Abstract
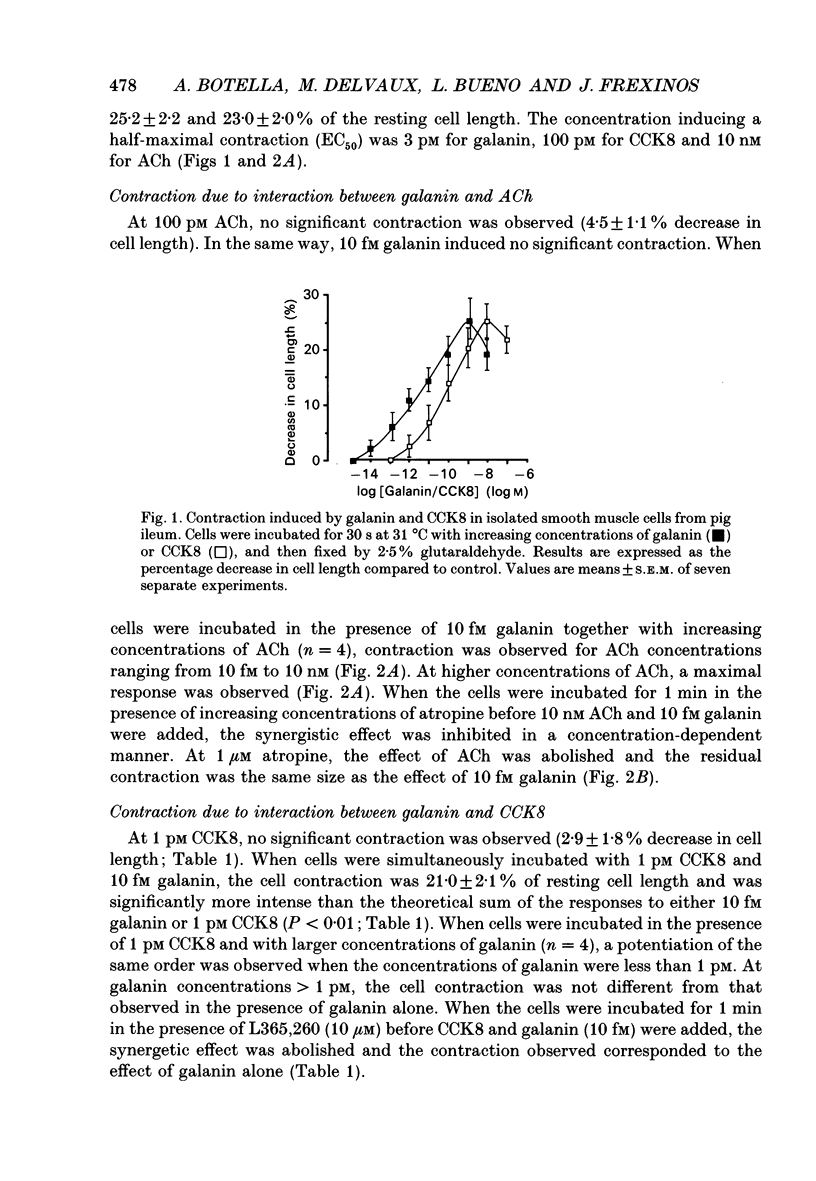
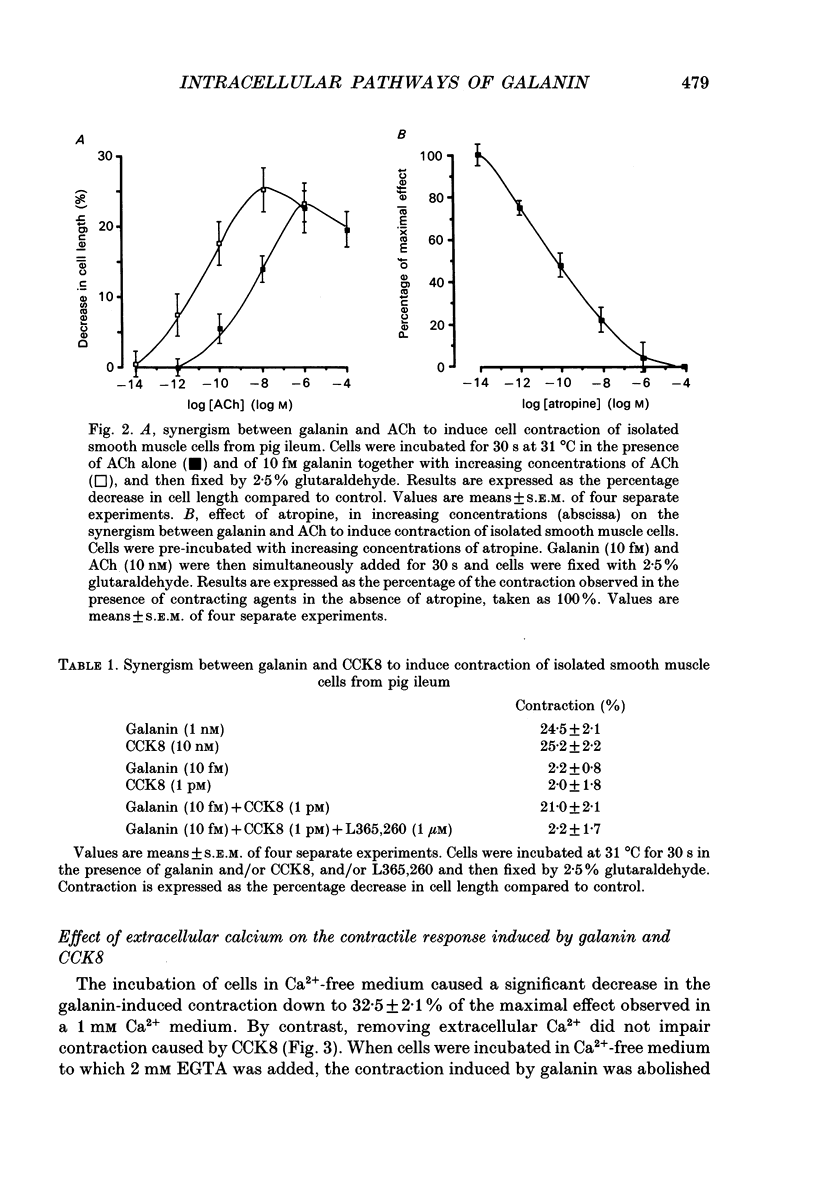
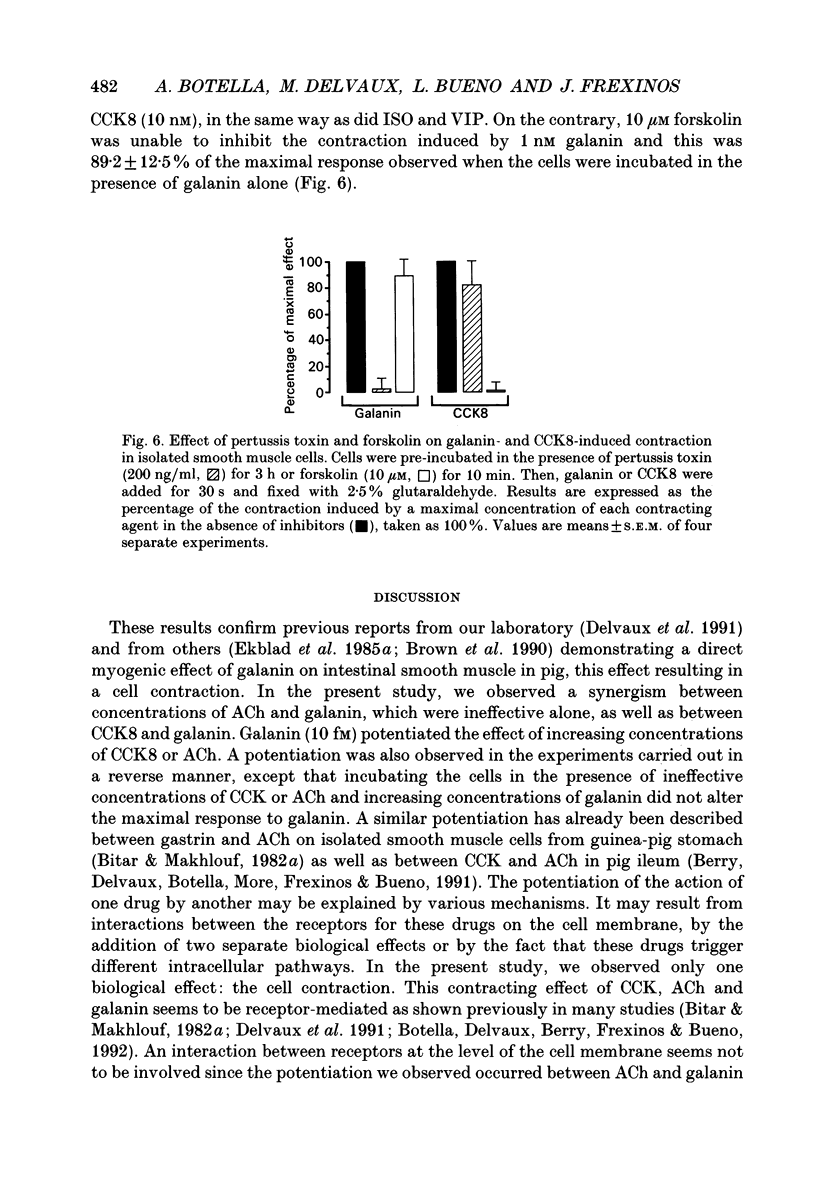
1. In order to determine the intracellular mechanisms by which galanin induces contraction of isolated smooth muscle cells from pig ileum, we examined the effects of external Ca2+, relaxing agents, pertussis toxin and forskolin on the galanin-induced contraction and compared these effects to those observed on the cholecystokinin derivative CCK8-induced contraction. 2. Galanin induced a concentration-dependent cell contraction. The maximal contraction (24.5 +/- 2.1% of the length of resting cells) was observed at 1 nM of galanin. When cells were incubated in the simultaneous presence of concentrations of galanin (10 fM) and CCK8 (1 pM) which were ineffective alone, or galanin (10 fM) and acetylcholine (100 pM), a synergistic action was observed corresponding to a submaximal contraction. 3. Incubation of cells in Ca(2+)-free medium caused a significant decrease in galanin- but not in CCK-induced contraction. Nifedipine, a Ca2+ channel blocker, provoked a concentration-dependent inhibition of galanin-induced contraction while it had no effect on the contraction induced by CCK8. 4. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) and isoprenaline, known to induce cell relaxation through an increase in intracellular cAMP level, inhibited CCK-induced cell contraction at concentrations ranging from 1 pM to 1 microM but failed to inhibit cell contraction induced by galanin. 5. When cells were pre-incubated for 3 h in the presence of 200 ng/ml of pertussis toxin, the contraction induced by galanin was abolished while the CCK-induced contraction remained unchanged. On the contrary, 10 microM forskolin abolished the contraction induced by 10 nM CCK but had no effect on galanin-induced contraction. 6. These results indicate that galanin induces a concentration-dependent contraction of pig ileum smooth muscle by a direct myogenic effect. This effect of galanin involves the activation of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein, which results in an influx of Ca2+ into the cell. This intracellular pathway is insensitive to the relaxing effect of cAMP.
Full text
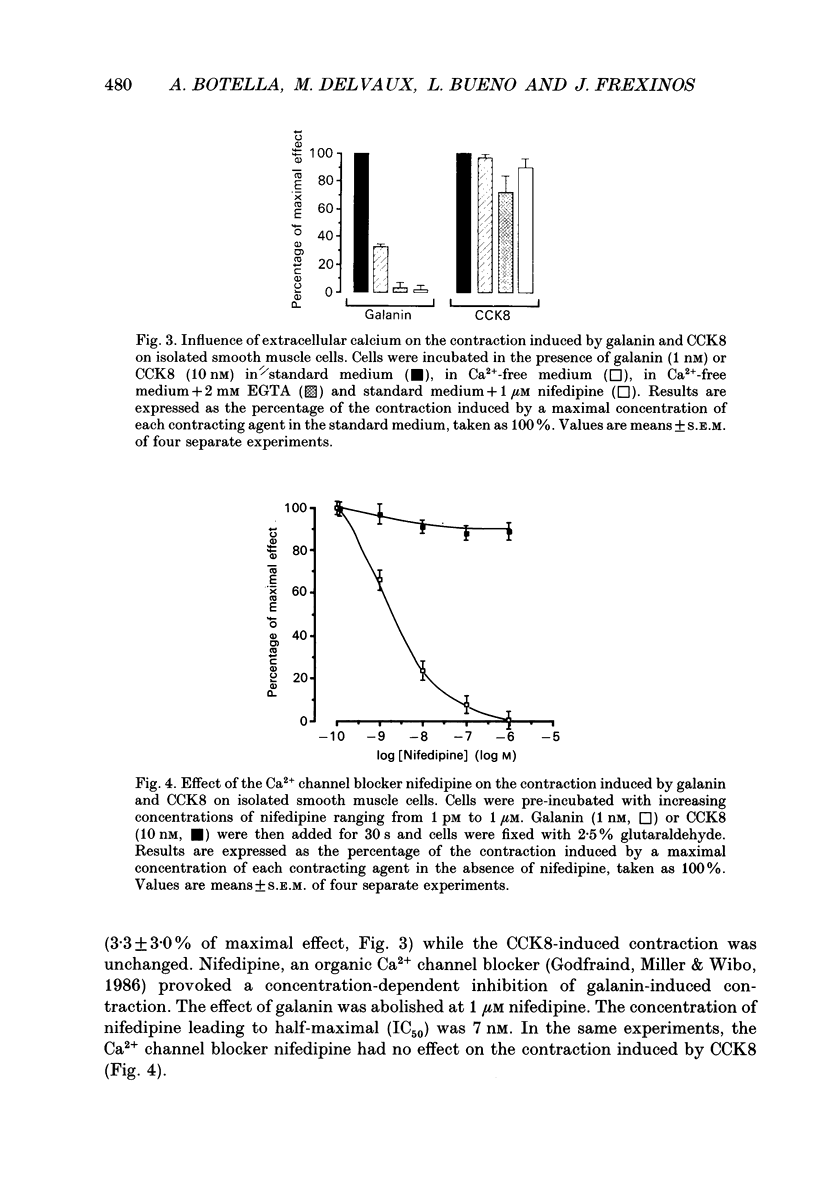
PDF


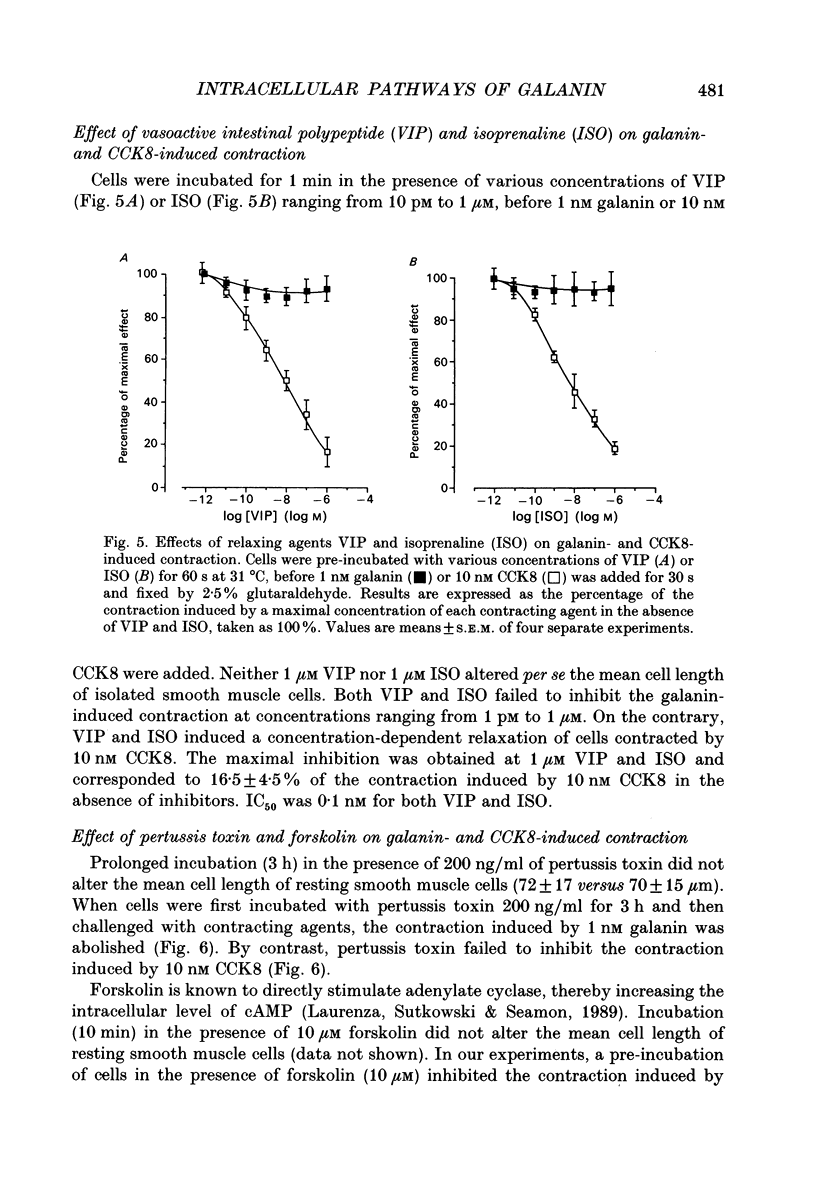




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Lagny-Pourmir I., Laburthe M. Mechanism of galanin-inhibited insulin release. Occurrence of a pertussis-toxin-sensitive inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):147–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer F. E., Zintel A., Kenny M. J., Calder D., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Inhibitory effect of galanin on postprandial gastrointestinal motility and gut hormone release in humans. Gastroenterology. 1989 Aug;97(2):260–264. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop A. E., Polak J. M., Bauer F. E., Christofides N. D., Carlei F., Bloom S. R. Occurrence and distribution of a newly discovered peptide, galanin, in the mammalian enteric nervous system. Gut. 1986 Jul;27(7):849–857. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.7.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitar K. N., Makhlouf G. M. Receptors on smooth muscle cells: characterization by contraction and specific antagonists. Am J Physiol. 1982 Apr;242(4):G400–G407. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.242.4.G400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitar K. N., Makhlouf G. M. Relaxation of isolated gastric smooth muscle cells by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):531–533. doi: 10.1126/science.6176025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefond C., Palacios J. M., Probst A., Mengod G. Distribution of Galanin mRNA Containing Cells and Galanin Receptor Binding Sites in Human and Rat Hypothalamus. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(7):629–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botella A., Delvaux M., Berry P., Frexinos J., Bueno L. Cholecystokinin and gastrin induce cell contraction in pig ileum by interacting with different receptor subtypes. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):779–786. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90158-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R., Hildebrand K. R., Parsons A. M., Soldani G. Effects of galanin on smooth muscle and mucosa of porcine jejunum. Peptides. 1990 May-Jun;11(3):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90049-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2577–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delvaux M., Botella A., Fioramonti J., Frexinos J., Bueno L. Galanin induces contraction of isolated cells from circular muscle layer of pig ileum. Regul Pept. 1991 Feb 26;32(3):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90030-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunning B. E., Ahren B., Veith R. C., Böttcher G., Sundler F., Taborsky G. J., Jr Galanin: a novel pancreatic neuropeptide. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):E127–E133. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.1.E127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Håkanson R., Sundler F., Wahlestedt C. Galanin: neuromodulatory and direct contractile effects on smooth muscle preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):241–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Rökaeus A., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Galanin nerve fibers in the rat gut: distribution, origin and projections. Neuroscience. 1985 Oct;16(2):355–363. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. W., Hodges T. D., Watanabe A. M. Pertussis toxin-treated dog: a whole animal model of impaired inhibitory regulation of adenylate cyclase. Circ Res. 1988 May;62(5):992–1000. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.5.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florholmen J., Malm D., Vonen B., Burhol P. G. Effect of cholecystokinin on the accumulation of inositol phosphates in isolated pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):G865–G870. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.6.G865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine J., Lebrun P. Galanin: Ca2+-dependent contractile effects on the isolated mouse distal colon. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):583–586. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A. Control of gastrointestinal motility by peptides: old peptides, new tricks--new peptides, old tricks. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1989 Jun;18(2):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Brooks B., McDonald T. J., Barnett W., Kostolanska F., Yanaihara C., Yanaihara N., Rökaeus A. Actions of galanin fragments on rat, guinea-pig, and canine intestinal motility. Peptides. 1988 Sep-Oct;9(5):1183–1189. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., McDonald T. J., Kostolanska F., Tatemoto K. Galanin: an inhibitory neural peptide of the canine small intestine. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 14;39(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90443-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T., Daniel E. E., McDonald T. J., Fox J. E., Brooks B. D., Oki M. Distribution and function of enteric GAL-IR nerves in dogs: comparison with VIP. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 1):G884–G896. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.5.G884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman T., Merriam P., Fay F. S. The effects of isoproterenol on adenosine cyclic 3', 5'- monophosphate and contractility in isolated smooth muscle cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;14(1):86–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagny-Pourmir I., Amiranoff B., Lorinet A. M., Tatemoto K., Laburthe M. Characterization of galanin receptors in the insulin-secreting cell line Rin m 5F: evidence for coupling with a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanosine triphosphate regulatory protein. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2635–2641. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenza A., Sutkowski E. M., Seamon K. B. Forskolin: a specific stimulator of adenylyl cyclase or a diterpene with multiple sites of action? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Nov;10(11):442–447. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(89)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiter D. M., Hooi S. C., Koenig J. I., Martin J. B. Galanin is a physiological regulator of spontaneous pulsatile secretion of growth hormone in the male rat. Endocrinology. 1990 Feb;126(2):1216–1222. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-2-1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Nilsson S., Brodin E. Visualization of galanin binding sites in the rat central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 May 27;124(3):381–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Staines W. A., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Eckenstein F., Salvaterra P. M., Wainer B. H. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in cholinergic neurons of the septum-basal forebrain complex projecting to the hippocampus of the rat. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 23;360(1-2):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moummi C., Magous R., Bali J. P. Gastrointestinal hormone receptors on isolated smooth muscle cells from gastric antrum of the rabbit. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 1;38(17):2895–2901. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90447-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Yanaihara N. Contribution of galanin to non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic transmission in rat ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1241–1249. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rökaeus A., Melander T., Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. A galanin-like peptide in the central nervous system and intestine of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 15;47(2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid C. R., Honeyman T. W., Fay F. S. Mechanism of beta-adrenergic relaxation of smooth muscle. Nature. 1979 Jan 4;277(5691):32–36. doi: 10.1038/277032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H. C., Bishop A. E., Power R. F., Hamada Y., Polak J. M. Dual intrinsic and extrinsic origins of CGRP- and NPY-immunoreactive nerves of rat gut and pancreas. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2674–2687. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02674.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Palmer J. M., Wood J. D. Galanin suppresses nicotinic synaptic transmission in the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 29;136(3):445–446. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau W. M., Dorsett J. A., Youther M. L. Evidence for galanin as an inhibitory neuropeptide on myenteric cholinergic neurons in the guinea pig small intestine. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Dec 23;72(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


