Abstract
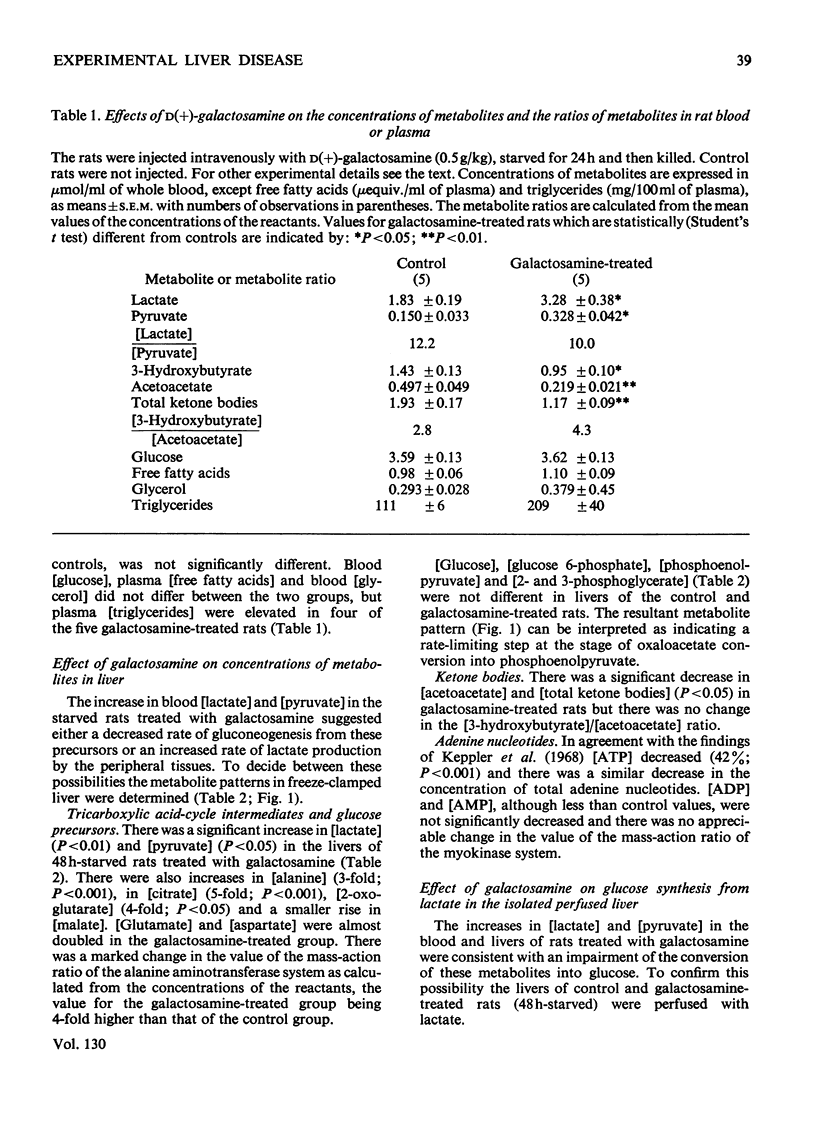
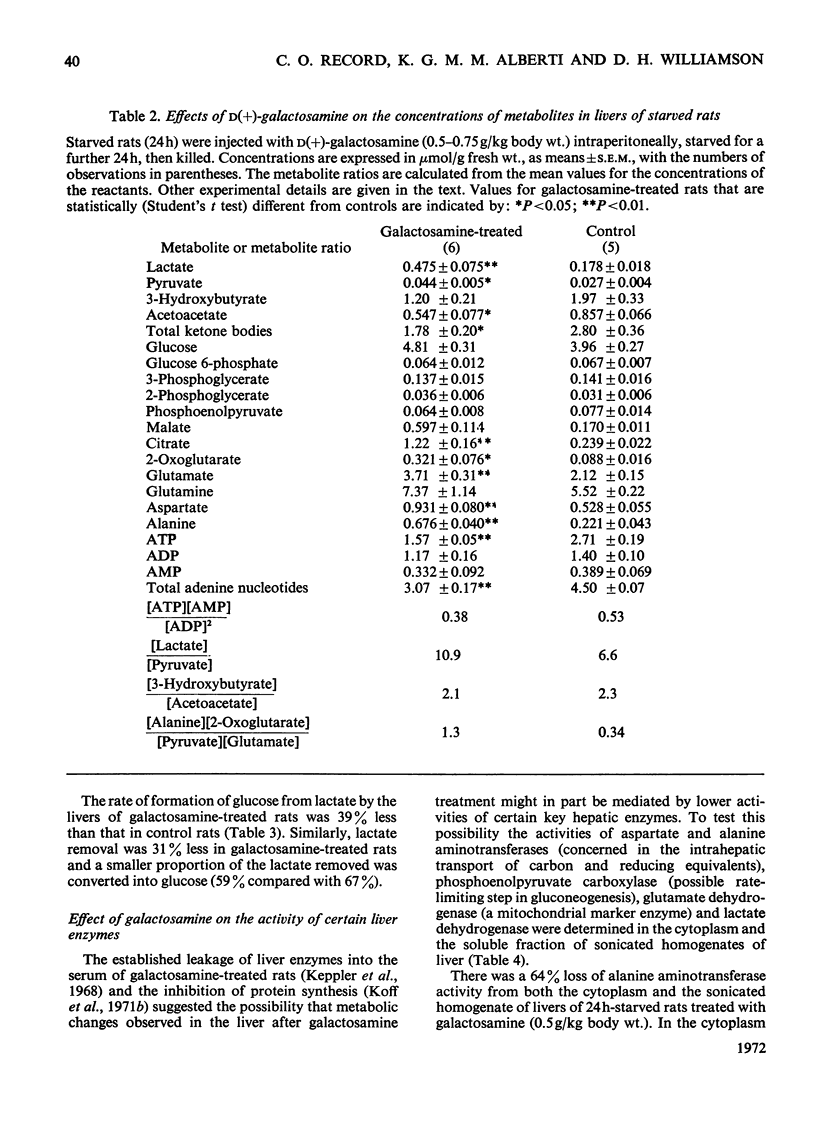
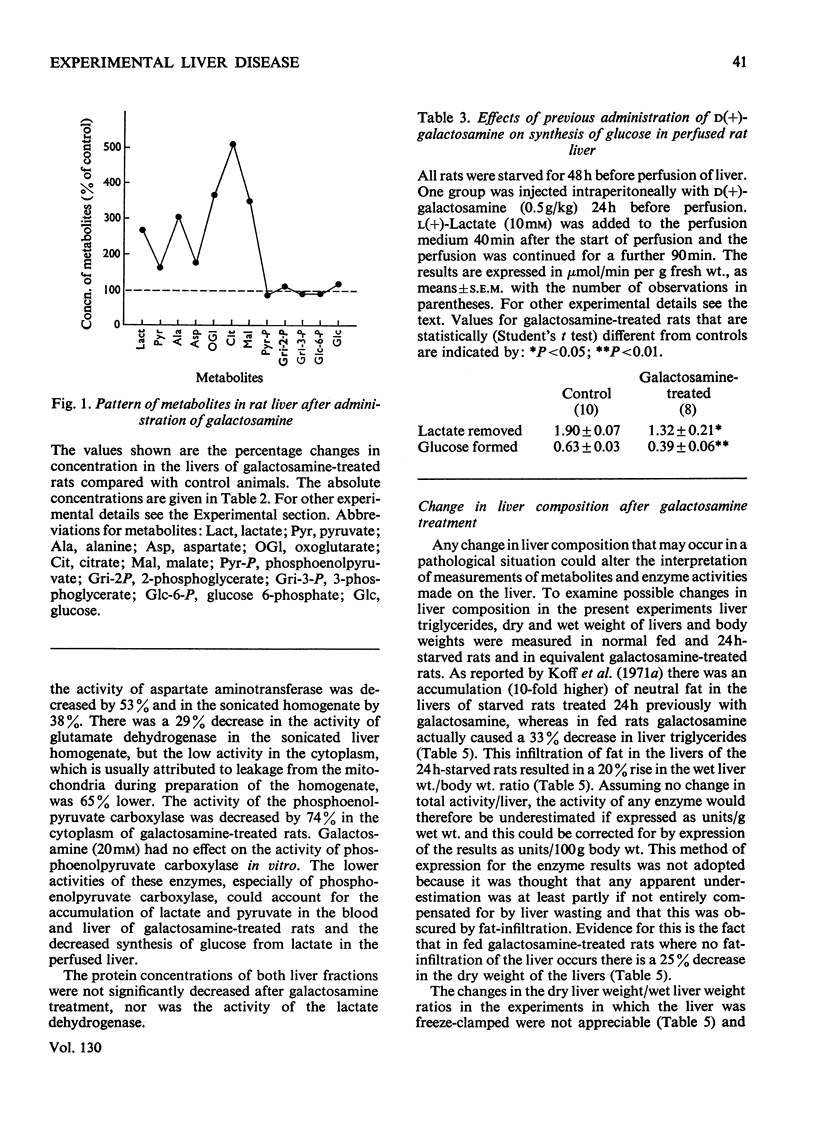
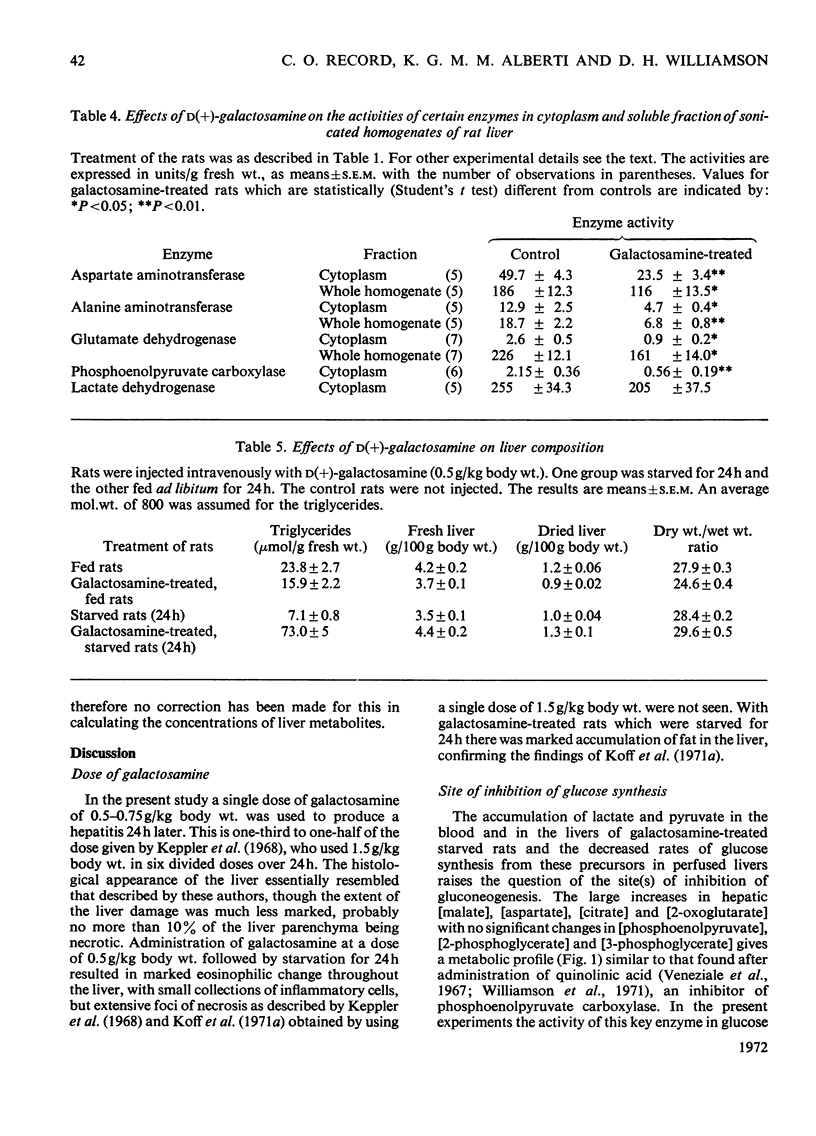
1. In confirmation of previous work, administration of d(+)-galactosamine (0.5–0.75g/kg body wt.) to rats caused a hepatitis with histological evidence of liver damage and a 9-fold rise in aspartate aminotransferase activity in serum. 2. There was a significant elevation of blood lactate and pyruvate concentrations in 24h-starved rats treated with galactosamine but no change in the [lactate]/[pyruvate] ratio. 3-Hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate concentrations in blood were decreased. 3. The changes in the concentrations of lactate, pyruvate and ketone bodies in the freeze-clamped liver were parallel to those observed in the blood. 4. In the livers of 24h-starved galactosamine-treated rats there were large increases in the concentrations of alanine (3-fold), citrate (5-fold), 2-oxoglutarate (4-fold), with smaller increases in malate, glutamate and aspartate. There was a 4-fold rise in the value of the mass-action ratio of the alanine aminotransferase system in the livers of galactosamine-treated rats when compared to controls. 5. There was a significant decrease in the activities of aspartate and alanine aminotransferases in the cytoplasm and the soluble fraction of sonicated homogenates of the livers of rats treated with galactosamine. The activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase was decreased by 75% of the control value. 6. Glucose synthesis from lactate in perfused livers from galactosamine-treated rats was inhibited 39% when compared with controls. 7. The results indicate that the conversion of lactate into glucose is decreased in the livers of galactosamine-treated rats and that this decrease may be due to the loss of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from damaged hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAWSON A. M., DE GROOTE J., ROSENTHAL W. S., SHERLOCK S. Blood pyruvic-acid and alpha-ketoglutaric-acid levels in liver disease and hepatic coma. Lancet. 1957 Feb 23;272(6965):392–396. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggstein M., Kreutz F. H. Eine neue Bestimmung der Neutralfette im Blutserum und Gewebe. I. Prinzip, Durchführung und Besprechung der Methode. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Mar 1;44(5):262–267. doi: 10.1007/BF01747716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Brown W. V., Levine R. A., Klatskin G. Glucose homeostasis in viral hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 24;283(26):1436–1440. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012242832604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLTEN D. D., NORDLIE R. C. COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF GUINEA PIG LIVER INTRA- AND EXTRAMITOCHONDRIAL PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE CARBOXYKINASES. Biochemistry. 1965 Apr;4:723–731. doi: 10.1021/bi00880a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Ross B. D., Berry M. N., Krebs H. A. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):284–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITAYA K., UI M. COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS IN BIOLOGICAL FLUIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D. O., Rudigier J. F., Bischoff E., Decker K. F. The trapping of uridine phosphates by D-galactosamine. D-glucosamine, and 2-deoxy-D-galactose. A study on the mechanism of galactosamine hepatitis. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):246–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Decker K. Studies on the mechanism of galactosamine-1-phosphate and its inhibition of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):219–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppler D., Lesch R., Reutter W., Decker K. Experimental hepatitis induced by D-galactosamine. Exp Mol Pathol. 1968 Oct;9(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(68)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff R. S., Fitts J. J., Sabesin S. M., Zimmerman H. J. D-galactosamine hepatotoxicity. II. Mechanism of fatty liver production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):89–92. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lardy H. A. Gluconeogenesis: pathways and hormonal regulation. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:261–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medline A., Schaffner F., Popper H. Ultrastructural features in galactosamine-induced hepatitis. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Apr;12(2):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering H., Gruber W. Determination of citrate with citrate lyase. Anal Biochem. 1966 Dec;17(3):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier D., Wagle S. R. Studies on gluconeogenesis in galactosamine induced hepatitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Feb;136(2):377–380. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRANQUADA R. E. LACTIC ACIDOSIS. Calif Med. 1964 Dec;101:450–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veneziale C. M., Walter P., Kneer N., Lardy H. A. Influence of L-tryptophan and its metabolites on gluconeogenesis in the isolated, perfused liver. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2129–2138. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., MELLANBY J., KREBS H. A. Enzymic determination of D(-)-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetoacetic acid in blood. Biochem J. 1962 Jan;82:90–96. doi: 10.1042/bj0820090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Lopes-Vieira O., Walker B. Concentrations of free glucogenic amino acids in livers of rats subjected to various metabolic stresses. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):497–502. doi: 10.1042/bj1040497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Lund P., Krebs H. A. The redox state of free nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of rat liver. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):514–527. doi: 10.1042/bj1030514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


