Abstract
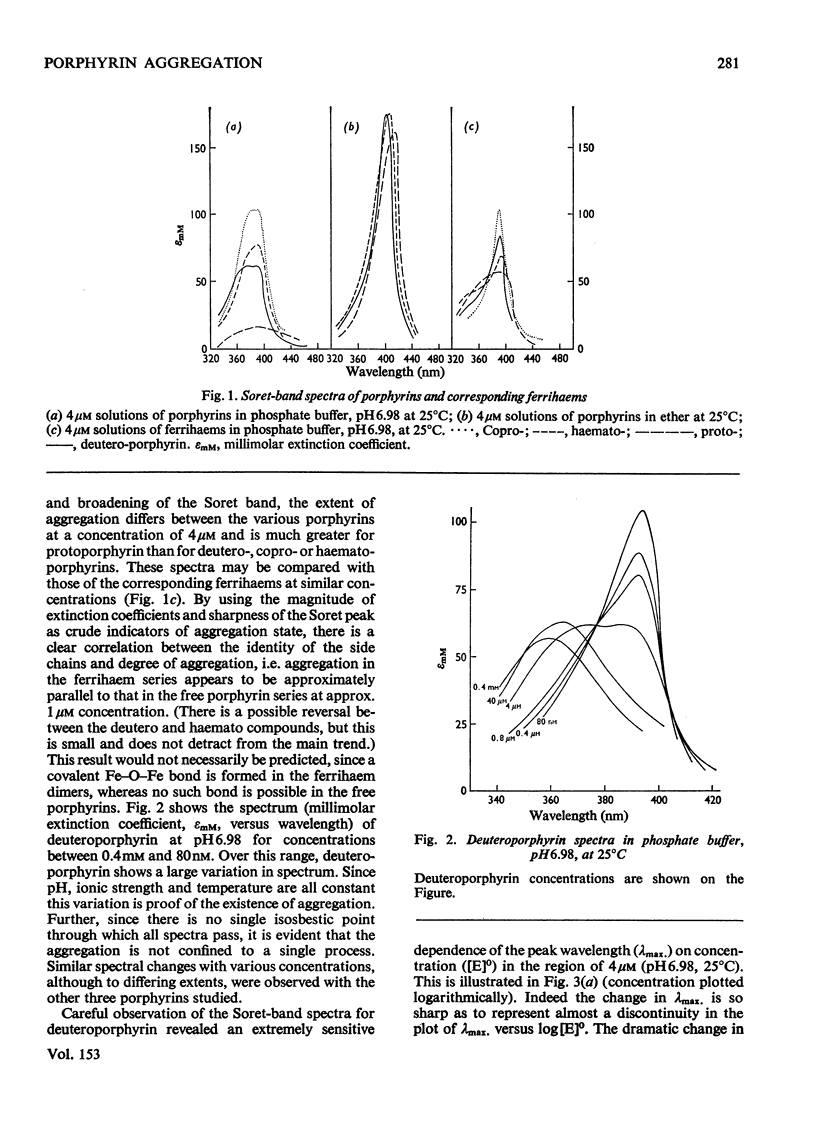
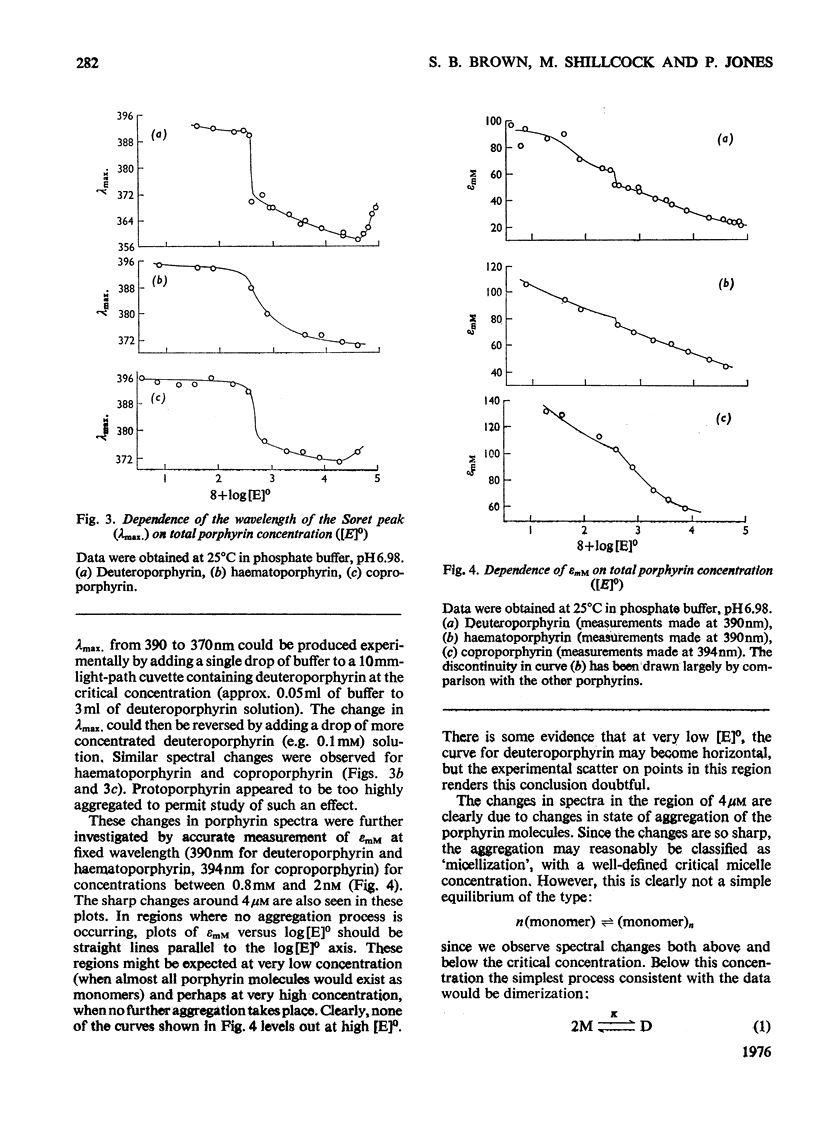
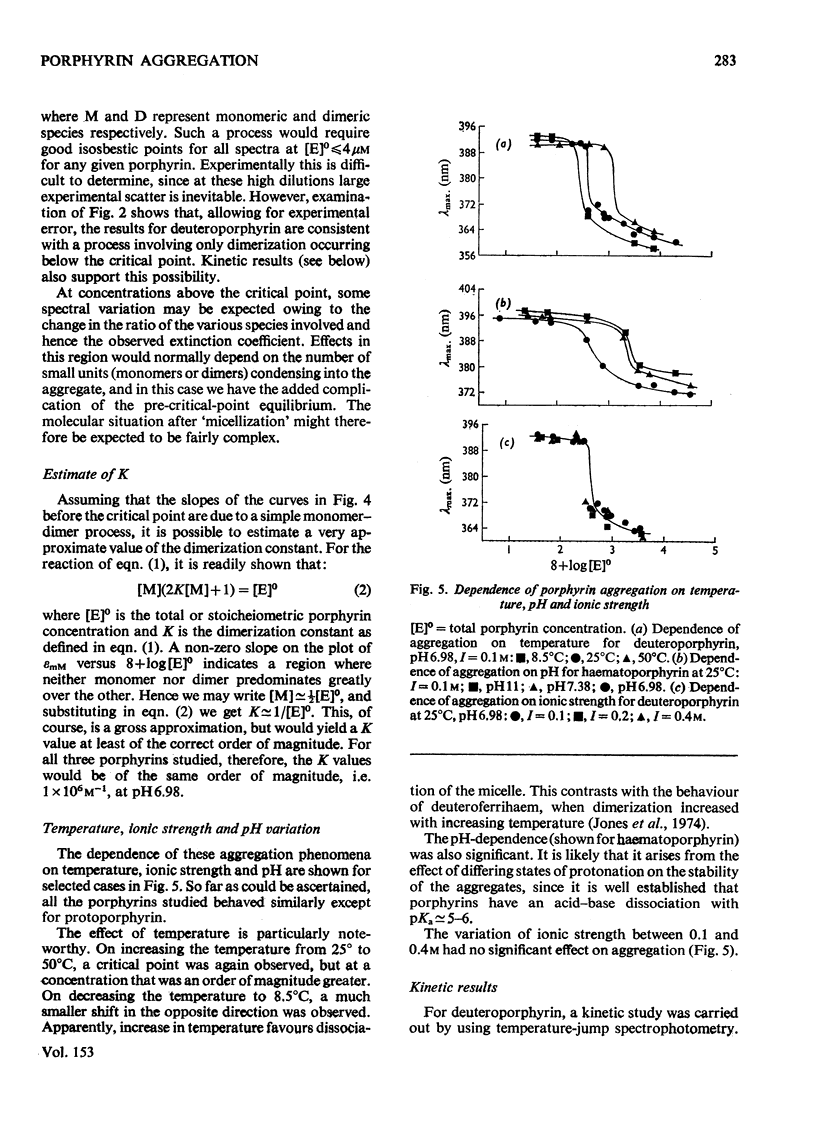
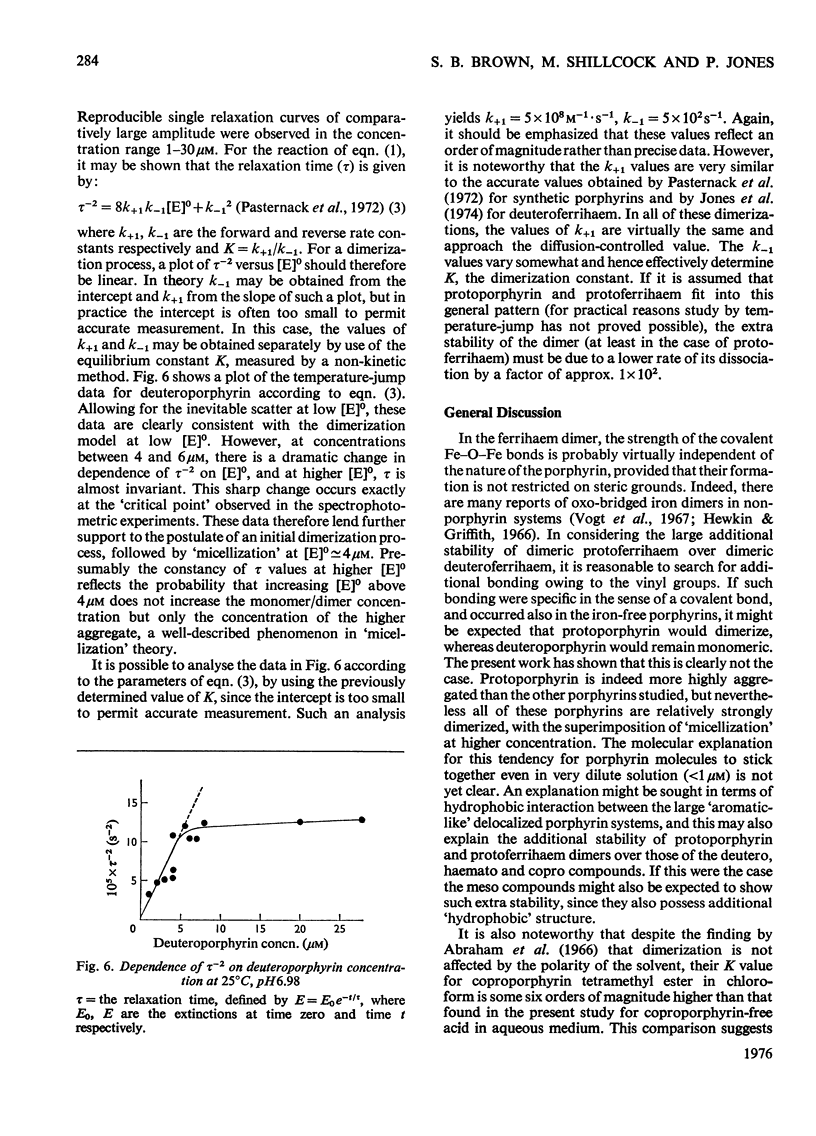
An investigation of the behavior of protoporphyrin IX, deuteroporphyrin IX, haematoporphyrin IX and coproporphyrin III in aqueous solution revealed extensive and complex aggregation processes. Protoporphyrin appears to be highly aggregated under all conditions studied. At concentrations below 4 muM, aggregation of deutero-, haemato- and coproporphyrin is probably restricted to dimerization. At approx. 4muM each of these three porphyrins exhibits sharp changes in spectra consistent with a "micellization" process to form large aggregates of unknown size. This critical concentration increases with increasing temperature and pH, but is not very sensitive to variation in ionic strength. Temperature-jump kinetic studies on deuteroporphyrin also imply an initial dimerization process, the rate constants for which are comparable with those for various synthetic porphyrins, followed by a further extensive aggragation. The ability of a particular porphyrin to dimerize appears to parallel that of the corresponding iron(III) complexes (ferrihaems), although it is thought that ferrihaems do not exhibit further aggregation under these conditions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown N. A., King R. F., Shillcock M. E., Brown S. B. Haemoglobin catabolism: the role of ferrihaems in studies of the degradation pathway. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;137(1):135–137. doi: 10.1042/bj1370135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B., Dean T. C., Jones P. Aggregation of ferrihaems. Dimerization and protolytic equilibria of protoferrihaem and deuteroferrihaem in aqueous solution. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):733–739. doi: 10.1042/bj1170733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B., Dean T. C., Jones P. Catalatic activity of iron(3)-centred catalysts. Role of dimerization in the catalytic action of ferrihaems. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):741–744. doi: 10.1042/bj1170741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. B., Jones P., Lantzke I. R. Infrared evidence for an oxo-bridged (Fe-O-Fe) haemin dimer. Nature. 1969 Aug 30;223(5209):960–961. doi: 10.1038/223960a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das R. R., Pasternack R. F., Plane R. A. Fast reaction kinetics of porphyrin dimerization in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Jun 3;92(11):3312–3316. doi: 10.1021/ja00714a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer E. B., Palmer J. M., Srivastava T. S., Chatterjee A. Thermodynamic and kinetic properties of an iron-porphyrin system. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jun 30;93(13):3162–3167. doi: 10.1021/ja00742a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. J. Letter: Polymerization of glutaraldehyde at fixative pH. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Sep;22(9):911–913. doi: 10.1177/22.9.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P., Prudhoe K., Robson T. Oxidation of deuteroferrihaem by hydrogen peroxide. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):361–365. doi: 10.1042/bj1350361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P., Robson T., Brown S. B. The catalase activity of ferrihaems. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):353–359. doi: 10.1042/bj1350353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. The synthesis of porphyrins and bacteriochlorophyll by cell suspensions of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):78–93. doi: 10.1042/bj0620078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack R. F., Huber P. R., Boyd P., Engasser G., Francesconi L., Gibbs E., Fasella P., Venturo G. C., Hinds L. de C. On the aggregation of meso-substituted water-soluble porphyrins. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 28;94(13):4511–4517. doi: 10.1021/ja00768a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


