Abstract
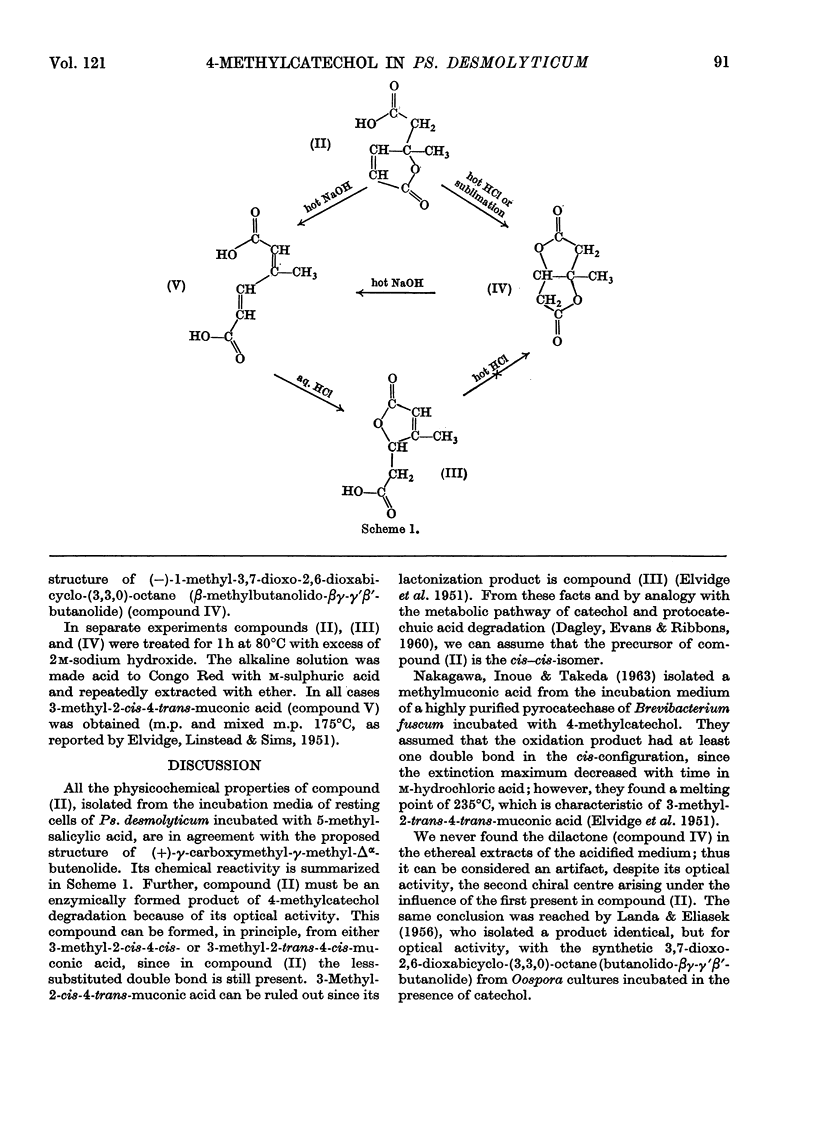
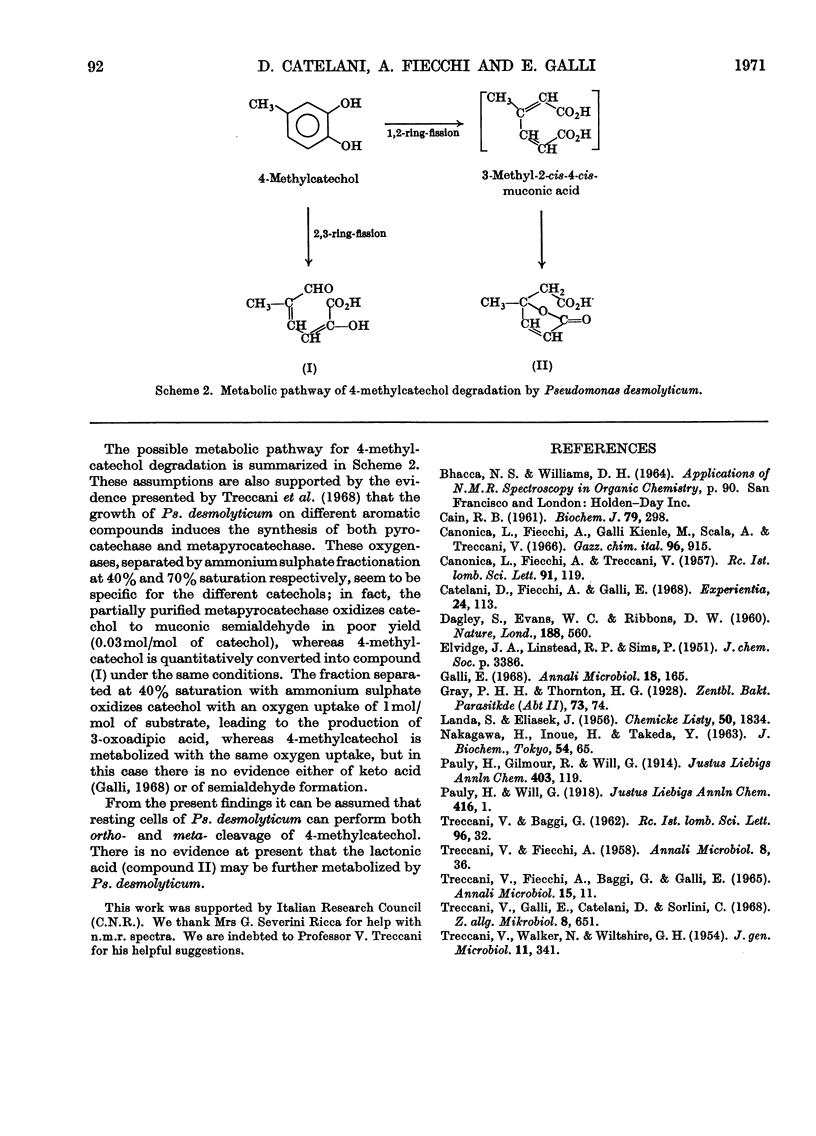
1. (+)-γ-Carboxymethyl-γ-methyl-Δα-butenolide was isolated from resting-cell cultures of Pseudomonas desmolyticum incubated in the presence of 5-methylsalicylic acid. 2. The structure of this metabolite was deduced from physical and chemical evidence. 3. The isolated compound must be formed in an enzymic reaction since it shows optical activity. 4. The degradative pathway of 4-methylcatechol by Ps. desmolyticum is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAIN R. B. The metabolism of protocatechuic acid by a vibrio. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:298–312. doi: 10.1042/bj0790298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catelani D., Fiecchi A., Galli E. Formation of 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-2, trans-4, trans-heptad-ienoic acid from 3-methylcatechol by a Pseudomonas. Experientia. 1968 Feb 15;24(2):113–113. doi: 10.1007/BF02146927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., EVANS W. C., RIBBONS D. W. New pathways in the oxidative metabolism of aromatic compounds by microorganisms. Nature. 1960 Nov 12;188:560–566. doi: 10.1038/188560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRECCANI V., WALKER N., WILTSHIRE G. H. The metabolism of naphthalene by soil bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Dec;11(3):341–348. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


