Abstract
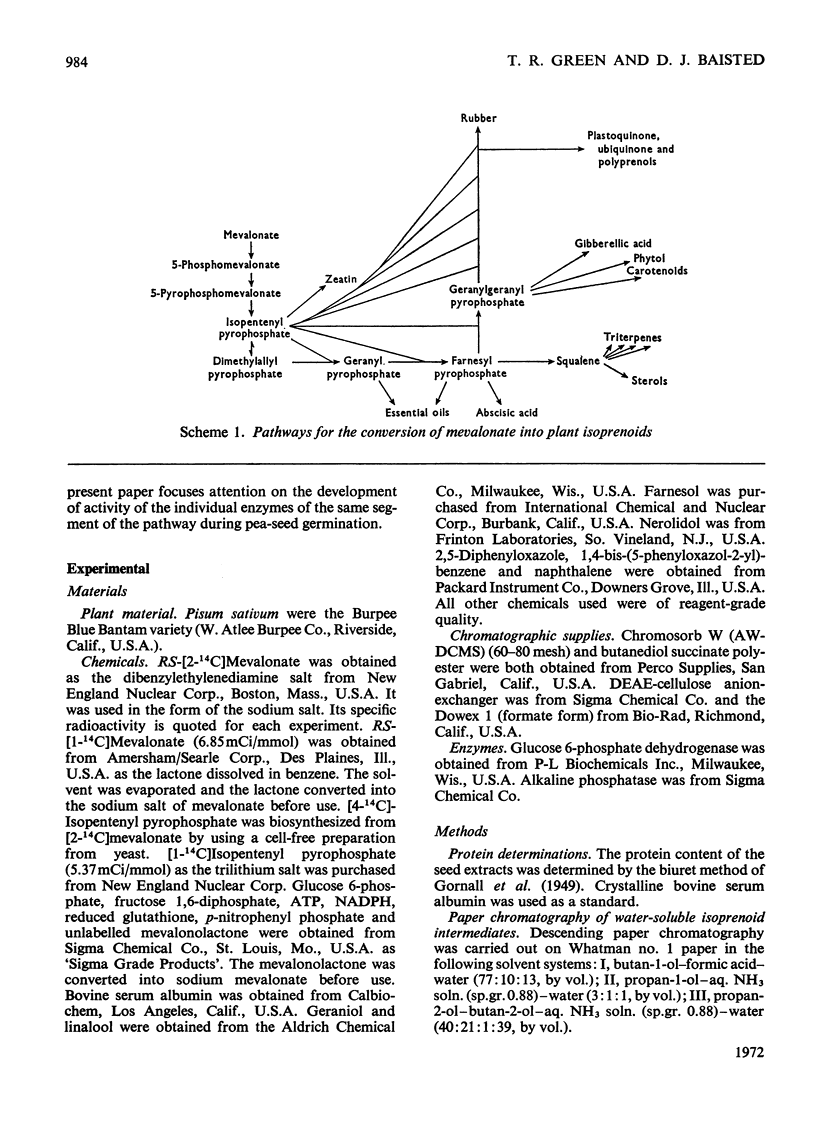
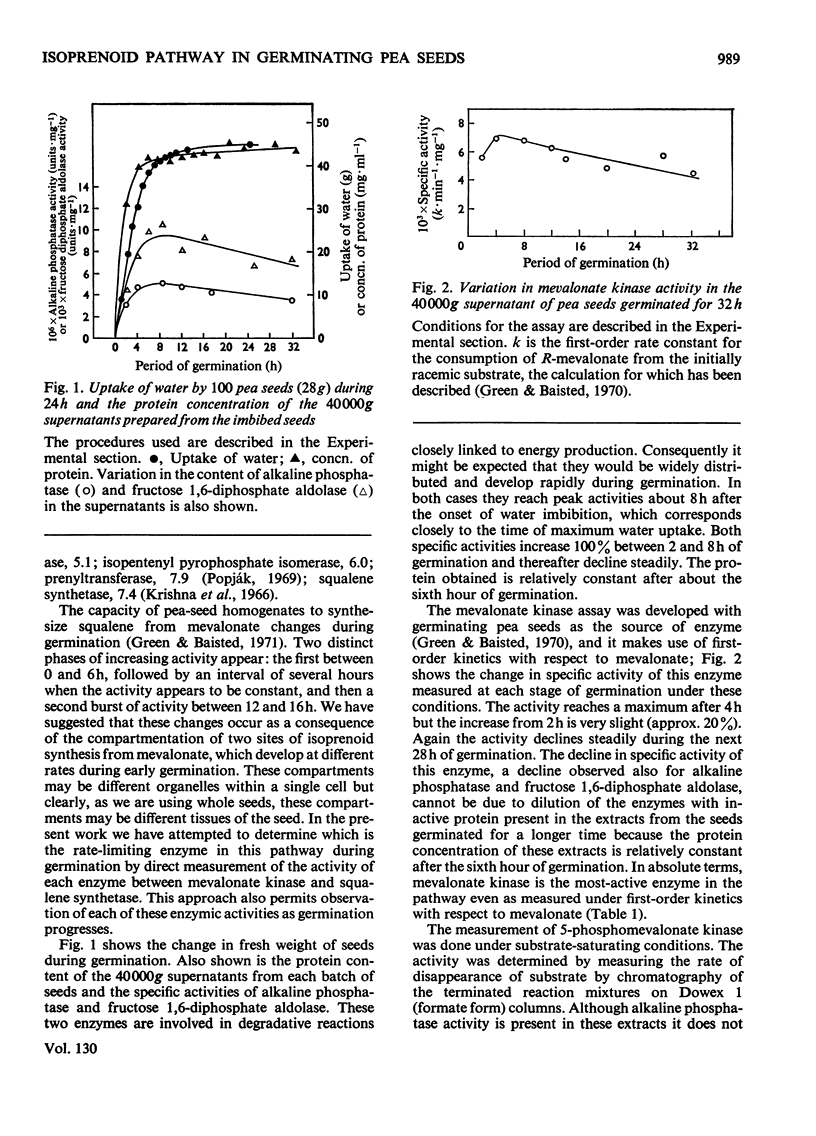
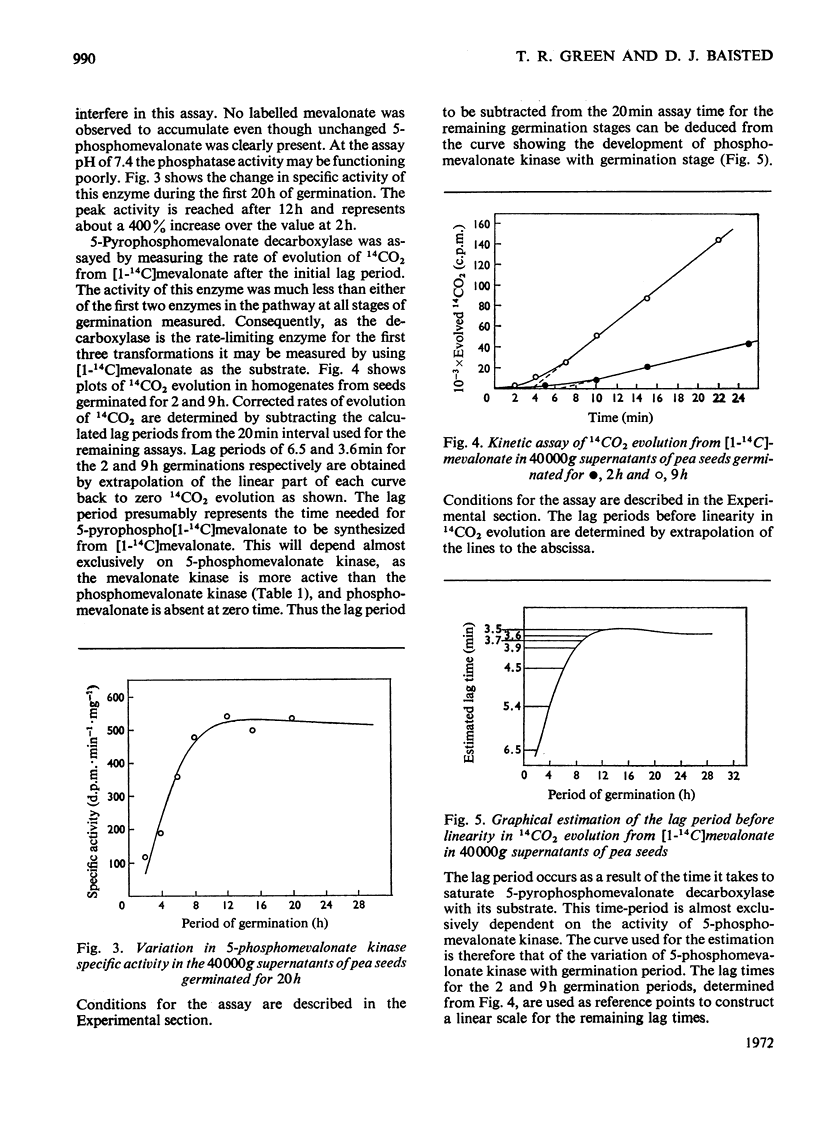
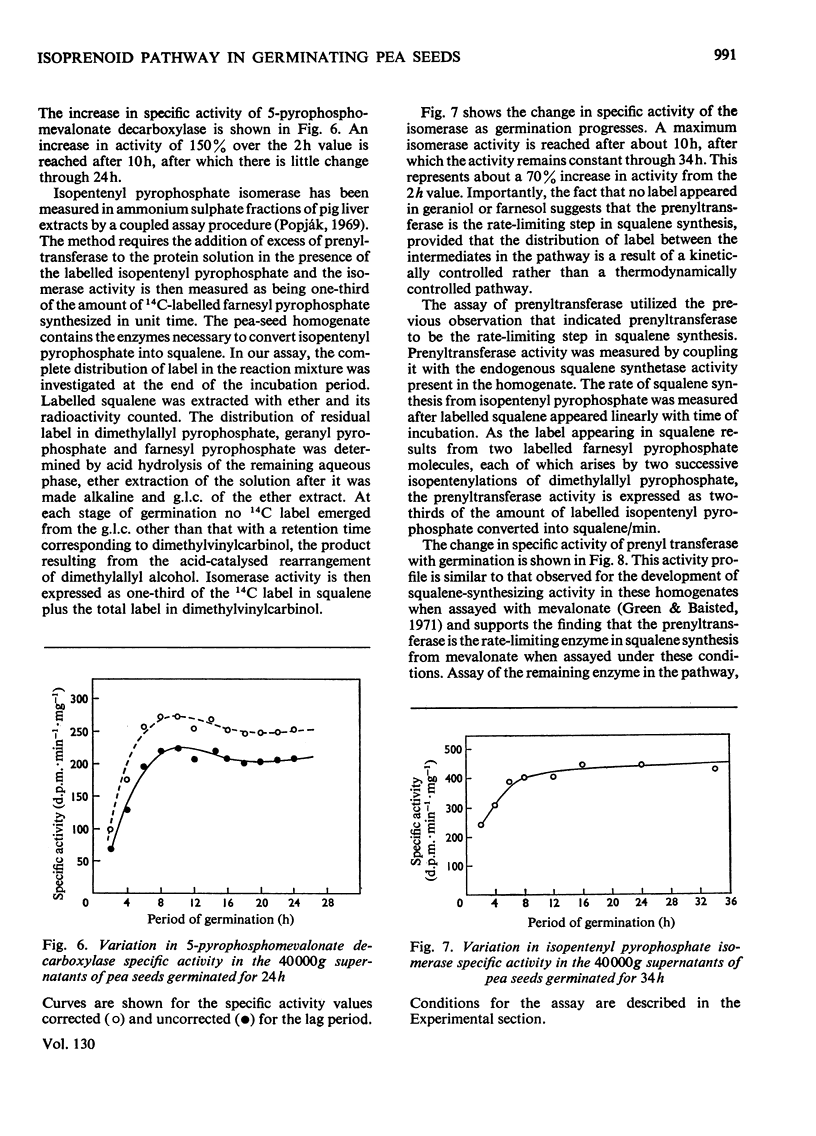
The activities of individual enzymes of the isoprenoid pathway from mevalonate kinase to squalene synthetase in homogenates of seeds germinated up to 32h were assayed. Changes in the activity of each enzyme were observed and compared with the activity at the 2h germination stage. Activities of alkaline phosphatase and fructose 1,6-diphosphate aldolase were similarly measured to provide a reference for changes in the general metabolic activity of seeds during imbibition of water. Water uptake reached a plateau after 12h. The reference enzymes almost doubled in activity between 2 and 8h and thereafter their activities steadily declined. All of the enzymes of the isoprenoid pathway increased in activity between 2 and 6h and, thereafter, with the exception of the prenyltransferase, their activities remained relatively constant. With the prenyltransferase activity the initial increase was followed by a short plateau between 6 and 9h and then a second increase to a maximum between 14 and 16h. After 16h the activity declined. The relative activities of the isoprenoid enzymes at 16h of germination were mevalonate kinase>phosphomevalonate kinase>pyrophosphomevalonate decarboxylase≈isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase>squalene synthetase>isopentenyl pyrophosphate/dimethylallyl pyrophosphate prenyltransferase. The finding that the prenyltransferase may be the rate-limiting enzyme in squalene synthesis from mevalonate is discussed in relation to regulation of isoprenoid synthesis during pea-seed germination.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOCH K., CHAYKIN S., PHILLIPS A. H., DE WAARD A. Mevalonic acid pyrophosphate and isopentenylpyrophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2595–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
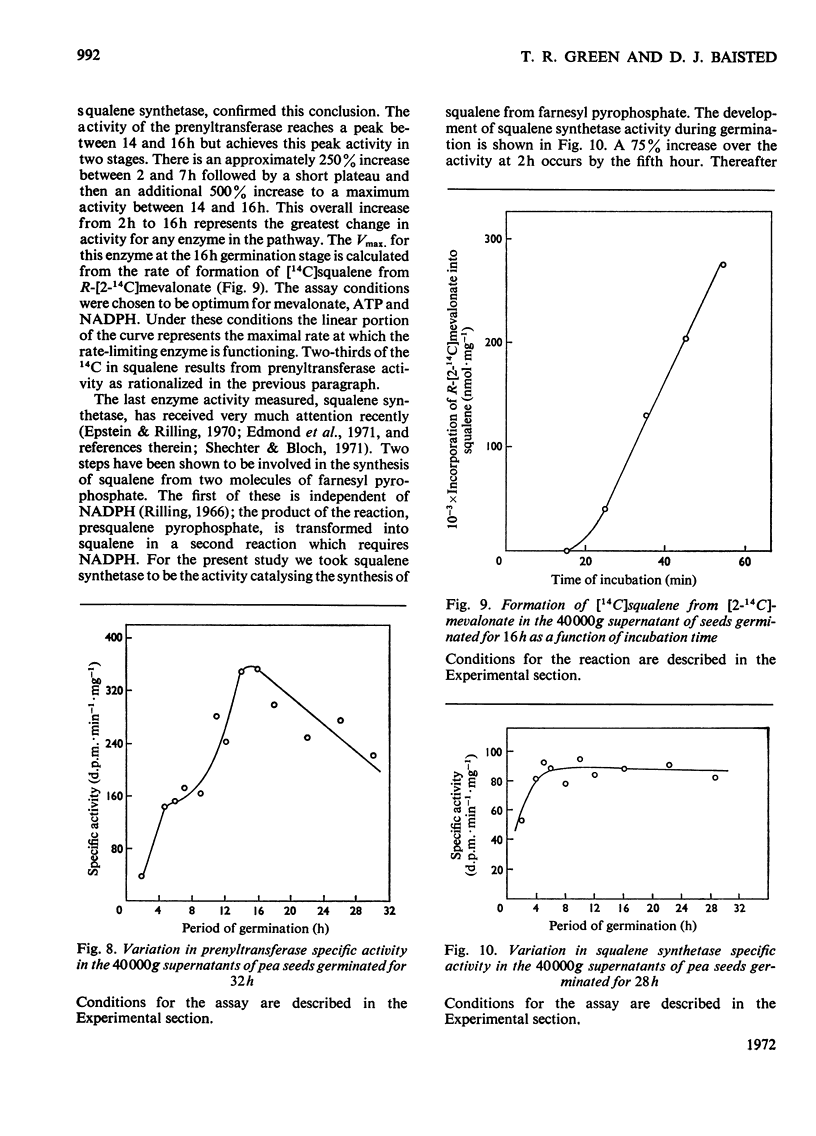
- CAPSTACKE J. R., ROSIN N., BLONDIN G. A., NES W. R. SQUALENE IN PISUM SATIVUM. ITS CYCLIZATION TO BETA-AMYRIN AND LABELING PATTERN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3258–3263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornforth J. W., Cornforth R. H. Chemistry of mevalonic acid. Biochem Soc Symp. 1970;29:5–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daves G. D., Jr, Friis P., Olsen R. K., Folkers K. The chemistry of ubiquinone. Vitam Horm. 1966;24:427–439. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugan R. E., Rasson E., Porter J. W. Separation of water-soluble steroid and carotenoid precursors by DEAE-cellulose column chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmond J., Popják G., Wong S. M., Williams V. P. Presqualene alcohol. Further evidence on the structure of a C 30 precursor of squalene. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6254–6271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. W., Rilling H. C. Studies on the mechanism of squalene biosynthesis. The structure of presqualene pyrophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4597–4605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filner P., Varner J. E., Wray J. L. Environmental or developmental changes cause many enzyme activities of higher plants to rise or fall. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):358–367. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg A., Stadtman E. R. Multienzyme systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:429–472. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goad L. J. Sterol biosynthesis. Biochem Soc Symp. 1970;29:45–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. R., Baisted D. J. A mevalonate kinase assay. Anal Biochem. 1970 Nov;38(1):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90163-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. R., Baisted D. J. Development of the squalene-synthesizing system during early stages of pea seed germination. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1145–1147. doi: 10.1042/bj1251145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNING E. C., VANDENHEUVEL W. J., CREECH B. G. SEPARATION AND DETERMINATION OF STEROIDS BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. Methods Biochem Anal. 1963;11:69–147. doi: 10.1002/9780470110294.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Strominger J. L., Sweeley C. C. Structure of a lipid intermediate in cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis: a derivative of a C55 isoprenoid alcohol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1878–1884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W., Popják G. The purification of 3,3-dimethylallyl- and geranyl-transferase and of isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase from pig liver. Biochem J. 1967 Jul;104(1):57–70. doi: 10.1042/bj1040057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAGANNATHAN V., SINGH K., DAMODARAN M. Carbohydrate metabolism in citric acid fermentation. 4. Purification and properties of aldolase from Aspergillus niger. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):94–105. doi: 10.1042/bj0630094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDUTSCH A. A., PAULUS H., LEVIN E., BLOCH K. PURIFICATION OF GERANYLGERANYL PYROPHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE FROM MICROCOCCUS LYSODEIKTICUS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2507–2515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Whitlock H. W., Jr, Feldbruegge D. H., Porter J. W. Enzymic conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to squalene. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Apr;114(1):200–215. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90322-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popják G., Cornforth J. W. Substrate stereochemistry in squalene biosynthesis: The first Ciba medal lecture. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):553.b4–553568. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILLING H. C., BLOCH K. On the mechanism of squaiene biogenesis from mevalonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1424–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUZICKA L. The isoprene rule and the biogenesis of terpenic compounds. Experientia. 1953 Oct 15;9(10):357–367. doi: 10.1007/BF02167631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards J. B., Evans P. J., Hemming F. W. Dolichol phosphates as acceptors of mannose from guanosine diphosphate mannose in liver systems. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):957–959. doi: 10.1042/bj1240957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling H. C. A new intermediate in the biosynthesis of squalene. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3233–3236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilling H. C. The effect of sterol carrier protein on squalene synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):470–475. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter M. C., Dempsey M. E. Specificity and role in cholesterol biosynthesis of a squalene and sterol carrier protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1536–1539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAH D. H., CLELAND W. W., PORTER J. W. THE PARTIAL PURIFICATION, PROPERTIES, AND MECHANISM OF ACTION OF PIG LIVER ISOPENTENYL PYROPHOSPHATE ISOMERASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1946–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scallen T. J., Schuster M. W., Dhar A. K. Evidence for a noncatalytic carrier protein in cholesterol biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):224–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher M., Lennarz W. J., Sweeley C. C. The biosynthesis of mannosyl-1-phosphoryl-polyisoprenol in Micrococcus lysodeikticus and its role in mannan synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1313–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter I., Bloch K. Solubilization and purification of trans-farnesyl pyrophosphate-squalene synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7690–7696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bosch H., Williamson J. R., Vagelos P. R. Localization of acyl carrier protein in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1970 Oct 24;228(5269):338–341. doi: 10.1038/228338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTING L. A., PORTER J. W. Intermediates in the conversion of mevalonic acid to squalene by a rat liver enzyme system. J Biol Chem. 1959 Nov;234:2841–2846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


