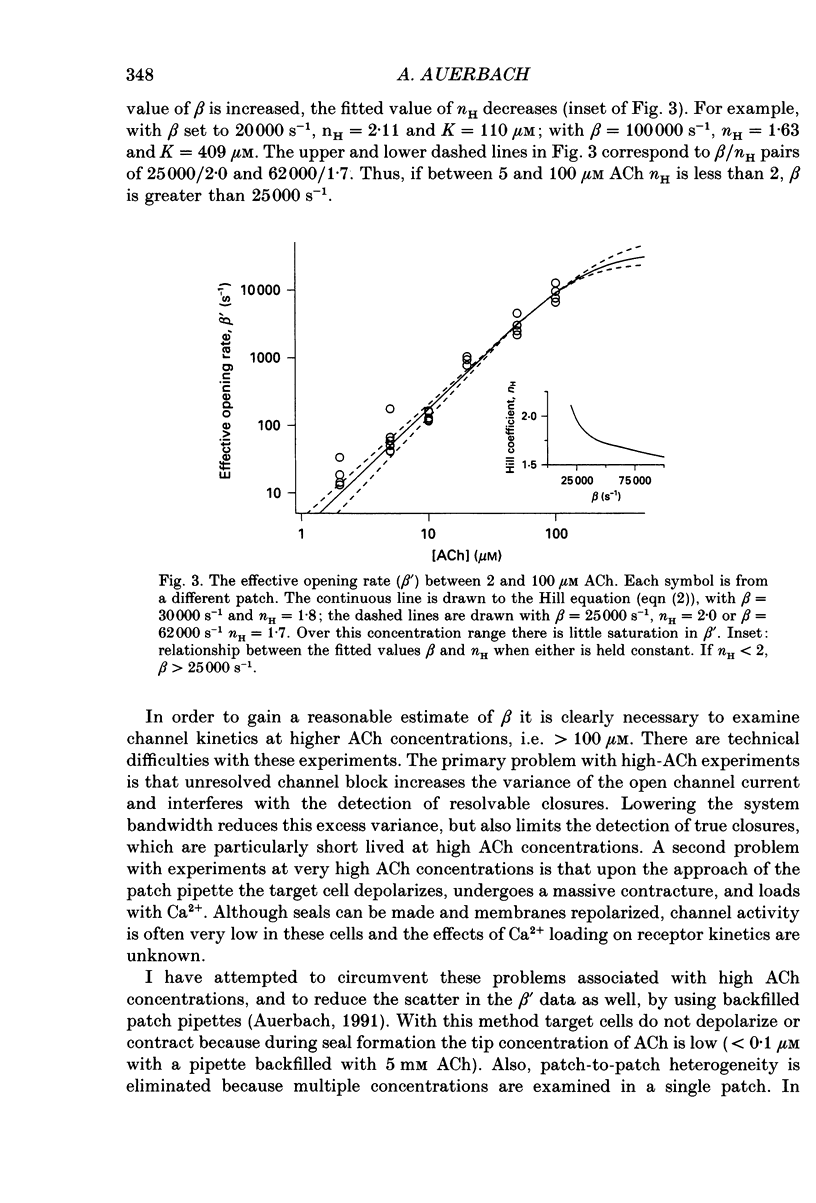
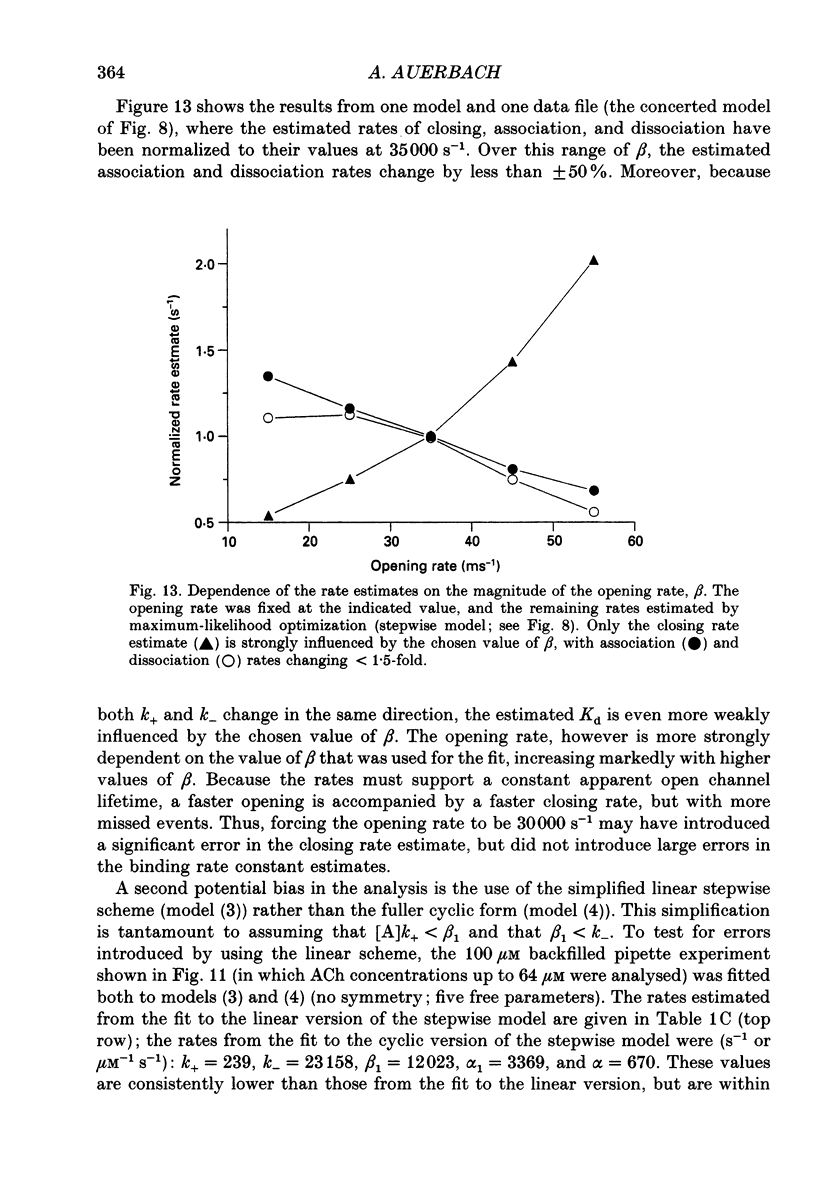
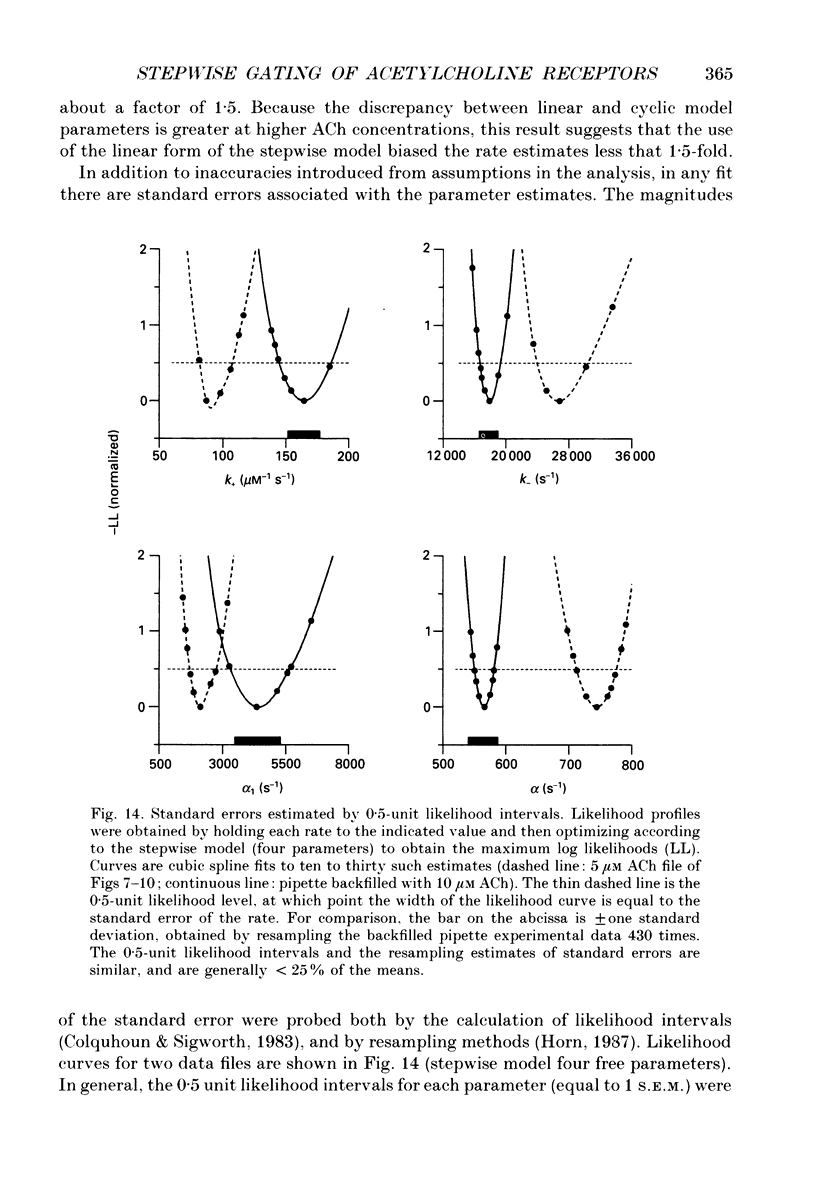
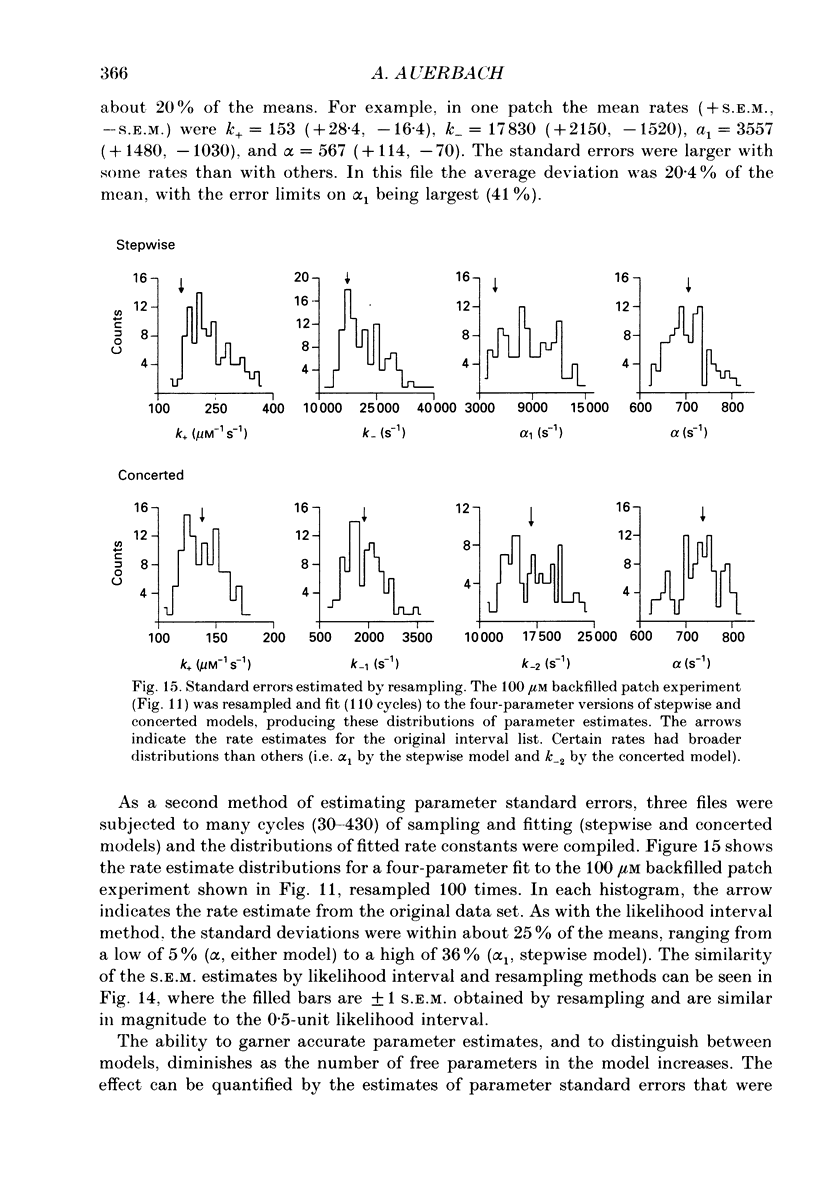
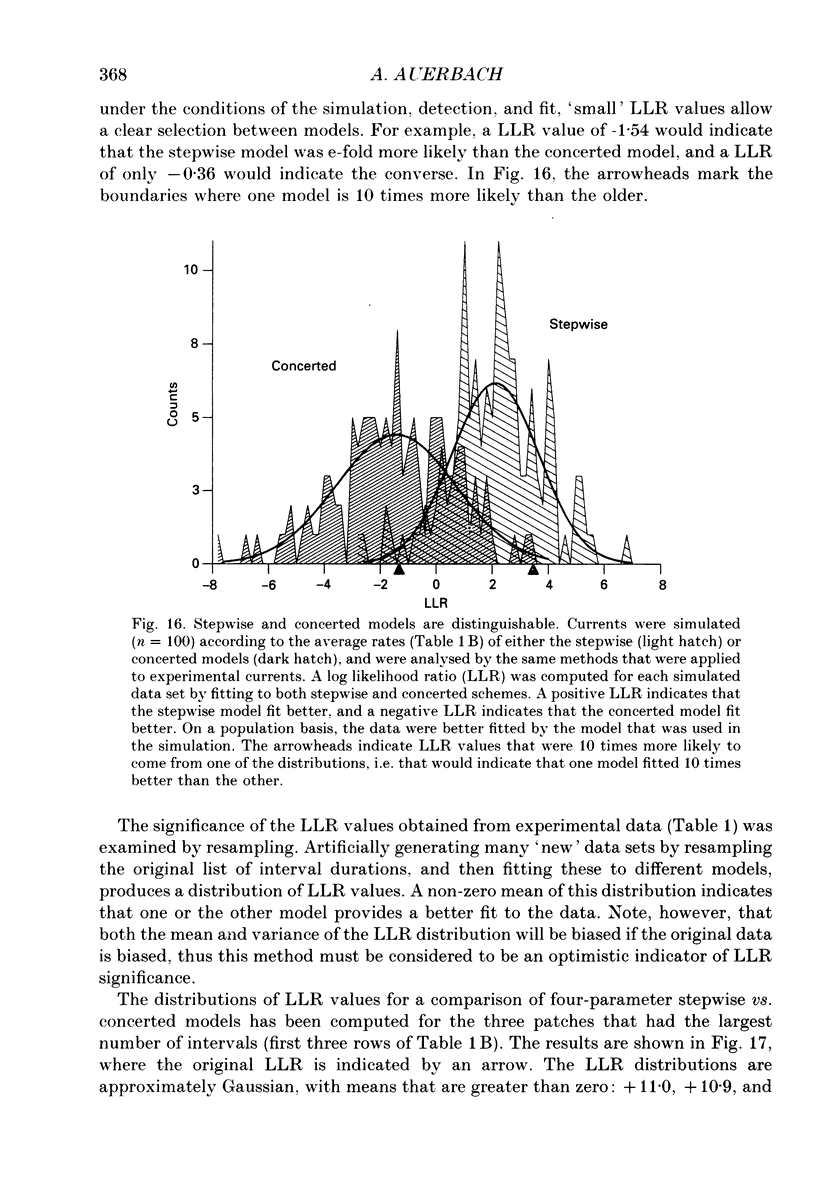
Abstract
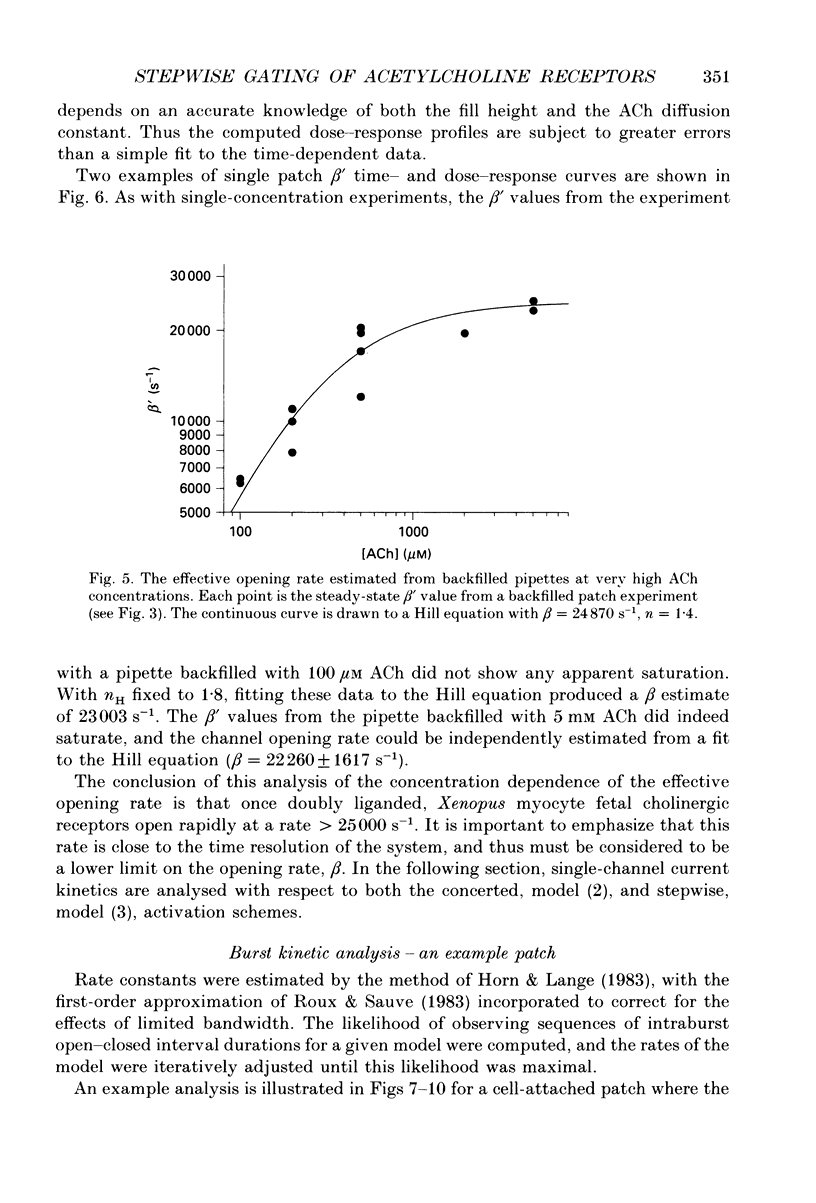
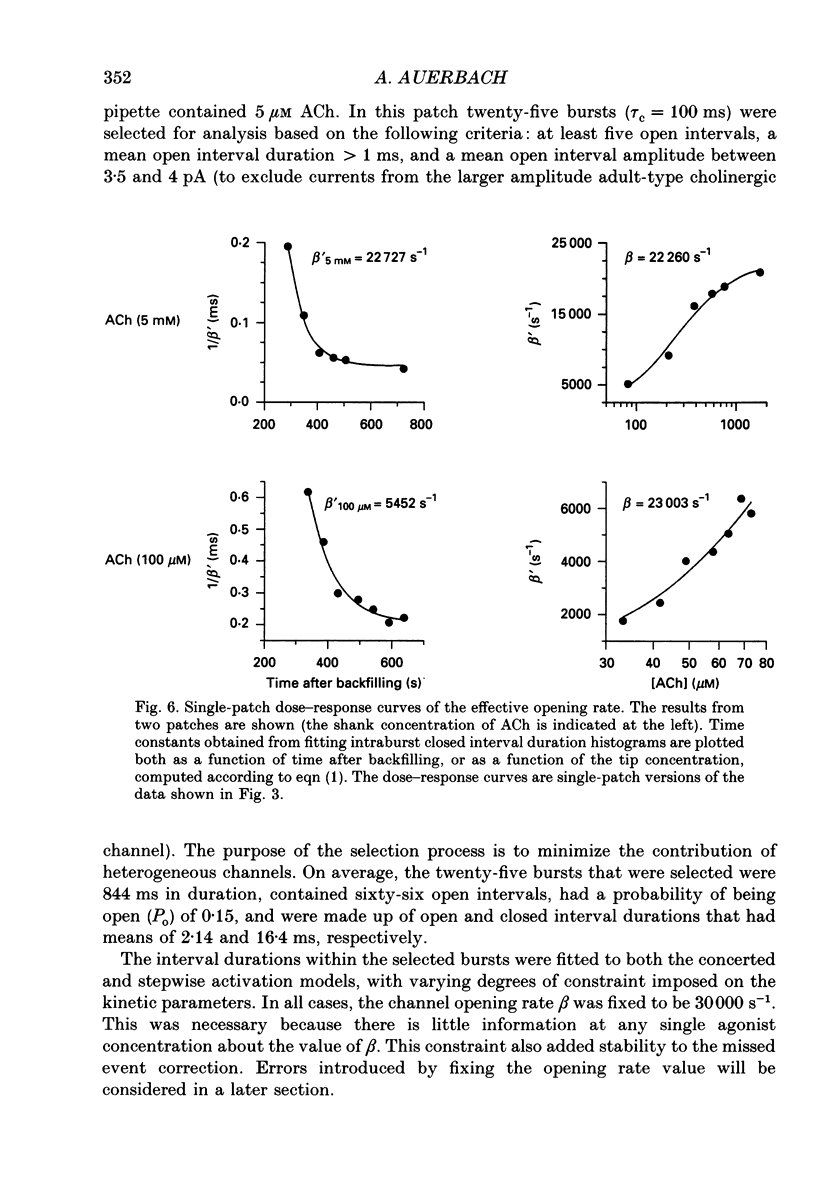
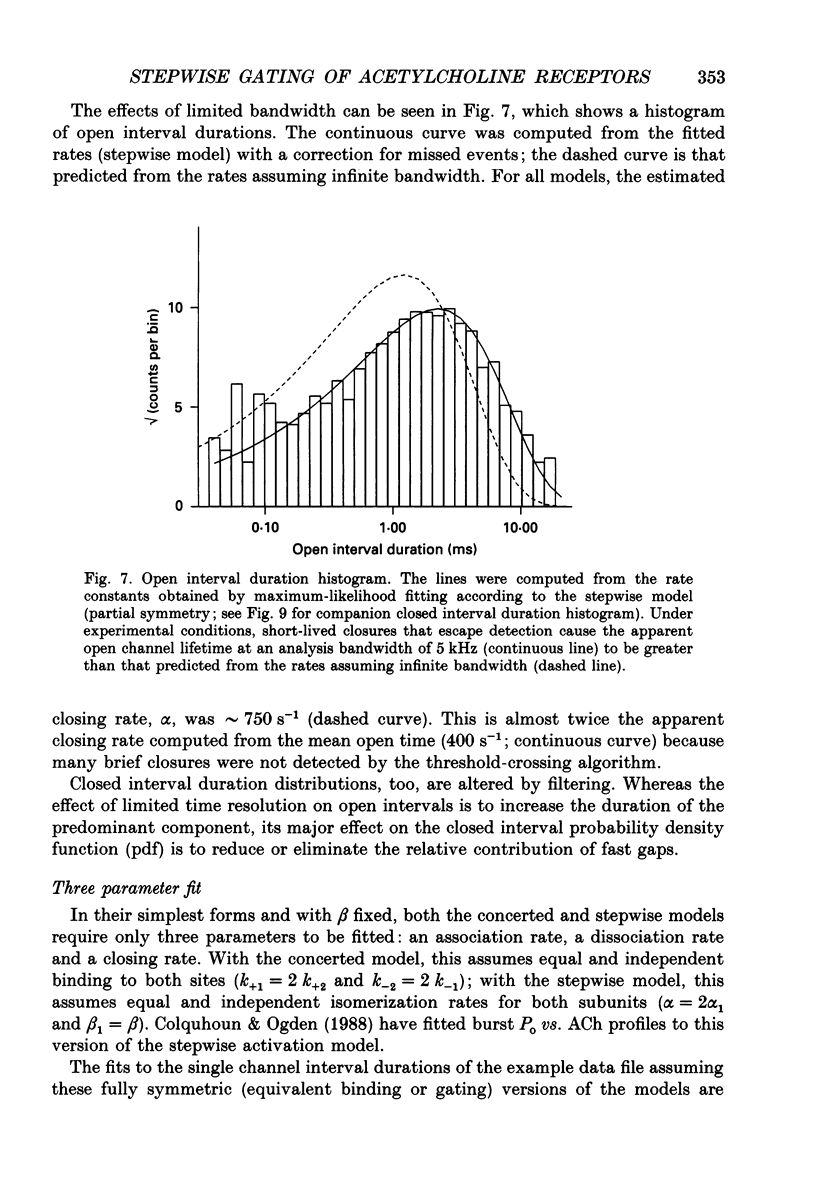
1. The kinetic properties of single channel currents from fetal-type acetylcholine receptors in embryonic Xenopus myocytes (60 h old) have been analysed by a maximum-likelihood method. 2. At very high acetylcholine (ACh) concentrations (up to 5 mM) the effective opening rate appears to saturate at approximately 30,000 s-1. 3. The kinetics were analysed according to the standard concerted scheme that postulates a single channel-opening conformational change after two agonists are bound, and a rarely invoked stepwise scheme that postulates semi-independent conformational changes in two distinct gating domains. Both models assume that agonist cannot escape from a channel (or domain) that is in its activated conformation. 4. With either activation scheme the kinetic analyses indicate that ACh binds at a rate of approximately 2 x 10(8) s-1 M-1 and dissociates from doubly liganded receptors at a rate of approximately 28,000 s-1, and that the activation process is asymmetric, i.e. the binding (concerted model) or gating (stepwise model) transitions are not equal and independent. 5. In eighteen of twenty-seven file-by-file comparisons, the likelihood of the stepwise model was greater than that of the concerted model. In seven such comparisons, the likelihood of the concerted model was greater than that of the stepwise model, and in two there was no difference. Log likelihood ratio distributions were obtained from three files (those with the most events) by multiple cycles of resampling and fitting. The means of these distributions were significantly greater than zero, indicating that the stepwise scheme was as good as, or better than, the concerted scheme in describing receptor activation. 6. According to the stepwise view, two binding sites must be occupied and two 'gates' activated for conduction to occur. Although equivalent binding is not an essential aspect of stepwise activation, the binding sites can be identical and have a low affinity for ACh (Kd approximately 130 microM). Either the isomerization rates of the gating domains are different, or they are influenced by the conformational status of its counterpart, with activation increasing approximately 3-fold and deactivation decreasing approximately 10-fold if the complementary domain is in the active conformation. Stepwise activation predicts that the decay of the endplate current is determined by five rates.
Full text
PDF


























Selected References
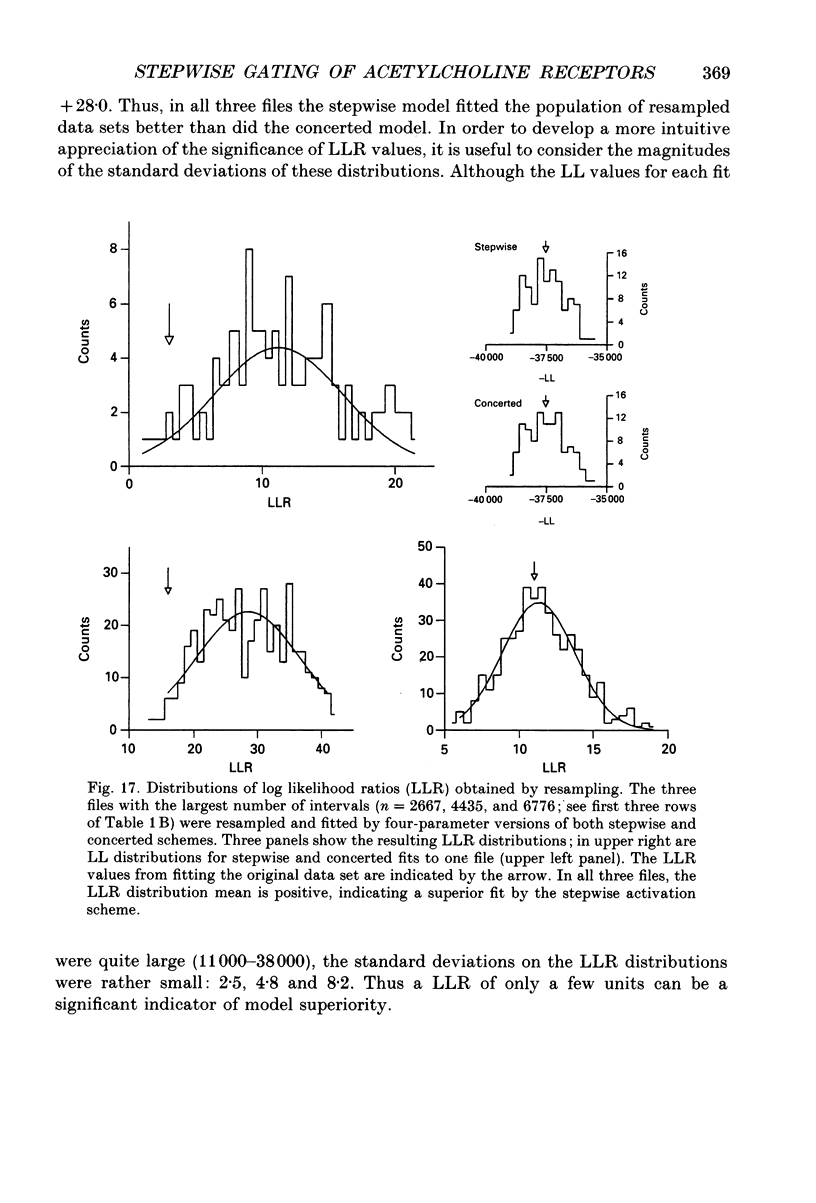
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackers G. K., Doyle M. L., Myers D., Daugherty M. A. Molecular code for cooperativity in hemoglobin. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):54–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1553532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Lingle C. J. Activation of the primary kinetic modes of large- and small-conductance cholinergic ion channels in Xenopus myocytes. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:437–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A., Lingle C. J. Heterogeneous kinetic properties of acetylcholine receptor channels in Xenopus myocytes. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:119–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach A. Single-channel dose-response studies in single, cell-attached patches. Biophys J. 1991 Sep;60(3):660–670. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82095-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S. E., Sansom M. S., Ball F. G., Ramsey R. L., Usherwood P. N. Glutamate receptor-channel gating. Maximum likelihood analysis of gigaohm seal recordings from locust muscle. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):219–229. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82367-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blount P., Merlie J. P. Molecular basis of the two nonequivalent ligand binding sites of the muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. Relaxation and fluctuations of membrane currents that flow through drug-operated channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):231–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Ogden D. C. Activation of ion channels in the frog end-plate by high concentrations of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:131–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouzy S. C., Sigworth F. J. Yet another approach to the dwell-time omission problem of single-channel analysis. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):731–743. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82416-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Interaction at end-plate receptors between different choline derivatives. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):369–381. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E. Characterization of drug iontophoresis with a fast microassay technique. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):705–717. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85723-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Lange K. Estimating kinetic constants from single channel data. Biophys J. 1983 Aug;43(2):207–223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84341-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R. Statistical methods for model discrimination. Applications to gating kinetics and permeation of the acetylcholine receptor channel. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):255–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83331-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Vandenberg C. A. Statistical properties of single sodium channels. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Oct;84(4):505–534. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Dependence of acetylcholine receptor channel kinetics on agonist concentration in cultured mouse muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:555–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Kinetics of unliganded acetylcholine receptor channel gating. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):663–672. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83693-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Perfection of a synaptic receptor: kinetics and energetics of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Brown R. D., Herz J. M., Berman H. A., Andreasen G. L., Taylor P. Decidium. A novel fluorescent probe of the agonist/antagonist and noncompetitive inhibitor sites on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14022–14029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph D., Petsko G. A., Karplus M. Anatomy of a conformational change: hinged "lid" motion of the triosephosphate isomerase loop. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1425–1428. doi: 10.1126/science.2402636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y., Rohrbough J. Acetylcholine receptor channels in Xenopus myocyte culture; brief openings, brief closures and slow desensitization. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:227–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land B. R., Salpeter E. E., Salpeter M. M. Kinetic parameters for acetylcholine interaction in intact neuromuscular junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7200–7204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Dilger J. P. Opening rate of acetylcholine receptor channels. Biophys J. 1991 Aug;60(2):424–432. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82068-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolis E., Petsko G. A. Crystallographic analysis of the complex between triosephosphate isomerase and 2-phosphoglycolate at 2.5-A resolution: implications for catalysis. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6619–6625. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Privé G. G., Milligan D. L., Scott W. G., Yeh J., Jancarik J., Koshland D. E., Jr, Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structures of the ligand-binding domain of the bacterial aspartate receptor with and without a ligand. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1342–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.1660187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden D. C., Colquhoun D. Ion channel block by acetylcholine, carbachol and suberyldicholine at the frog neuromuscular junction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Sep 23;225(1240):329–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. E., Cohen J. B. d-Tubocurarine binding sites are located at alpha-gamma and alpha-delta subunit interfaces of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pompliano D. L., Peyman A., Knowles J. R. Stabilization of a reaction intermediate as a catalytic device: definition of the functional role of the flexible loop in triosephosphate isomerase. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3186–3194. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrbough J., Kidokoro Y. Changes in kinetics of acetylcholine receptor channels after initial expression in Xenopus myocyte culture. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:245–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., Sauvé R. A general solution to the time interval omission problem applied to single channel analysis. Biophys J. 1985 Jul;48(1):149–158. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83768-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F., Neil J., Barkakati N. The automated analysis of data from single ionic channels. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):331–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00580798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J., Sine S. M. Data transformations for improved display and fitting of single-channel dwell time histograms. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83298-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Claudio T., Sigworth F. J. Activation of Torpedo acetylcholine receptors expressed in mouse fibroblasts. Single channel current kinetics reveal distinct agonist binding affinities. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Aug;96(2):395–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Agonists block currents through acetylcholine receptor channels. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84022-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


