Abstract
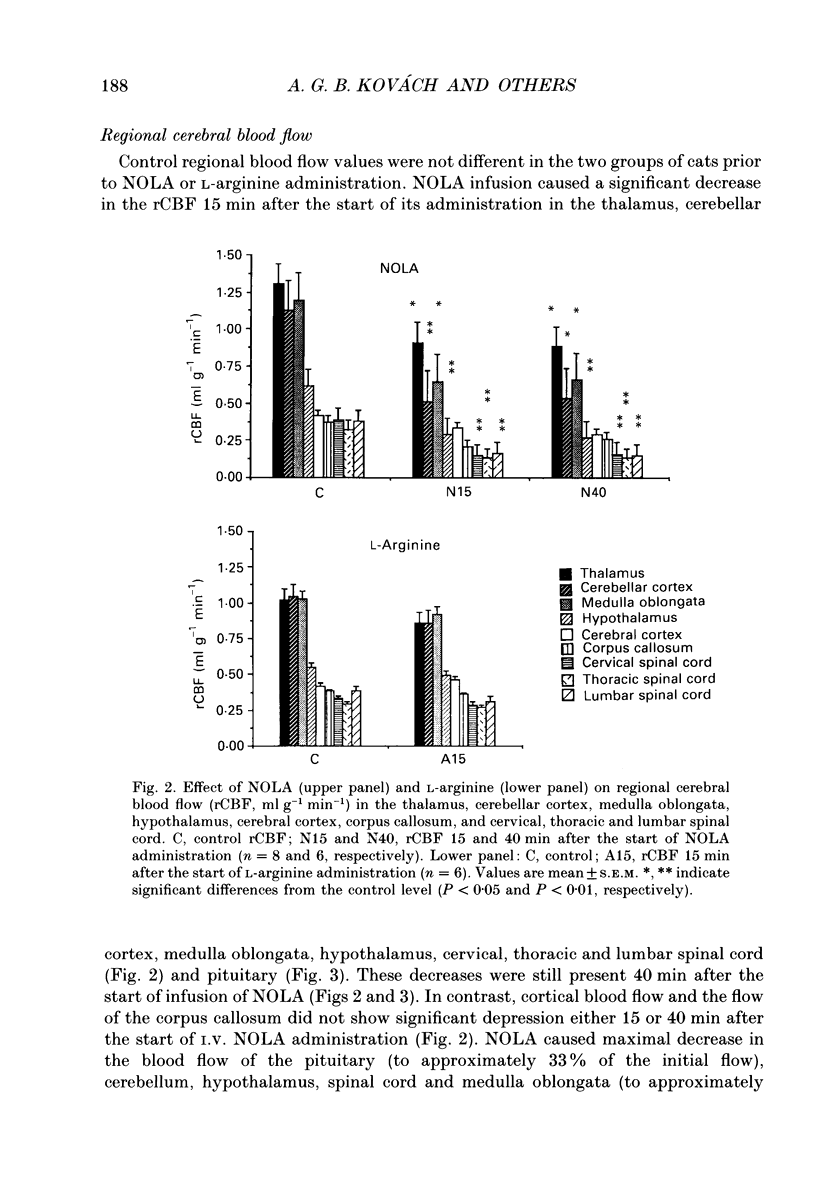
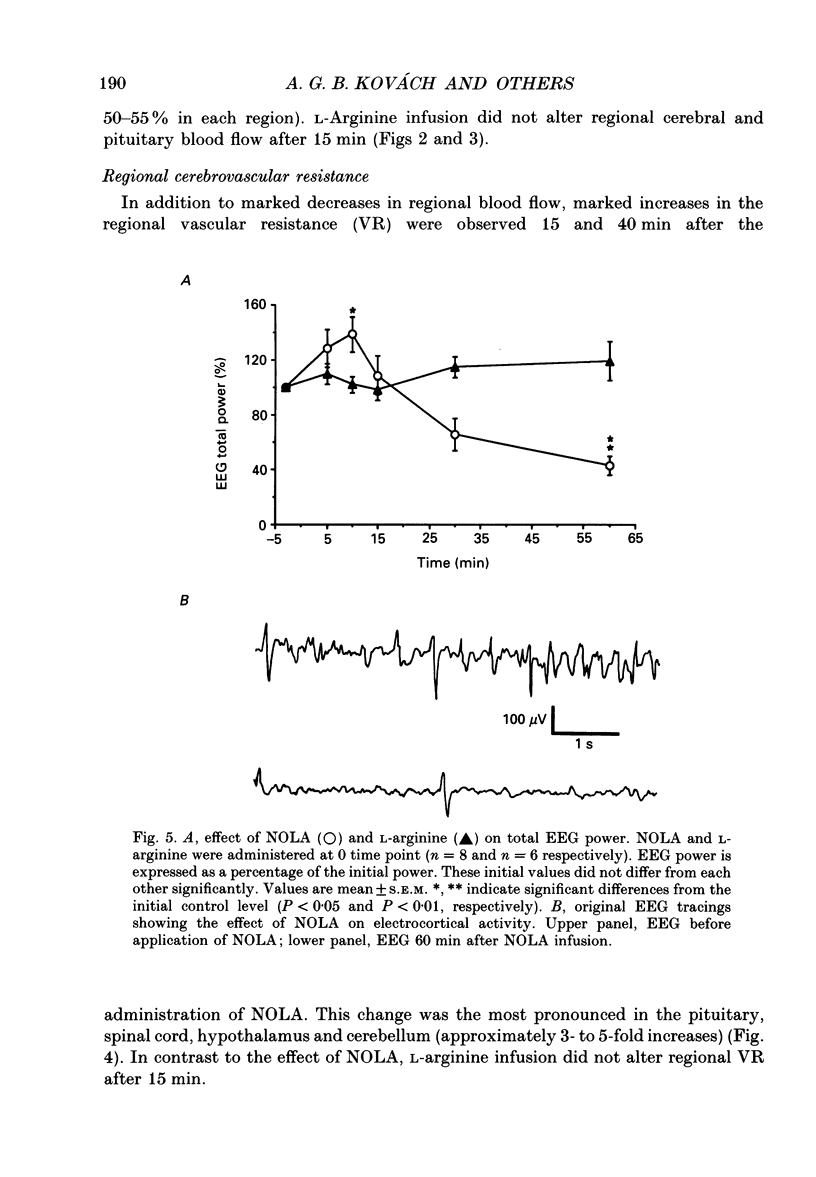
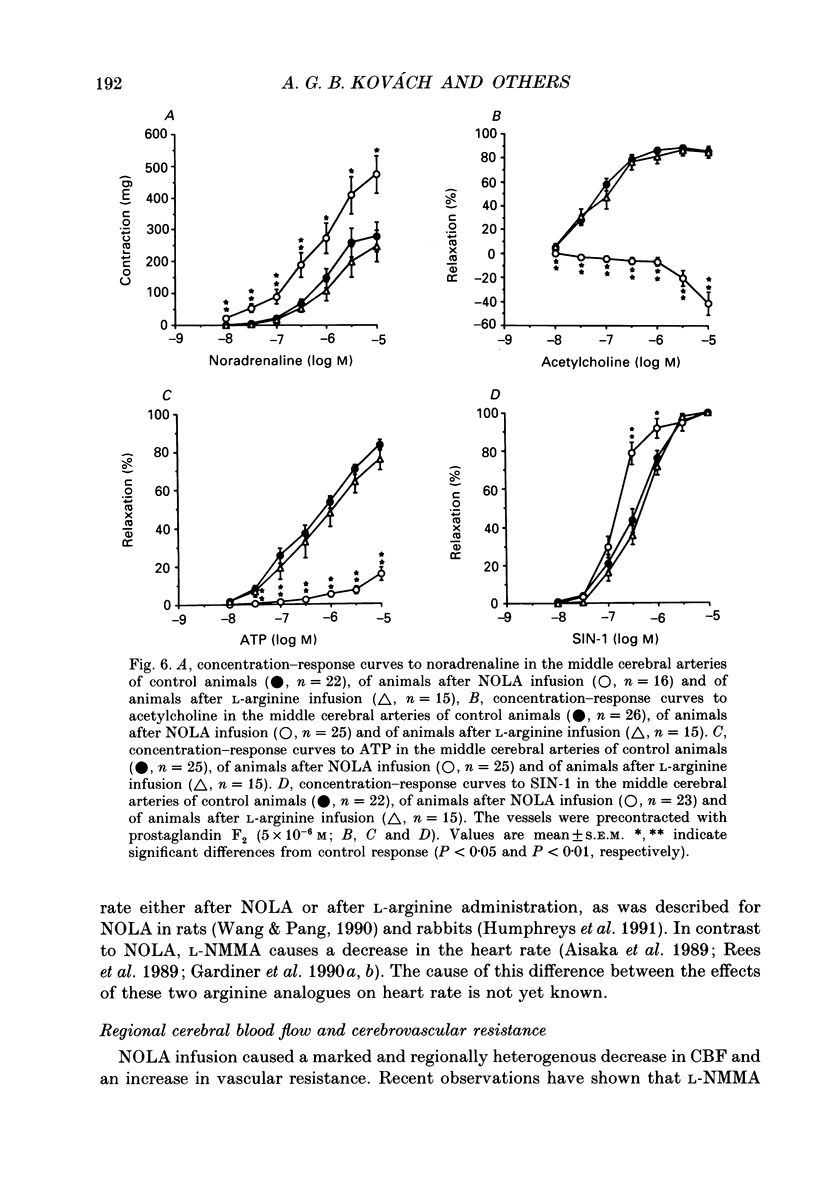
1. We studied the effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine (NOLA), a potent inhibitor of the L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway, and L-arginine, the precursor of nitric oxide, on regional cerebral blood flow, electrocortical activity and ex vivo cerebrovascular reactivity in the cat. Flow was measured via radiolabelled microspheres, and vascular responses were studied by measuring isometric tension of isolated middle cerebral arterial rings. 2. NOLA (30 mg kg-1 bolus followed by 1 mg kg-1 min-1 infusion) caused an approximately 40 mmHg elevation in the mean arterial blood pressure, a regionally heterogenous increase of the regional cerebrovascular resistance and a decrease in the regional cerebral blood flow 15 and 40 min after the start of its administration. In contrast L-arginine (30 mg kg-1 bolus followed by 10 mg kg-1 min-1 infusion) did not alter blood pressure, cerebrovascular resistance nor regional cerebral blood flow 15 min after the start of its administration. The NOLA-induced changes in tissue flow were the most pronounced in the cerebellum, pituitary and medulla oblongata, whereas there was no decrease in the flow of the cortex and white matter. 3. NOLA caused characteristic changes in total fronto-occipital EEG power and in power spectra which were unlikely to have been due to cerebral ischaemia. In addition, the ex vivo reactivity of the middle cerebral arteries showed signs of impaired endothelial nitric oxide synthesis: there were enhanced noradrenaline-induced contractions and N-ethoxycarbonyl-3-morpholino-sydnonimine (SIN-1)-induced relaxations and markedly attenuated acetylcholine- and ATP-induced relaxations after NOLA treatment. 4. The present data indicate that resting cerebral blood flow and cerebrovascular resistance are regulated by nitric oxide derived from L-arginine in a regionally heterogenous way and that exogenous L-arginine availability is not a limiting factor in this nitric oxide generation. Possibly, both the vascular endothelium and the neurons contribute to this basal nitric oxide release.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisaka K., Gross S. S., Griffith O. W., Levi R. NG-methylarginine, an inhibitor of endothelium-derived nitric oxide synthesis, is a potent pressor agent in the guinea pig: does nitric oxide regulate blood pressure in vivo? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):881–886. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj R., Moore P. K. The effect of arginine and nitric oxide on resistance blood vessels of the perfused rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):739–744. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9030–9033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busija D. W., Leffler C. W., Wagerle L. C. Mono-L-arginine-containing compounds dilate piglet pial arterioles via an endothelium-derived relaxing factor-like substance. Circ Res. 1990 Dec;67(6):1374–1380. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.6.1374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraci F. M. Role of nitric oxide in regulation of basilar artery tone in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):H1216–H1221. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.4.H1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Noack E. A. Correlation between nitric oxide formation during degradation of organic nitrates and activation of guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Gorsky L. D., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Regional distribution of EDRF/NO-synthesizing enzyme(s) in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 30;168(2):727–732. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92382-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Montague P. R., Reeke G. N., Jr, Edelman G. M. The NO hypothesis: possible effects of a short-lived, rapidly diffusible signal in the development and function of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3547–3551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Control of regional blood flow by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Hypertension. 1990 May;15(5):486–492. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Regional haemodynamic changes during oral ingestion of NG-monomethyl-L-arginine or NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester in conscious Brattleboro rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):10–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girerd X. J., Hirsch A. T., Cooke J. P., Dzau V. J., Creager M. A. L-arginine augments endothelium-dependent vasodilation in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Circ Res. 1990 Dec;67(6):1301–1308. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.6.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. E., Wood K. S., Byrns R. E., Fukuto J., Ignarro L. J. NG-methyl-L-arginine causes endothelium-dependent contraction and inhibition of cyclic GMP formation in artery and vein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groll-Knapp E., Haider M., Kienzl K., Handler A., Trimmel M. Changes in discrimination learning and brain activity (ERP's) due to combined exposure to NO and CO in rats. Toxicology. 1988 May;49(2-3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(88)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Stuehr D. J., Aisaka K., Jaffe E. A., Levi R., Griffith O. W. Macrophage and endothelial cell nitric oxide synthesis: cell-type selective inhibition by NG-aminoarginine, NG-nitroarginine and NG-methylarginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91245-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymann M. A., Payne B. D., Hoffman J. I., Rudolph A. M. Blood flow measurements with radionuclide-labeled particles. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1977 Jul-Aug;20(1):55–79. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(77)80005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. G., Carr R. D., Nicol A. K., Tomlinson W., O'Connor S. E. Coronary vasoconstriction in the conscious rabbit following intravenous infusion of L-NG-nitro-arginine. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):565–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högestätt E. D., Andersson K. E., Edvinsson L. Mechanical properties of rat cerebral arteries as studied by a sensitive device for recording of mechanical activity in isolated small blood vessels. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jan;117(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: a transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5159–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Kinetic characteristics of nitric oxide synthase from rat brain. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):207–210. doi: 10.1042/bj2690207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabe H., Nagai H., Takagi T., Umemura S., Ohno M. Effect of nimodipine on cerebral functional and metabolic recovery following ischemia in the rat brain. Stroke. 1986 May-Jun;17(3):501–505. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhan W. G., Amundsen S. M., Faraci F. M., Heistad D. D. Responses of cerebral arteries after ischemia and reperfusion in cats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H879–H884. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Rees D. D., Schulz R., Palmer R. M. Development and mechanism of a specific supersensitivity to nitrovasodilators after inhibition of vascular nitric oxide synthesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2166–2170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Oluyomi A. O., Babbedge R. C., Wallace P., Hart S. L. L-NG-nitro arginine methyl ester exhibits antinociceptive activity in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):198–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., al-Swayeh O. A., Chong N. W., Evans R. A., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine (L-NOARG), a novel, L-arginine-reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):408–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Busse R. NG-nitro-L-arginine (N5-[imino(nitroamino)methyl]-L-ornithine) impairs endothelium-dependent dilations by inhibiting cytosolic nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;341(1-2):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00195071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Hishikawa K., Suzuki H., Saruta T., Kato R. L-arginine-induced hypotension. Lancet. 1990 Sep 15;336(8716):696–696. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92196-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum W. I., Nishimura H., Nelson G. H. Endothelium-dependent L-Arg- and L-NMMA-sensitive mechanisms regulate tone of brain microvessels. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):H1396–H1401. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.5.H1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma I., Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Nathan C., Levi R. Identification of arginine as a precursor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8664–8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scavini C., Rozza A., Bo P., Lanza E., Favalli L., Savoldi F., Racagni G. Kappa-opioid receptor changes and neurophysiological alterations during cerebral ischemia in rabbits. Stroke. 1990 Jun;21(6):943–947. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.6.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Wilke P., Evers B., Böhme E. Enzymatic formation of nitrogen oxides from L-arginine in bovine brain cytosol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 30;165(1):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Greenberg J. H., Gonatas N. K., Reivich M. Regional flow-metabolism couple following middle cerebral artery occlusion in cats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Jun;5(2):241–252. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. X., Pang C. C. Pressor effect of NG-nitro-L-arginine in pentobarbital-anesthetized rats. Life Sci. 1990;47(24):2217–2224. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90152-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


