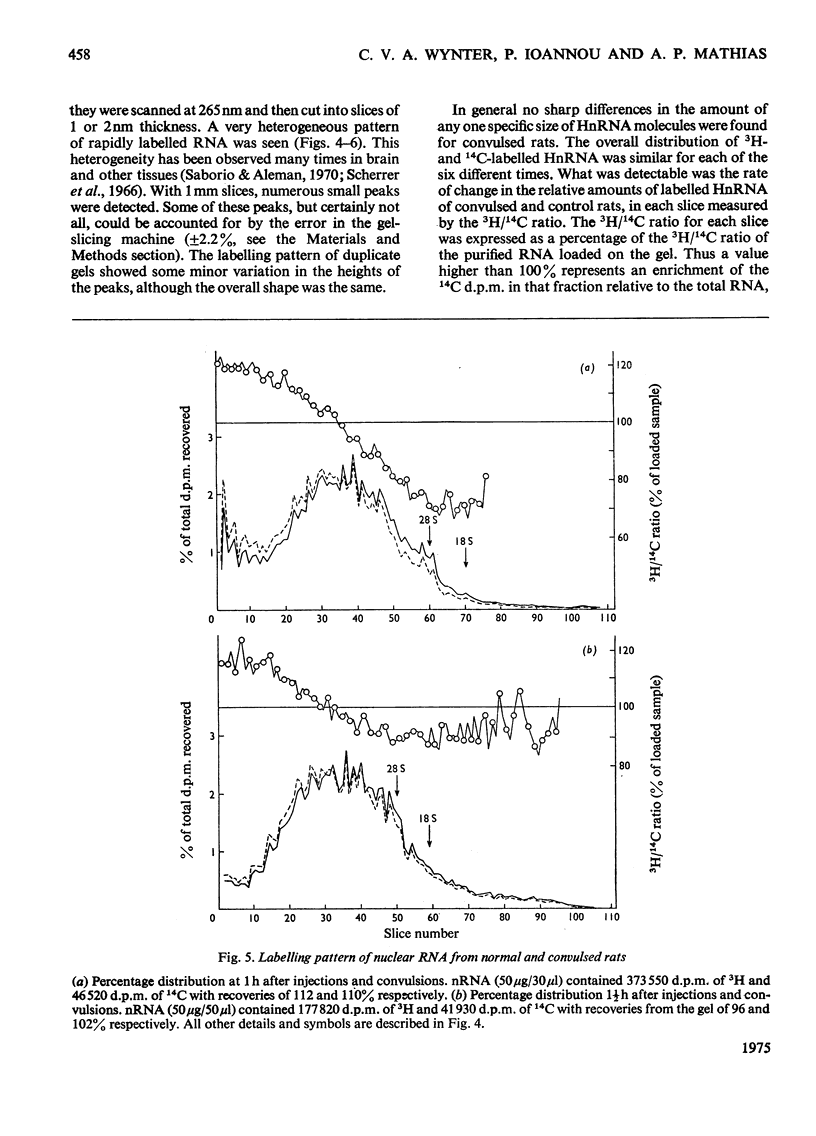
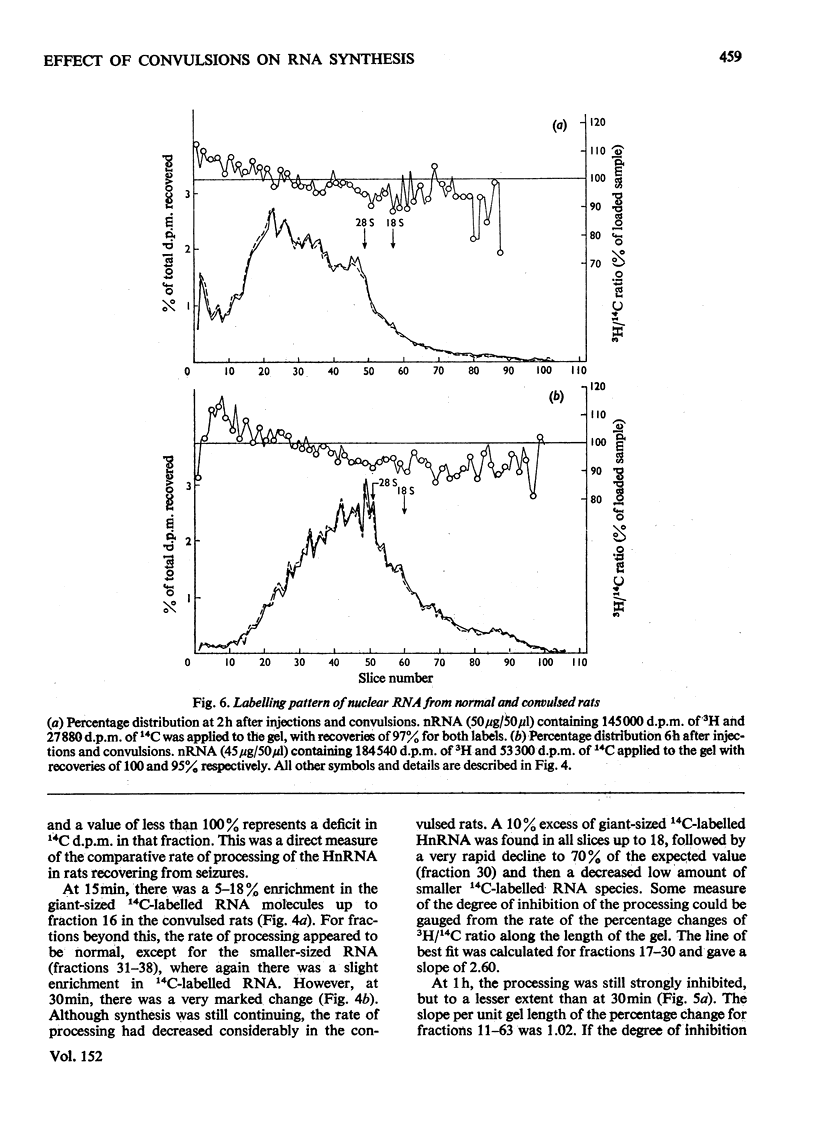
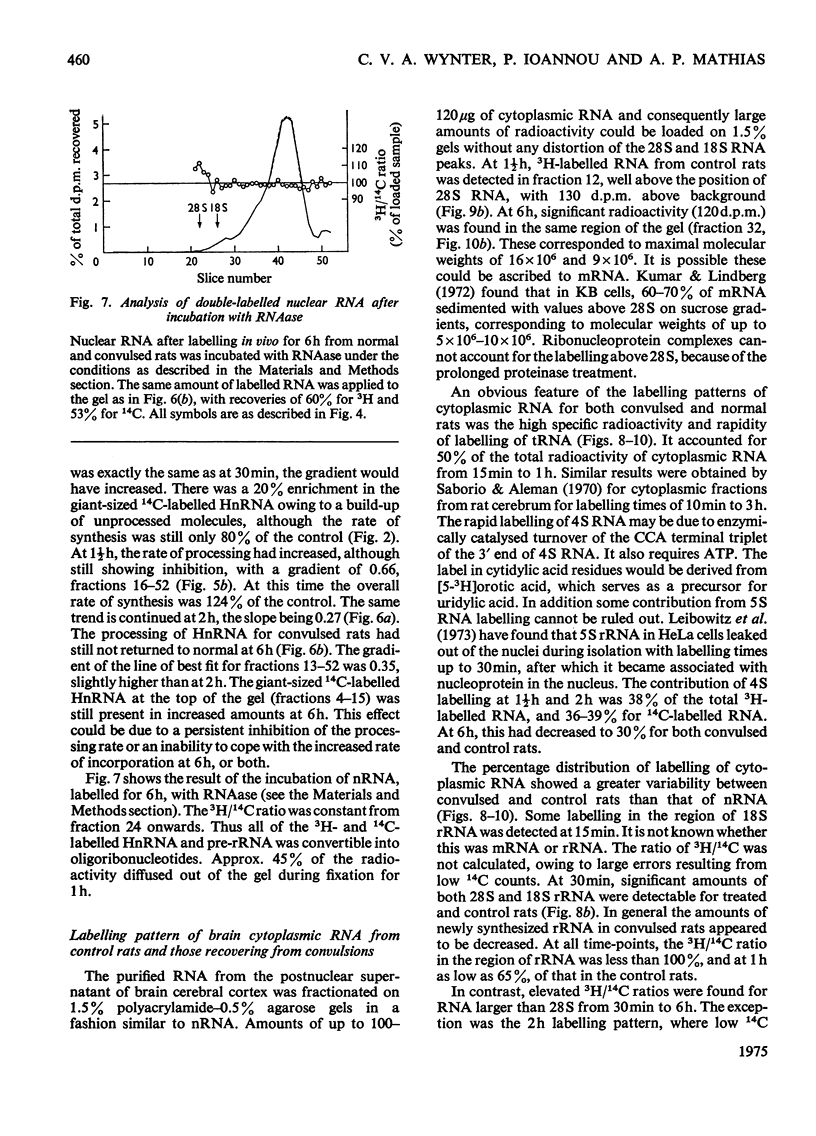
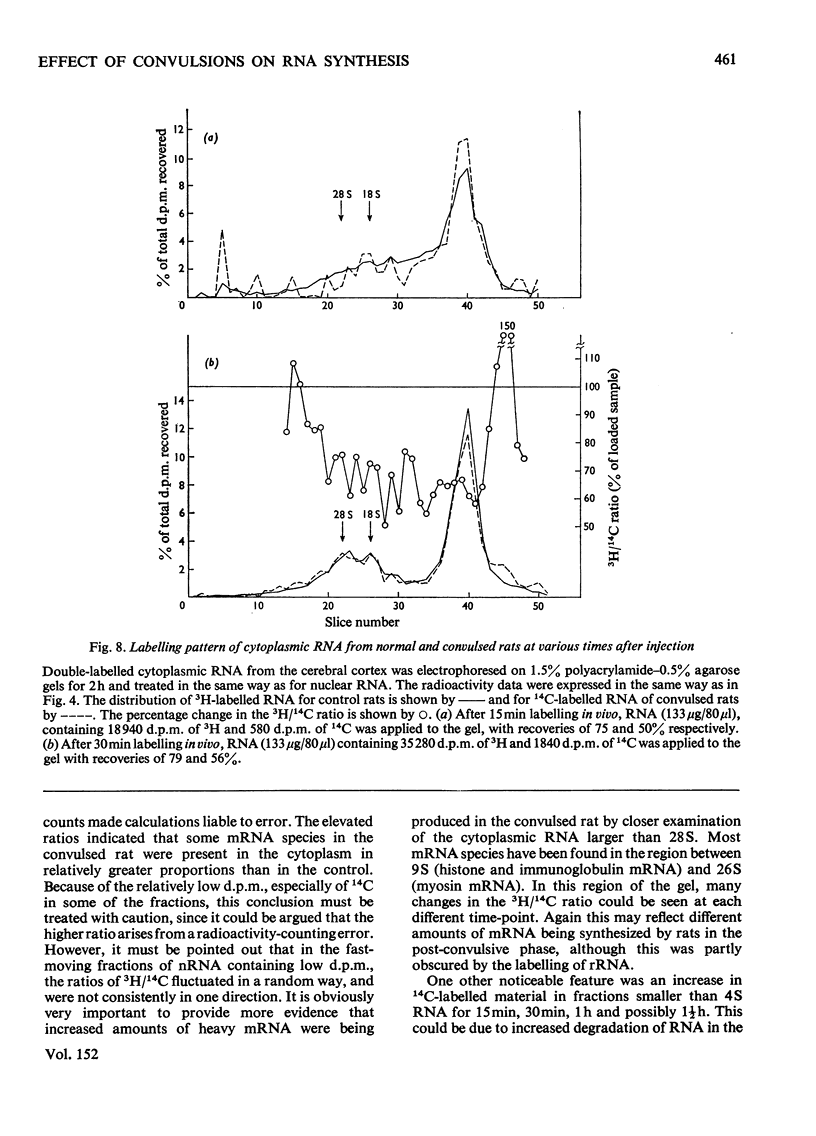
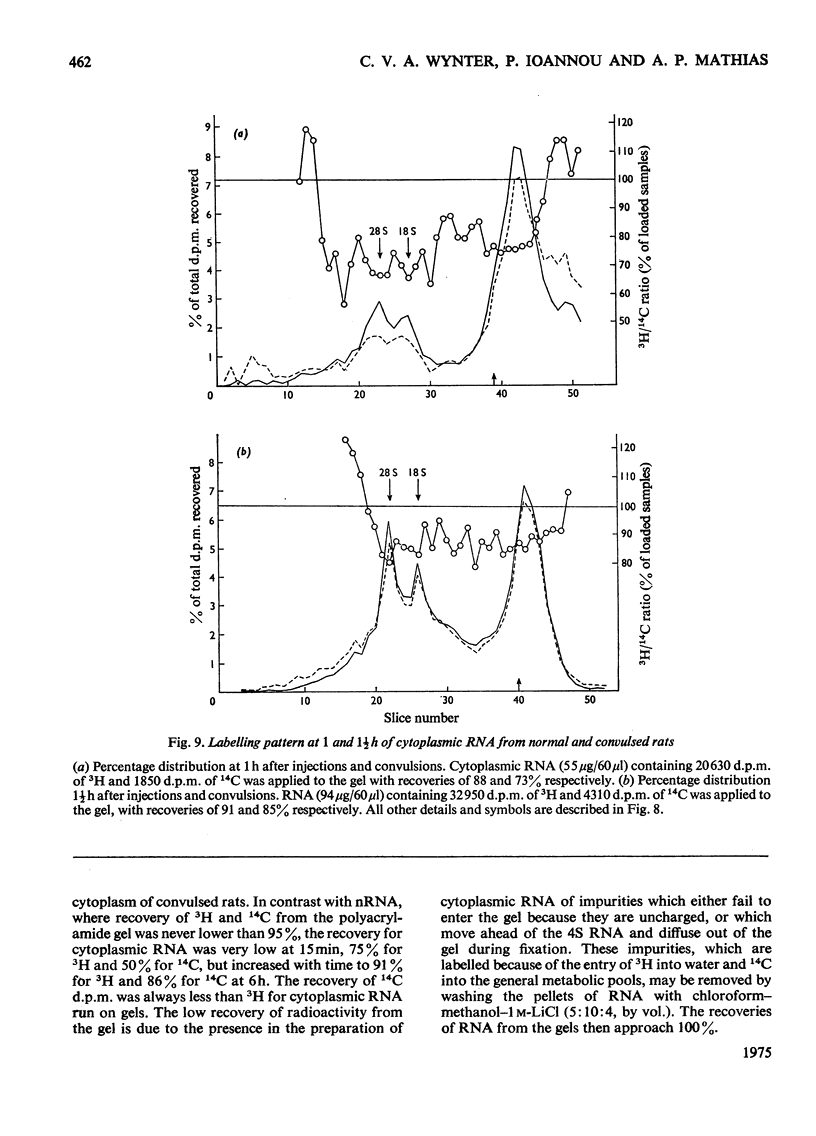
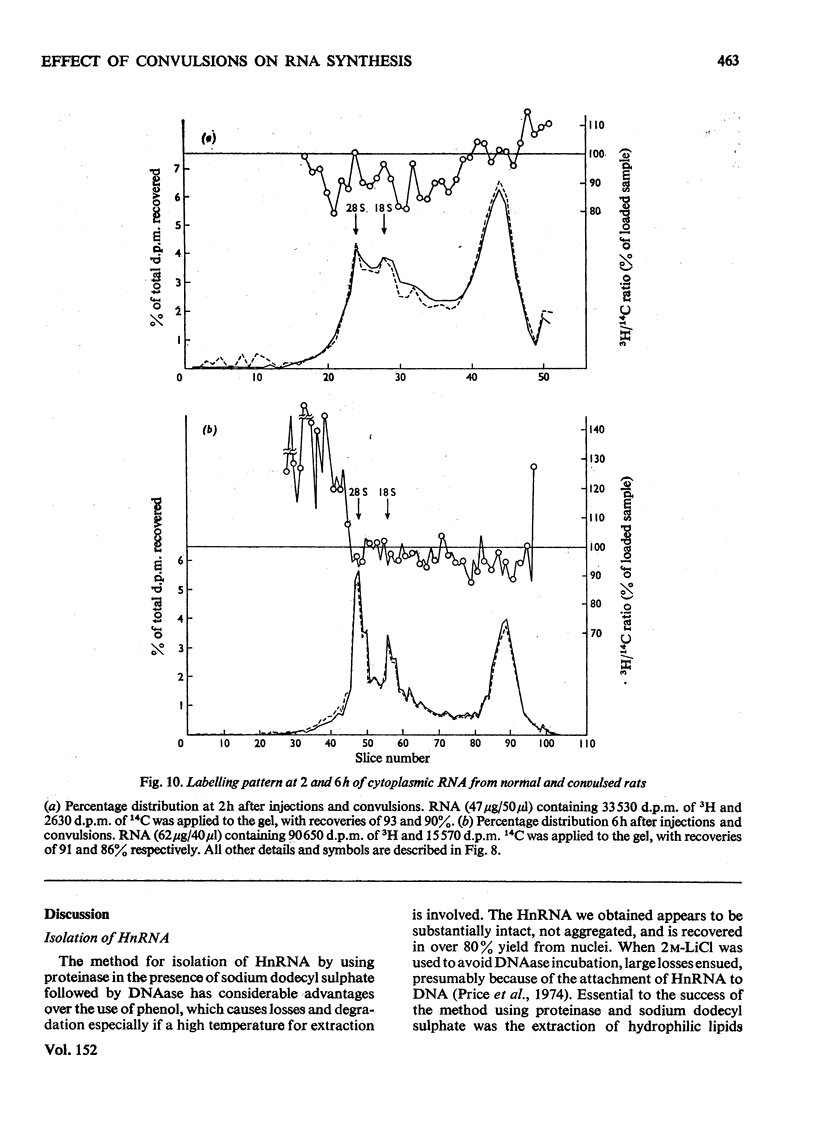
The effect of convulsions, induced by flurothyl, on RNA synthesis in purified unfractionated nuclei and the cytoplasm of rat cerebral cortex was studied by using a double-label technique involving injection of [3H]- and [14C]-orotate intracisternally. 2. Intact RNA was extracted in 80% yield by an enzymic method by using a proteinase in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate followed by deoxyribonuclease. Electrophoresis on 1.5% polyacrylamide-0.5% agarose gels revealed the presence of giant nuclear RNA of size up to approx. 300X 10(6) daltons and mRNA of maximal mol.wt. 9 X 10(6)-16 X 10(6). 3. Nuclear RNA synthesis was decreased to 27% in the first 15 min after convulsions but rapidly increased, so that at 1 1/2 h it was 124% of the control, and at 6 h 147%. 4. Labelling of cytoplasmic RNA was decreased to 15% at 15 min after convulsions but had not recovered to control values by 6 h. 5. Analysis of radioactive gel patterns and the 3H/14C ratio at six time-points (15 min-6h) showed that the major effect was inhibition of the processing of heterogeneous nuclear RNA resulting in a sharp decline in the export of newly synthesized RNA from the nucleus. 6. Cytoplasmic RNA patterns indicated that specific messengers were synthesized at different times during the recovery of the cell after convulsions.
Full text
PDF




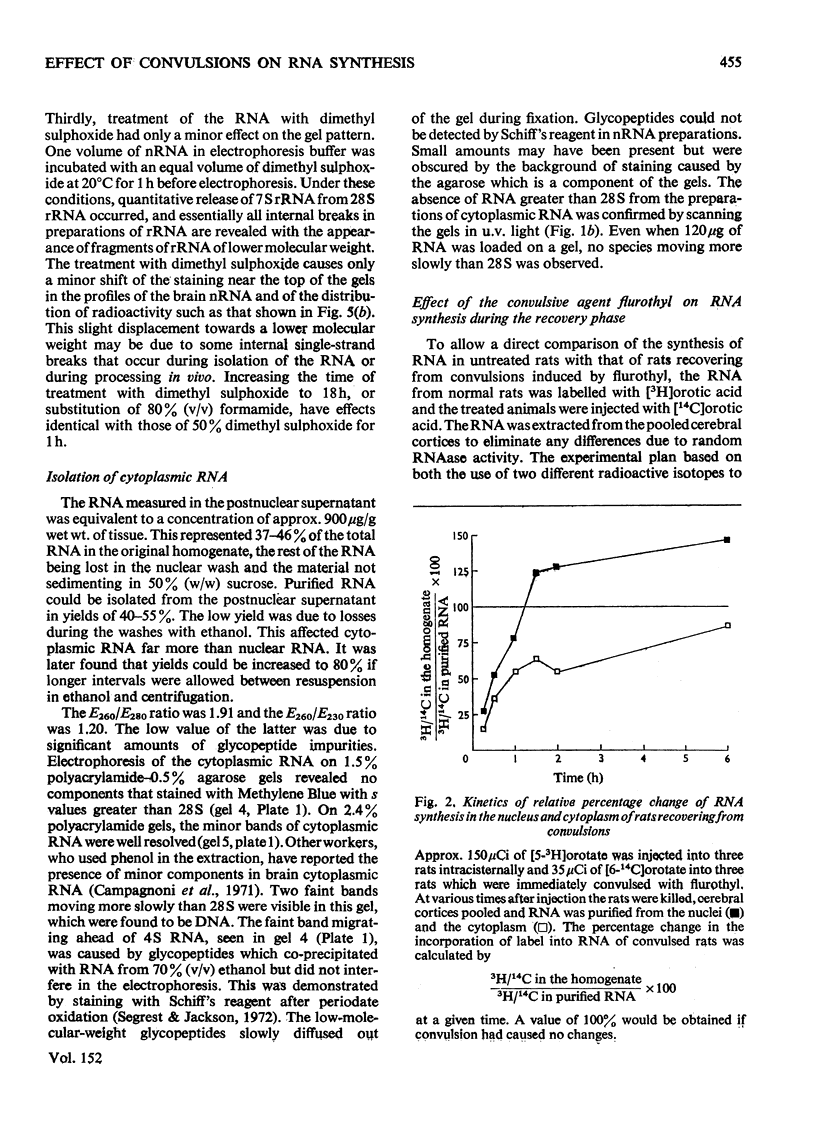




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERS R. W., KOVAL G. J. The interaction of gangliosides with cationic molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:359–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90411-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austoker J., Cox D., Mathias A. P. The synthesis of ribonucleic acid in vivo in the nuclei of rat brain fractionated by zonal centrifugation. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;132(4):813–819. doi: 10.1042/bj1320813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R., Cocks W. A. RNA metabolism in subcellular fractions of brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1967 Nov;14(11):1035–1055. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R., Kovács S., Teichgräber P., Cocks W. A., Eayrs J. T. Biochemical effects of thyroid deficiency on the developing brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Nov;15(11):1335–1349. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharucha A. D., Elliott K. A. Effects of electrically induced convulsions and transmitter substances on ribonucleic acid turnover in brain slices. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Jan 31;19(2):119–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00238528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. Denaturation of rat liver ribosomal ribonucleic acid with dimethyl sulfoxide. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4588–4591. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocharova L. S., Borovyagin V. L., Dyakonova T. L., Warton S. S., Veprintsev B. N. Ultrastructure and RNA synthesis in a molluscan giant neuron under electrical stimulation. Brain Res. 1972 Jan 28;36(2):371–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90741-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramwell M. E. The behaviour of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleic acid in partially and completely denaturing conditions. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):477–484. doi: 10.1042/bj1410477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHITRE V. S., CHOPRA S. P., TALWAR G. P. CHANGES IN THE RIBONUCLEIC ACID CONTENT OF THE BRAIN DURING EXPERIMENTALLY INDUCED CONVULSIONS. J Neurochem. 1964 Jun;11:439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb11603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnoni A. T., Dutton G. R., Mahler H. R., Moore W. J. Fractionation of the RNA components of rat brain polysomes. J Neurochem. 1971 Apr;18(4):601–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb11990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn A. Brain protein synthesis after electroshock. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 10;35(1):254–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90613-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn A. The dependence of brain ATP content on cerebral electroshock current. Brain Res. 1973 Oct 26;61:442–445. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekholm R., Hydén H. Polysomes from microdissected fresh neurons. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Oct;13(3):269–280. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Jr, Morrell F. Turnover of RNA in normal and secondarily epileptogenic rabbit cortex. Exp Neurol. 1970 Feb;26(2):221–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(70)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essman W. B. Neurochemical changes in ECS and ECT. Semin Psychiatry. 1972 Feb;4(1):67–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev G. P., Samarina O. P. D-RNA containing ribonucleoprotein particles. Adv Cell Biol. 1971;2:47–110. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9588-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson W., Gilson R., Rueckert R. R. An automatic high-precision acrylamide gel fractionator. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert R. B., Hardy D., Stankovich M., Coleman R. D. Mechanism of turnover of rapidly labeled RNA in rat liver nuclei. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1973;11:323–341. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(73)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Lindberg U. Characterization of messenger ribonucleoprotein and messenger RNA from KB cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):681–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz R. D., Weinberg R. A., Penman S. Unusual metabolism of 5 S RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan;73(1):139–144. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90166-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIHAILOVIC L., JANKOVIC B. D., PETKOVIC M., ISAKOVIC K. Effect of electroshock upon nucleic acid concentrations in various parts of cat brain. Experientia. 1958 Apr 15;14(4):144–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02157127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchisio P. C., Bondy S. C. The kinetics of cerebral RNA synthesis in relation to the route of injection. Experientia. 1974 Apr 15;30(4):335–336. doi: 10.1007/BF01921648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T. Proteins associated with heterogeneous nuclear RNA in eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., LaTorre J. Synthesis and turnover of nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylic acid in mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. P., Erulkar S. D. Parameters of stimulation of RNA synthesis and characterization by hybridization in a molluscan neuron. Brain Res. 1973 Sep 28;60(1):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90856-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. P. RNA in single identified neurons of aplysia. J Neurochem. 1970 Mar;17(3):325–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevzner L. Z., Saudargene E. D. Two-wave length visible cytospectrophotometry of nucleic acids and proteins in the motor and sensory neurons and their glial cell-satellites of rat spinal cord during corazol seizures. Acta Histochem. 1971;39(1):101–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli F., Camarda R., Bonavita V. Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides in the brain of normal and convulsant rats. J Neurochem. 1969 Feb;16(2):159–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G. Nucleotide pools in Novikoff rat hepatoma cells growing in suspension culture. 3. Effects of nucleosides in medium on levels of nucleotides in separate nucleotide pools for nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):131–146. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohle W., Matthies H. Incorporation of RNA-precursors into neuronal and glial cells of rat brain during a learning experiment. Brain Res. 1974 Jan 11;65(2):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. P., Ransom L., Penman S. Identification of a small subfraction of hnRNA with the characteristics of a precursor to mRNA. Cell. 1974 Aug;2(4):253–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Quastel J. H. Effect of cerebral stimulation on biosynthesis of nucleotides and RNA in brain slices in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;182(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R. The behavior of presumed glial cells during seizure discharge in cat cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 29;69(1):83–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E., McKnight G. S., Schimke R. T. Quantitative measurement of ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid activity. Localization in polysomes, induction by estrogen, and effect of actinomycin D. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2031–2039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringborg U., Rydlander L. Nucleolar-derived ribonucleic acid in chromosomes, nuclear sap, and cytoplasm of Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):355–368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S. THE OPERON: ON ITS THIRD ANNIVERSARY. MODULATION OF TRANSFER RNA SPECIES CAN PROVIDE A WORKABLE MODEL OF AN OPERATOR-LESS OPERON. Science. 1964 May 15;144(3620):816–820. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3620.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Alemán V. Study of RNA in subcellular fractions from rat brain: simultaneous incorporation of [14C]uridine and [3H]methyl-L-methionine. J Neurochem. 1970 Jan;17(1):91–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb00505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacktor B., Wilson J. E., Tiekert C. G. Regulation of glycolysis in brain, in situ, during convulsions. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 10;241(21):5071–5075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherrer K., Marcaud L., Zajdela F., London I. M., Gros F. Patterns of RNA metabolism in a differentiated cell: a rapidly labeled, unstable 60S RNA with messenger properties in duck erythroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1571–1578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. G., Small I. F. Clinical results: indoklon versus ECT. Semin Psychiatry. 1972 Feb;4(1):13–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K. The pattern of mammalian brain gangliosides. II. Evaluation of the extraction procedures, postmortem changes and the effect of formalin preservation. J Neurochem. 1965 Jul;12(7):629–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernadakis A., Woodbury D. M. The developing animal as a model. Epilepsia. 1969 Jun;10(2):163–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1969.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesco C., Guiditta A. Disaggregation of brain polysomes induced by electroconvulsive treatment. J Neurochem. 1968 Feb;15(2):81–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb06177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA and its precursors as determined by electron microscopy. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:525–535. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]