Abstract
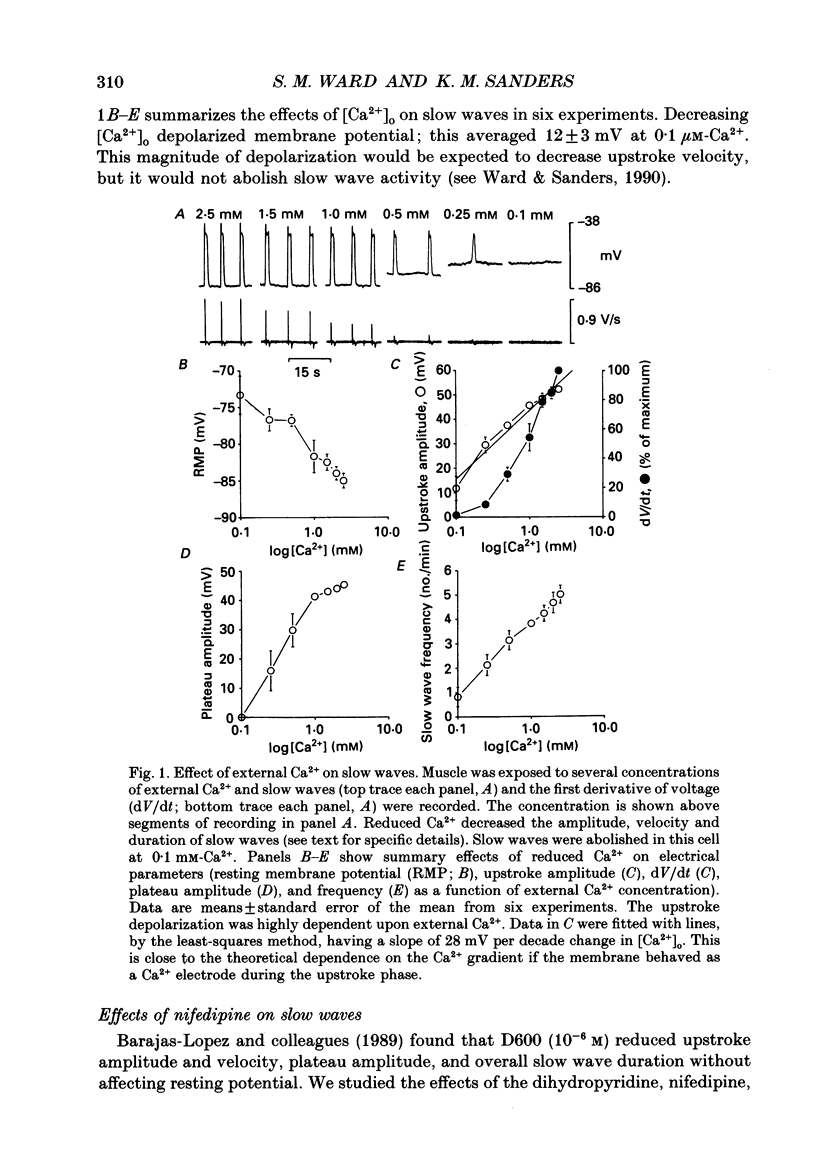
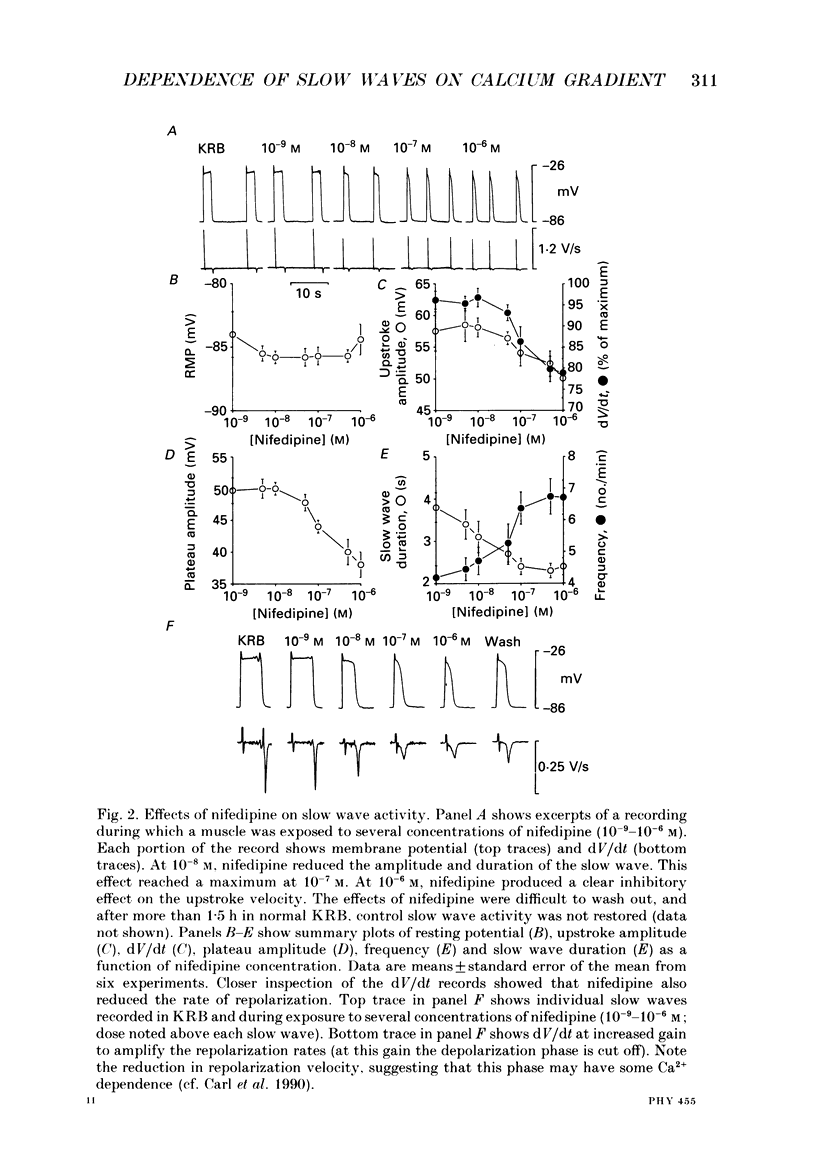
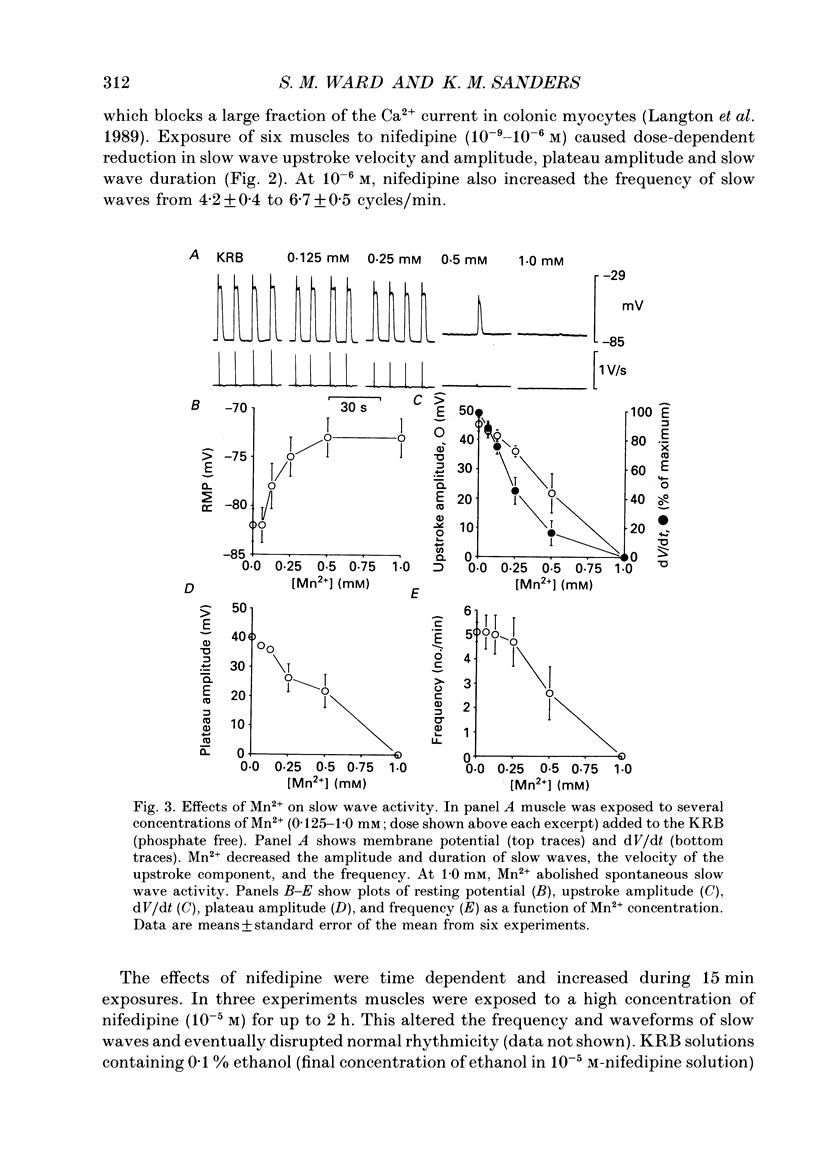
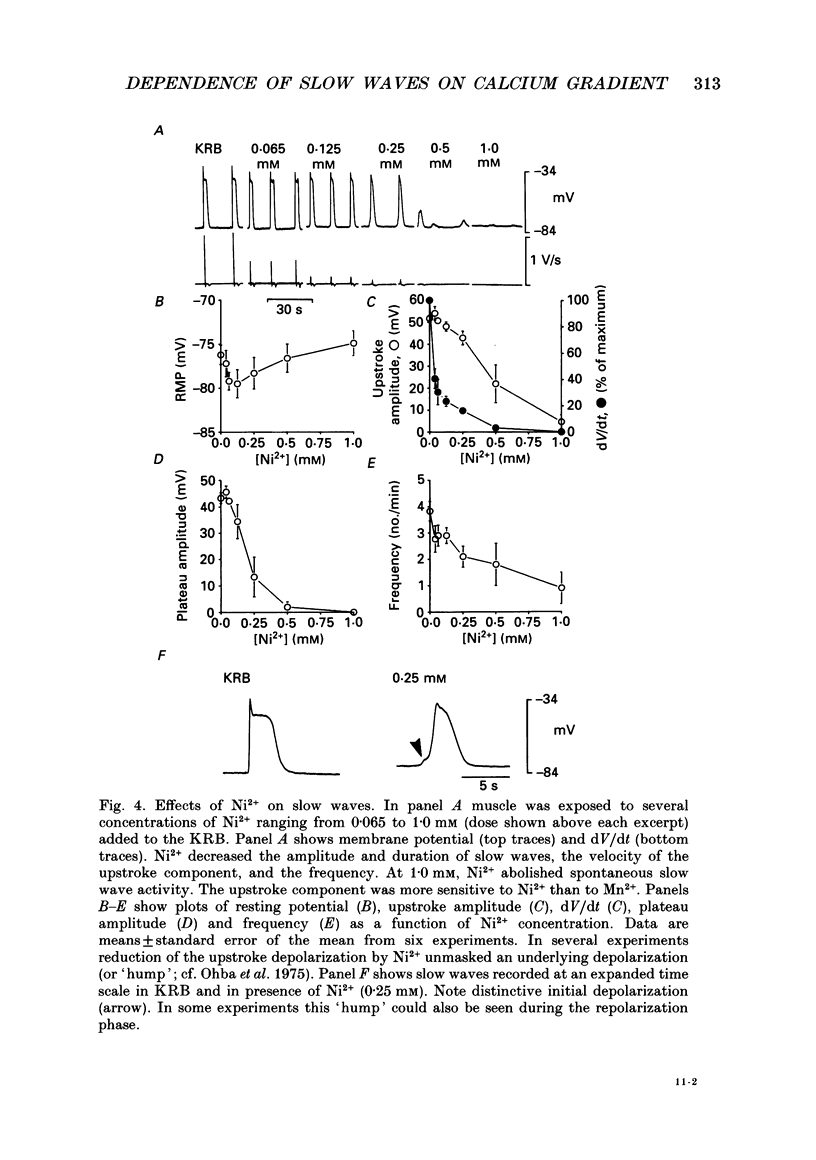
1. The ionic dependence of the upstroke and plateau components of slow waves of canine colonic circular muscles was studied. 2. Reduced extracellular Ca2+ caused a decrease in the amplitude of the upstroke and plateau components, a decrease in the depolarization velocity, and a decrease in frequency. The reduction in the upstroke phase per 10-fold reduction in external Ca2+ was close to the value predicted by the Nernst relationship, suggesting that the membrane permeability to Ca2+ increases steeply during this phase. 3. Nifedipine (10(-9)-10(-6)) reduced the plateau component, but concentrations of 10(-6) M did not abolish the upstroke component. The data suggest that a nifedipine-resistant component of Ca2+ current may be involved in the upstroke. 4. Inorganic Ca2+ channel blockers (Mn2+ and Ni2+) blocked spontaneous slow waves at concentrations of 1.0 mM or less. 5. The upstroke component was more sensitive to Ni2+ than to Mn2+; a concentration of 0.040 mM-Ni2+ caused more than a 50% reduction in upstroke velocity. Ni2+ also reduced the plateau phase of slow waves. 6. The results suggest that the upstroke and plateau components of slow waves are dependent upon activation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents. The current responsible for the upstroke is partially resistant to dihydropyridines (at least at 10(-6) M). The current responsible for the plateau component is nifedipine-sensitive.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barajas-López C., Den Hertog A., Huizinga J. D. Ionic basis of pacemaker generation in dog colonic smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:385–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barajas-López C., Huizinga J. D. Different mechanisms of contraction generation in circular muscle of canine colon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):G570–G580. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.3.G570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. J., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. Slow wave heterogeneity within the circular muscle of the canine gastric antrum. J Physiol. 1985 Sep;366:221–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer A. J., Sanders K. M. Gradient in excitation-contraction coupling in canine gastric antral circular muscle. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:283–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Nitrendipine block of cardiac calcium channels: high-affinity binding to the inactivated state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. L., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr, Fay F. S. Regulation of calcium concentration in voltage-clamped smooth muscle cells. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):211–214. doi: 10.1126/science.2704996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Denbigh J. S., Lang R. J. Inward rectification in freshly isolated single smooth muscle cells of the rabbit jejunum. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:461–476. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke E. P., Sanders K. M. Effects of ouabain on background and voltage-dependent currents in canine colonic myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 1):C402–C408. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.3.C402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl A., McHale N. G., Publicover N. G., Sanders K. M. Participation of Ca2(+)-activated K+ channels in electrical activity of canine gastric smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:205–221. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Caprilli R., Lund G. F. Electric slow waves in circular muscle of cat colon. Am J Physiol. 1969 Sep;217(3):771–776. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.3.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole W. C., Sanders K. M. Characterization of macroscopic outward currents of canine colonic myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C461–C469. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. A study of the ionic nature of the pace-maker current in calf Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:377–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D., Ojeda C. Properties of the current if in the sino-atrial node of the rabbit compared with those of the current iK, in Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:353–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga J. D., Farraway L., Den Hertog A. Generation of slow-wave-type action potentials in canine colon smooth muscle involves a non-L-type Ca2+ conductance. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:15–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langton P. D., Burke E. P., Sanders K. M. Participation of Ca currents in colonic electrical activity. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C451–C460. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K. G., Szurszewski J. H. Mechanisms of phasic and tonic actions of pentagastrin on canine gastric smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:229–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Worley J. F. Dihydropyridine inhibition of single calcium channels and contraction in rabbit mesenteric artery depends on voltage. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:65–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohba M., Sakamoto Y., Tomita T. The slow wave in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig stomach. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):505–516. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Burke E. P., Stevens R. J. Effects of methylene blue on rhythmic activity and membrane potential in the canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):G779–G784. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.4.G779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M. Excitation-contraction coupling without Ca2+ action potentials in small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):C356–C361. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.5.C356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Smith T. K. Enteric neural regulation of slow waves in circular muscle of the canine proximal colon. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:297–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M., Smith T. K. Motoneurones of the submucous plexus regulate electrical activity of the circular muscle of canine proximal colon. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:293–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. K., Reed J. B., Sanders K. M. Origin and propagation of electrical slow waves in circular muscle of canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):C215–C224. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.2.C215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. M., Sanders K. M. Pacemaker activity in septal structures of canine colonic circular muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):G264–G273. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.2.G264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. M., Sanders K. M. Upstroke component of electrical slow waves in canine colonic smooth muscle due to nifedipine-resistant calcium current. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:321–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Sharkawy T. Y., Morgan K. G., Szurszewski J. H. Intracellular electrical activity of canine and human gastric smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:291–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


