Abstract
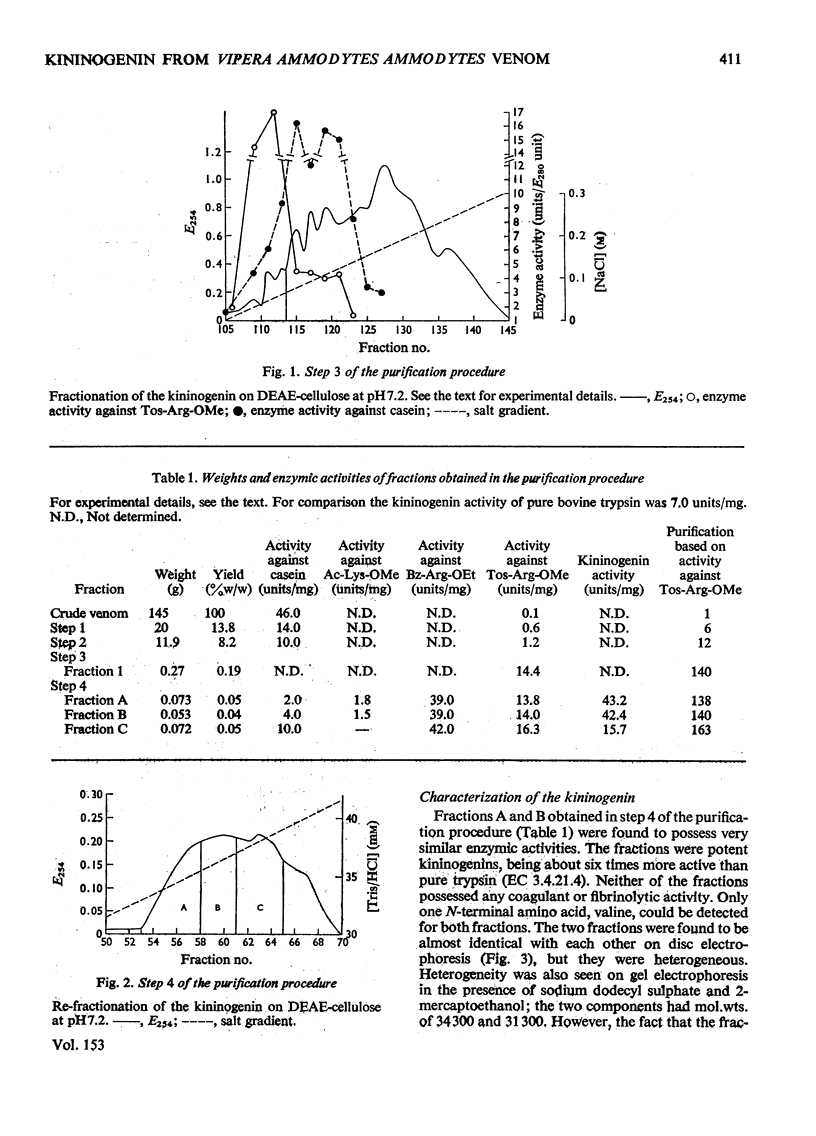
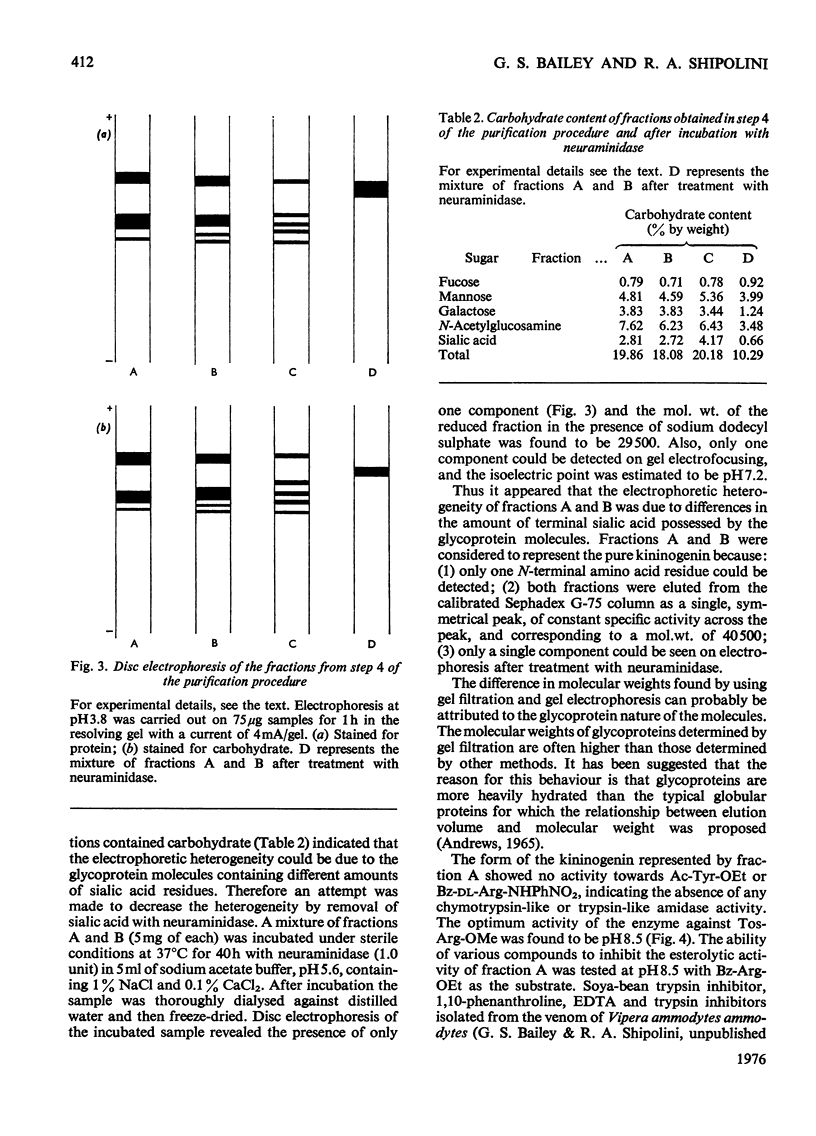
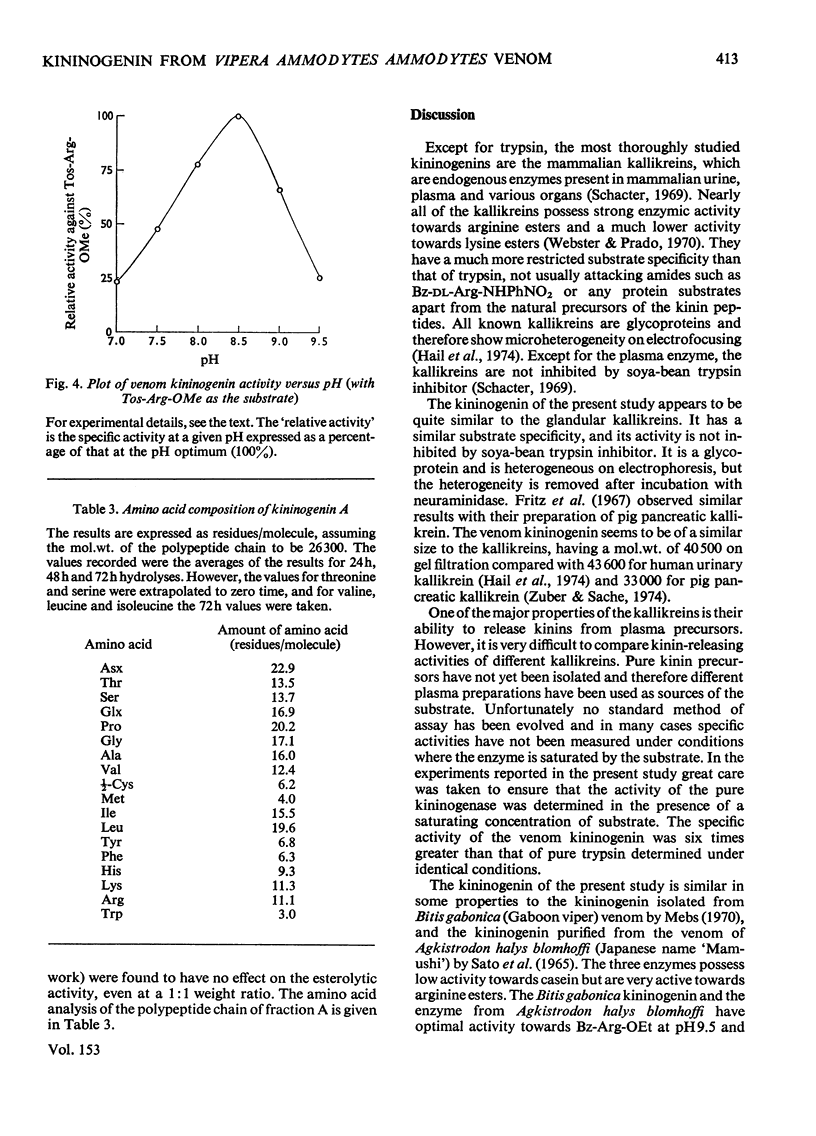
A kininogenin (EC 3.4.21.8) was purified from the venom of Vipera ammodytes ammodytes (European sand viper) by a combination of gel filtration and ion-exchange chromatography. The enzyme is approximately six times more active than bovine trypsin in its ability to release vasoactive peptides from a plasma precursor. The kininogenin is a glycoprotein containing 18-20% by weight of carbohydrate. It showed a mol. wt. of 40500 on gel filtration. Gel electrophoresis of the reduced sample in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate and 2-mercaptoethanol revealed the presence of two major components of mol.wt. 34300 and 31300. The heterogeneity, which was also observed on disc electrophoresis, was removed by incubation with neuraminidase. After incubation with neuraminidase the kininogenin retained full enzymic activity and possessed an isoelectric point of pH7.2. The carbohydrate content has been decreased to 10% by weight, and the single component seen on electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate and 2-mercaptoethanol corresponded to a mol.wt. of 29500.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARGETZI J. P. KUMAR KS, COX DJ, WALSH KA, NEURATH H: THE AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF BOVINE PANCREATIC CARBOXYPEPTIDASE A. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1468–1474. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE J. T. SIMPLIFIED "DISC" (POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL) ELECTROPHORESIS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:428–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., KOKOWSKY N., COHEN W. The preparation and properties of two new chromogenic substrates of trypsin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Nov;95:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90145-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Bartelt D. C., Greene L. J. Isolation of bradykinin-potentiating peptides from Bothrops jararaca venom. Biochemistry. 1970 Jun 23;9(13):2583–2593. doi: 10.1021/bi00815a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Eckert I., Werle E. Isolierung und Charakterisierung von sialinsäurehaltigem und sialinsäurefreiem Kallikrein aus Schweinepankreas. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Sep;348(9):1120–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Diniz C. R., Mares-Guia M. Purification and properties of a human urinary kallikrein (kininogenase). Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4311–4318. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Sato T., Mizushima Y., Suzuki T. Studies on snake venoms. XVII. Properties of the bradykinin releasing enzyme in the venom of Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii. J Biochem. 1965 Aug;58(2):123–129. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Suzuki T. Bradykinin-potentiating peptides from the venom of Agkistrodon halys blomhoffi. Isolation of five bradykinin potentiators and the amino acid sequences of two of them, potentiators B and C. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):972–980. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce F. L., Banks B. E., Banthorpe D. V., Berry A. R., Davies H. S., Vernon C. A. The isolation and characterization of nerve-growth factor from the venom of Vipera russelli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):417–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATO T., IWANAGA S., MIZUSHIMA Y., SUZUKI T. STUDIES ON SNAKE VENOMS. XV. SEPARATION OF ARGININE ESTER HYDROLASE OF AGKISTRODON HALYS BLOMBOFFII VENOM INTO THREE ENZYMATIC ENTITIES: "BRADYKININ RELEASING", "CLOTTING" AND "PERMEABILITY INCREASING". J Biochem. 1965 Mar;57:380–391. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERT G. W., TAKENAKA Y. A spectrophotometric determination of trypsin and chymotrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Apr;16(4):570–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander G. E., West D. W., Huggins C. G. Inhibitors of the pulmonary angiotensin I-converting enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 7;289(2):392–400. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M., Sache E. Isolation and characterization of porcine pancreatic kallikrein. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 16;13(15):3098–3110. doi: 10.1021/bi00712a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


