Abstract
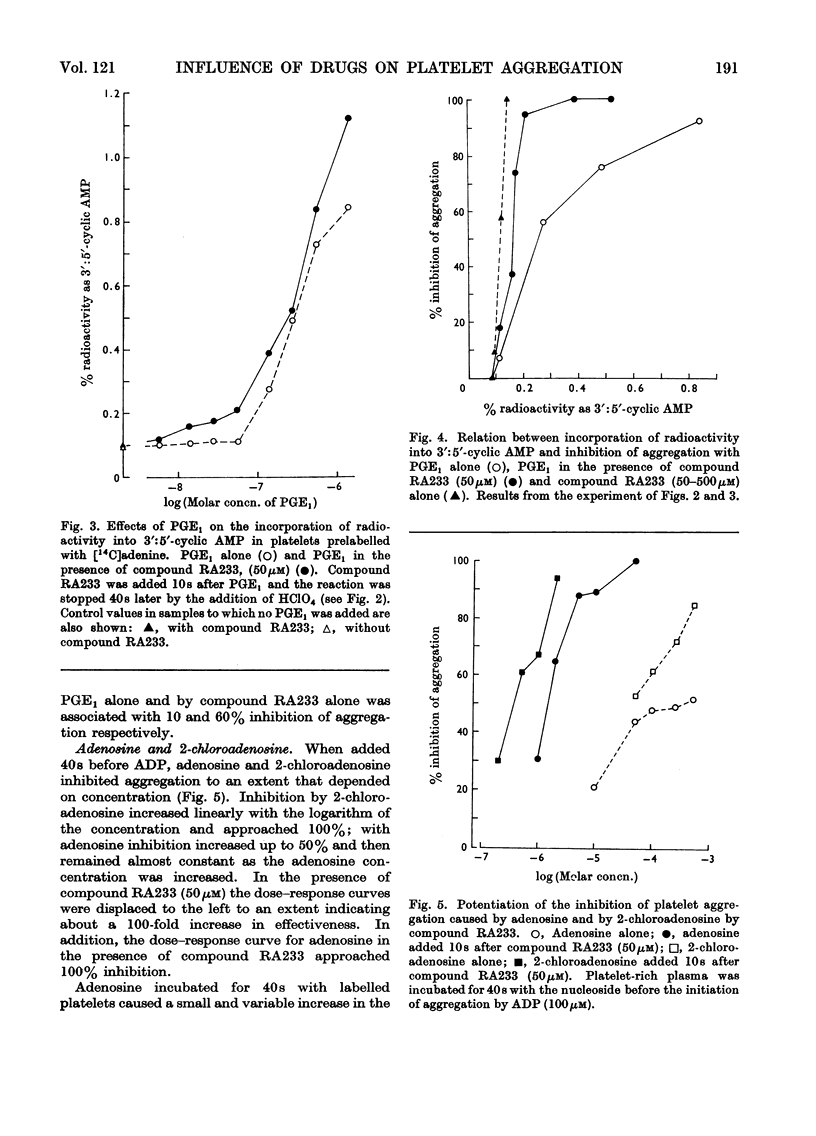
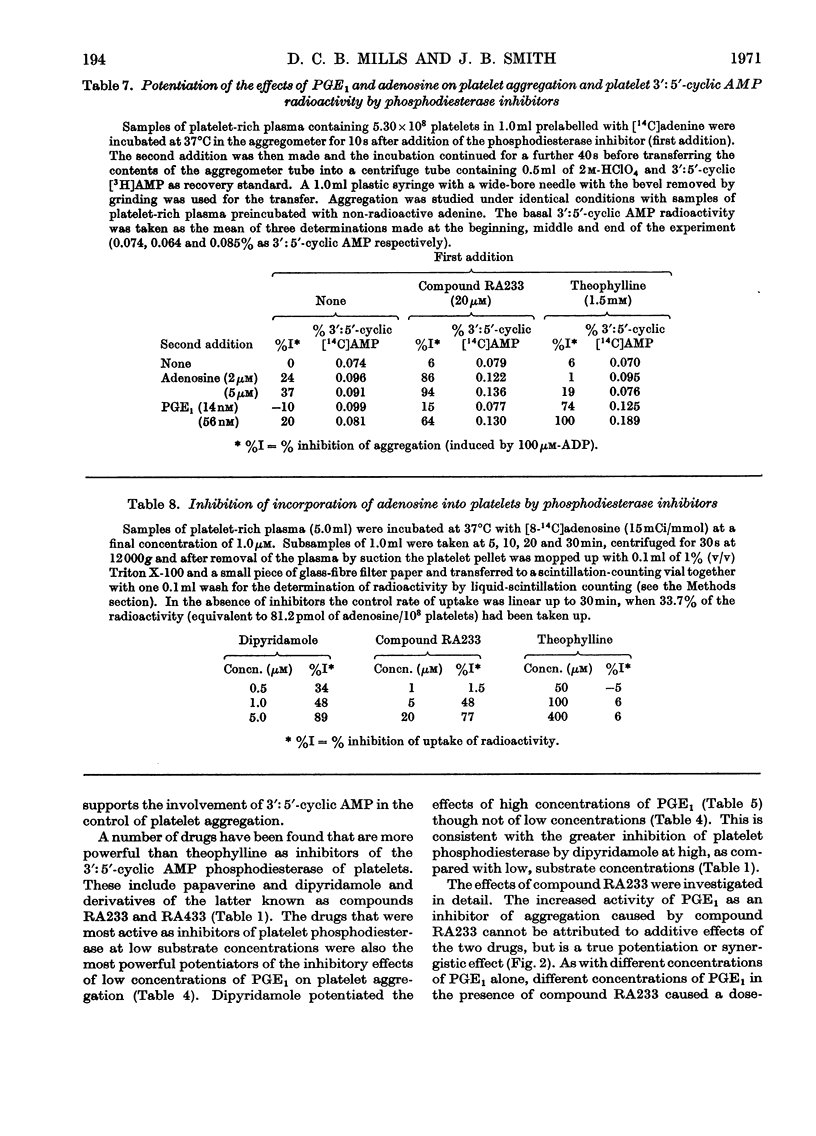
1. The involvement of intracellular 3′:5′-cyclic AMP in the inhibition of platelet aggregation by prostaglandin E1, isoprenaline and adenosine has been examined by a radiochemical technique. Platelet-rich plasma was incubated with radioactive adenine to incorporate 14C radioactivity into platelet nucleotides. Pairs of identically treated samples were taken, one for the photometric measurement of platelet aggregation induced by ADP, the other for estimation of the radioactivity of 3′:5′-cyclic AMP. 2. Theophylline, papaverine, dipyridamole and 2,6-bis-(diethanolamino)-4-piperidinopyrimido[5,4d]pyrimidine (compound RA233) were found to inhibit 3′:5′-cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase from platelets. At concentrations of 3′:5′-cyclic AMP greater than 50μm the most active inhibitor was dipyridamole; at 3′:5′-cyclic AMP concentrations less than 19μm, papaverine and compound RA233 were more active than dipyridamole. 3. In the presence of compound RA233 (50μm), the effectiveness of prostaglandin E1 as an inhibitor of platelet aggregation was increased tenfold. Compound RA233 also increased the stimulation by prostaglandin E1 of the incorporation of radioactivity into 3′:5′-cyclic AMP. 4. Compound RA233 (50μm) increased the effectiveness of both adenosine and 2-chloroadenosine as inhibitors of aggregation by 70–100-fold, and in the presence of compound RA233 both adenosine and 2-chloroadenosine stimulated the incorporation of radioactivity into 3′:5′-cyclic AMP; the extent of the stimulation was proportional to the logarithm of the nucleoside concentration. 5. Compound RA233 (100–500μm) inhibited platelet aggregation by itself and caused small increases in the radioactivity of 3′:5′-cyclic AMP. Partial positive correlations were found between the radioactivity of 3′:5′-cyclic AMP in platelets measured at the time of addition of the aggregating agent (ADP) and the extent to which the aggregation was inhibited. 6. The results are interpreted as indicating that adenosine, 2-chloroadenosine, isoprenaline, prostaglandin E1 and drugs that inhibit platelet 3′:5′-cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase all inhibit aggregation by a common mechanism involving intracellular 3′:5′-cyclic AMP.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdulla Y. H. Beta-adrenergic receptors in human platelets. J Atheroscler Res. 1969 Mar-Apr;9(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(69)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardlie N. G., Glew G., Schultz B. G., Schwartz C. J. Inhibition and reversal of platelet aggregation by methyl xanthines. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Dec 31;18(3-4):670–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V. STRONG INHIBITION BY 2-CHLOROADENOSINE OF THE AGGREGATION OF BLOOD PLATELETS BY ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Nature. 1964 Apr 4;202:95–96. doi: 10.1038/202095b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball G., Brereton G. G., Fulwood M., Ireland D. M., Yates P. Effet of prostaglandin E1 alone and in combination with theophylline or aspirin on collagen-induced platelet aggregation and on platelet nucleotides including adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):709–718. doi: 10.1042/bj1200709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball G., Fulwood M., Ireland D. M., Yates P. Effect of some inhibitors of platelet aggregation on platelet nucleotides. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):669–671. doi: 10.1042/bj1140669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons P. R., Hampton J. R., Harrison M. J., Honour A. J., Mitchell J. R. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on platelet behaviour in vitro and in vivo. Br Med J. 1967 May 20;2(5550):468–472. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5550.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlington M., Watson P. A. Inhibition of 3'5'-cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase by some platelet aggregation inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Mar;19(3):955–956. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland D. M., Mills D. C. Detection and determination of adenosine diphosphate and related substances in plasma. Biochem J. 1966 May;99(2):283–296. doi: 10.1042/bj0990283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. H., Michal F. Powerful new aggregator of blood platelets--2-chloroadenosine-5'-diphosphate. Nature. 1968 Feb 10;217(5128):571–573. doi: 10.1038/217571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwardt F., Barthel W., Glusa E., Hoffman A. Untersuchungen über den Einfluss von Papaverin auf Reaktionen der Blutplättchen. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1967;257(4):420–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis N. R., Vigdahl R. L., Tavormina P. A. Platelet aggregation. I. Regulation by cyclic AMP and prostaglandin E1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 10;36(6):965–972. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. C., Roberts G. C. Effects of adrenaline on human blood platelets. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):443–453. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. C., Thomas D. P. Blood platelet nucleotides in man and other species. Nature. 1969 Jun 7;222(5197):991–992. doi: 10.1038/222991a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki K., Foà P. P. Inhibition of rat liver adenyl cyclase by adenosine and adenine nucleotides. Experientia. 1970 Jan 15;26(1):22–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01900365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham M. A., Ardlie N. G., Mustard J. F. Effect of adenine compounds on platelet aggregation. Am J Physiol. 1969 Oct;217(4):1009–1017. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.4.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöch G., Juan H., Kukovetz W. R. Einfluss von herz- und gefässwirksamen Substanzen auf die Aktivität der Phosphodiesterase. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol. 1969;264(3):293–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenberg M. C., Holmsen H. Adenine nucleotide metabolism of blood platelets. II. Uptake of adenosine and inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):342–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Ashford T. P., Chambers D. A., Neri L. L., Dempster A. P. Platelet volume: effect of temperature and agents affecting platelet aggregation. Am J Physiol. 1969 Nov;217(5):1330–1338. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.5.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Neri L. L. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate in human blood platelets. Nature. 1969 Nov 8;224(5219):609–610. doi: 10.1038/224609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattin A., Rall T. W. The effect of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on the cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-phosphate content of guinea pig cerebral cortex slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;6(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scales B. A new scintillator for liquid scintillation counting. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1967 Jan;18(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(67)90165-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoza L., Zucker M. B., Jerushalmy Z., Grant R. Kinetic studies of platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate and its inhibition by chelating agents, guanidino compounds, and adenosine. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Dec 31;18(3-4):713–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigdahl R. L., Marquis N. R., Tavormina P. A. Platelet aggregation. II. Adenyl cyclase, prostaglandin E1, and calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 22;37(3):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90930-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. M., Shulman N. R. Adenyl cyclase activity in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve P. D., Greenough W. B., 3rd Adenyl cyclase in human platelets: activity and responsiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):462–466. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


