Abstract
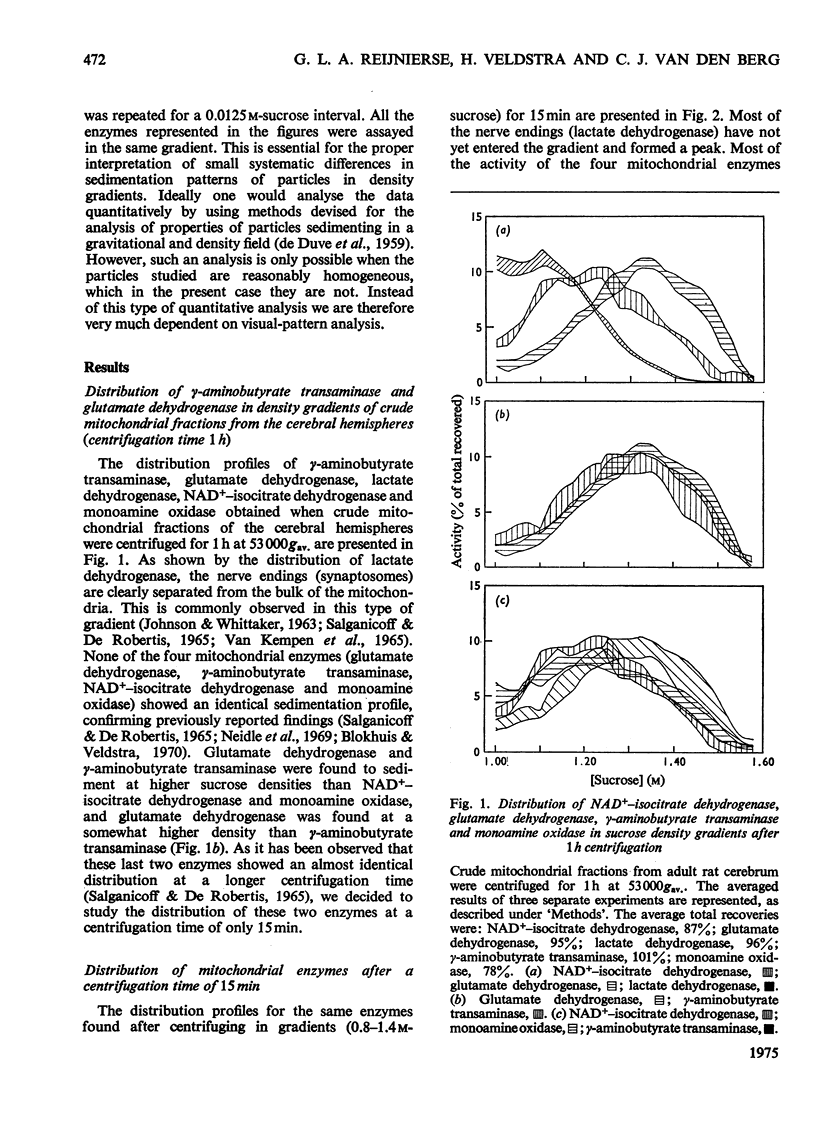
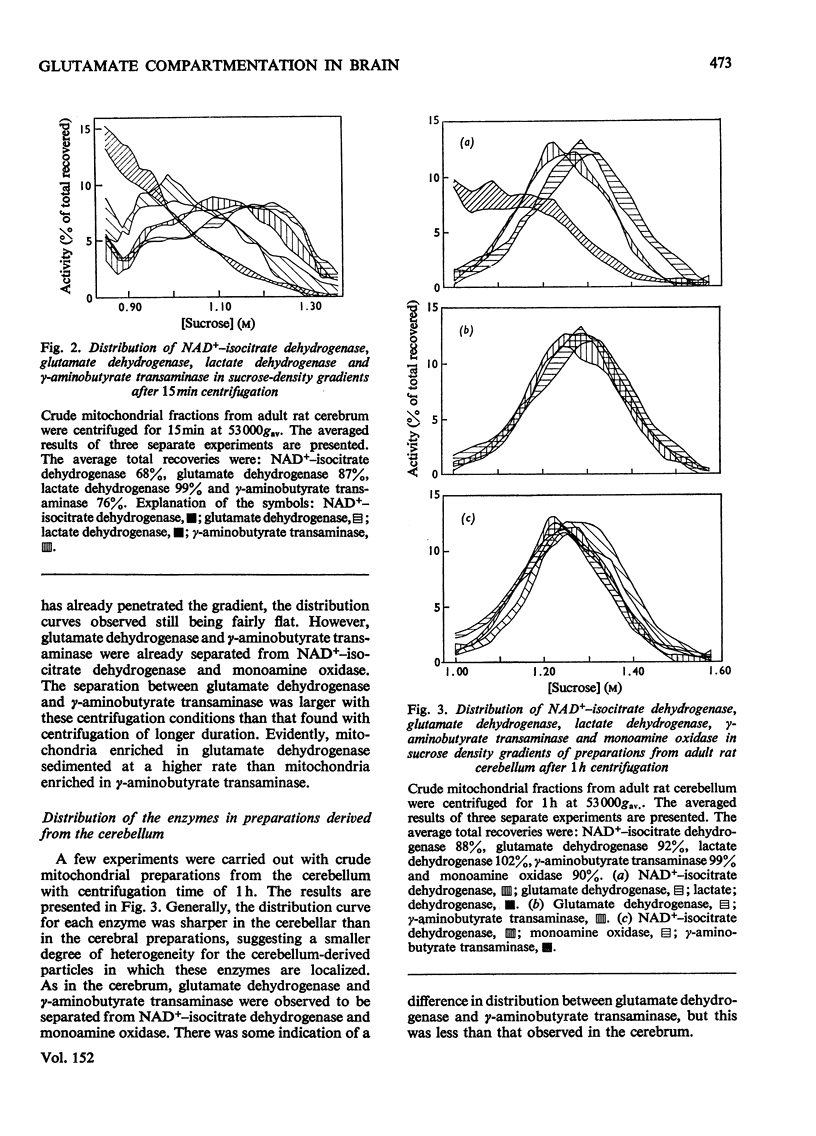
The subcellular localizations of gamma-aminobutyrate transaminase (EC 2.6.1.19) and glutamate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.2) in brain tissue of adult rats were compared with each other and with those of NAD+-isocitrate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.41) and monoamine oxidase (EC 1.4.3.4; kynuramine as substrate). Crude mitochondrial fractions from brain tissue were centrifuged in continuous sucrose density gradients. gamma-Aminobutyrate transaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase were always found at a higher density than NAD+-isocitrate dehydrogenase and monoamine oxidase. When centrifuged for 1 h at 53 000gav., there was a slight difference between the distribution profiles of glutamate dehydrogenase and gamma-aminobutyrate transaminase. This difference was larger when the centrifugation time was only 15 min. It is concluded that there are subpopulations of brain mitochondria with differing proportions of gamma-aminobutyrate transaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase. The results are discussed in relation to evidence obtained with labelled precursors in vivo that there are at least two small glutamate compartments in adult brain.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERL S., TAKAGAKI G., CLARKE D. D., WAELSCH H. Carbon dioxide fixation in the brain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2570–2573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERL S., TAKAGAKI G., CLARKE D. D., WAELSCH H. Metabolic compartments in vivo. Ammonia and glutamic acid metabolism in brain and liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2562–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R., Machiyama Y., Hammond B. J., Julian T., Richter D. The operation of the gamma-aminobutyrate bypath of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in brain tissue in vitro. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):445–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1160445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter C. F. Intrinsic amino acid levels and the blood-brain barrier. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:429–450. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blokhuis G. G.D., Veldstra H. Heterogeneity of mitochondria in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):197–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E., PELLEGRINO DE IRALDI A., RODRIGUEZ DE LORES GARNAIZ G., SALGANICOFF L. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic nerve endings in rat brain. I. Isolation and subcellular distribution of acetylcholine and acetylcholinesterase. J Neurochem. 1962 Jan-Feb;9:23–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1962.tb07489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOEBELL H., KLINGENBERG M. DPN-SPEZIFISCHE ISOCITRAT-DEHYDROGENASE DER MITOCHONDRIEN. I. KINETISCHE EIGENSSCHAFTEN, VORKOMMEN UND FUNKTION DER DPN-SPEZIFISCHEN ISOCITRAT-DEHYDROGENASE. Biochem Z. 1964 Sep 28;340:441–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammeraat C., Veldstra H. Characterization of succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jan 8;151(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson D. F., van den Berg C. J. Ammonia and brain glutamine: inhibition of glutamine degradation by ammonia. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(4):525–528. doi: 10.1042/bst0030525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidle A., van den Berg C. J., Grynbaum A. The heterogeneity of rat brain mitochondria isolated on continuous sucrose gradients. J Neurochem. 1969 Feb;16(2):225–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'neal R. M., Koeppe R. E., Williams E. I. Utilization in vivo of glucose and volatile fatty acids by sheep brain for the synthesis of acidic amino acids. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):591–597. doi: 10.1042/bj1010591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALGANICOFF L., DEROBERTIS E. SUBCELLULAR DISTRIBUTION OF THE ENZYMES OF THE GLUTAMIC ACID, GLUTAMINE AND GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID CYCLES IN RAT BRAIN. J Neurochem. 1965 Apr;12:287–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada Y. Amino acid metabolism and its relation to brain functions. Prog Brain Res. 1966;21:268–291. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62981-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg C. J., Krzalić L., Mela P., Waelsch H. Compartmentation of glutamate metabolism in brain. Evidence for the existence of two different tricarboxylic acid cycles in brain. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj1130281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattiaux R., Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Ronveaux-Dupal M. F. Deterioration of rat-liver mitochondria during centrifugation in a sucrose gradient. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Sep 13;22(1):31–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil-Malherbe H. Ammonia formation in brain slices. Mol Cell Biochem. 1974 Aug 1;4(1):31–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01731101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kempen G. M., van den Berg C. J., van der Helm H. J., Veldstra H. Intracellular localization of glutamate decarboxylase, gamma-aminobutyrate transaminase and some other enzymes in brain tissue. J Neurochem. 1965 Jul;12(7):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg C. J., Garfinkel D. A simulation study of brain compartments. Metabolism of glutamate and related substances in mouse brain. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj1230211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg C. J., Matheson D. F. The formation of glutamine in mouse brain: effect of amino-oxyacetic acid and ammonia. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(4):528–530. doi: 10.1042/bst0030528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg C. J., van Kempen G. M. Glutamate decarboxylase and gamma-aminobutyrate transaminase in developing rat brain. Maturational changes in cerebral cortex IV. Experientia. 1964 Jul 15;20(7):375–376. doi: 10.1007/BF02147969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


