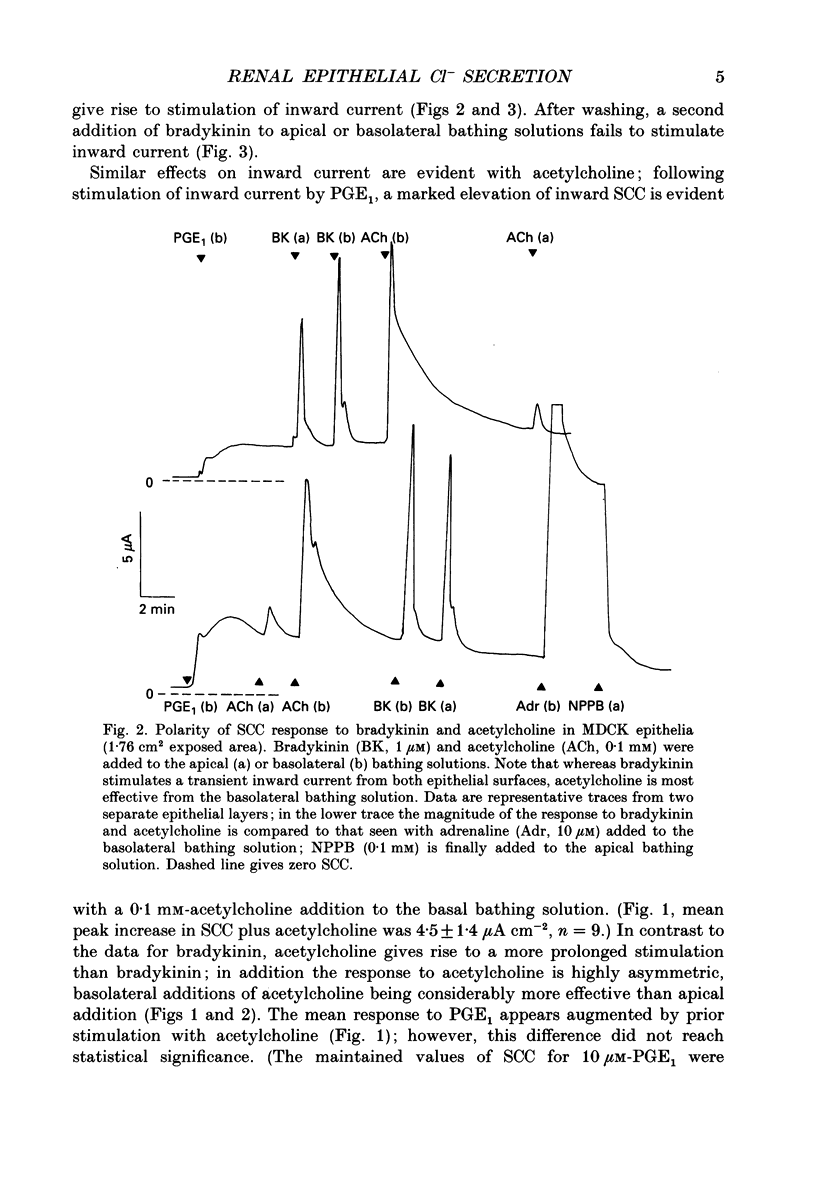
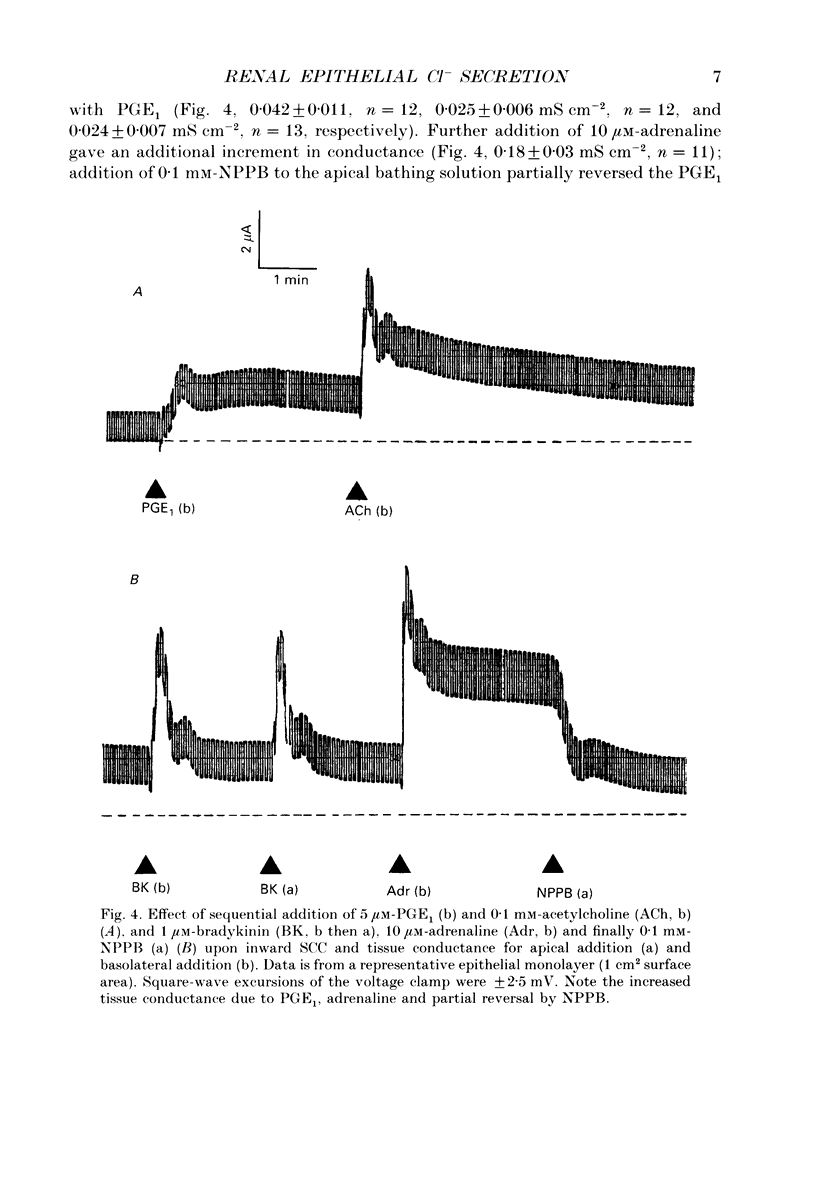
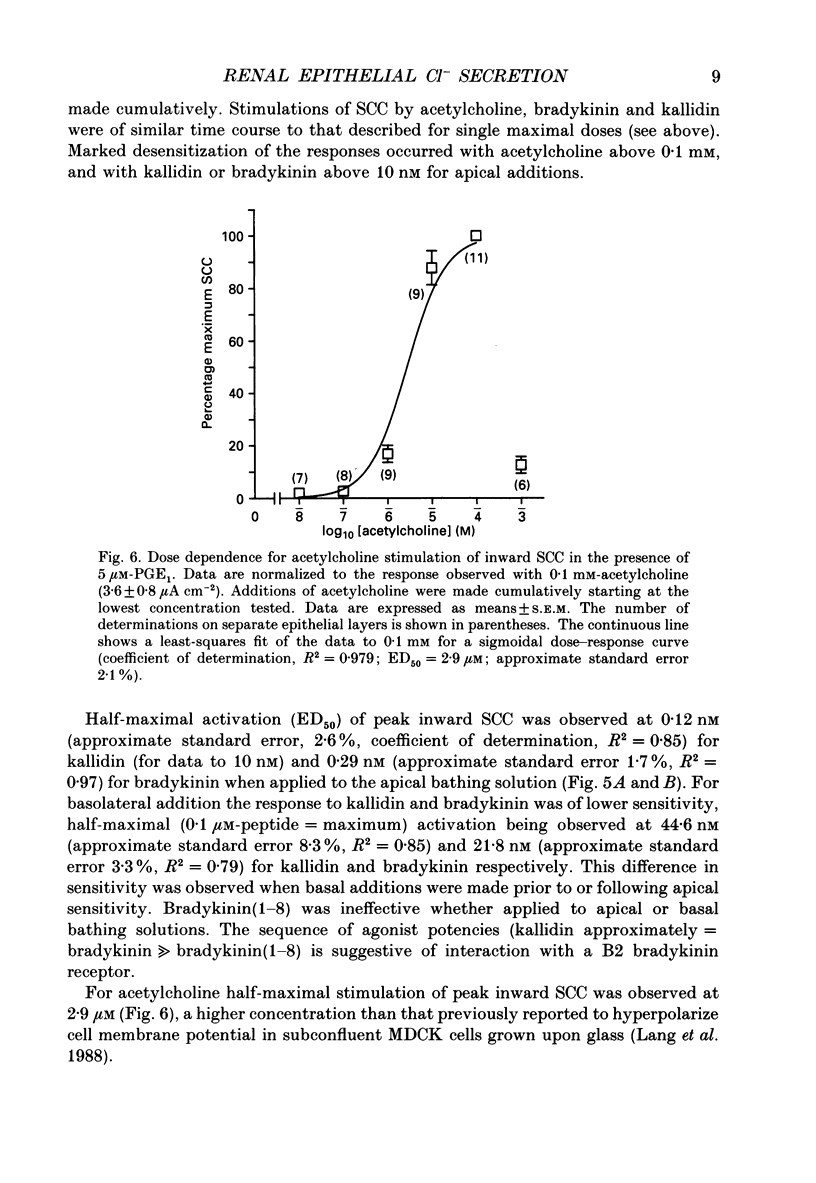
Abstract
1. The actions of kinins and of acetylcholine upon transepithelial ion transport in a renal-derived cultured epithelium (Madin-Darby canine kidney cells, MDCK) have been investigated. 2. In voltage-clamped epithelial layers mounted in Ussing chambers and with prior stimulation of inward short-circuit current (SCC) by 5 or 10 microM-prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), both bradykinin (1 microM) and acetylcholine (0.1 mM) stimulate an additional, but transient, inward SCC. In the absence of PGE1 minimal effects of both bradykinin and acetylcholine upon SCC are observed. The SCC response to bradykinin and acetylcholine are attenuated with prior stimulation by 10 microM-adrenaline. 3. Measurements of bradykinin and acetylcholine-stimulated inward SCC with cation and anion replacement of the bathing media and the use of the Cl channel blocker 5-nitro-2(3-phenylpropylamino)-benzoic acid (NPPB) together with bumetanide to inhibit Na(+)-K(+)-Cl- 'co-transport', are consistent with the bradykinin- and acetylcholine-stimulated SCC being the result of basal to apical Cl- secretion. 4. Bradykinin (1 microM) is capable of stimulation of inward SCC from both epithelial surfaces, whilst acetylcholine is only effective from the basolateral surface. Kallidin (lys-bradykinin) was similar in effect to bradykinin from both epithelial surfaces whereas bradykinin (1-8) was ineffective, suggesting that B2 bradykinin receptors mediate the effect of bradykinin upon SCC. Dose-response relationships show that the response to kallidin and bradykinin was of higher sensitivity for additions to the apical cell aspects. 5. The data are discussed in relation to a model for epithelial Cl- secretion, and to the mechanism of natriuresis observed with kinins and acetylcholine in vivo.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboolian A., Vander Molen M., Nord E. P. Differential effects of phorbol esters on PGE2 and bradykinin-induced elevation of [Cai2+] in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F1135–F1143. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer W. V., Mack E., Rothstein A. Activation of K+ and Cl- channels by Ca2+ and cyclic AMP in dissociated kidney epithelial (MDCK) cells. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Apr;411(4):450–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00587726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. D., Rugg E. L., Simmons N. L. Loop-diuretic inhibition of adrenaline-stimulated Cl- secretion in a cultured epithelium of renal origin (MDCK). Q J Exp Physiol. 1986 Apr;71(2):183–193. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1986.sp002977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. D., Simmons N. L. Catecholamine-stimulation of Cl- secretion in MDCK cell epithelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 7;649(2):427–435. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90432-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. D., Simmons N. L. K+ transport in 'tight' epithelial monolayers of MDCK cells. Evidence for a calcium-activated K+ channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 25;690(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., George A. M., MacVinish L. Kinin effects on electrogenic ion transport in primary cultures of pig renal papillary collecting tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 2):F439–F447. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.3.F439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emond C., Bascands J. L., Cabos-Boutot G., Pecher C., Girolami J. P. Effect of changes in sodium or water intake on glomerular B2-kinin-binding sites. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):F353–F358. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.3.F353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Perez A., Smith W. L. Apical-basolateral membrane asymmetry in canine cortical collecting tubule cells. Bradykinin, arginine vasopressin, prostaglandin E2 interrelationships. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):63–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI111419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths N. M., Rugg E. L., Simmons N. L. Vasoactive intestinal peptide control of renal adenylate cyclase: in vitro studies of canine renal membranes and cultured canine renal epithelial (MDCK) cells. Q J Exp Physiol. 1989 May;74(3):339–353. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1989.sp003276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassid A. Modulation of cyclic 3'5'-adenosine monophosphate in cultured renal (MDCK) cells by endogenous prostaglandins. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Sep;116(3):297–302. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted R. F., Welsh M. J., Stokes J. B. Variability of functional characteristics of MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):C214–C221. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.2.C214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. S., Fabre R. D., Beal J. A. Identification of noradrenergic nerve terminals immunoreactive for neuropeptide Y and vasoactive intestinal peptide in the rat kidney. Am J Anat. 1989 Mar;184(3):190–204. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001840303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Pfeilschifter J., Brown C. D., Bauer C. NaCl transport stimulates prostaglandin release in cultured renal epithelial (MDCK) cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 1):C676–C681. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.5.C676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang F., Defregger M., Paulmichl M. Apparent chloride conductance of subconfluent Madin Darby canine kidney cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):158–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00580668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang F., Friedrich F., Paulmichl M., Schobersberger W., Jungwirth A., Ritter M., Steidl M., Weiss H., Wöll E., Tschernko E. Ion channels in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1990 Jan-Apr;13(1-2):82–93. doi: 10.1159/000173350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang F., Klotz L., Paulmichl M. Effect of acetylcholine on electrical properties of subconfluent Madin Darby canine kidney cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 22;941(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liedtke C. M. Regulation of chloride transport in epithelia. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:143–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., Schwiebert E. M., Fejes-Toth G., Naray-Fejes-Toth A., Karlson K. H., McCann F. V., Stanton B. A. Chloride channels in the apical membrane of cortical collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F273–F280. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Burillo S., O'Brien J. A., Ilundain A., Wreggett K. A., Sepúlveda F. V. Activation of basolateral membrane K+ permeability by bradykinin in MDCK cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 7;939(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. C., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin receptors localized by quantitative autoradiography in kidney, ureter, and bladder. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F909–F915. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti J., Taniguchi S., Lebrun F., Morel F. Cholinergic agonists increase cell calcium in rat medullary collecting tubules. A fura-2 study. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jul;416(5):561–567. doi: 10.1007/BF00382690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S. The kallikrein-kinin system and the kidney. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:309–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle S., Garg L. C., Crews F. T. Cholinergic receptors in renal medullary collecting duct cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):12–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills I. H., Obika L. F. Increased urinary kallikrein excretion during prostaglandin E1 infusion in anaesthetized dogs and its relation to natriuresis and diuresis. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):459–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulmichl M., Friedrich F., Lang F. Effects of bradykinin on electrical properties of Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelioid cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):408–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00581137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidikiti N., Gamero D., Gamero J., Hassid A. Bradykinin-evoked modulation of cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations in cultured renal epithelial (MDCK) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 31;130(2):807–813. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90488-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirola C. J., Alvarez A. L., Balda M. S., Finkielman S., Nahmod V. E. Evidence for cholinergic innervation in dog renal tissue. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F746–F754. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Chuman L. M., Shaffer L., Saier M. H., Jr Retention of differentiated properties in an established dog kidney epithelial cell line (MDCK). J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):635–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A. Renal kallikrein-kinin system. Kidney Int. 1986 Jan;29(1):120–130. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons N. L., Brown C. D., Rugg E. L. The action of epinephrine on Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Fed Proc. 1984 May 15;43(8):2225–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons N. L. Chloride secretion stimulated by prostaglandin E1 and by forskolin in a canine renal epithelial cell line. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:459–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons N. L. Stimulation of Cl- secretion by exogenous ATP in cultured MDCK epithelial monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 20;646(2):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. J., McCann J. D., Welsh M. J. Bradykinin stimulates airway epithelial Cl- secretion via two second messenger pathways. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):L369–L377. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.6.L369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Pisano J. J. Binding of [3H]bradykinin in isolated nephron segments of the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):F732–F737. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.5.F732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S. Active and passive chloride transport by the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1388–F1393. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Jabs K., Kikeri D., Silva P. Kinins inhibit conductive Na+ uptake by rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 2):F1584–F1591. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.6.F1584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M., Keiser H. R. Prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by rabbit renomedullary interstitial cells in tissue culture. Mechanism of stimulation by angiotensin II, bradykinin, and arginine vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2069–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


