Abstract
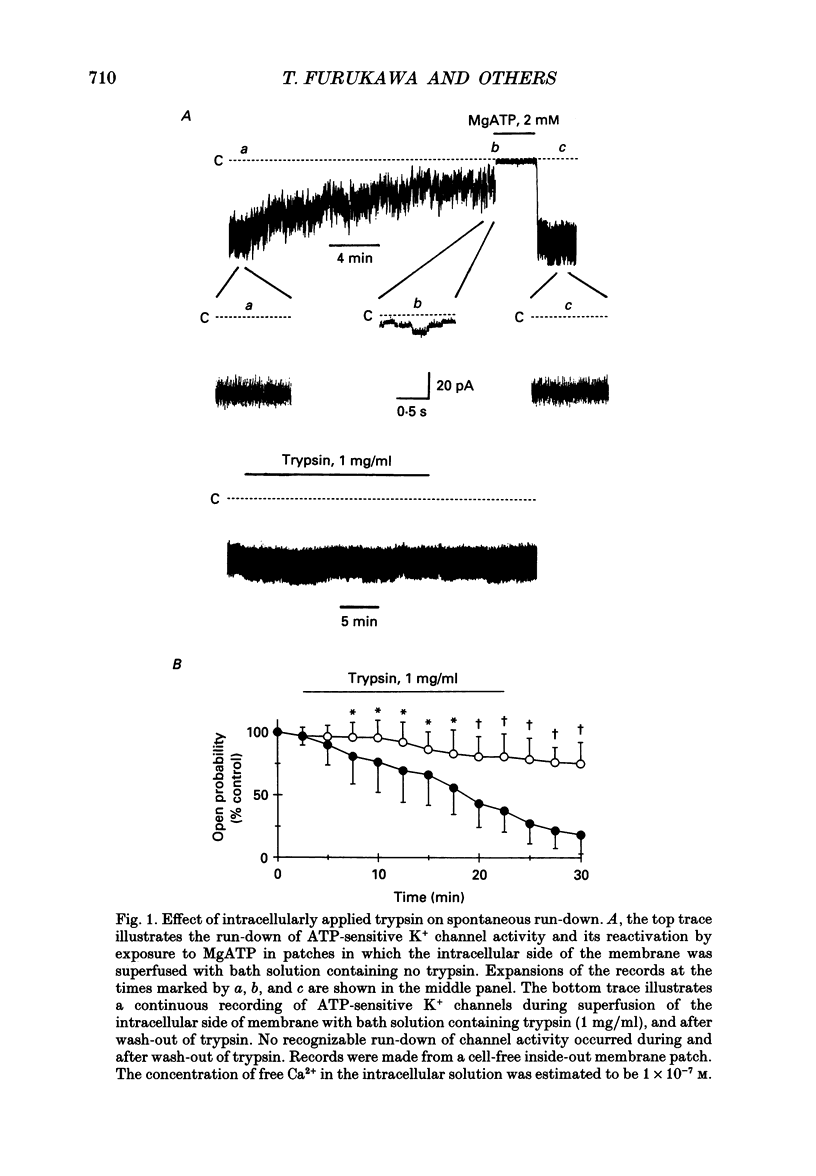
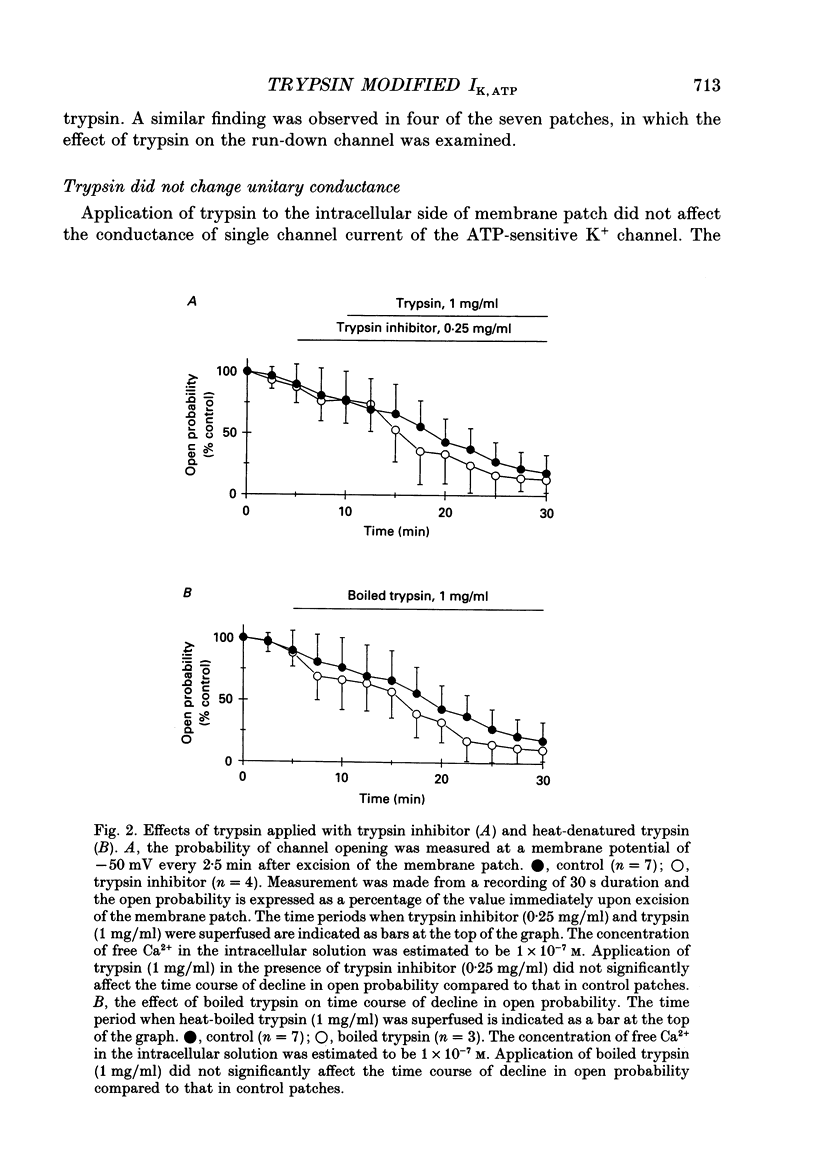
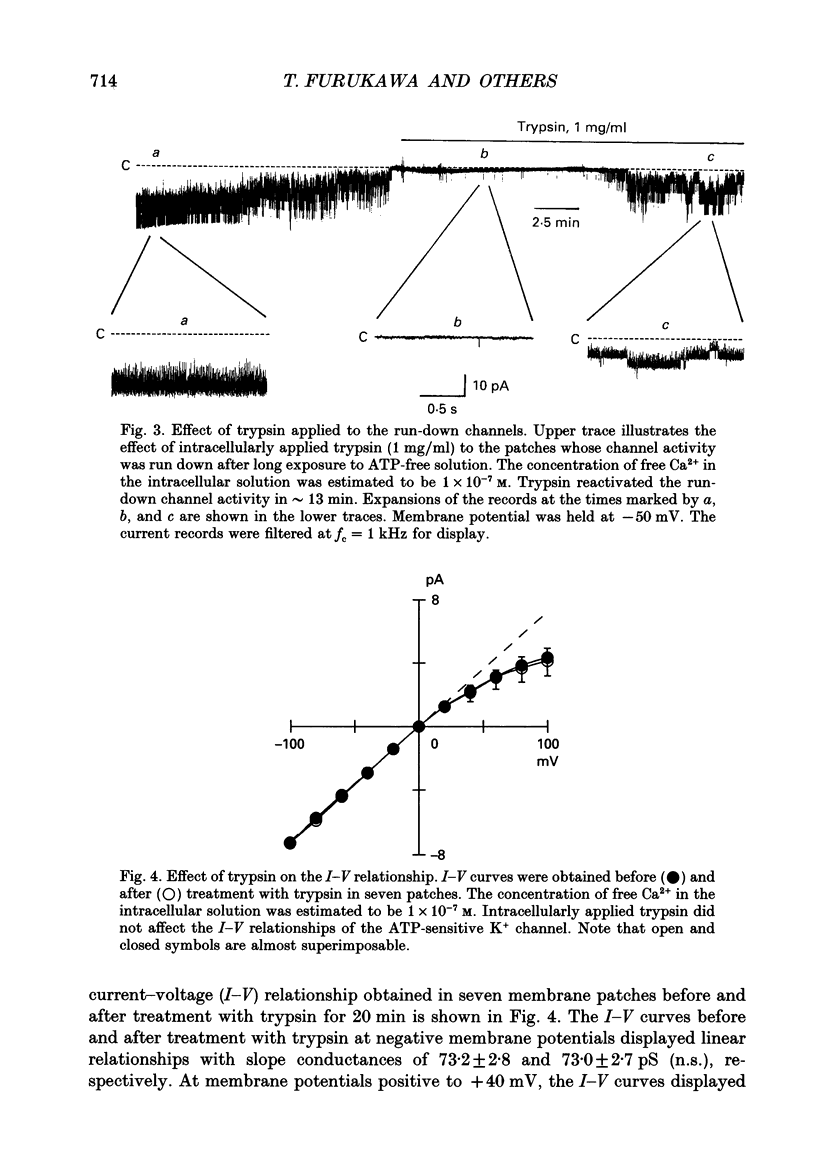
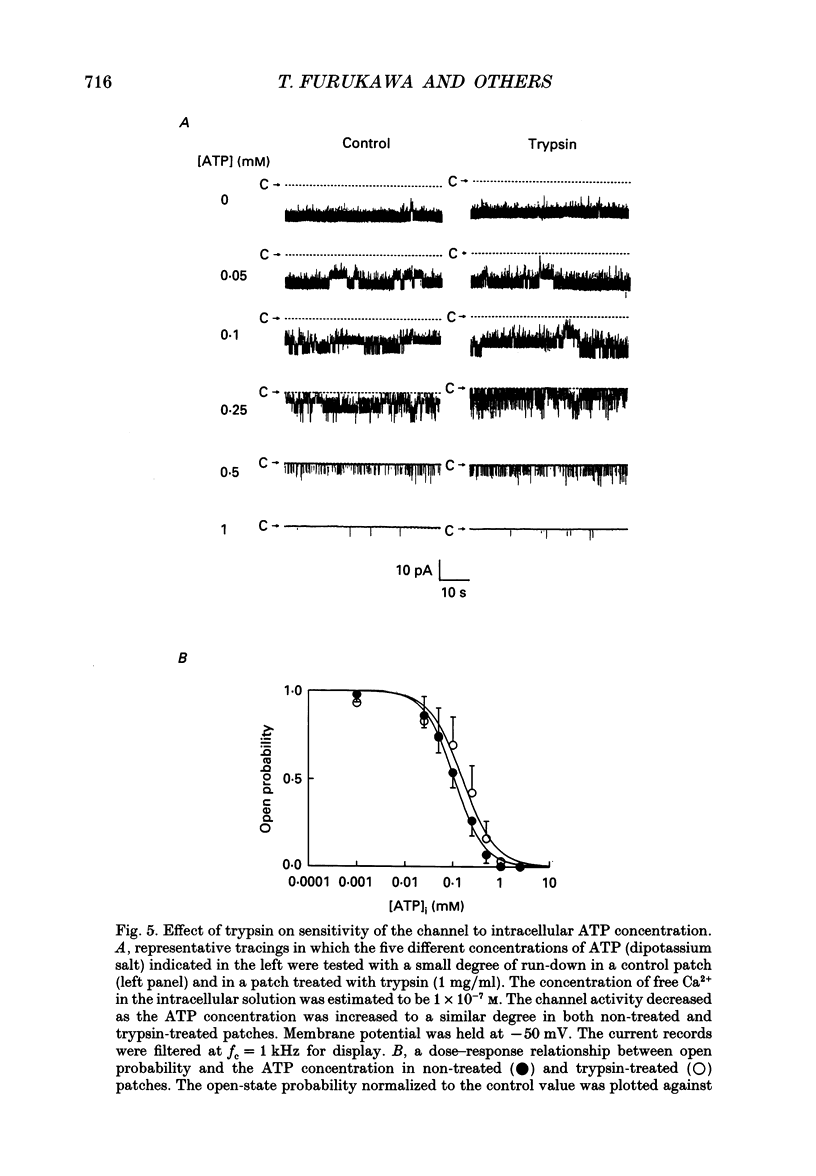
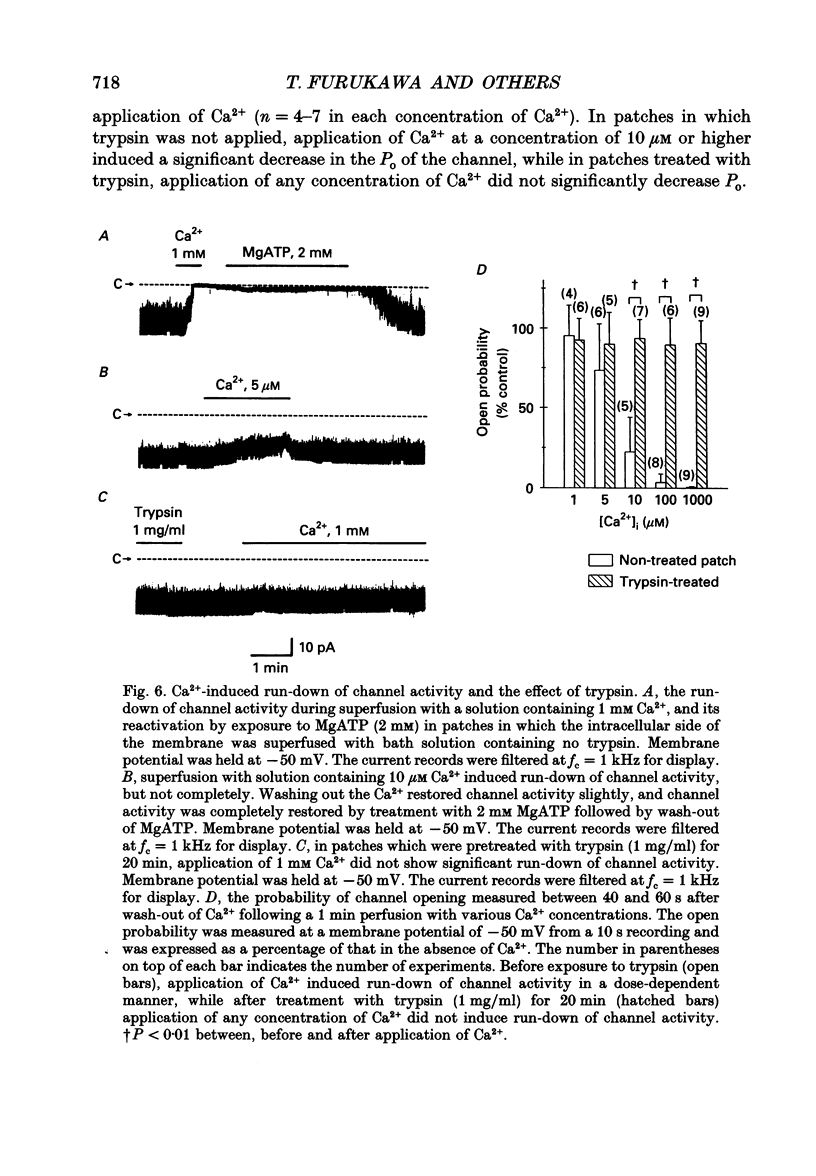
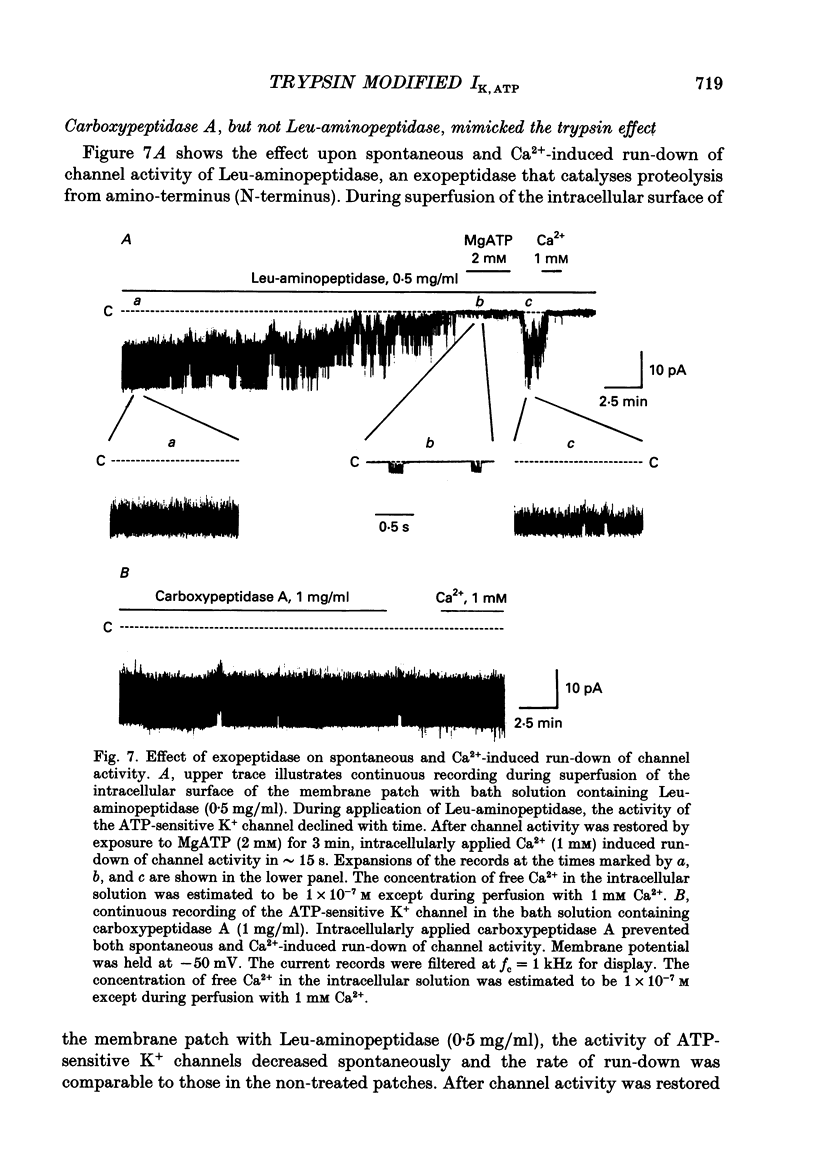
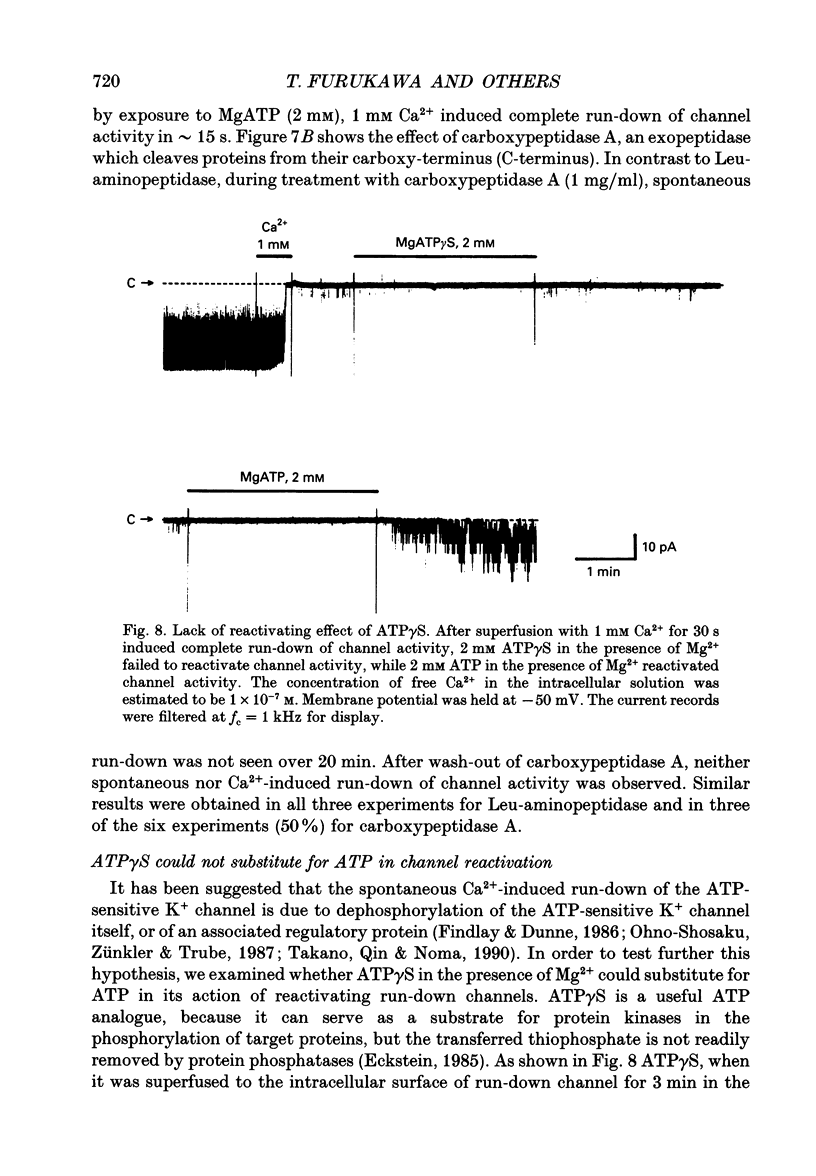
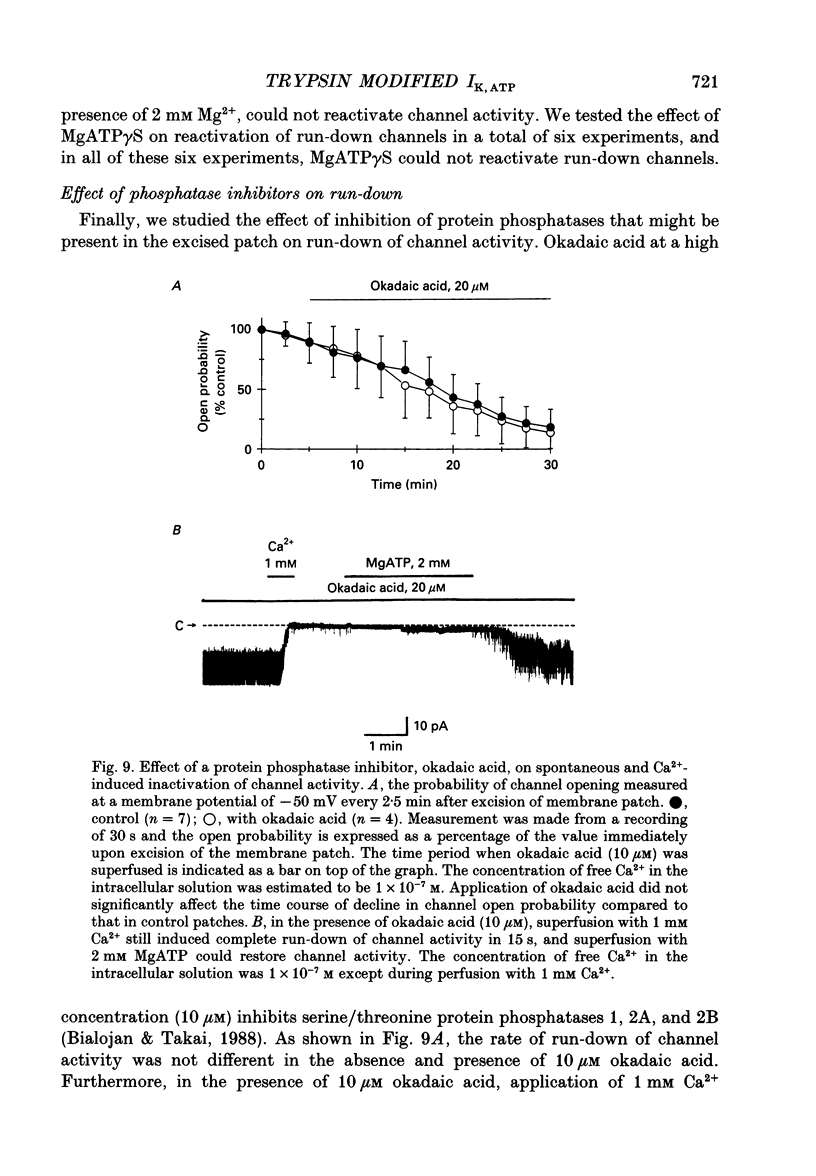
1. The adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive K+ channel current was recorded in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes using the patch clamp technique with inside-out patch configuration. Modification of the channel activity by intracellular application of an endoprotease trypsin was studied, and was related to a possible model of regulation of this channel. 2. Maximal ATP-sensitive K+ channel activity was observed immediately upon formation of inside-out patches in the ATP-free internal solution, thereafter activity declined both spontaneously and gradually with time; a phenomenon known as rundown. When trypsin (1 mg/ml) was applied to the intracellular side of the membrane upon formation of inside-out patches, spontaneous run-down did not occur, and this trypsin action was irreversible. Neither trypsin (1 mg/ml) applied with trypsin inhibitor (0.25 mg/ml) nor heat-denatured trypsin (1 mg/ml) could mimic this effect. When trypsin was applied to the patches after run-down, channels were reactivated at approximately 13 min. 3. Treatment with trypsin did not affect unitary current amplitude, channel gating kinetics, or sensitivity to intracellular ATP. 4. Intracellularly applied Ca2+ induced run-down of channel activity in a dose-dependent manner. In membrane patches that were treated with trypsin (1 mg/ml) for 20 min, intracellularly applied Ca2+ up to 1 mM did not induce run-down of channel activity. 5. Intracellular application of an exopeptidase, carboxypeptidase A (1 mg/ml), but not Leu-aminopeptidase (0.5 mg/ml), prevented spontaneous or Ca(2+)-induced run-down of channel activity. 6. As postulated for several other channels, such as Na+ and Ca2+ channels, there may be a possible 'chemical gate' that is responsible for run-down of this channel activity. Application of trypsin might somehow modify this 'chemical gate', resulting in prevention of spontaneous or Ca(2+)-induced run-down. This target site for trypsin may be situated on the carboxy-terminus of the channel proteins, or of associated regulatory units. Because ATP sensitivity remained intact after trypsin treatment, the trypsin-selective site for channel inhibition is not related physically to the ATP binding site.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F., Rojas E. Destruction of sodium conductance inactivation in squid axons perfused with pronase. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Oct;62(4):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:97–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashford M. L., Sturgess N. C., Trout N. J., Gardner N. J., Hales C. N. Adenosine-5'-triphosphate-sensitive ion channels in neonatal rat cultured central neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Aug;412(3):297–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00582512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F. Nucleoside phosphorothioates. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:367–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. Calcium-dependent inactivation of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel of rat ventricular myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 18;943(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J. ATP maintains ATP-inhibited K+ channels in an operational state. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):238–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00580683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol. 1985;88(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01868430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Trautwein W. Modification of L-type calcium current by intracellularly applied trypsin in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:259–274. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano Y., Hiraoka M. Barium-induced automatic activity in isolated ventricular myocytes from guinea-pig hearts. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:455–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie M., Irisawa H., Noma A. Voltage-dependent magnesium block of adenosine-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:251–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Biophysical and molecular mechanisms of Shaker potassium channel inactivation. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):533–538. doi: 10.1126/science.2122519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M. Trypsin activation of atrial muscarinic K+ channels. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):H334–H338. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.1.H334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski R. Z., Ashford M. L. ATP-sensitive K(+)-channel run-down is Mg2+ dependent. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jun 22;240(1298):397–410. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Nichols C. G. Nucleotide modulation of the activity of rat heart ATP-sensitive K+ channels in isolated membrane patches. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:193–211. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno-Shosaku T., Zünkler B. J., Trube G. Dual effects of ATP on K+ currents of mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Feb;408(2):133–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00581342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J., Horn R. Effect of N-bromoacetamide on single sodium channel currents in excised membrane patches. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Mar;79(3):333–351. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Voltage-dependent ATP-sensitive potassium channels of skeletal muscle membrane. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):736–738. doi: 10.1038/316736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Qin D. Y., Noma A. ATP-dependent decay and recovery of K+ channels in guinea pig cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):H45–H50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.1.H45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Sequence of a probable potassium channel component encoded at Shaker locus of Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):770–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2441471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Hescheler J. Inward-rectifying channels in isolated patches of the heart cell membrane: ATP-dependence and comparison with cell-attached patches. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jun;401(2):178–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00583879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung R. T., Kurachi Y. On the mechanism of nucleotide diphosphate activation of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in ventricular cell of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1991 Jun;437:239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberter Y., Burnashev N., Papin A., Portnov V., Khodorov B. Gating kinetics of ATP-sensitive single potassium channels in myocardial cells depends on electromotive force. Pflugers Arch. 1988 May;411(5):584–589. doi: 10.1007/BF00582382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


