Abstract
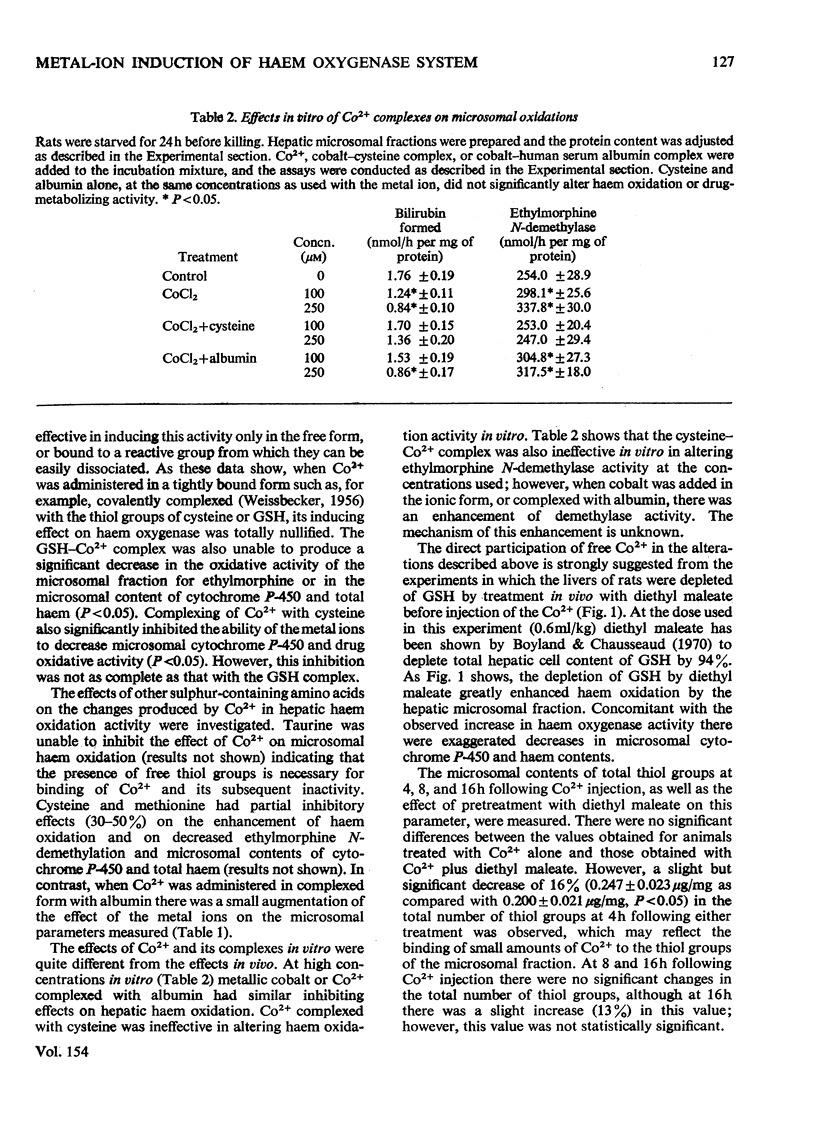
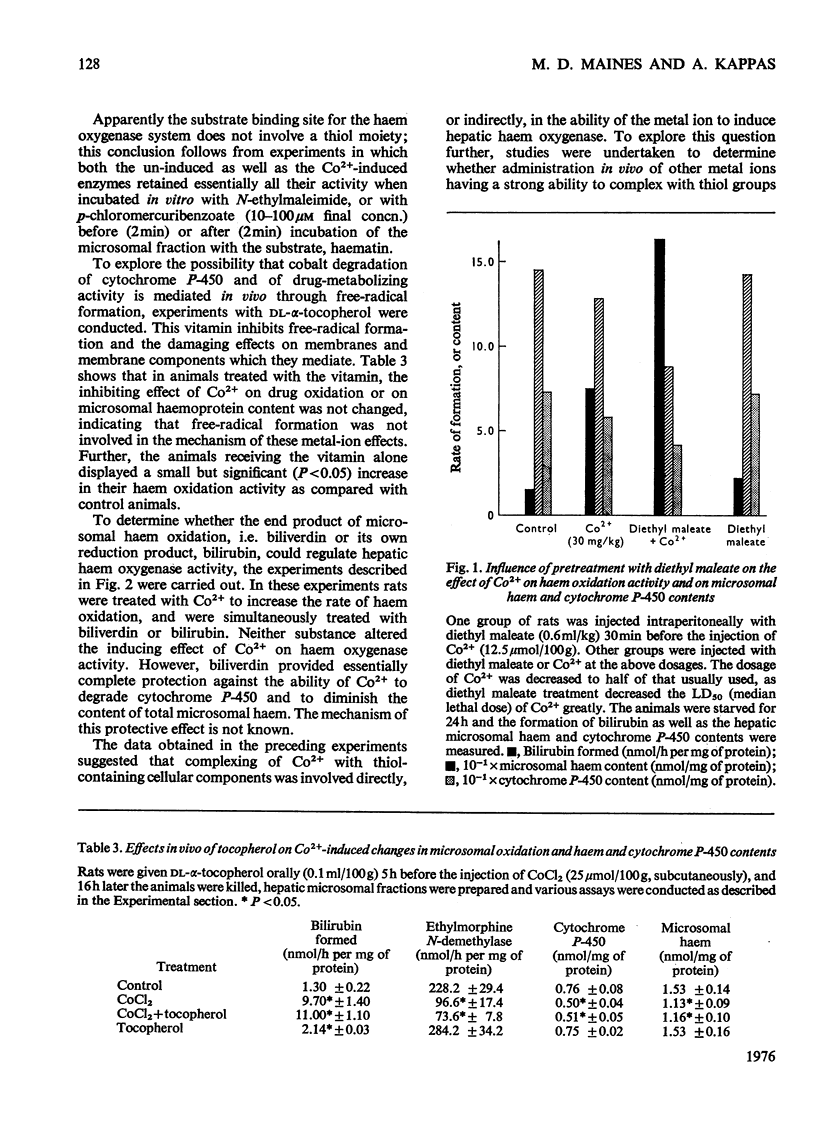
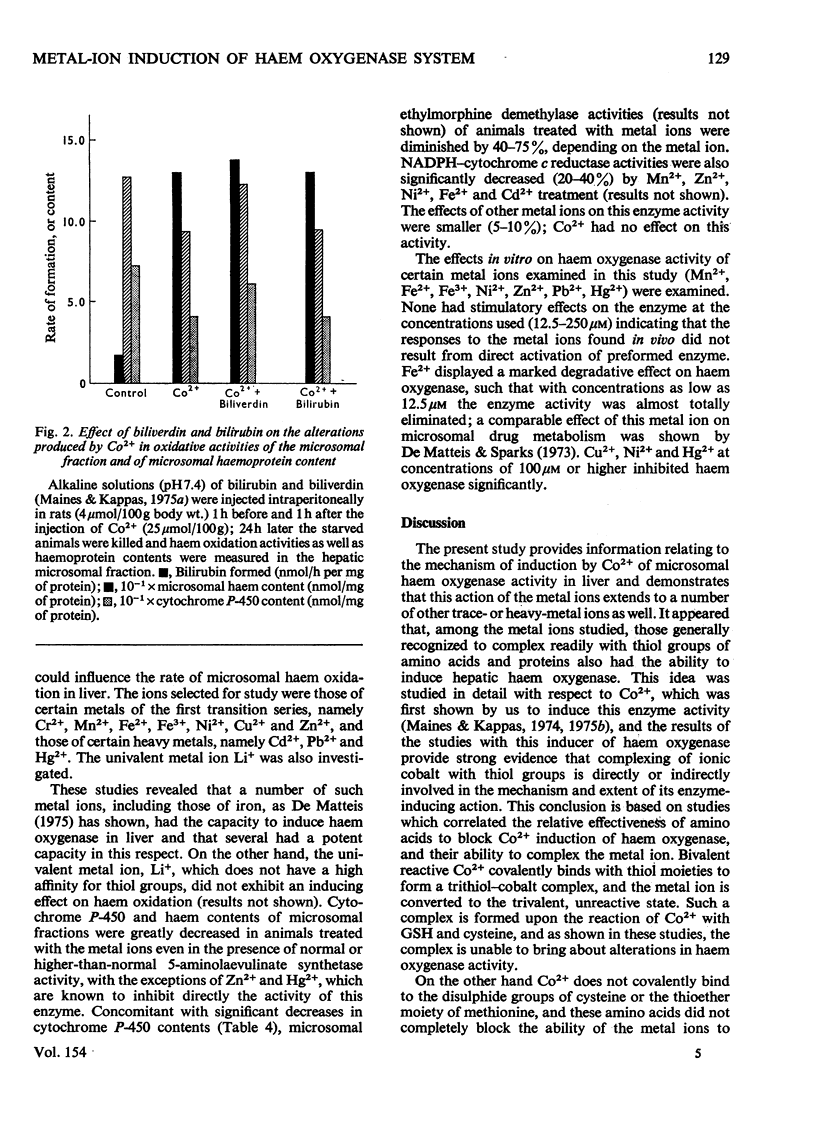
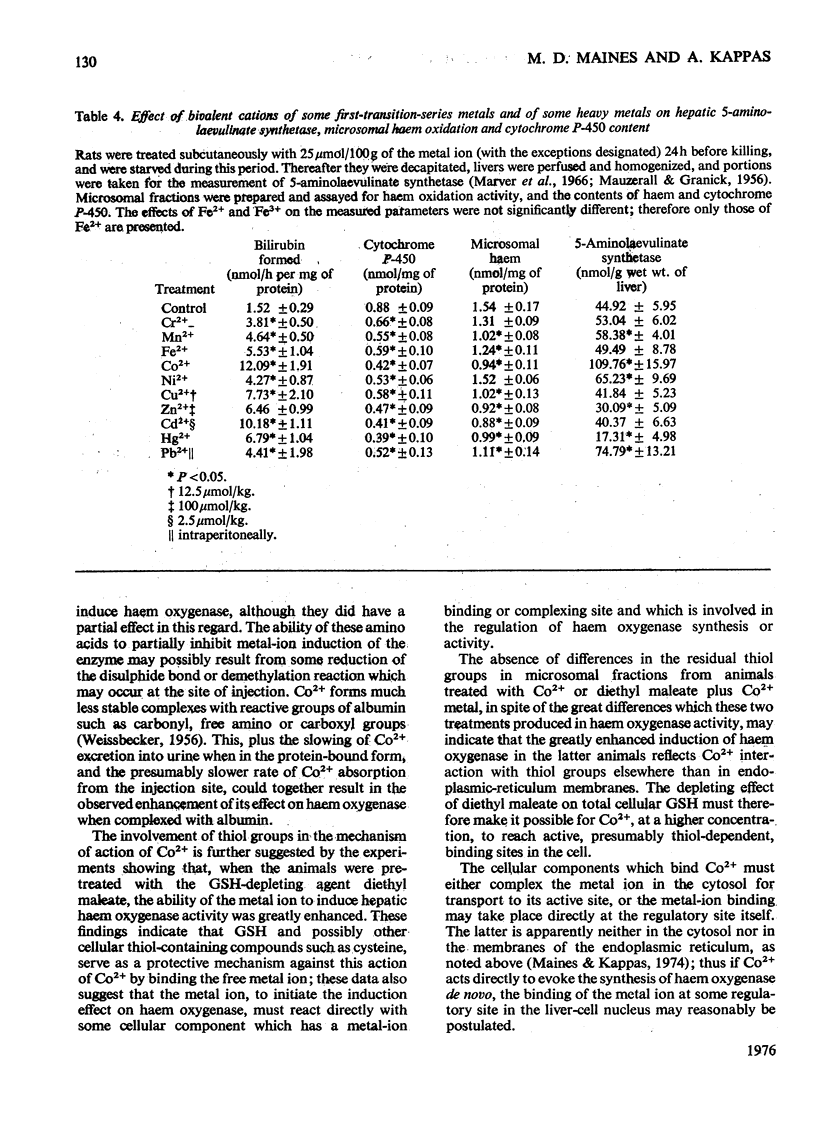
Cobalt ions (Co2+) are potent inducers of haem oxygenase in liver and inhibit microsomal drug oxidation probably by depleting microsomal haem and cytochrome P-450. Complexing of Co2+ ions with cysteine or glutathione (GSH) blocked ability of the former to induce haem oxygenase. When hepatic GSH content was depleted by treatment of animals with diethyl maleate, the inducing effect of Co2+ on haem oxygenase was significantly augmented. Other metal ions such as Cr2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ and Pb2+ were also capable of inducing haem oxygenase and depleting microsomal haem and cytochrome P-450. None of these metal ions had a stimulatory effect on hepatic haem oxidation activity in vitro. It is suggested that the inducing action of Co2+ and other metal ions on microsomal haem oxygenase involves either the covalent binding of the metal ions to some cellular component concerned directly with regulating haem oxygenase or non-specific complex-formation by the metal ions, which depletes some regulatory system in liver cells of an essential component involved in controlling synthesis or activity of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- 'Carra P. O., Colleran E. HAEM catabolism and coupled oxidation of haemproteins. FEBS Lett. 1969 Nov 29;5(4):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80372-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyland E., Chasseaud L. F. The effect of some carbonyl compounds on rat liver glutathione levels. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;19(4):1526–1528. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F., Sparks R. G. Iron-dependent loss of liver cytochrome P-450 haem in vivo and in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80545-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSEN L., ERIKSEN N., HAAVALDSEN S. The effect of cobalt ions on the biosynthesis of hemoglobin by rabbit reticulocytes in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Nov-Dec;53:300–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Anders M. W., Muller-Eberhard U. Studies on heme transfer from microsomal hemoproteins to heme-binding plasma proteins. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;10(2):204–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Kappas A. Cobalt induction of hepatic heme oxygenase; with evidence that cytochrome P-450 is not essential for this enzyme activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4293–4297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Kappas A. Cobalt stimulation of heme degradation in the liver. Dissociation of microsomal oxidation of heme from cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4171–4177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Kappas A. Study of the developmental pattern of heme catabolism in liver and the effects of cobalt on cytochrome P-450 and the rate of heme oxidation during the neonatal period. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1400–1410. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Kappas A. The degradative effects of porphyrins and heme compounds on components of the microsomal mixed function oxidase system. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2363–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver H. S., Tschudy D. P., Perlroth M. G., Collins A. Delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase. I. Studies in liver homogenates. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 25;241(12):2803–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol A. W. The formation of biliverdin from haemin suspensions by chicken macrophages in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 21;244(3):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. II. SOLUBILIZATION, PURIFICATION, AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai H. Quantitative microdetermination of total--SH groups in proteins. Anal Biochem. 1968 Nov;26(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tephly T. R., Hibbeln P. The effect of cobalt chloride administration on the synthesis of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 19;42(4):589–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90528-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS C. H., Jr, KAMIN H. Microsomal triphosphopyridine nucleotide-cytochrome c reductase of liver. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:587–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Takahashi S., Kikuchi G. Partial purification and reconstitution of the heme oxygenase system from pig spleen microsomes. J Biochem. 1974 May;75(5):1187–1191. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


