Abstract
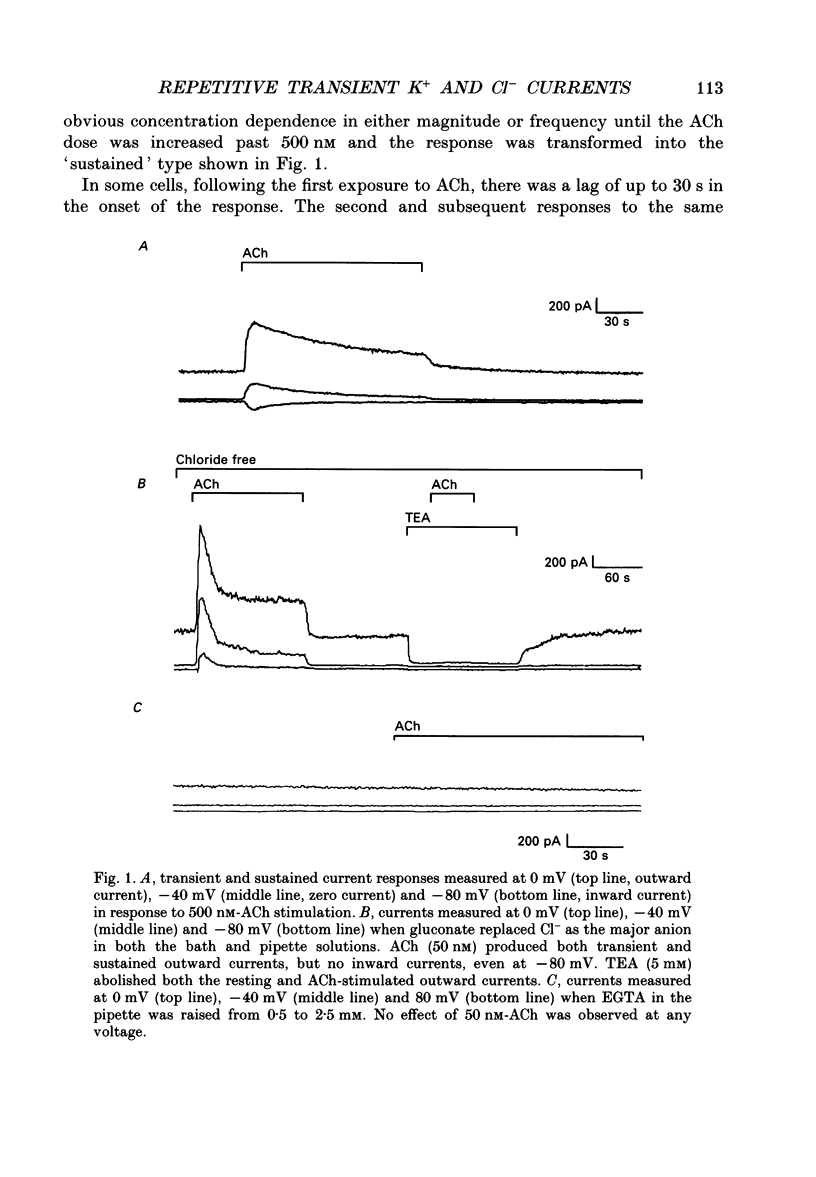
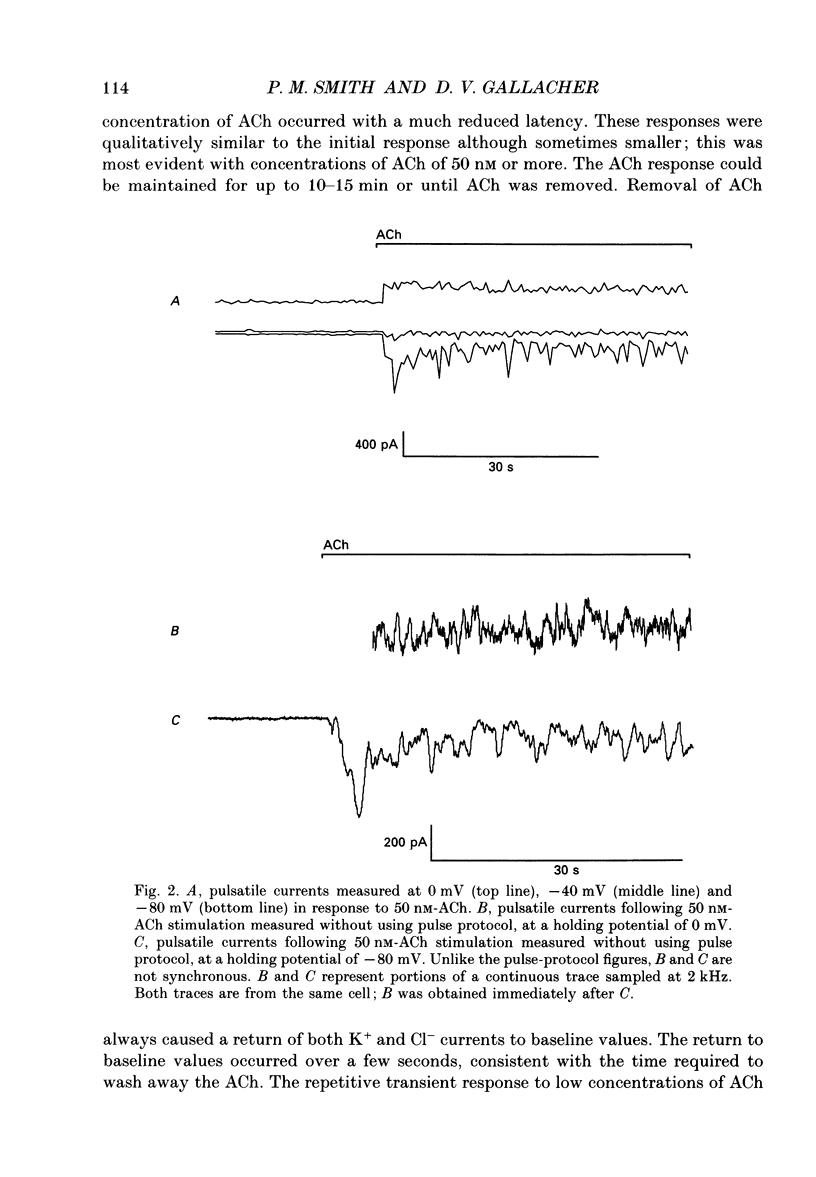
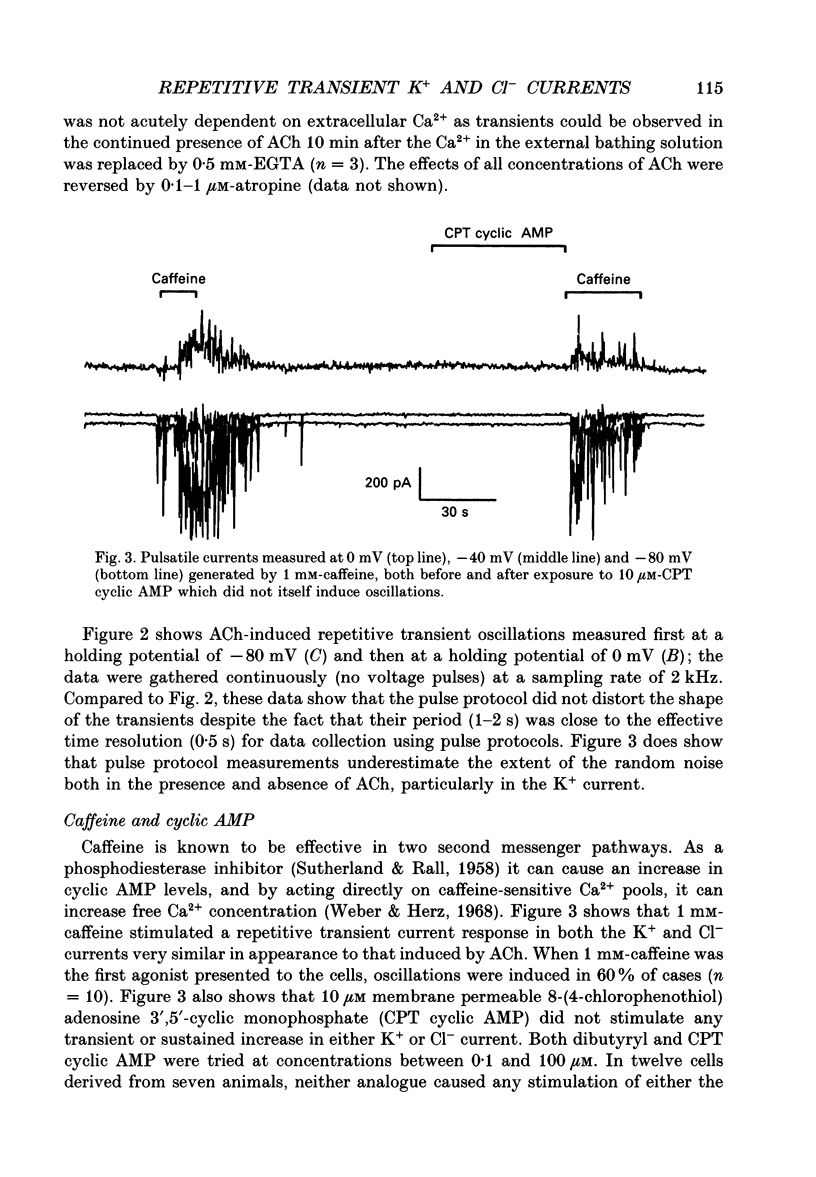
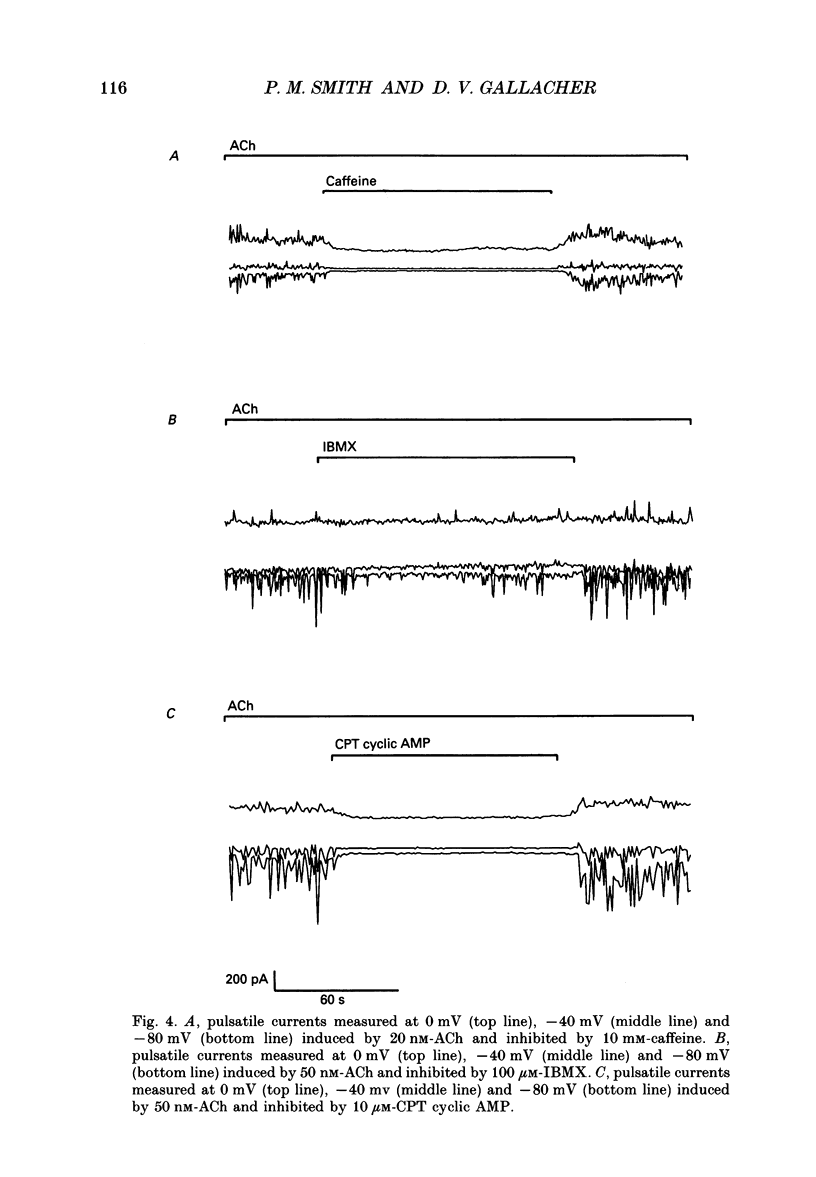
1. Resting and acetylcholine-induced membrane currents were measured in single mouse submandibular acinar cells using the patch-clamp whole-cell current recording technique. 2. Micromolar ACh activated a large, sustained outward, Ca(2+)-dependent K+ current and a single transient inward Ca(2+)-dependent C1-current. 3. Nanomolar ACh induced a series of transients in both the K+ and C1- currents; C1- current activation was now observed throughout the period of agonist application. We consider this repetitive transient current activation better able to support sustained fluid and electrolyte secretion than the response elicited by a high dose of agonist. 4. Repetitive K+ and C1- current transients were also induced by 1 mM-caffeine, consistent with caffeine-induced Ca2+ release from the Ca(2+)-sensitive Ca2+ stores which are thought to comprise part of the pathway for activation of secretion. 5. The ACh-induced current transients were inhibited by 10 mM-caffeine, 100 microM-IBMX and 10 microM membrane-permeable cyclic AMP. Therefore, it seems likely that caffeine is able to inhibit agonist-induced calcium mobilization via a cyclic AMP-dependent pathway.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. I., Day M. L., Champion M. P., Young J. A. Ca2+ not cyclic AMP mediates the fluid secretory response to isoproterenol in the rat mandibular salivary gland: whole-cell patch-clamp studies. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Nov;413(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00581230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Bianca V., De Togni P., Grzeskowiak M., Vicentini L. M., Di Virgilio F. Cyclic AMP inhibition of phosphoinositide turnover in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 29;886(3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich B. E., Watras J. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate activates a channel from smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):583–586. doi: 10.1038/336583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:179–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming N., Sliwinski-Lis E., Burke D. N. G regulatory proteins and muscarinic receptor signal transduction in mucous acini of rat submandibular gland. Life Sci. 1989;44(15):1027–1035. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90554-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallacher D. V., Morris A. P. A patch-clamp study of potassium currents in resting and acetylcholine-stimulated mouse submandibular acinar cells. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:379–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Dupont G., Berridge M. J. Minimal model for signal-induced Ca2+ oscillations and for their frequency encoding through protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. T. Oscillations of free cytosolic calcium evoked by cholinergic and catecholaminergic agonists in rat parotid acinar cells. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;406:35–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. P., Donaldson J., Hill S. J. Inhibition of histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis by agents which increase cyclic AMP levels in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):603–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11992.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Maruyama Y., Matsumoto O., Nishiyama A. Activation of Ca2+-dependent Cl- and K+ conductances in rat and mouse parotid acinar cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1985;35(6):933–944. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.35.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K. Release of calcium ions linked to the activation of potassium conductance in a caffeine-treated sympathetic neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:251–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Takeshita S. Simulation of intracellular Ca2+ oscillation in a sympathetic neurone. J Theor Biol. 1981 Dec 21;93(4):1009–1031. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison J. M., Brown J. K. Differential inhibitory effects of forskolin, isoproterenol, and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate on phosphoinositide hydrolysis in canine tracheal smooth muscle. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1462–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channel in baso-lateral acinar cell membranes of mammalian salivary glands. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):827–829. doi: 10.1038/302827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):653–655. doi: 10.1038/330653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. Inhibition by cAMP of the phosphoinositide response to alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation in rat kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):441–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Petersen O. H. Membrane potential and resistance measurement in acinar cells from salivary glands in vitro: effect of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(1):173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osipchuk Y. V., Wakui M., Yule D. I., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations evoked by receptor stimulation, G-protein activation, internal application of inositol trisphosphate or Ca2+: simultaneous microfluorimetry and Ca2+ dependent Cl- current recording in single pancreatic acinar cells. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):697–704. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Ivorra I. Caffeine inhibits inositol trisphosphate-mediated liberation of intracellular calcium in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:229–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons W. J., Ramkumar V., Stiles G. L. Isobutylmethylxanthine stimulates adenylate cyclase by blocking the inhibitory regulatory protein, Gi. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;34(1):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Gallacher D. V. Electrophysiology of pancreatic and salivary acinar cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:65–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.000433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Wakui M. Oscillating intracellular Ca2+ signals evoked by activation of receptors linked to inositol lipid hydrolysis: mechanism of generation. J Membr Biol. 1990 Nov;118(2):93–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01868467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr Role of calcium in the fade of the potassium release response in the rat parotid gland. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:383–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puurunen J., Lohse M. J., Schwabe U. Interactions between intracellular cyclic AMP and agonist-induced inositol phospholipid breakdown in isolated gastric mucosal cells of the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;336(5):471–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00169301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Kelley G., Douglas J. S. Interactions between Ca2+ and cAMP messenger system in regulation of airway smooth muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):L279–L288. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.6.L279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson P. L., Bruno G. R., Datta S. C. Glutamate-stimulated, guanine nucleotide-mediated phosphoinositide turnover in astrocytes is inhibited by cyclic AMP. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1727–1733. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., RALL T. W. Fractionation and characterization of a cyclic adenine ribonucleotide formed by tissue particles. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):1077–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Gallacher D. V. Extracellular ATP activates receptor-operated cation channels in mouse lacrimal acinar cells to promote calcium influx in the absence of phosphoinositide metabolism. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 7;264(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80782-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Osipchuk Y. V., Petersen O. H. Receptor-activated cytoplasmic Ca2+ spiking mediated by inositol trisphosphate is due to Ca2(+)-induced Ca2+ release. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90505-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui M., Potter B. V., Petersen O. H. Pulsatile intracellular calcium release does not depend on fluctuations in inositol trisphosphate concentration. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):317–320. doi: 10.1038/339317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J. Electrolyte transport by airway epithelia. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1143–1184. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yule D. I., Gallacher D. V. Oscillations of cytosolic calcium in single pancreatic acinar cells stimulated by acetylcholine. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 7;239(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80951-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


