Abstract
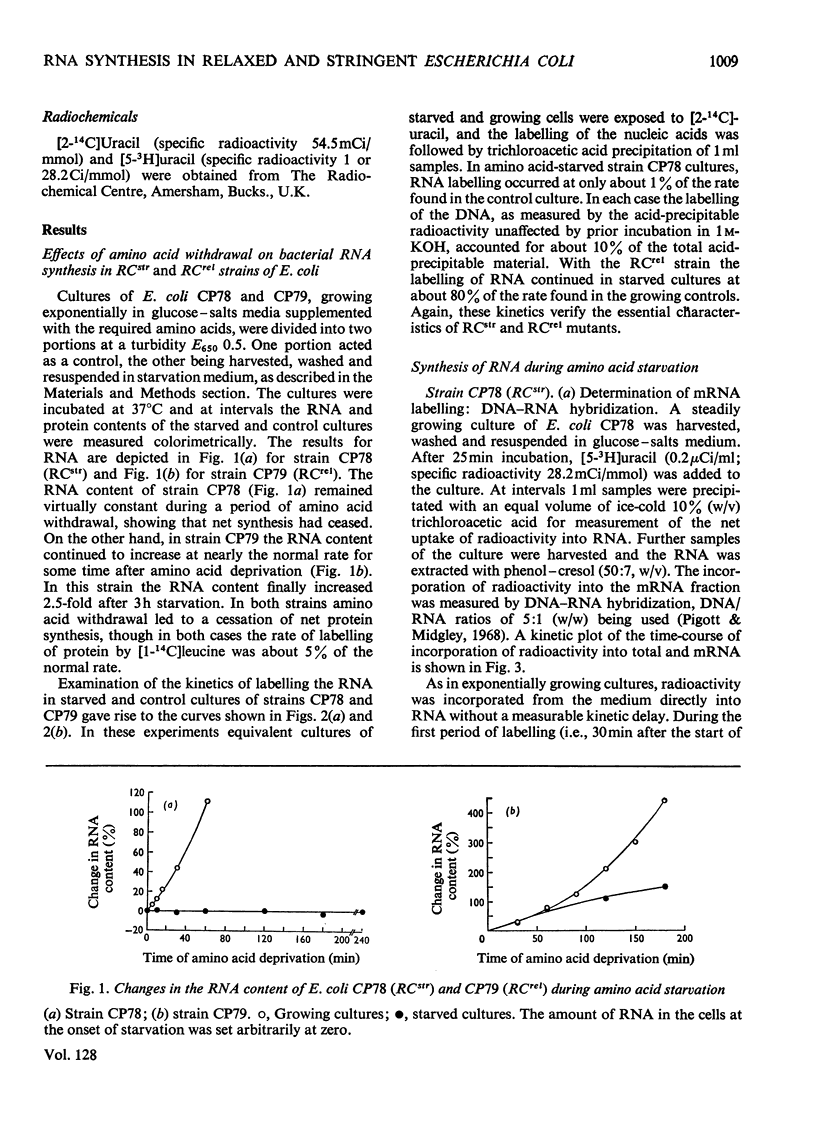
The biosynthesis and stability of various RNA fractions was studied in RCstr and RCrel multiple amino acid auxotrophs of Escherichia coli. In conditions of amino acid deprivation, RCstr mutants were labelled with exogenous nucleotide bases at less than 1% of the rate found in cultures growing normally in supplemented media. Studies by DNA–RNA hybridization and by other methods showed that, during a period of amino acid withdrawal, not more than 60–70% of the labelled RNA formed in RCstr mutants had the characteristics of mRNA. Evidence was obtained for some degradation of newly formed 16S and 23S rRNA species to heterogeneous material of lower molecular weight. This led to overestimations of the mRNA content of rapidly labelled RNA from such methods as simple examination of sucrose-density-gradient profiles. In RCrel strains the absolute and relative rates of synthesis of the various RNA fractions were not greatly affected. However, the stability of about half of the mRNA fraction was increased in RCrel strains during amino acid starvation, giving kinetics of mRNA labelling and turnover that were identical with those found in either RCstr or RCrel strains inhibited by high concentrations of chloramphenicol. Coincidence hybridization techniques showed that the mRNA content of amino acid-starved RCstr auxotrophs was unchanged from that found in normally growing cells. In contrast, RCrel strains deprived of amino acids increased their mRNA content about threefold. In such cultures the mRNA content of accumulating newly formed RNA was a constant 16% by wt.
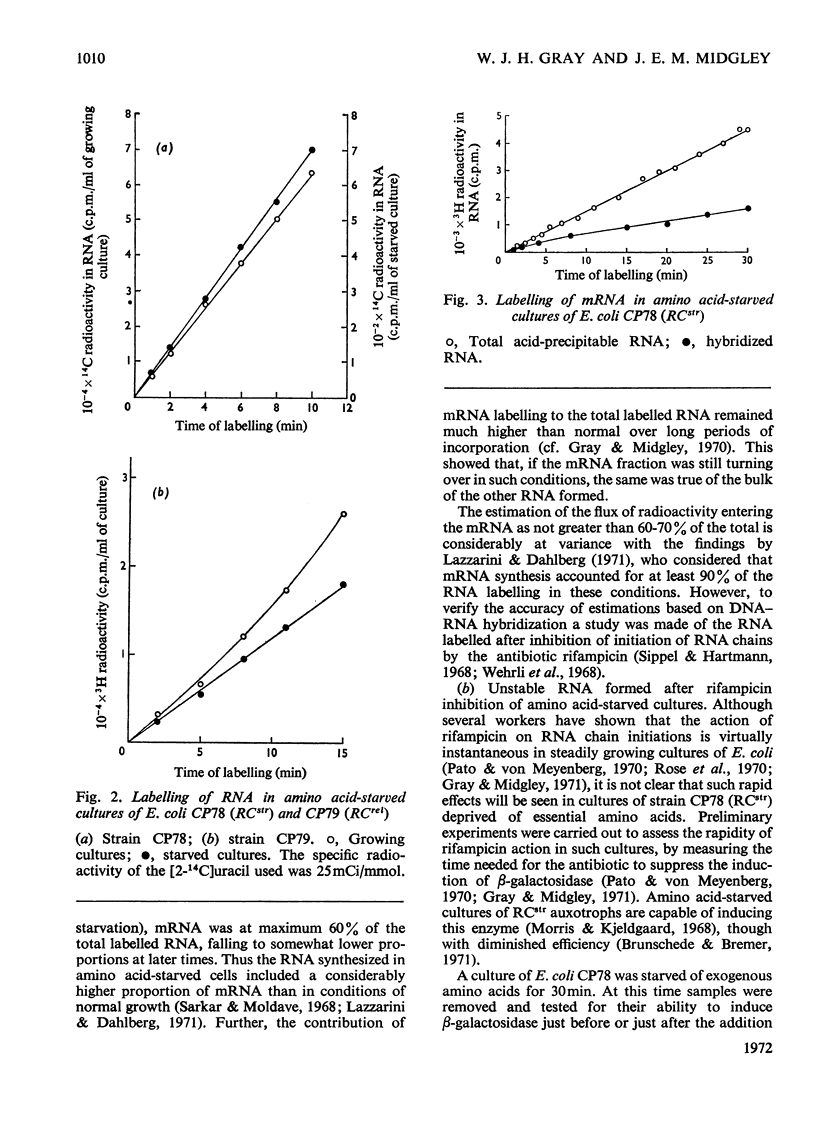
Full text
PDF

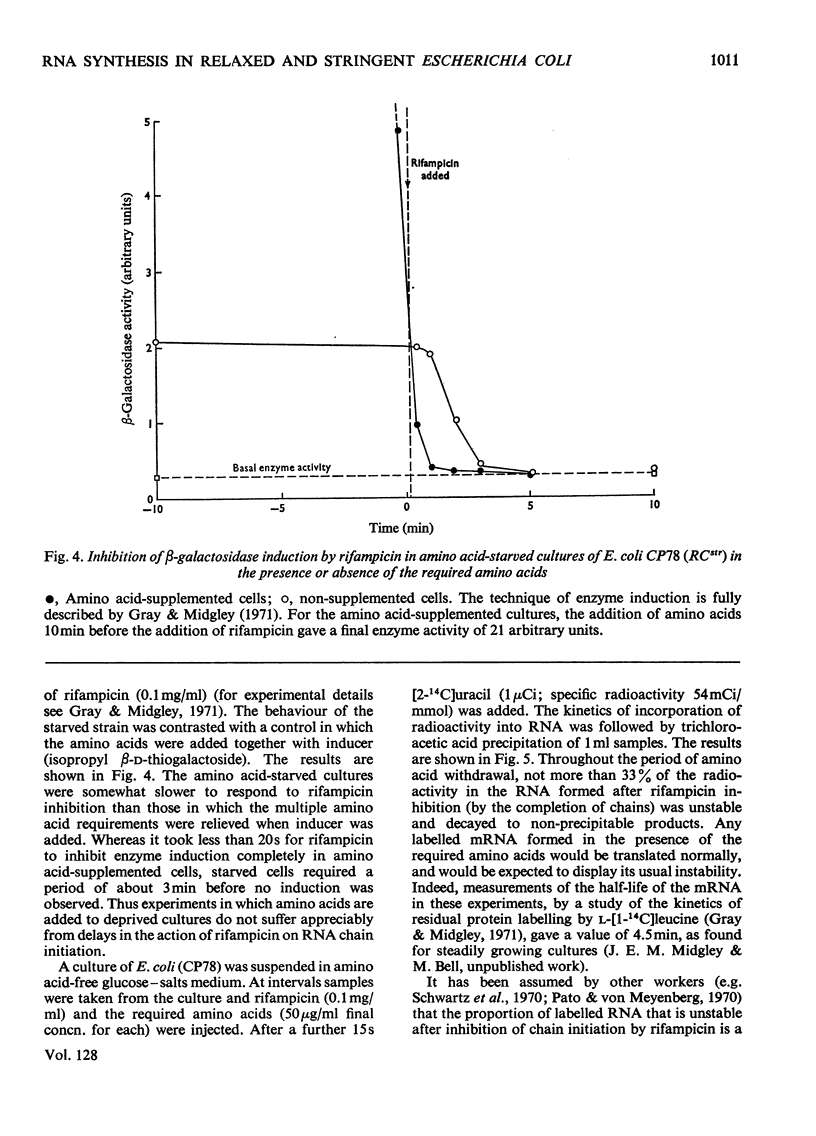

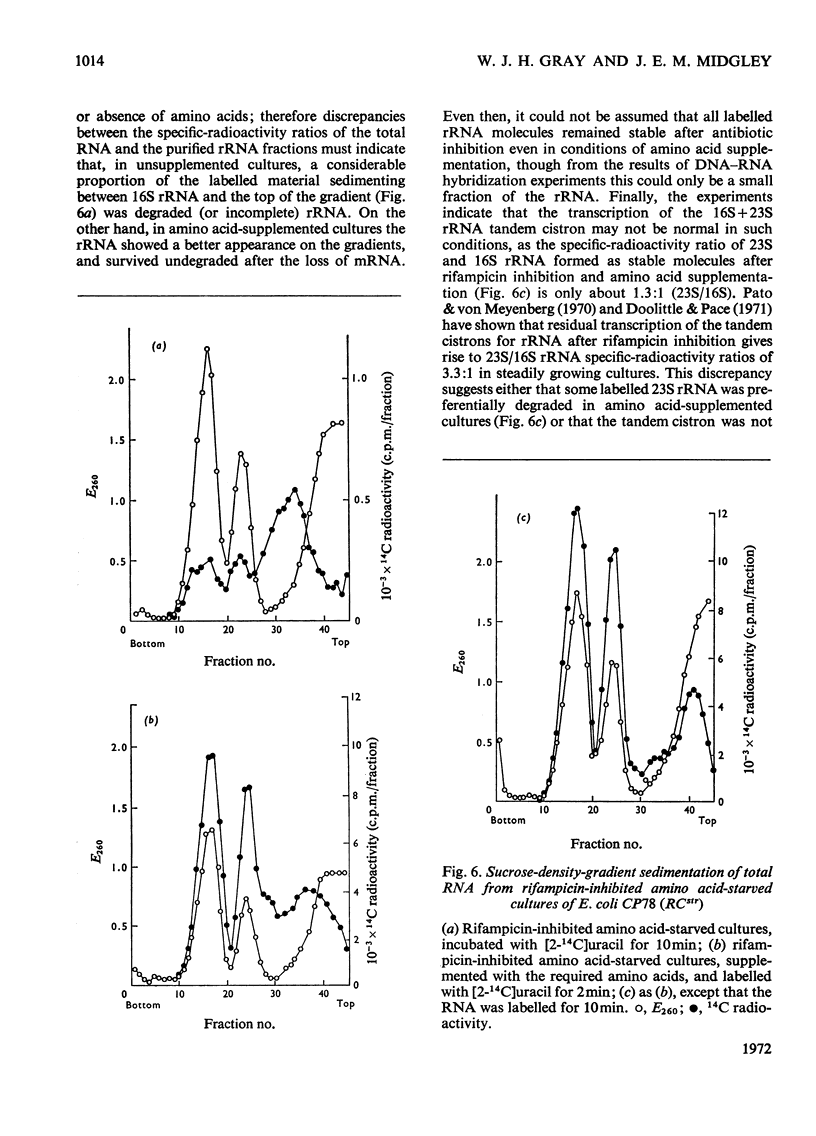
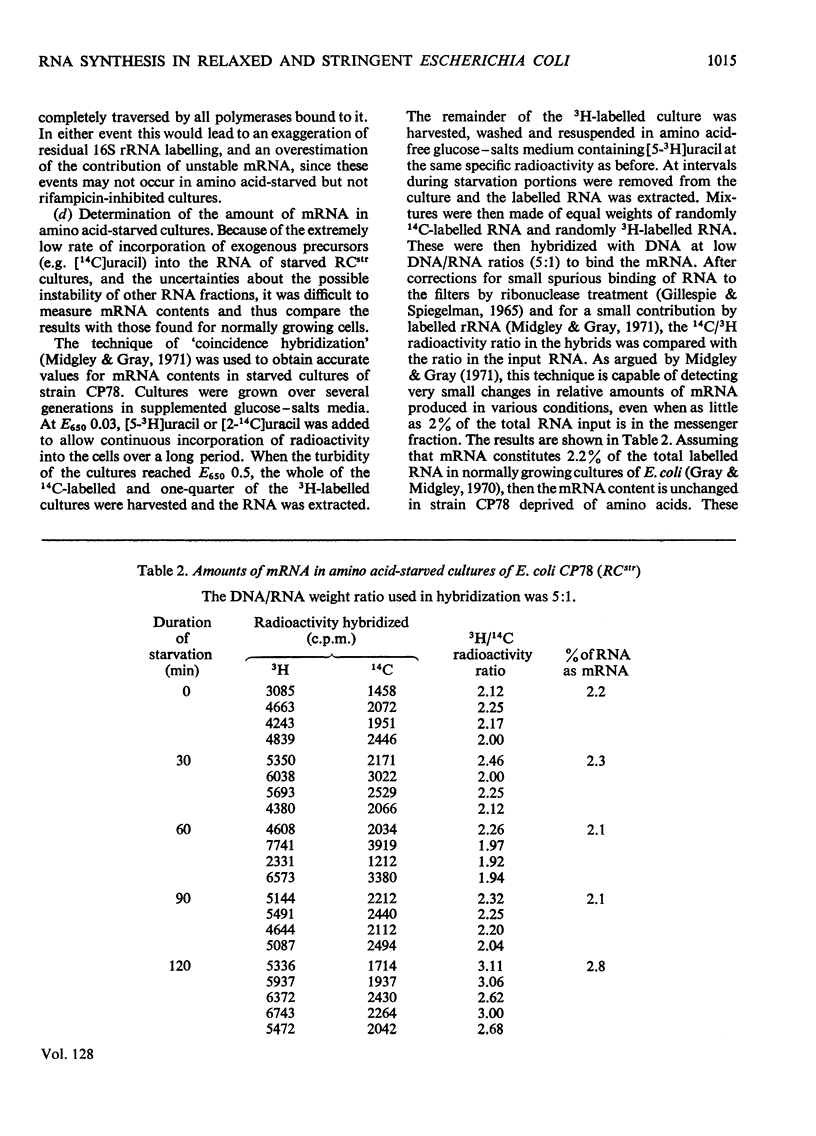
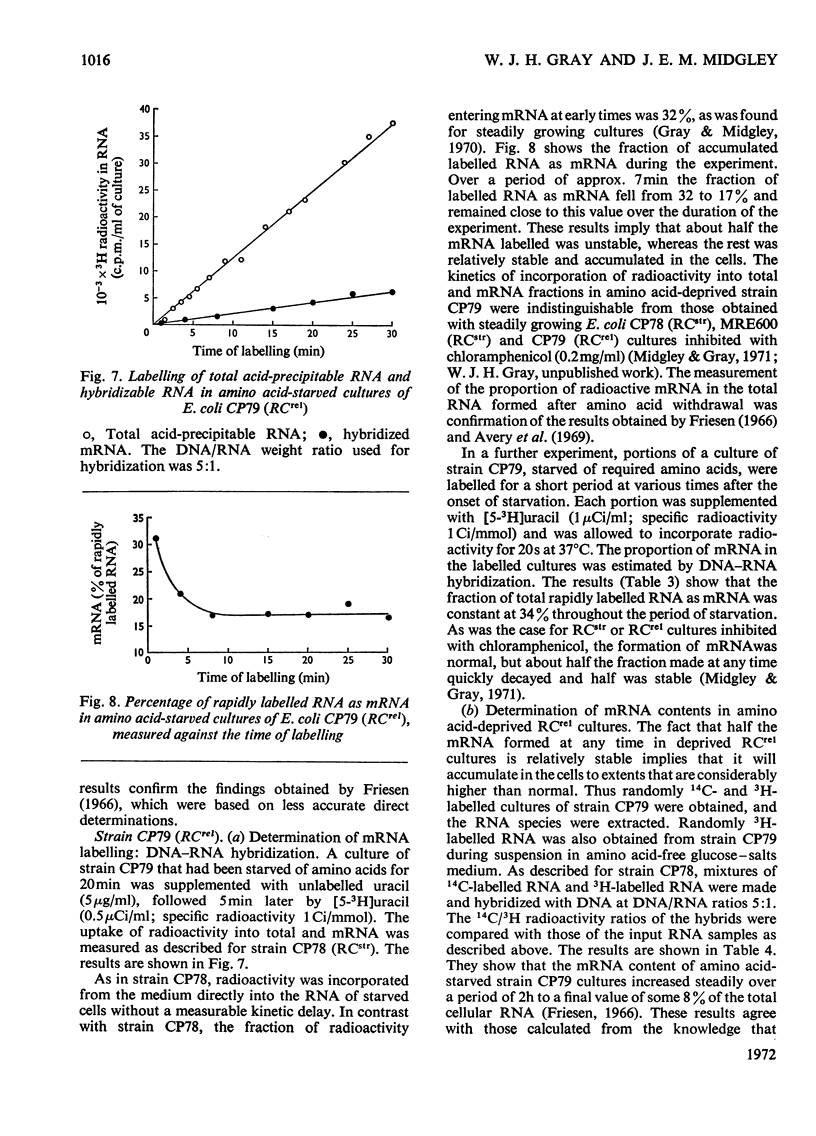
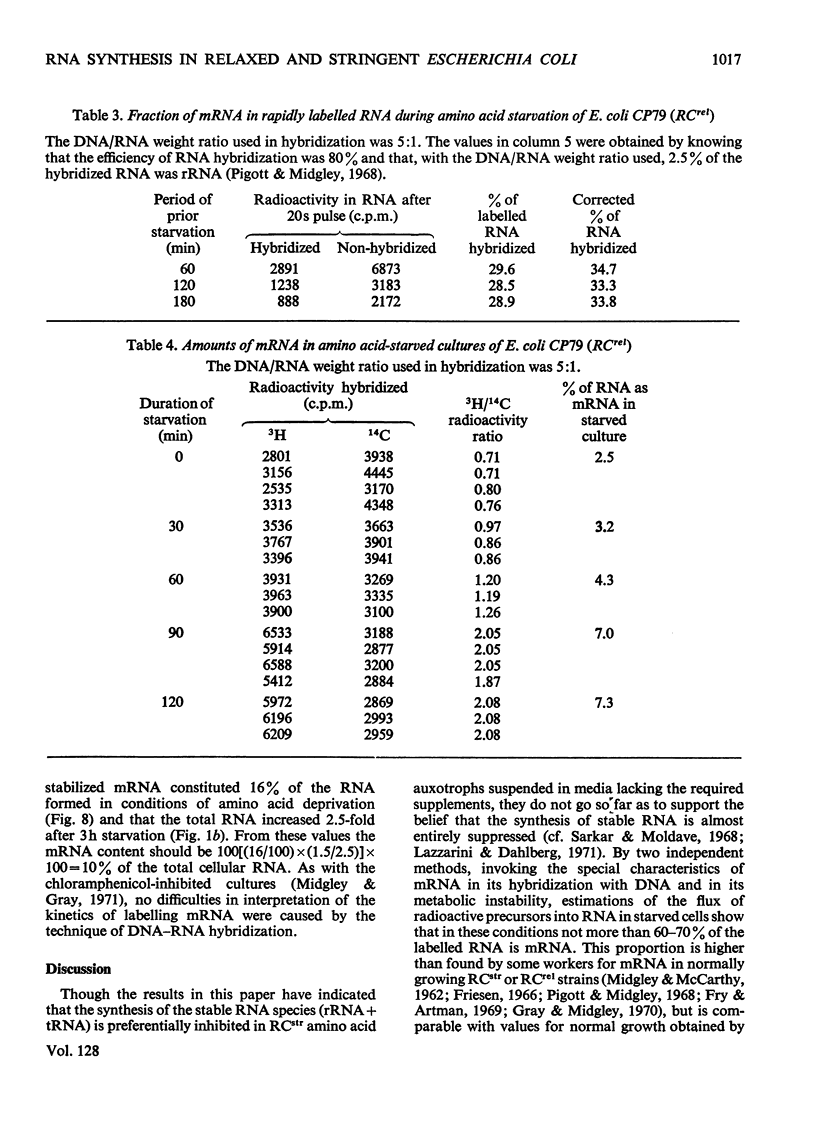



Selected References
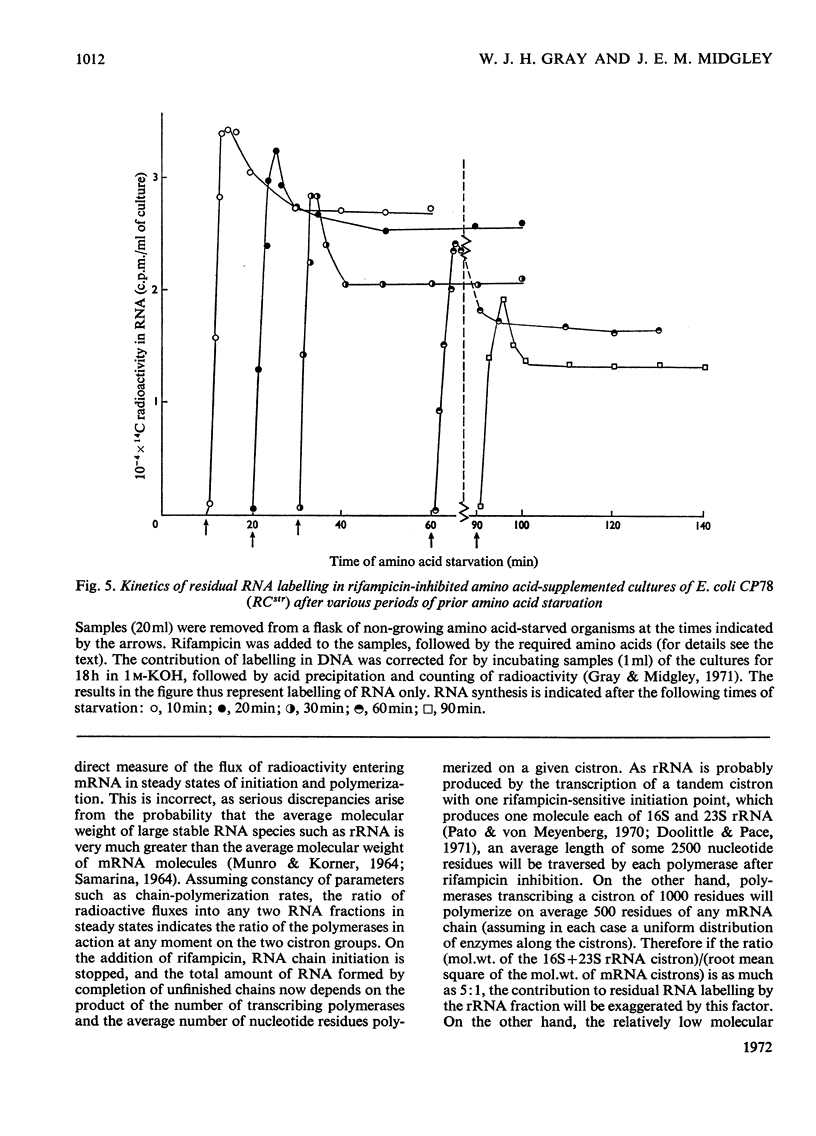
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman S. Isolation of tyrosine tRNA precursor molecules. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 6;229(1):19–21. doi: 10.1038/newbio229019a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony D. D., Goldthwait D. A., Wu C. W. Studies with the ribonucleic acid polymerase. II. Kinetic aspects of initiation and polymerization. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):246–256. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery R. J., Midgley J. E. A new approach to the analysis of hybridization of bacterial nucleic acids. Analysis of the ribosomal ribonucleic acids of Bacillus subtilis. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):383–394. doi: 10.1042/bj1150383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avery R. J., Midgley J. E., Pigott G. H. An analysis of the ribosomal ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli by hybridization techniques. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):395–403. doi: 10.1042/bj1150395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOREK E., RYAN A., ROCKENBACH J. Nucleic acid metabolism in relation to the lysogenic phenomenon. J Bacteriol. 1955 Apr;69(4):460–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.4.460-467.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOREK E., RYAN A. Studies on a mutant of Escherichia coli with unbalanced ribonucleic acid synthesis. II. The concomitance of ribonucleic acid synthesis with resumed protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jan;75(1):72–76. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.1.72-76.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunschede H., Bremer H. Synthesis and breakdown of proteins in Escherichia coli during amino-acid starvation. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):35–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. IV. Relevance of unusual phosphorylated compounds from amino acid-starved stringent strains. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3133–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., TURNOCK G., WILD D. G. THE ACCUMULATION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID BY A MUTANT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:555–566. doi: 10.1042/bj0880555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle W. F., Pace N. R. Transcriptional organization of the ribosomal RNA cistrons in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1786–1790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlin G., Stent G. S., Baker R. F., Yanofsky C. Synthesis of a specific messenger RNA during amino acid starvation of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 28;37(2):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISSNER E., BOREK E. A new enzyme of RNA synthesis: RNA methylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1199–1203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL D. G., NEIDHARDT F. C. Use of chloramphenicol to study control of RNA synthesis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:96–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90797-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil N., Friesen J. D. Isolation of "relaxed" mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.729-731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forchhammer J., Kjeldgaard N. O. Regulation of messenger RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 28;37(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen J. D. A study of the relationship between polyribosomes and messenger RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):183–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen J. D. Control of messenger RNA synthesis and decay in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct;20(3):559–573. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M., Artman M. Studies of newly synthesized ribosomal ribonucleic acid of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):295–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1150295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J., Cashel M. On the mechanism of amino acid control of ribonucleic acid biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant J., Harada B. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. 3. The functional relationship between purine ribonucleoside triphosphate pool sizes and the rate of ribonucleic acid accumulation. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3125–3132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. J., Midgley J. E. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteria. Steady-state content of messenger ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli M.R.E. 600. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):279–288. doi: 10.1042/bj1200279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. J., Midgley J. E. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteria. The synthesis and stbility of ribonucleic acid in rifampicin-inhibited cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Apr;122(2):161–169. doi: 10.1042/bj1220161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurgo C., Apirion D., Schlessinger D. Polyribosome metabolism in Escherichia coli treated with chloramphenicol, neomycin, spectinomycin or tetracycline. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):205–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G., Gallant J. A. Effect of the RC gene product on constitutive enzyme synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):271–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen S. E., Buch L. B., Nierlich D. P. Nucleoside triphosphate termini from RNA synthesized in vivo by Escherichia coli. Science. 1969 May 30;164(3883):1067–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3883.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND C. G., MAALOE O. Regulation of ribosomal and transfer RNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:193–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel D. Titration of the gene sites on DNA by DNA-RNA hybridization. II. The Escherichia coli chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):85–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Schlessinger D., Apirion D. Ribonuclease V of Escherichia coli requires ribosomes and is inhibited by drugs. Nature. 1970 May 9;226(5245):514–516. doi: 10.1038/226514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavallé R., De Hauwer G. Messenger RNA synthesis during amino acid starvation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 28;37(2):269–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90267-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Dahlberg A. E. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis during amino acid deprivation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):420–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDGLEY J. E., McCARTHY B. J. The synthesis and kinetic behavior of deoxyribonucleic acid-like ribonucleic acid in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 26;61:696–717. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90053-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNRO A. J., KORNER A. MESSENGER RIBONUCLEIC ACID OF RAT LIVER CYTOPLASM. Nature. 1964 Mar 21;201:1194–1197. doi: 10.1038/2011194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley J. E., Gray W. J. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in bacteria. The synthesis and stability of ribonucleic acid in chloramphenicol-inhibited cultures of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Apr;122(2):149–159. doi: 10.1042/bj1220149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. E., Guertin M. Regulation of mRNA utilization and degradation by amino-acid starvation. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 11;232(2):165–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio232165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller K., Bremer H. Rate of synthesis of messenger ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):329–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierlich D. P. Amino acid control over RNA synthesis: a re-evaluation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1345–1352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pigott G. H., Midgley J. E. Characterization of rapidly labelled ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli by deoxyribonucleic acid-ribonucleic acid hybridization. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(2):251–263. doi: 10.1042/bj1100251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Gruber M. Control of stable-RNA synthesis and maturation of 5-S RNA in Salmonella typhimurium RC-str and RC-rel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 11;232(2):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Mosteller R. D., Yanofsky C. Tryptophan messenger ribonucleic acid elongation rates and steady-state levels of tryptophan operon enzymes under various growth conditions. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAMARINA O. P. THE DISTRIBUTION AND PROPERTIES OF CYTOPLASMIC DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID-LIKE RIBONUCLEIC ACID (MESSENGER RIBONUCLEIC ACID). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 16;91:688–691. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., BRENNER S. A genetic locus for the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2005–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W., Janin J., Levinthal C. Measurement of the unstable RNA in exponentially growing cultures of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):237–266. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Moldave K. Characterization of the ribonucleic acid synthesized during amino acid-deprivation of a stringent auxotroph of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz T., Craig E., Kennell D. Inactivation and degradation of messenger ribnucleic acid from the lactose operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):299–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokawa Y., Sokawa J., Kaziro Y. Function of the rel gene in Escherichia coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 3;234(44):7–10. doi: 10.1038/newbio234007a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs J. D., Hall B. D. Level of tryptophan messenger RNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 28;37(2):289–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman A. J., Gilvarg C. Protein turnover in amino acid-starved strains of Escherichia coli K-12 differing in their ribonucleic acid control. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6304–6306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNOCK G., WILD D. G. THE SYNTHESIS OF RIBOSOMES BY A MUTANT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:597–607. doi: 10.1042/bj0950597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. A., Varney N. F., Burton K. Nucleic acid synthesis and nucleotide pools in purine-deficient Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):117–124. doi: 10.1042/bj1200117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. Control of transcription in bacteria. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 20;229(3):69–74. doi: 10.1038/newbio229069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAZQUEZ D. UPTAKE AND BINDING OF CHLORAMPHENICOL BY SENSITIVE AND RESISTANT ORGANISMS. Nature. 1964 Jul 18;203:257–258. doi: 10.1038/203257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varney N. F., Thomas G. A., Burton K. Synthesis of ribonucleic acid in purine-deficient Escherichia coli and a comparison with the effects of amino acid starvation. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(1):125–132. doi: 10.1042/bj1200125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers T. G., Midgley J. E. Evidence for tRNA precursors in bacteria. Nature. 1971 Oct 13;233(5320):210–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Nüesch J., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycins on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. M., Lazzarini R. A. Amino acid regulation of the rates of synthesis and chain elongation of ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3387–3392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. M., Lazzarini R. A. The rates of synthesis and chain elongation of ribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1128–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Goldthwait D. A. Studies of nucleotide binding to the ribonucleic acid polymerase by a fluoresence technique. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4450–4458. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Goldthwait D. A. Studies of nucleotide binding to the ribonucleic acid polymerase by equilibrium dialysis. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4458–4464. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


