Abstract
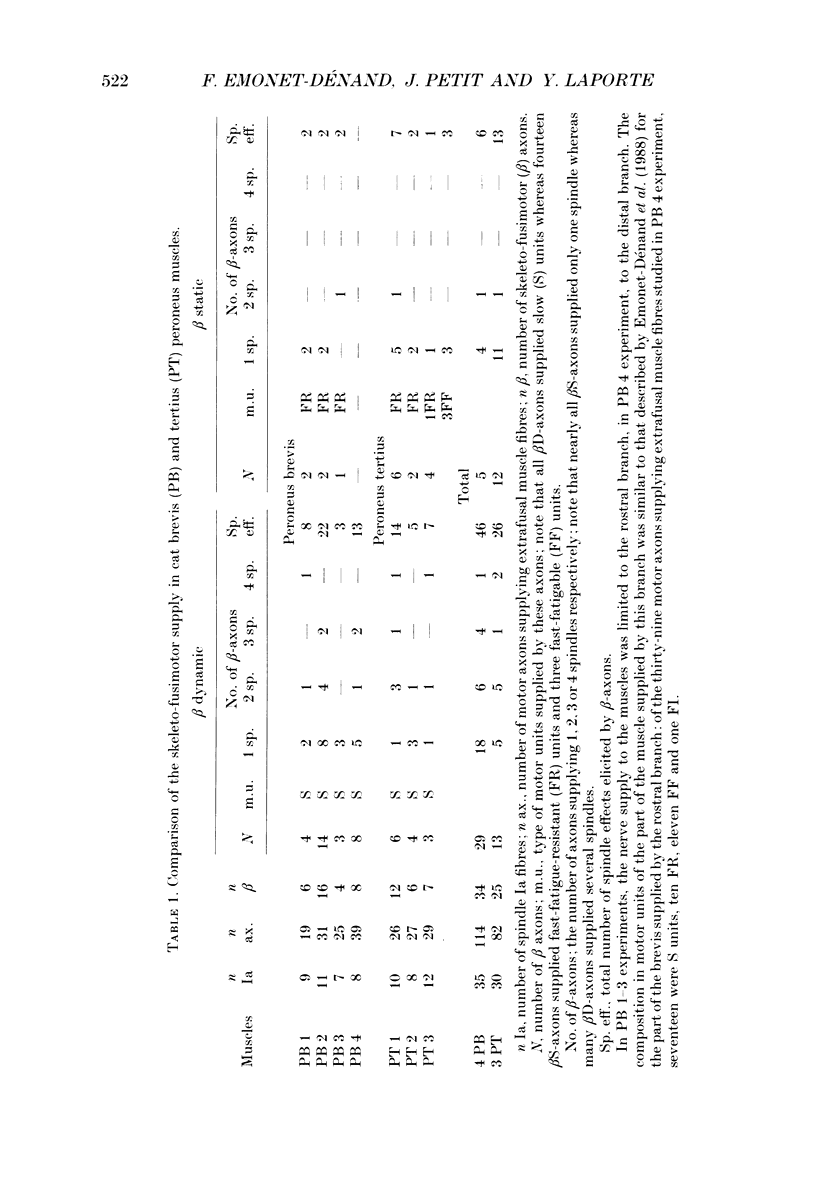
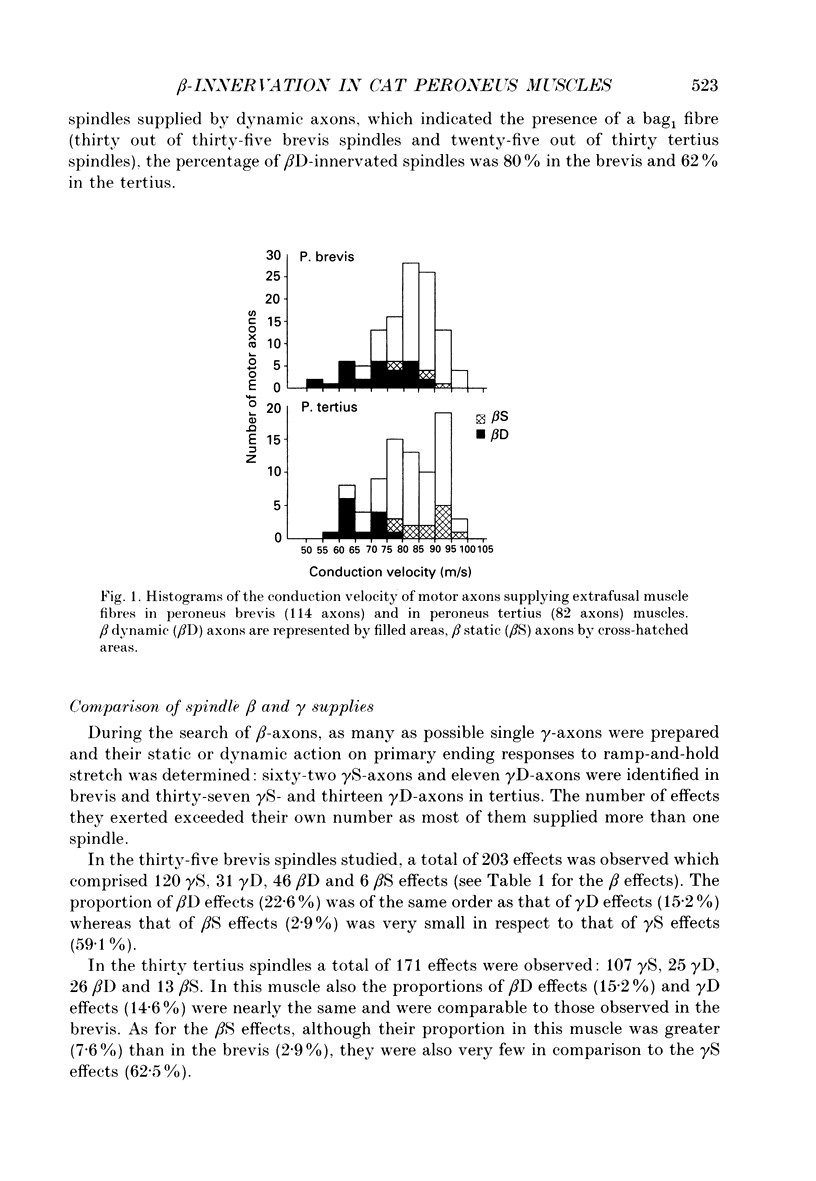
1. The skeleto-fusimotor or beta innervation was compared in cat peroneus brevis and peroneus tertius muscles, which differ in their composition of fatigue-resistant motor units; the slow (S) units predominate in brevis and the fast units (FR) in tertius. 2. In four brevis muscles, of thirty-four beta-axons (from a total of 114 axons supplying extrafusal muscle fibres) twenty-nine were dynamic (beta D) and only five static (beta S). In contrast, in three tertius muscles, of twenty-five beta-axons (from a total of 82 axons) twelve were static and thirteen dynamic. 3. In a population of thirty-five brevis and thirty tertius spindles, the proportion of beta D-innervated spindles was greater in the brevis (68.5%) than in the tertius (50%) whereas that of beta S-innervated spindles was greater in the tertius (40%) than in the brevis (17.1%). In a population of thirty-two brevis and twenty-seven tertius spindles in which the presence of bag1 fibres was deduced from the existence of a dynamic innervation, the proportion of spindles innervated by beta D-axons was 80% in the brevis and 62% in the tertius. 4. In both muscles, the number of beta D effects was greater than that of beta S effects. beta S-axons were rarely found to supply more than one spindle whereas beta D-axons supplying more than one spindle (up to four) were common. Spindles were often coinnervated by beta D- and beta S-axons.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks R. W. The distribution of static gamma-axons in the tenuissimus muscle of the cat. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:489–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y. Types of intra- and extrafusal muscle fibre innervated by dynamic skeleto-fusimotor axons in cat peroneus brevis and tenuissimus muscles, as determined by the glycogen-depletion method. J Physiol. 1977 Apr;266(3):713–726. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E., Levine D. N., Tsairis P., Zajac F. E., 3rd Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):723–748. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Hunt C. C., Petit J., Pollin B. Proportion of fatigue-resistant motor units in hindlimb muscles of cat and their relation to axonal conduction velocity. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:135–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Jankowska E., Laporte Y. Skeleto-fusimotor fibres in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):669–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Blocage neuromusculaire sélectif des jonctions extrafusales des axones squeletto-fusimoteurs produit par leur stimulation répétitive á fréquence élevée. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Dec 23;279(26):2083–2085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Matthews P. B., Petit J. On the subdivision of static and dynamic fusimotor actions on the primary ending of the cat muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;268(3):827–861. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Proportion of muscles spindles supplied by skeletofusimotor axons (beta-axons) in peroneus brevis muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1390–1394. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker D. W., Jami L., Laporte Y., Petit J. Fast-conducting skeletofusimotor axons supplying intrafusal chain fibers in the cat peroneus tertius muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Jul;40(4):791–799. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.4.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horcholle-Bossavit G., Jami L., Thiesson D., Zytnicki D. Motor nuclei of peroneal muscles in the cat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Nov 15;277(3):430–440. doi: 10.1002/cne.902770308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Lan-Couton D., Malmgren K., Petit J. "Fast" and "slow" skeleto-fusimotor innervation in cat tenuissimus spindles; a study with the glycogen-depletion method. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):284–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Lan-Couton D., Malmgren K., Petit J. Histophysiological observations on fast skeleto-fusimotor axons. Brain Res. 1979 Mar 23;164:53–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jami L., Murthy K. S., Petit J. A quantitative study of skeletofusimotor innervation in the cat peroneus tertius muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:125–144. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera J. Histological identification of (static) skeletofusimotor innervation to a cat muscle spindle. Brain Res. 1984 Mar 5;294(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit J., Filippi G. M., Emonet-Dénand F., Hunt C. C., Laporte Y. Changes in muscle stiffness produced by motor units of different types in peroneus longus muscle of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jan;63(1):190–197. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.1.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. J., Young H. The number and distribution of muscle spindles and tendon organs in the peroneal muscles of the cat. J Anat. 1987 Apr;151:143–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


