Abstract
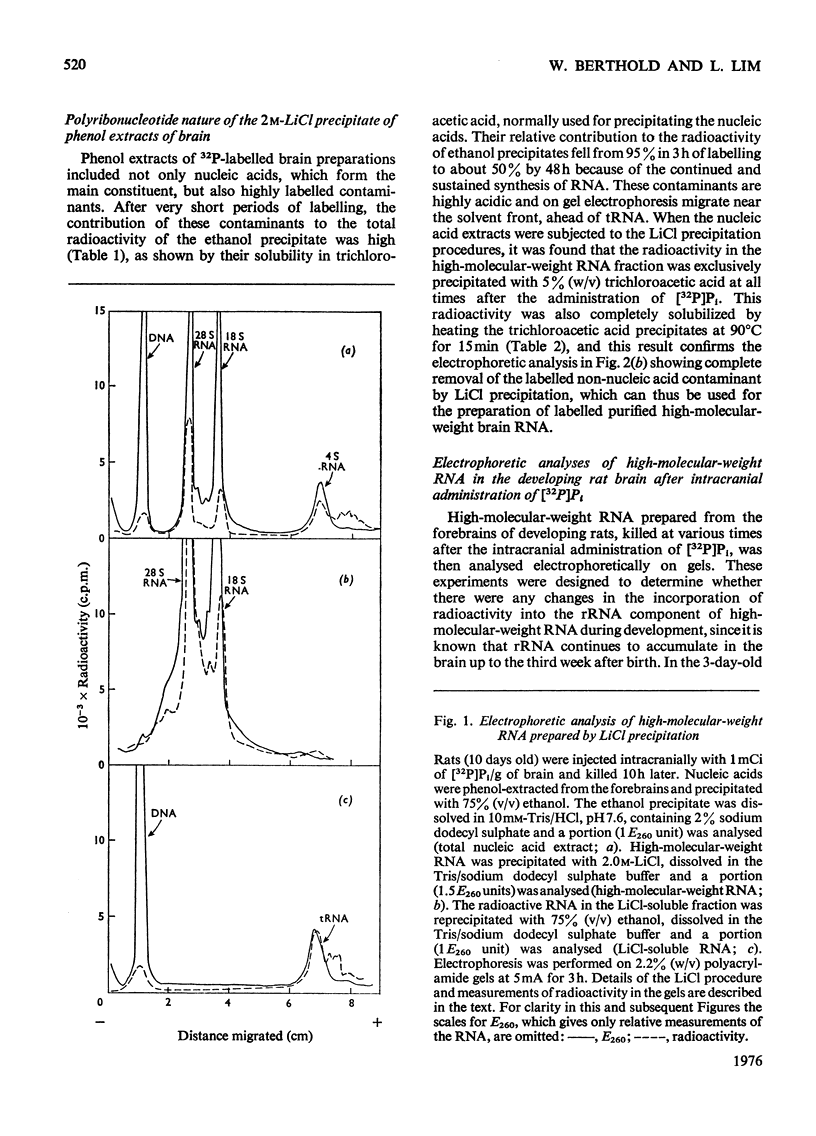
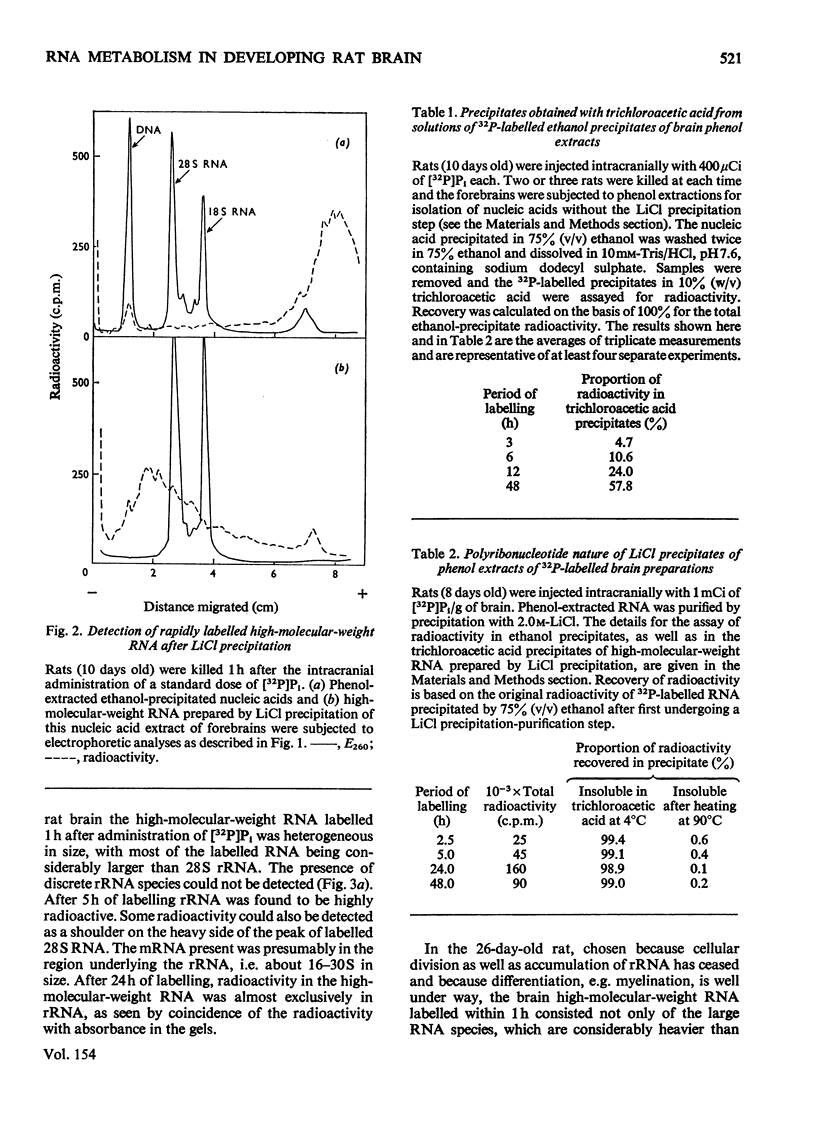
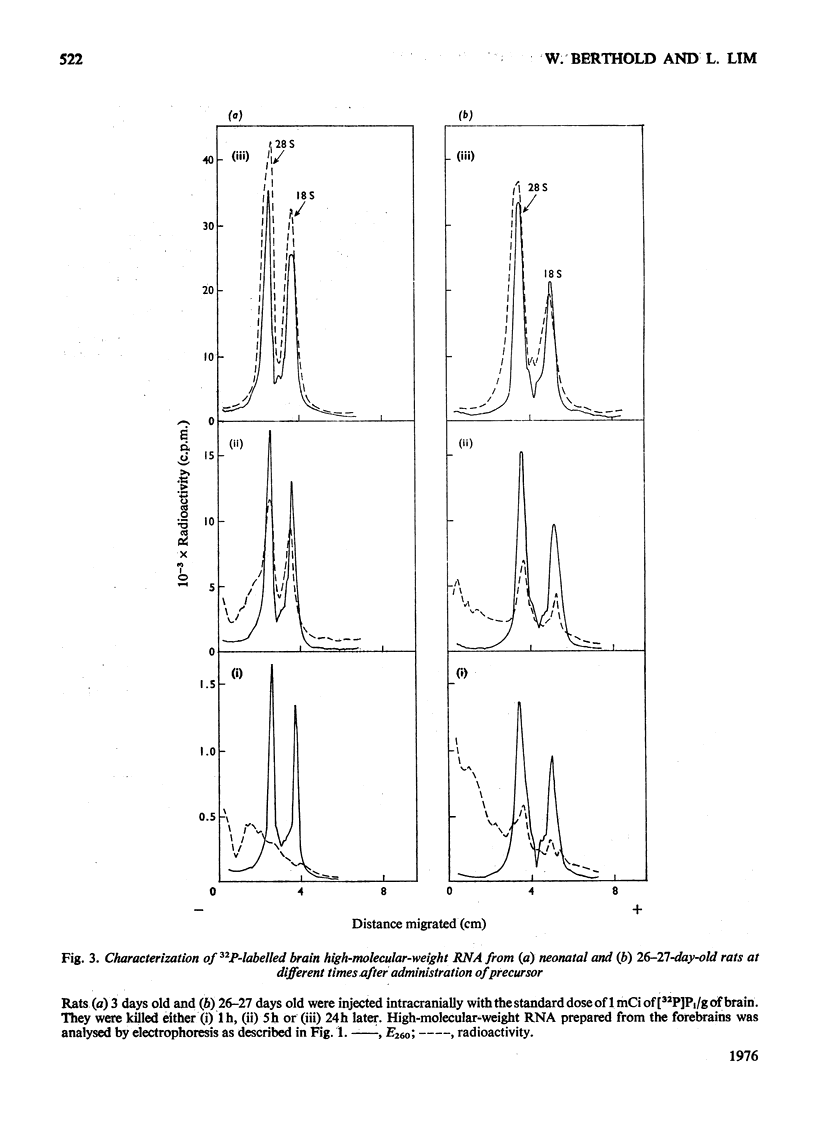
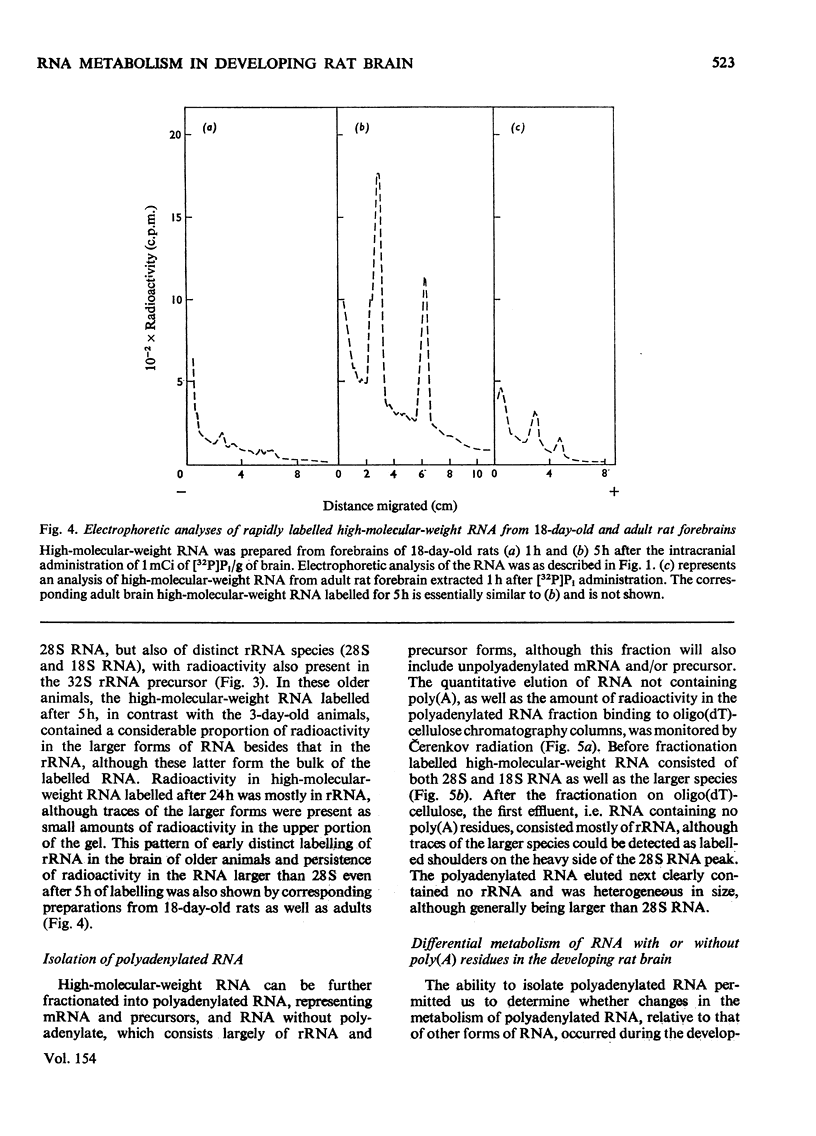
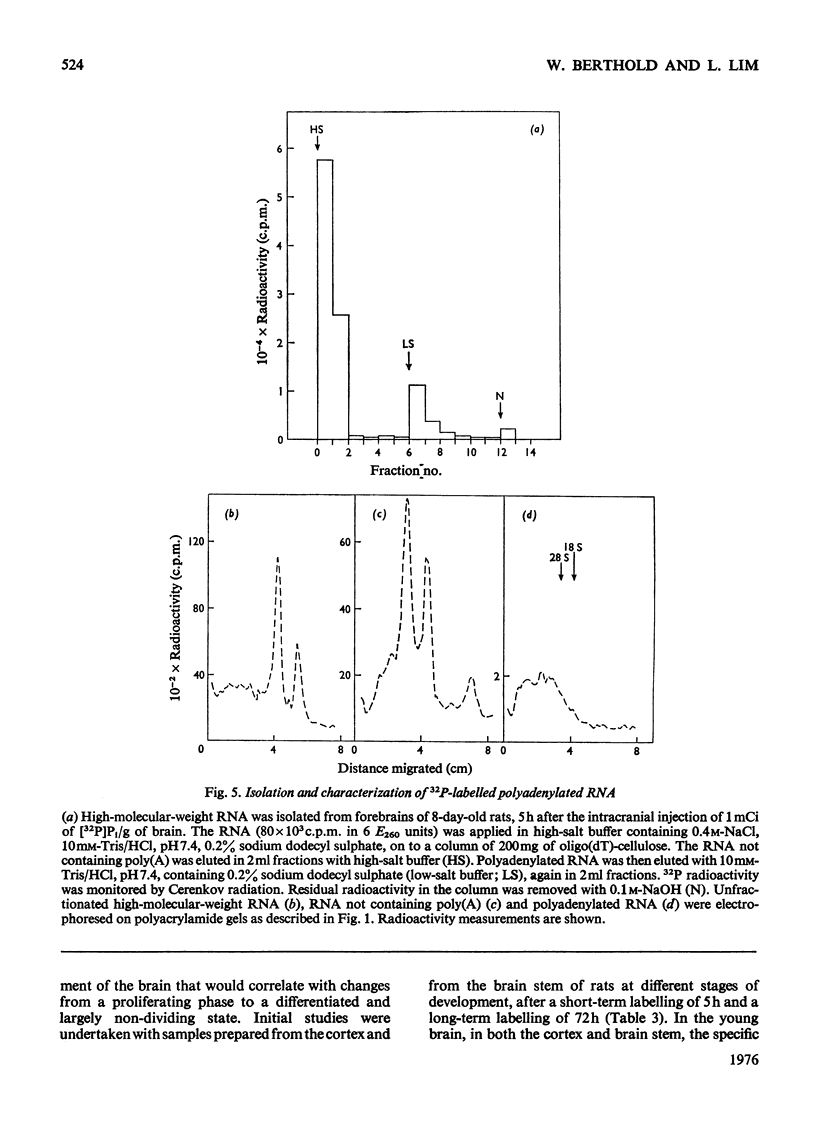
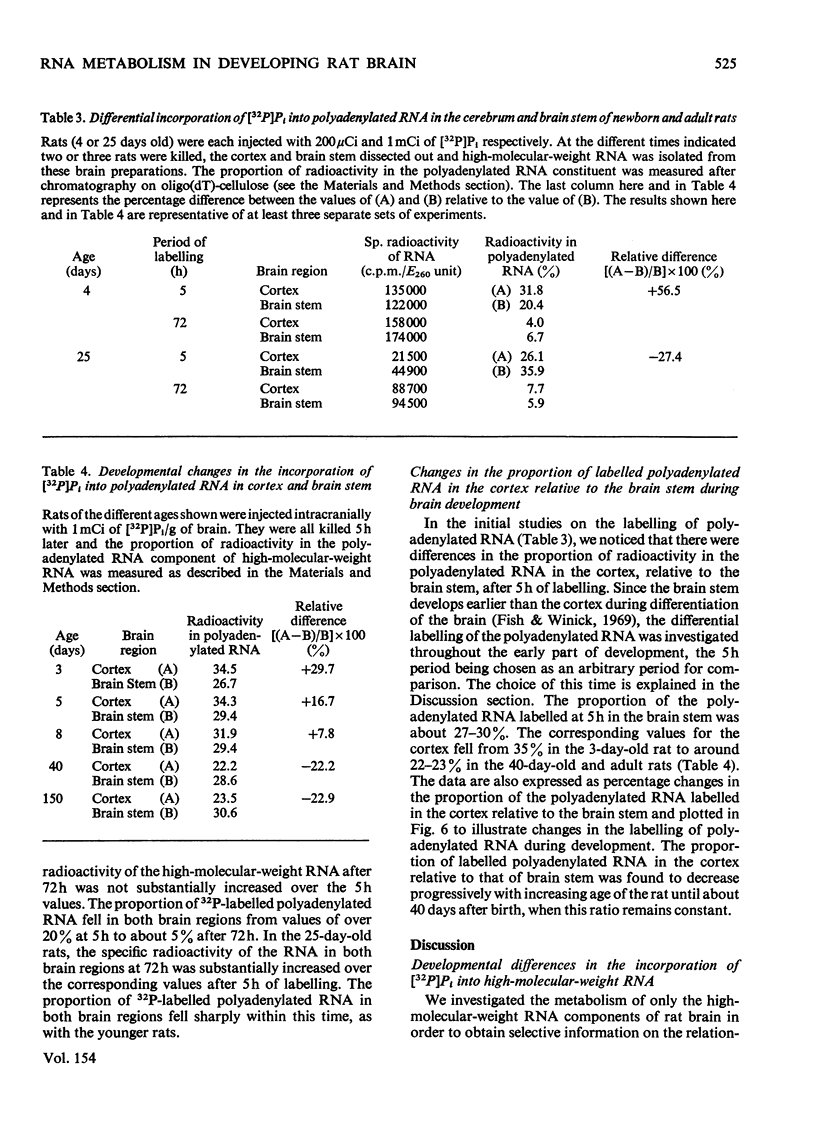
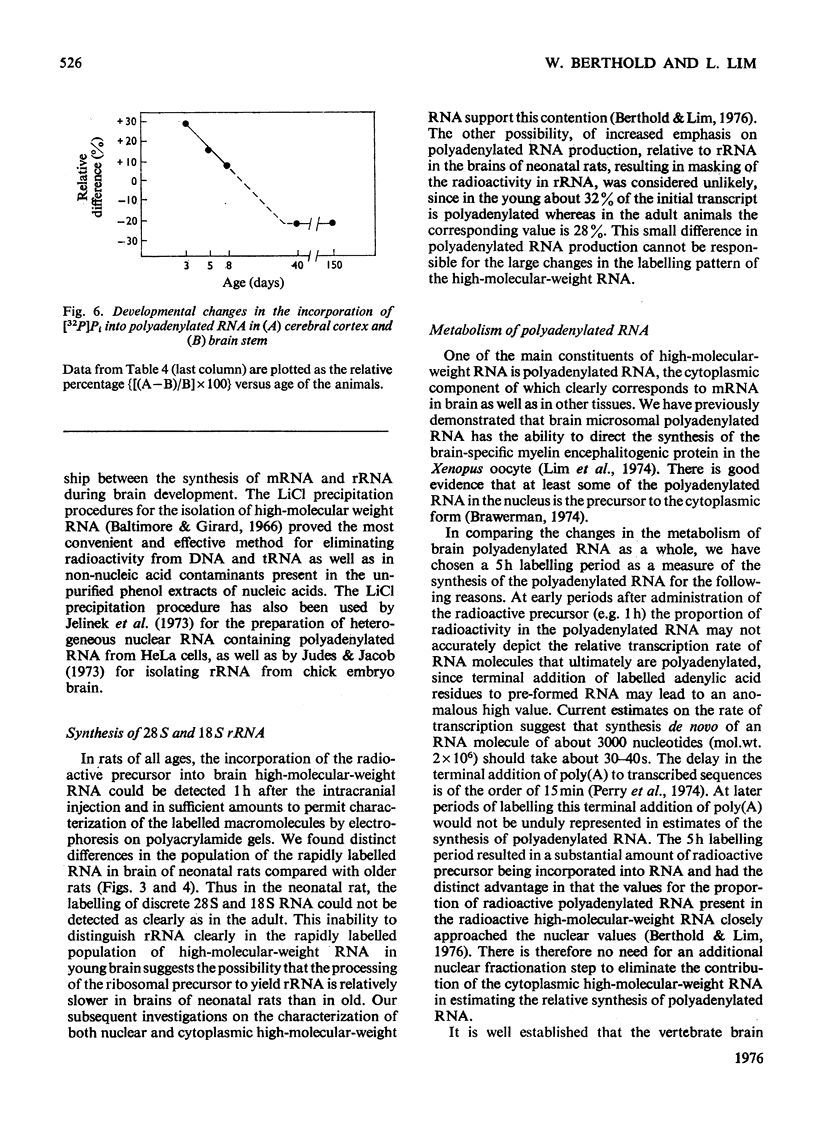
High-molecular-weight RNA was isolated from rat brain at various times after the intracranial administration of [32P]Pi. The synthesis of 28S and 18S rRNA could be detected within 1h of the injection of the radioactive precursor and appeared to be more pronounced, relative to other high-molecular-weight RNA, in the brains of older rats compared with those of newborn rats. Polyadenylated RNA, representing most mRNA and their precursors, was isolated by chromatography on oligo(dT)-cellulose. The contribution of this polyadenylated RNA to total RNA synthesis was investigated in the cerebral cortex and the phylogenetically older brain stem at different stages in the development of the rats by using a 5h period of labelling as an arbitrary index of transcription. In the brain stem the proportion of labelled polyadenylated RNA comprised 27-30% of the total RNA. The corresponding values for the cortex decreased from 34% in newborn rats to 23% in 40-150-day-old rats. These data indicated that proportionately more polyadenylated RNA is synthesized in the cortex of the newborn than in the adult rat and that there is a progressive decrease in the synthesis of polyadenylated RNA relative to rRNA during development.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. H. The relationship between cellular nucleic acids in the developing rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):636–640. doi: 10.1042/bj0980636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R. Influence of metabolic factors on brain development. Br Med Bull. 1974 May;30(2):126–134. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balázs R., Kovács S., Teichgräber P., Cocks W. A., Eayrs J. T. Biochemical effects of thyroid deficiency on the developing brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Nov;15(11):1335–1349. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold W., Lim L. Nucleo-cytoplasmic relationships of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid, including polyadenylated species, in the developing rat brain. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 15;154(2):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1540529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy S. C., Roberts S. Hybridizable ribonucleic acid of rat brain. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1090533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Eukaryotic messenger RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):621–642. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish I., Winick M. Cellular growth in various regions of the developing rat brain. Pediatr Res. 1969 Sep;3(5):407–412. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196909000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Adesnik M., Salditt M., Sheiness D., Wall R., Molloy G., Philipson L., Darnell J. E. Further evidence on the nuclear origin and transfer to the cytoplasm of polyadenylic acid sequences in mammalian cell RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):515–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judes C., Jacob M. Differentiation of chick embryo cerebral hemispheres. II. Incorporation of ( 3 H)uridine into 29 S, 18 S, 5 S and 4 S RNA. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 15;51:253–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90377-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis E. S. Adenine-rich polymer associated with rabbit reticulocyte messenger RNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):710–712. doi: 10.1038/227710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis Z. N., Canellakis E. S. Metabolism of naturally occurring homopolymers. I. The isolation and metabolism of adenine-rich polynucleotides of mouse liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 21;209(1):112–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., White J. O., Hall C., Berthold W., Davison A. N. Isolation of microsomal poly(A)-RNA from rat brain directing the synthesis of the myelin encephalitogenic protein in Xenopus oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 29;361(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., LaTorre J. Synthesis and turnover of nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylic acid in mouse L cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


