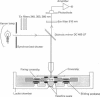
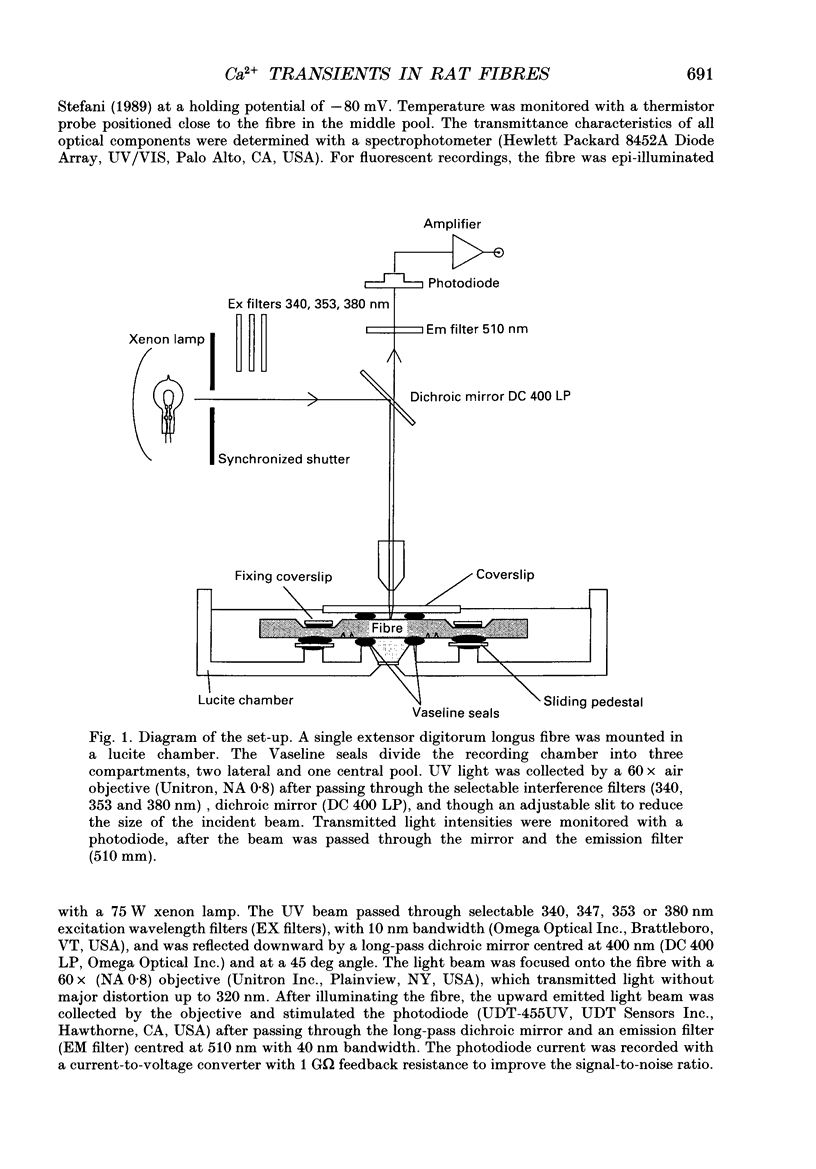
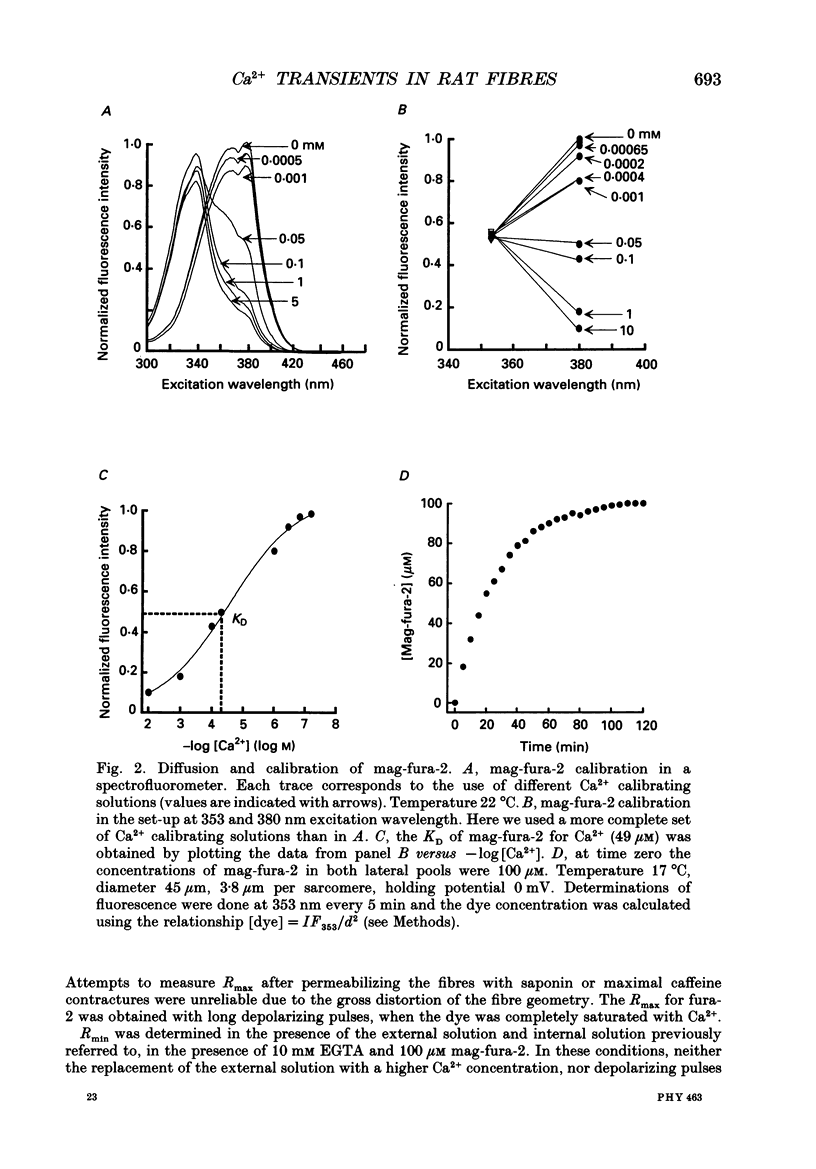
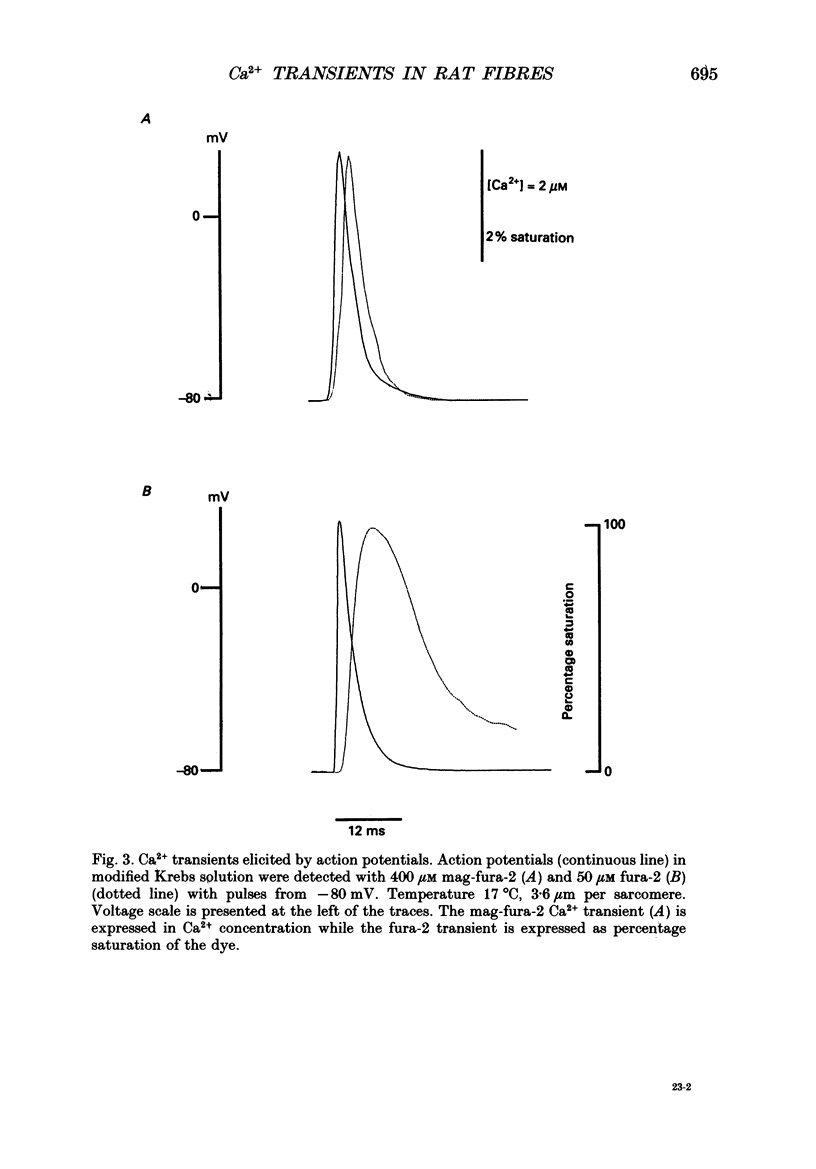
Abstract
1. We studied the transient changes in myoplasmic Ca2+ concentration under current- and voltage-clamp (double Vaseline-gap technique) in cut fibres of rat extensor digitorum longus muscle using mag-fura-2 (furaptra) as Ca2+ indicator, at 3.6-3.8 microns sarcomere length and 17 degrees C. Mag-fura-5 and fura-2 were also used in order to characterize some aspects of the Ca2+ transients. 2. The peak [Ca2+] in response to a single action potential was 4.6 +/- 0.4 microM (n = 5). The time to peak of the Ca2+ transient was 4.6 +/- 0.42 ms, with half-width of 8.2 +/- 1.5 ms, time constant of the rising phase 1.15 +/- 0.25 ms, time constant of the decaying phase 3.26 +/- 0.65 ms, and delay between action potential and Ca2+ transient 2.0 +/- 0.2 ms. 3. Ca2+ transients were studied under voltage-clamp conditions at different voltages and pulse durations. The rising phase showed a complex temporal course with a fast initial increase and a second component. Both components were separated by a plateau or a brief decrease of the Ca2+ concentration. The peak Ca2+ transient was 10.5 +/- 1.3 microM (n = 22). 4. After interrupting the pulse, Ca2+ concentration decayed exponentially. The time constant of decay of the Ca2+ transient increased with the pulse voltage and duration, reaching a maximum value at potentials more positive than +10 mV and pulses longer than 200 ms. An analysis of the decaying phases of the Ca2+ transients suggests that only the removal process operates after fibre repolarization. 5. The rate of Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum was calculated using the Melzer, Ríos & Schneider model. The value of 17.2 +/- 3.1 micronM ms-1 (n = 10) estimated in these calculations was intermediate between those obtained by other authors from cut frog muscles (10 microM ms-1) and intact frog fibres (100 microM ms-1) using antipyrylazo III (AP III) as the Ca2+ indicator.
Full text
PDF




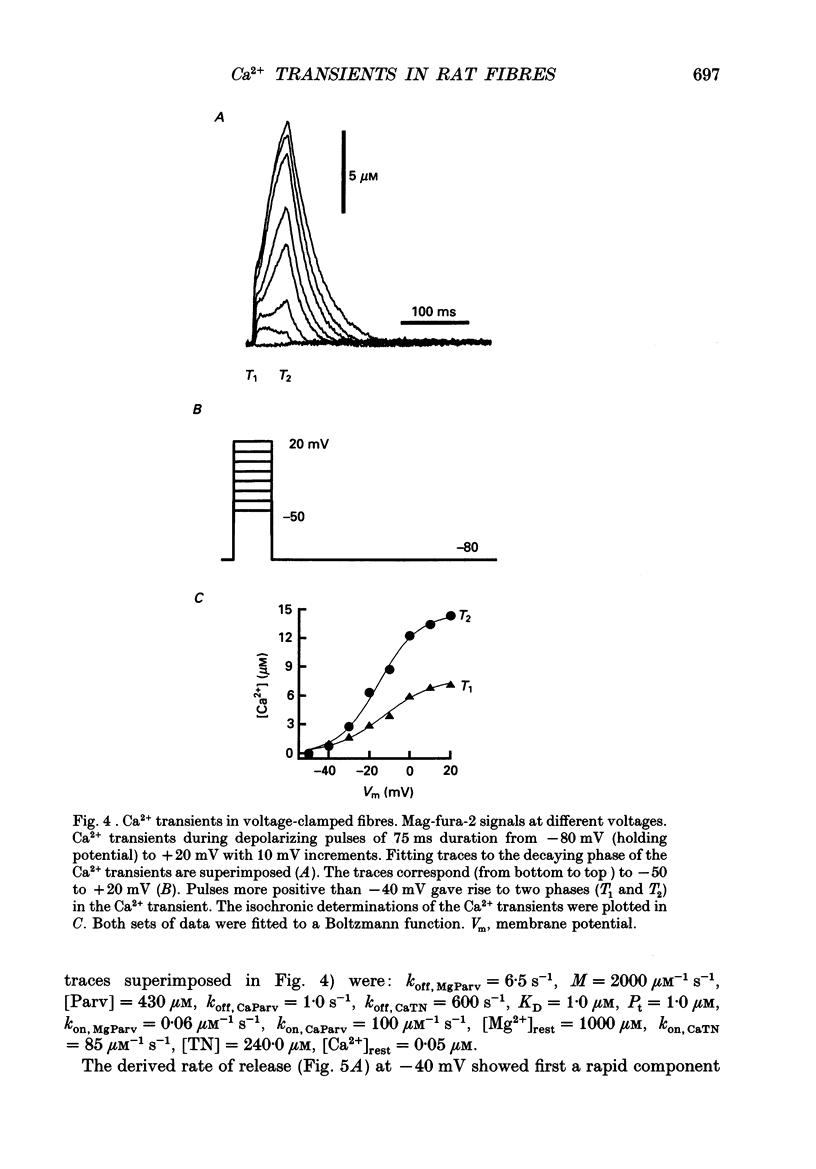
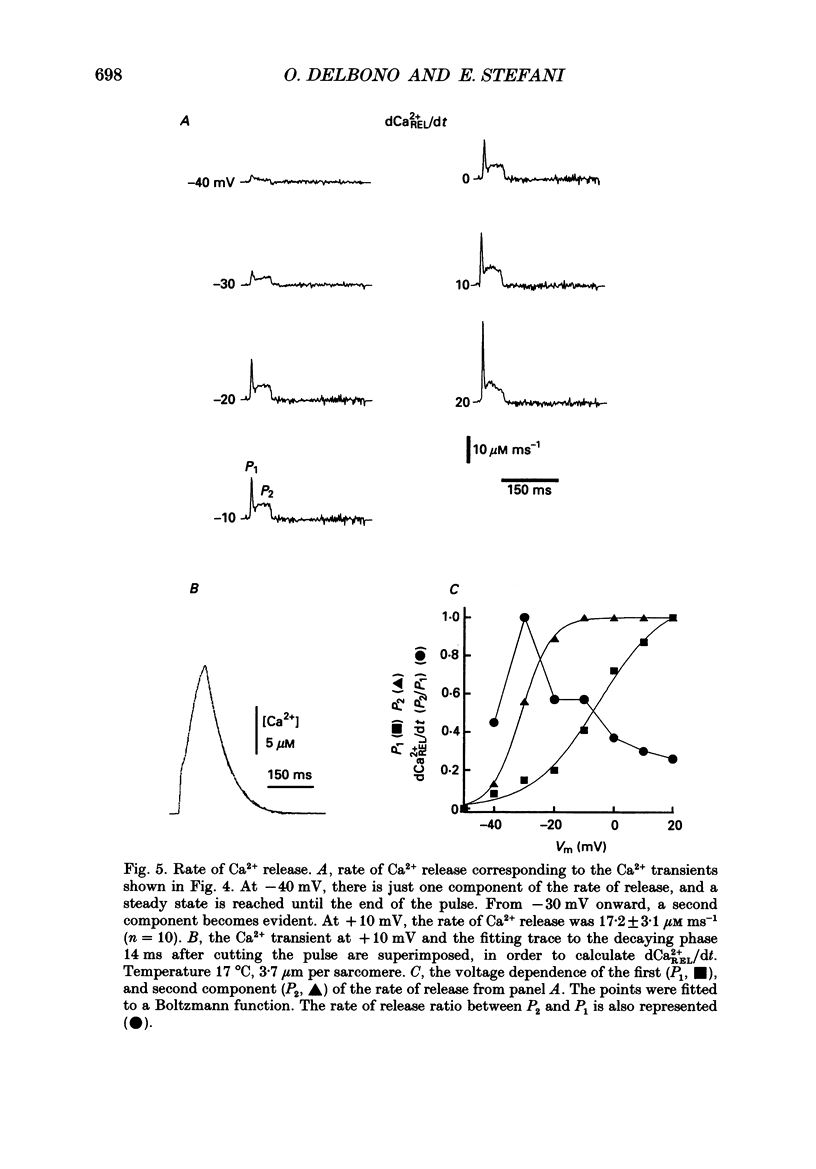
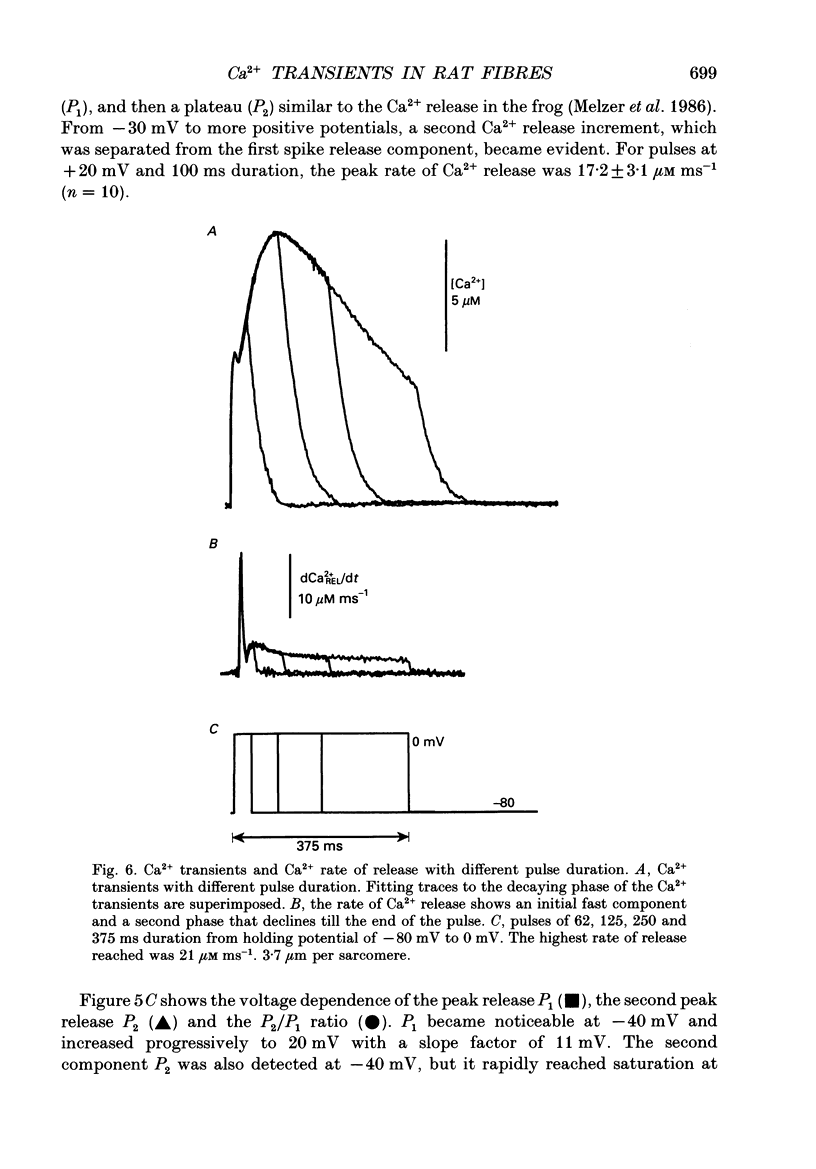
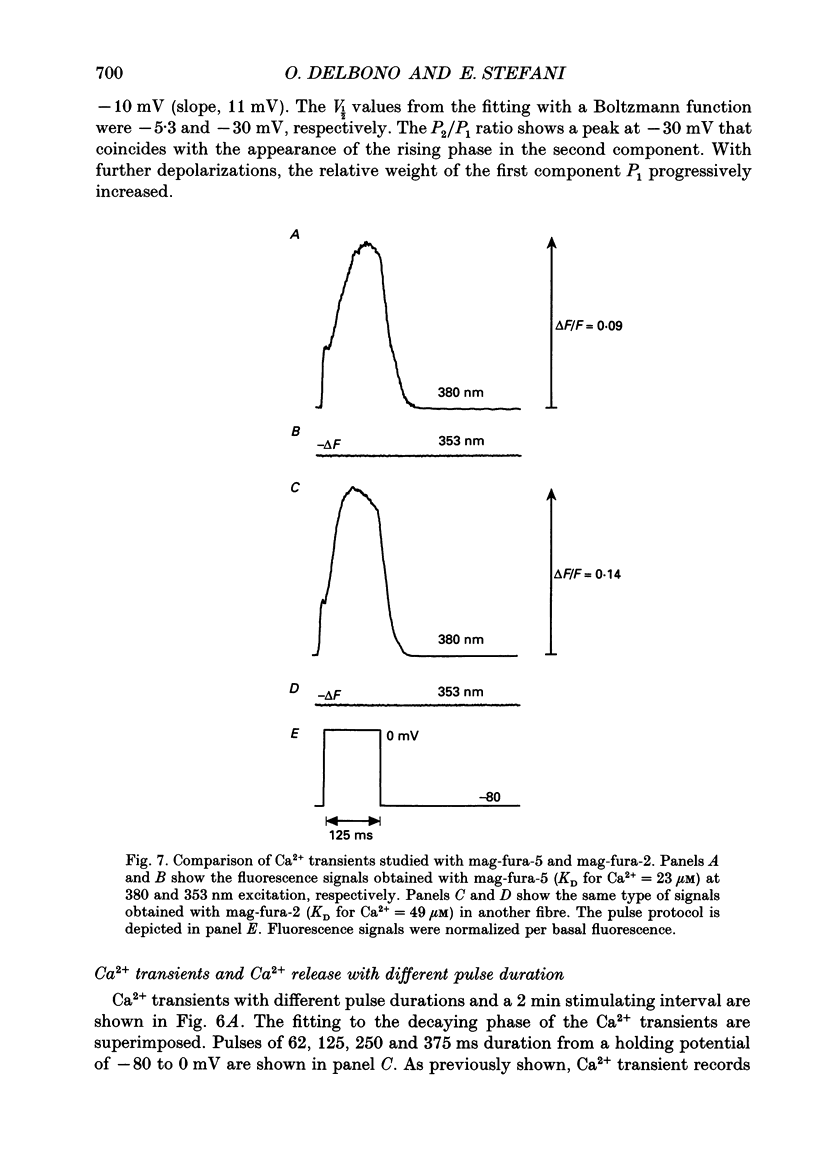

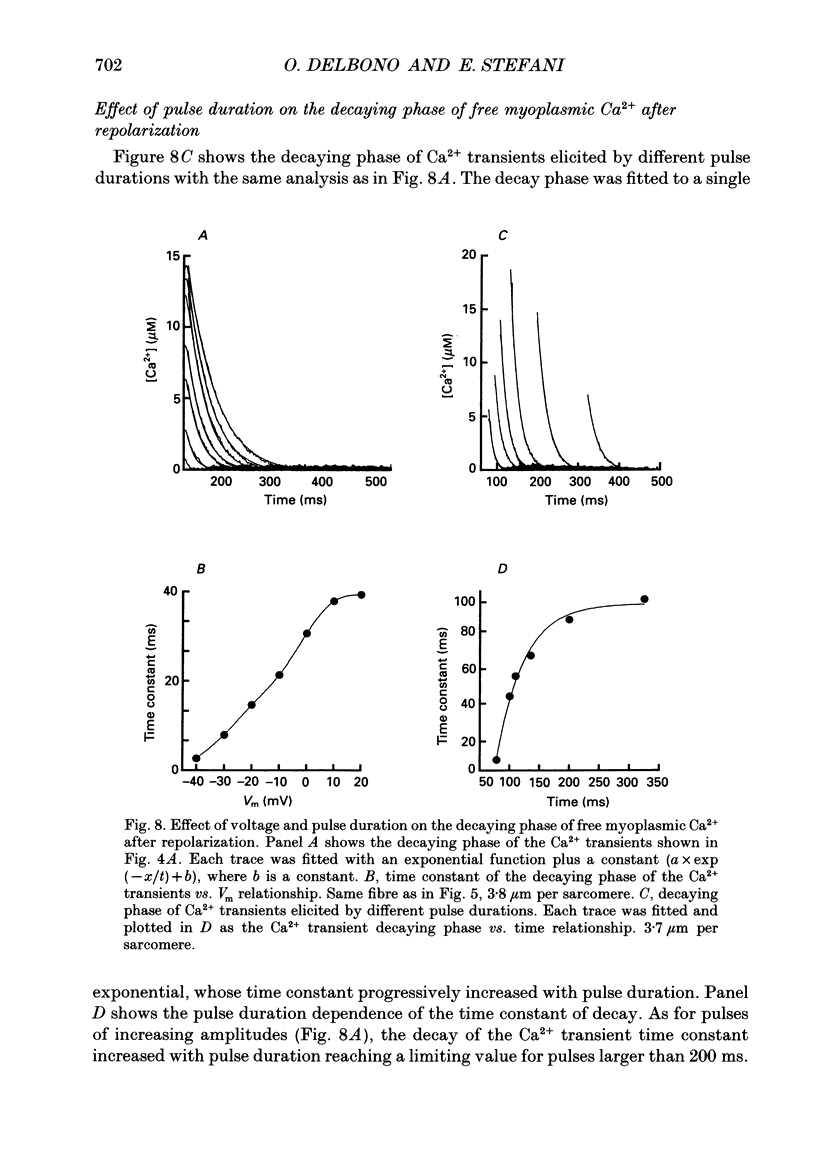





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S. Fura-2 calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:151–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuckelmann D. J., Wier W. G. Mechanism of release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Lehky P., Kohler L., Stein E. A., Fischer E. H. Comparative properties of vertebrate parvalbumins. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2834–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Ríos E., Stéfani E. Effects of extracellular calcium on calcium movements of excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:441–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbono O. Calcium current activation and charge movement in denervated mammalian skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992;451:187–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbono O., García J., Appel S. H., Stefani E. Calcium current and charge movement of mammalian muscle: action of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis immunoglobulins. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:723–742. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi F., Miledi R., Takahashi T. Calcium transients in mammalian muscles. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):560–561. doi: 10.1038/284560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francini F., Stefani E. Decay of the slow calcium current in twitch muscle fibers of the frog is influenced by intracellular EGTA. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Nov;94(5):953–969. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.5.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann C. W., Malencik D. A., Fischer E. H. Generation of parvalbumin-like proteins from troponin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80371-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann C. W. Parvalbumin, an intracellular calcium-binding protein; distribution, properties and possible roles in mammalian cells. Experientia. 1984 Sep 15;40(9):910–921. doi: 10.1007/BF01946439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota A., Chandler W. K., Southwick P. L., Waggoner A. S. Calcium signals recorded from two new purpurate indicators inside frog cut twitch fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Oct;94(4):597–631. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.4.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou T. T., Johnson J. D., Rall J. A. Parvalbumin content and Ca2+ and Mg2+ dissociation rates correlated with changes in relaxation rate of frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:285–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., Maylie J., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Simultaneous monitoring of changes in magnesium and calcium concentrations in frog cut twitch fibers containing antipyrylazo III. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Apr;93(4):585–608. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Kovacs L., Simon B. J., Schneider M. F. Decline of myoplasmic Ca2+, recovery of calcium release and sarcoplasmic Ca2+ pump properties in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:639–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Simon B. J., Szucs G., Schneider M. F. Simultaneous recording of calcium transients in skeletal muscle using high- and low-affinity calcium indicators. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):971–988. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83178-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic calcium transients monitored with purpurate indicator dyes injected into intact frog skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Feb;97(2):245–270. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Hollingworth S., Harkins A. B., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic calcium transients in intact frog skeletal muscle fibers monitored with the fluorescent indicator furaptra. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Feb;97(2):271–301. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs L., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Measurement and modification of free calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres by a metallochromic indicator dye. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:161–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Calcium transients and intramembrane charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):391–396. doi: 10.1038/279391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Control of calcium release and the effect of ryanodine in skinned muscle fibres of the toad. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:519–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. A general procedure for determining the rate of calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1987 Jun;51(6):849–863. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83413-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. The removal of myoplasmic free calcium following calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:261–292. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Schneider M. F., Simon B. J., Szucs G. Intramembrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:481–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Calcium transients in normal and denervated slow muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:191–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju B., Murphy E., Levy L. A., Hall R. D., London R. E. A fluorescent indicator for measuring cytosolic free magnesium. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):C540–C548. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.3.C540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Potter J. D. The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin, and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84868-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Schneider M. F. Time course of activation of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1159–1163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83050-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R., Pozzan T. Measurement of cytosolic free Ca2+ with quin2. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:230–262. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]