Abstract
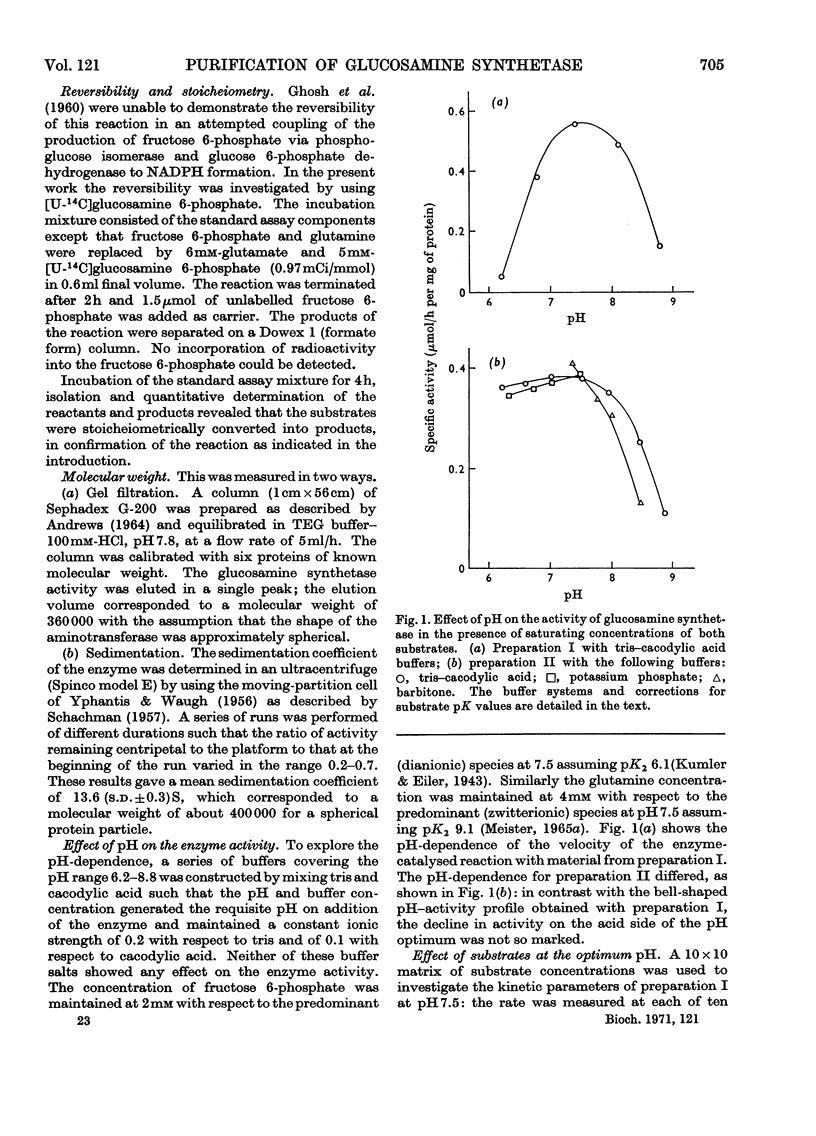
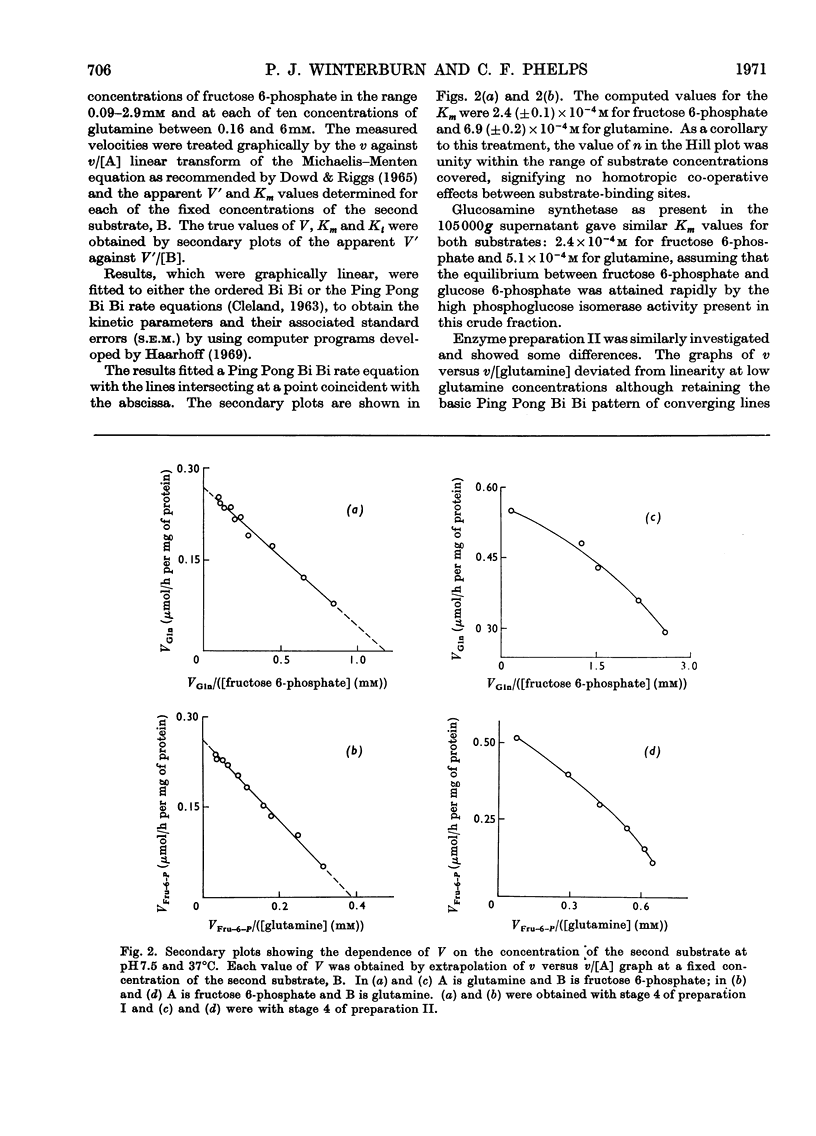
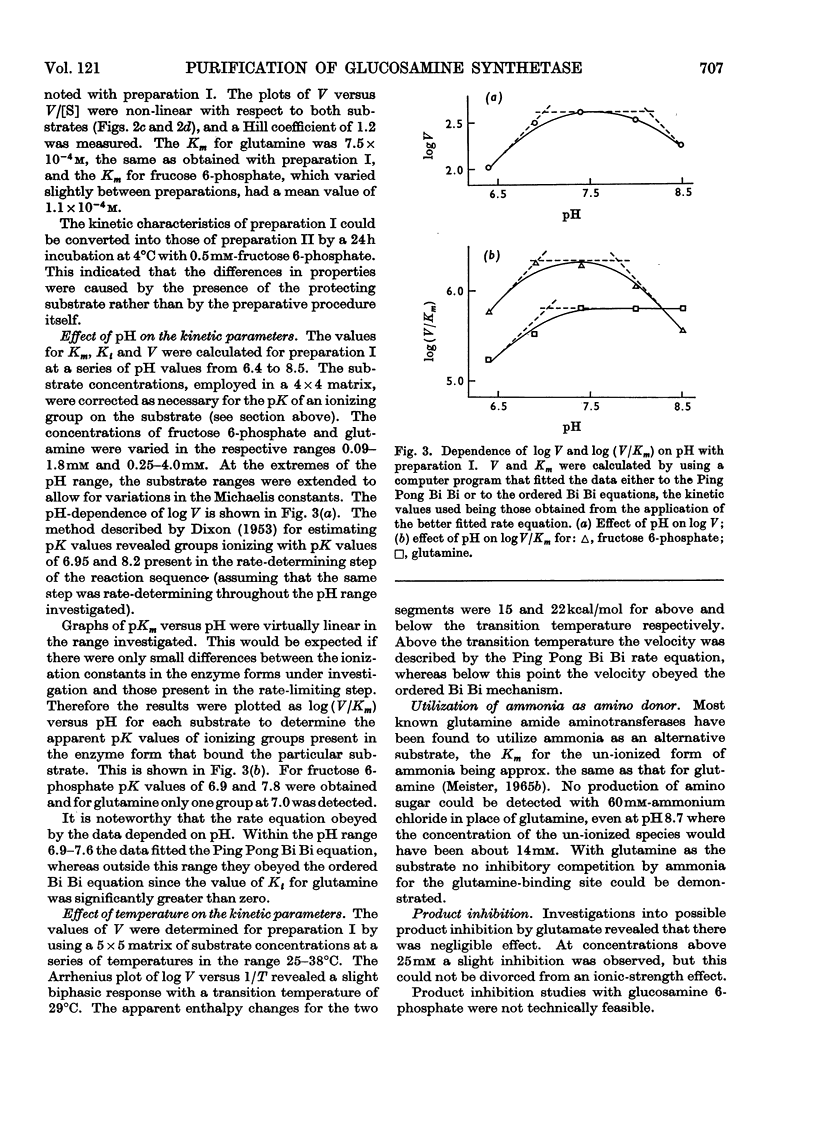
1. Glucosamine synthetase (l-glutamine–d-fructose 6-phosphate aminotransferase, EC 2.6.1.16) was purified about 300-fold from rat liver by two techniques. One procedure utilized the protective action of fructose 6-phosphate and gave a relatively stable preparation, the other yielded an unstable enzyme (half-life of about 20h), free of contaminant activities, on which kinetic experiments were performed. Although the properties of the two preparations showed slight differences, the unstabilized form could be converted into the stabilized form. 2. During preparation the enzyme retained its sensitivity to the feedback inhibitor, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine. 3. The reversibility of the enzyme-catalysed reaction could not be demonstrated. There was no apparent requirement for a cofactor. 4. The pH optimum was at 7.5, at which pH the reaction obeyed a Ping Pong Bi Bi rate equation. At pH values outside the range 6.9–7.6 and at temperatures below 29°C the velocity was described by an ordered Bi Bi rate equation. 5. The molecular weight of the enzyme, determined by two procedures, was 360000–400000. 6. The aminotransferase was unable to utilize ammonia as a substrate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMB D. G., ROSEMAN S. Glucosamine metabolism. IV. Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):807–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The effect of pH on the affinities of enzymes for substrates and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):161–170. doi: 10.1042/bj0550161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWD J. E., RIGGS D. S. A COMPARISON OF ESTIMATES OF MICHAELIS-MENTEN KINETIC CONSTANTS FROM VARIOUS LINEAR TRANSFORMATIONS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:863–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHOSH S., BLUMENTHAL H. J., DAVIDSON E., ROSEMAN S. Glucosamine metabolism. V. Enzymatic synthesis of glucosamine 6-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1265–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOOD T. A., BESSMAN S. P. DETERMINATION OF GLUCOSAMINE AND GALACTOSAMINE USING BORATE BUFFERS FOR MODIFICATION OF THE ELSON-MORGAN AND MORGAN-ELSON REACTIONS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Nov;9:253–262. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRYDER R. M., POGELL B. M. Further studies on glucosamine 6-phosphate synthesis by rat liver enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S., LEVIN O., TISELIUS A. Protein chromatography on calcium phosphate columns. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1956 Nov;65(1):132–155. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(56)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarhoff K. N. Use of multivariate non-linear regression analysis in fitting enzyme kinetic models. An empirical study of the inhibition of aspartate aminotransferase by dicarboxylic acid substrate analogues. J Theor Biol. 1969 Jan;22(1):117–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(69)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Phelps C. F. The tissue content and turnover rates of intermediates in the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans in young rat skin. Biochem J. 1968 Jun;108(1):9–16. doi: 10.1042/bj1080009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IZUMI K. INTRACELLULAR DISTRIBUTION OF ENZYMES INVOLVED IN GLUCOSAMINE METABOLISM IN RAT LIVER. J Biochem. 1965 Apr;57:539–546. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNFELD S., KORNFELD R., NEUFELD E. F., O'BRIEN P. J. THE FEEDBACK CONTROL OF SUGAR NUCLEOTIDE BIOSYNTHESIS IN LIVER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:371–379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R. Studies on L-glutamine D-fructose 6-phosphate amidotransferase. I. Feedback inhibition by uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3135–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POGELL B. M., GRYDER R. M. Enzymatic synthesis of glucosamine 6-phosphate in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):701–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERWOOD A. H., NEWSHOLME E. A. PROPERTIES OF PHOSPHOFRUCTOKINASE FROM RAT LIVER AND THEIR RELATION TO THE CONTROL OF GLYCOLYSIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:868–875. doi: 10.1042/bj0950868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterburn P. J., Phelps C. F. Binding of substrates and modifiers to glucosamine synthetase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):721–730. doi: 10.1042/bj1210721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterburn P. J., Phelps C. F. Studies on the control of hexosamine biosynthesis by glucosamine synthetase. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(4):711–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1210711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


