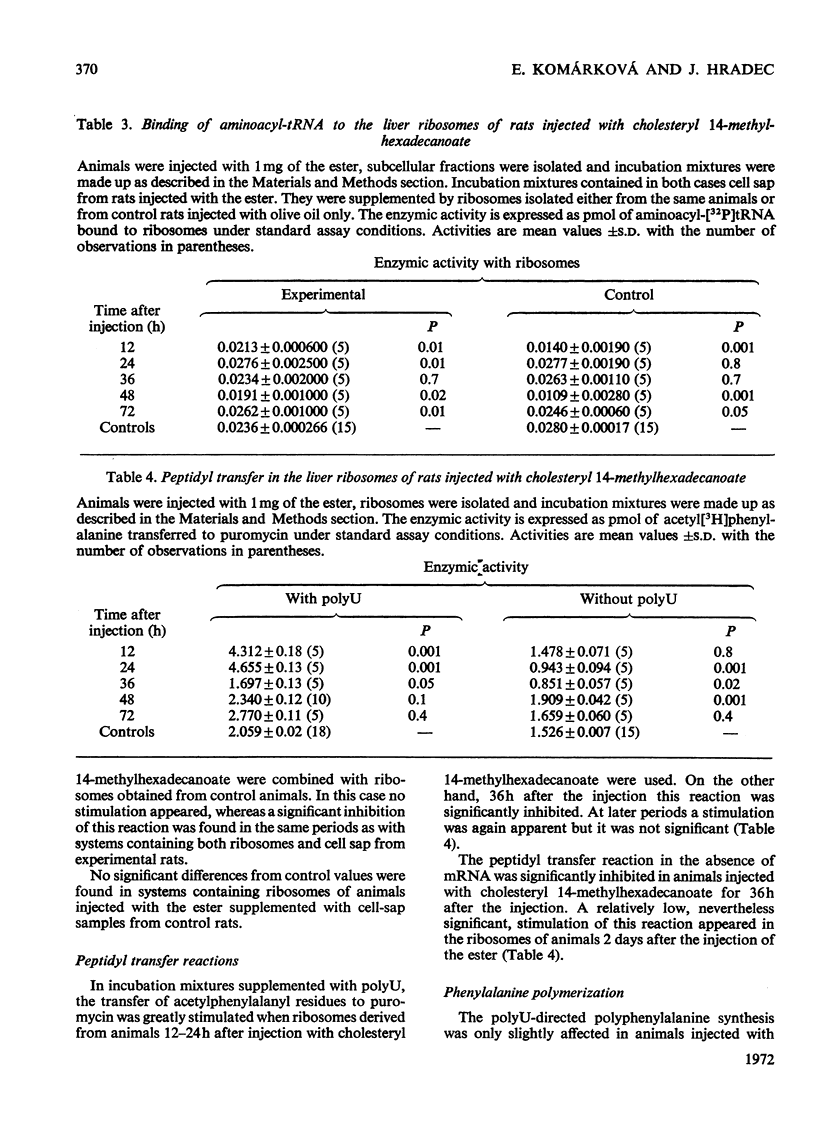
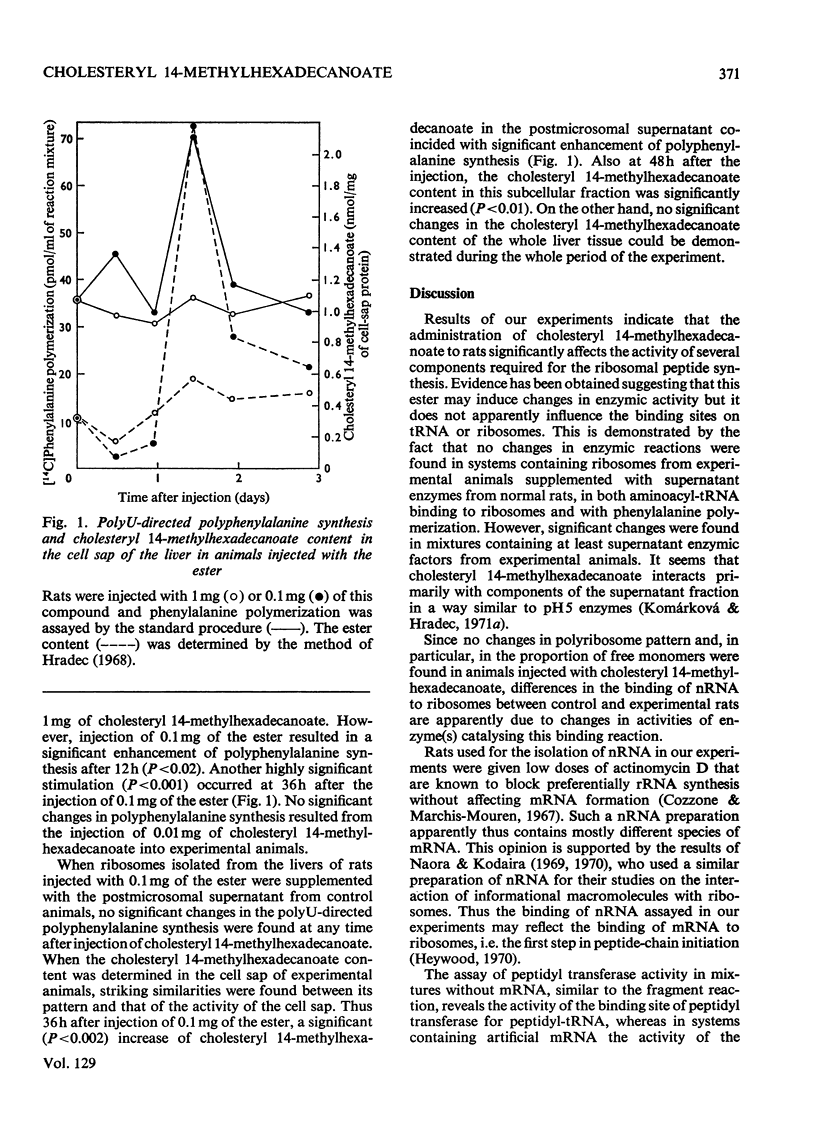
Abstract
1. Rats were injected intraperitoneally with cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate and killed after various intervals of time up to 3 days; ribosomes and cell sap were isolated from their liver tissue. These fractions were tested for their ability to participate in protein synthesis. 2. Protein synthesis in complete systems containing ribosomes, cell sap and all necessary cofactors was significantly enhanced at 12 and 72h after the injection and significantly inhibited at 24h. At early times after injection isolated ribosomes had a slightly enhanced ability to bind nRNA. Peptide-elongation processes (i.e. binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to ribosomes, peptidyl transfer and polyphenylalanine synthesis) showed significant stimulation or inhibition depending on the time after injection of the ester. 3. A correlation was found between the ability of cell sap to stimulate polyphenylalanine synthesis and the relative cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate content in the postmicrosomal supernatant at different time-intervals after administration of the ester. No significant changes were found in its content in the whole liver tissue. 4. Since the injected ester has previously been shown to accumulate in some enzymic fractions, the changes in its relative content may represent a regulatory mechanism modulating the rate of protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cozzone A., Marchis-Mouren G. Messenger ribonucleic acid stability in rat pancreas and liver. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3911–3917. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnoff J. S., Maitra U. Isolation and properties of polypeptide chain initiation factor FII from Escherichia coli: evidence for a dual function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):318–323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnoff J. S., Maitra U. Protein factors involved in polypeptide chain initiation in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:301–306. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Chapeville F. The behaviour of acetylphenylalanyl soluble ribonucleic acid in polyphenylalanine synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M. Specificity of mRNA binding factor in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1782–1788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Thompson W. C. Studies on the formation of the initiation complex in eukaryotes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):470–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J. A chromatographic method for the quantitative determination of cholesterol 14-methylhexadecanoate (carcinolipin) in biological materials. J Chromatogr. 1968 Feb 6;32(3):511–518. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dolejs L. The chemical constitution of carcinolipin. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1070129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dusek Z., Bermek E., Matthaei H. The role of cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate in peptide elongation reactions. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):959–966. doi: 10.1042/bj1230959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dusek Z. Effect of cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate on the activity of some amino acid-transfer ribonucleic acid ligases from mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1969 Dec;115(5):873–880. doi: 10.1042/bj1150873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J., Dusek Z. Effect of lipids, in particular cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate, on the incorporation of labelled amino acids into transfer ribonucleic acid in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Nov;110(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bj1100001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradec J. Intermediate reactions in the binding of aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid to rat liver ribosomes. Formation and properties of an aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid-transferase I complex. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):923–931. doi: 10.1042/bj1260923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerwar S. S., Spears C., Weissbach H. Studies on the initiation of protein synthesis in animal tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):78–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komárková E., Hradec J. Changes of aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis in the liver of rats administered cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr;14(2):130–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80118-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komárková E., Hradec J. Effect of cholesteryl 14-methylhexadecanoate on the RNA polymerase activity of rat liver nuclei in vivo and in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 15;18(1):109–111. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80420-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Bursztyn H. Initiation of protein synthesis II. A convenient assay for the ribosome-dependent synthesis of N-formyl-C14-methionylpuromycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Haenni A. L. Release of transfer RNA during peptide chain elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):93–97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthaei H., Sander G., Swan D., Kreuzer T., Caffier H., Parmeggiani A. Reaktionsschritte der Polypeptidsynthese an Ribosomen. Mechanismen der Proteinsynthese X. Naturwissenschaften. 1968 Jun;55(6):281–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00591706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeehan W. L., Hardesty B. Purification and partial characterization of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding enzyme from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4330–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertelsmann R. Purification and some properties of a soluble DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from nuclei of human placenta. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(3):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Marcker K. A. Ribosome-catalysed reaction of puromycin with a formylmethionine-containing oligonucleotide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Staehelin T., Celma M. L., Vazquez D. The peptidyl transferase activity of ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:357–368. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naora H., Kodaira K. Interaction of informational macromolecules with ribosomes. 3. Binding of nuclear RNA by normal liver and hepatoma ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 14;224(2):498–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naora H., Kodaira K. Interaction of informational macromolecules with ribosomes. I. Binding of labeled nuclear RNA by rat liver ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;182(2):469–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneir M., Moldave K. The isolation and biological activity of multiple forms of aminoacyl transferase I of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug 23;166(1):58–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siler J., Moldave K. Studies on the kinetics of peptidyl transfer RNA translocase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 19;195(1):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90610-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogerson L., Moldave K. Evidence for the role of aminoacyltransferase II in peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid translocation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5361–5367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D., Battaner E., Neth R., Heller G., Monro R. E. The function of 80 S ribosomal subunits and effects of some antibiotics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:369–375. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


